NURS 203: Final Exam Review (Didn't add unit 9 because it's literally a summary of everything, as well as urinalysis and pregnancy because I heard it's not going to be tested)
1/1067
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
1068 Terms
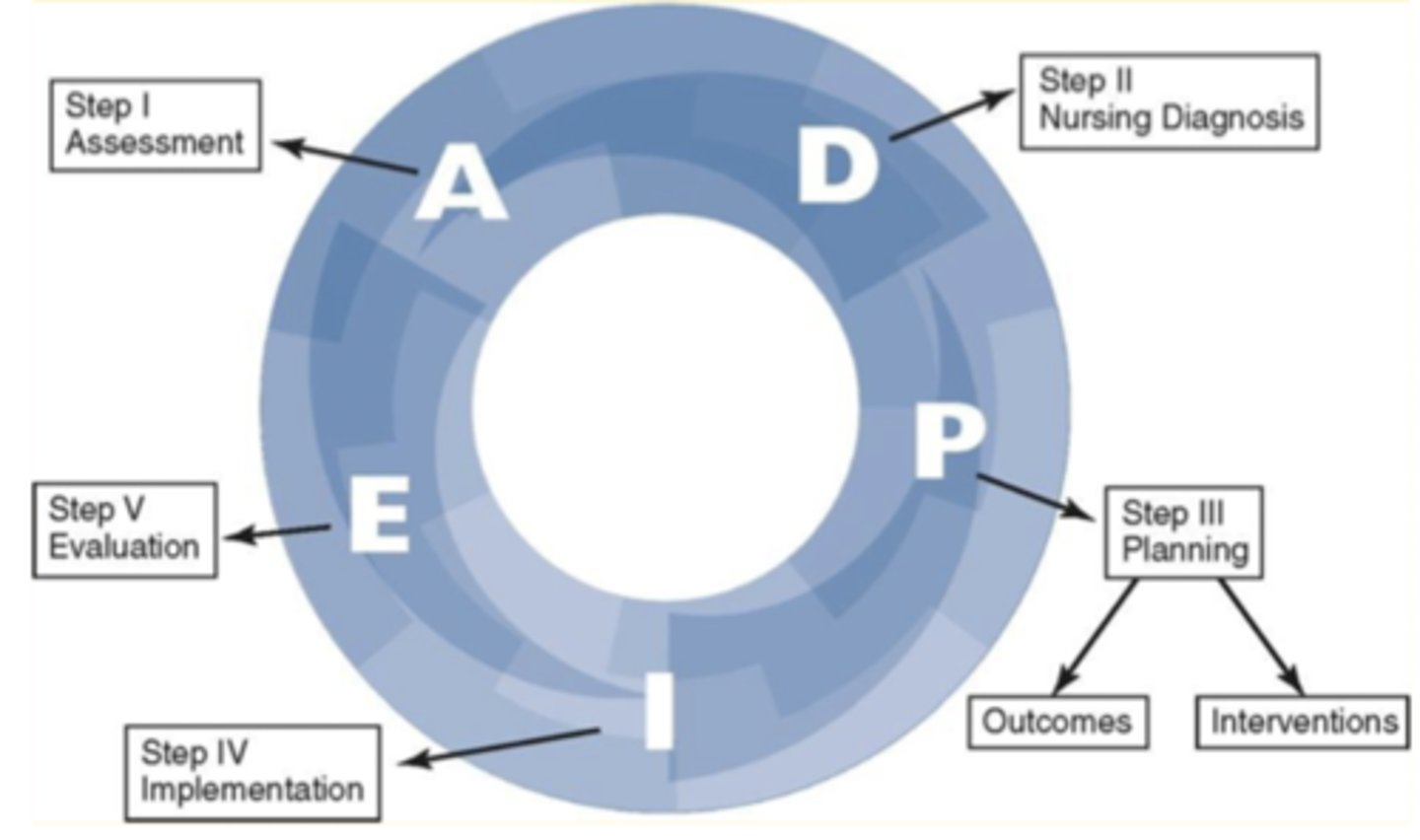
Nursing Process
A problem solving approach to identifying and treating client problems (ADPIE)
3 Main Goals of the Nursing Process
- Determine response to human problems, level of wellness, and need for assistance
- Provide care, teaching, guidance, and counselling
- Implement interventions for prevention, assisting the client to meet own needs and health-related goals
ADPIE
- Assessment
- Diagnosis
- Planning
- Implementation
- Evaluation
Assessment
The first phase of the nursing process; to gather and analyze information about the patient from their perspective
"Patient's Story"
A term used to describe the objective and subjective information about the client
Open-Ended Questions
Questions that allow respondents to answer however they want; used in assessments (Ex. What does your pain feel like?)
Close-Ended Questions
Questions that can be answered in short or single word responses (Ex. Are you hurting?)
Diagnosis
The second phase of the nursing process; to make a nursing diagnosis
4 Types of Nursing Diagnosis
- Problem-focused
- Risk
- Health
- Syndrome
Problem-Focused Diagnosis
A nursing diagnosis that describes an existing problem (Ex. Dizziness (r/t) Lack of hydration)
Risk Diagnosis
A nursing diagnosis that describes a potential problem that the client is vulnerable to (Ex. Risk for seizures (r/t) Can cause injury if they fall)
Health Promotion Diagnosis
A nursing diagnosis that describes a desire to realize human health potential; focus is on being as healthy as possible, and not preventing illness
Syndrome Diagnosis
A nursing diagnosis that is based on a group of signs and symptoms that occur together
Nursing Diagnosis Creation Process
- Underline the relevant symptoms
- Make a list of the symptoms
- Cluster similar symptoms
- Analyze the symptoms
- Select a nursing diagnosis label
(UMCAS)
Etiology
Cause of disease; appears as r/t (related to)
AEB
as evidenced by
3 multiple choice options
Three-Part System (PES System)
A naming system used in nursing diagnosis that uses a problem, etiology, and symptom to make a diagnosis (Ex. Diarrhea r/t lack of fibre in diet aeb watery stool)
Planning
The third phase of the nursing process that includes the identification of priorities and determination of appropriate outcomes and interventions
SMART
- Specific
- Measurable
- Attainable
- Realistic
- Timed
3 Parts of Planning
- Goal
- Outcome
- Criteria
(Ex. Patient will demonstrate better physical outcomes aeb the ability to walk up a flight of stairs without shortness of breath over 1 week)
Implementation
The fourth phase of the nursing process where the interventions are carried out with rationale
Evaluation
The fifth and final phase in the nursing process that involves evaluating the intervention to assess if it need to be altered or not
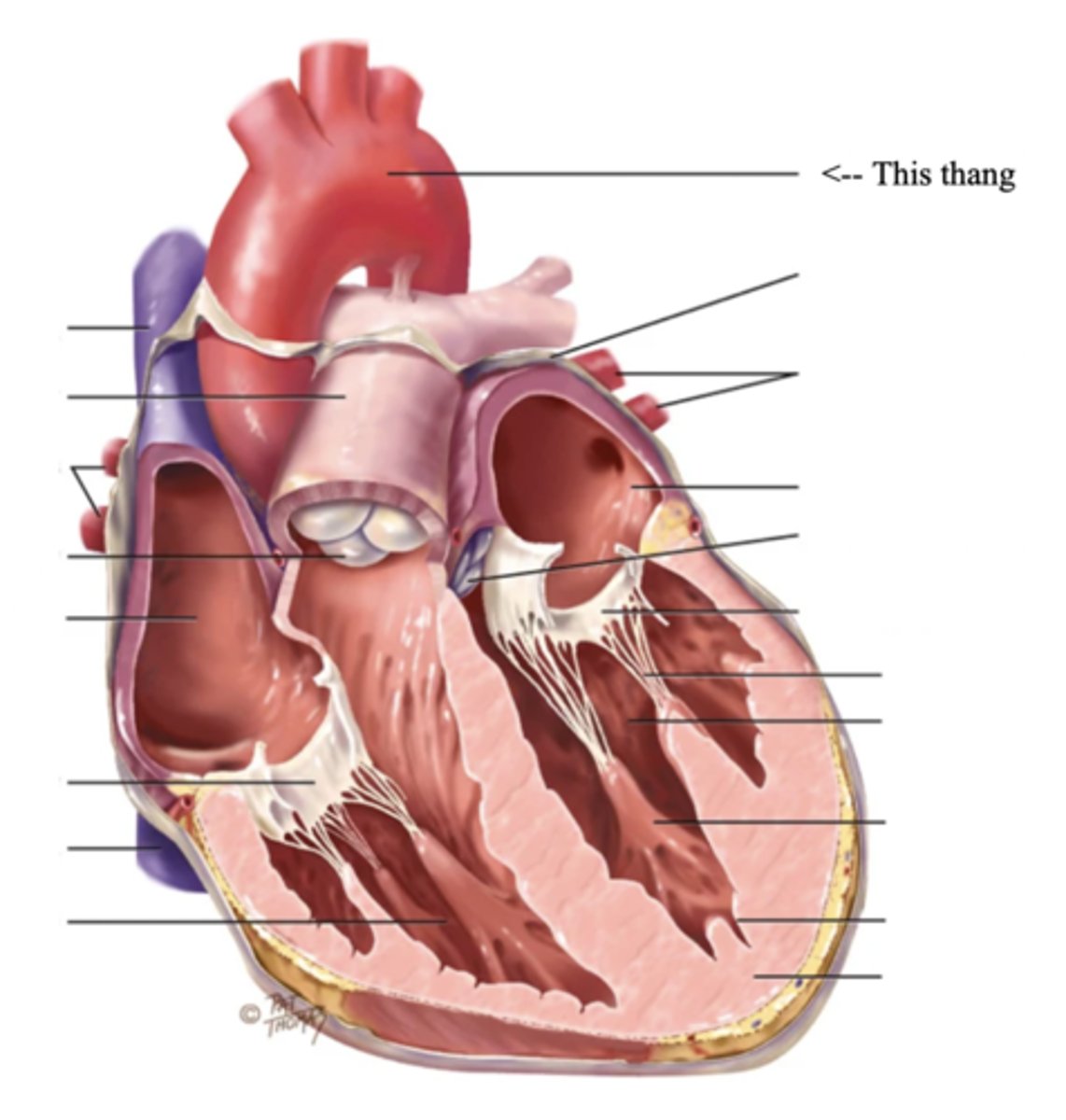
Artery
A blood vessel that carries blood Away from the heart
Vein
A blood vessel that carries blood back to the heart
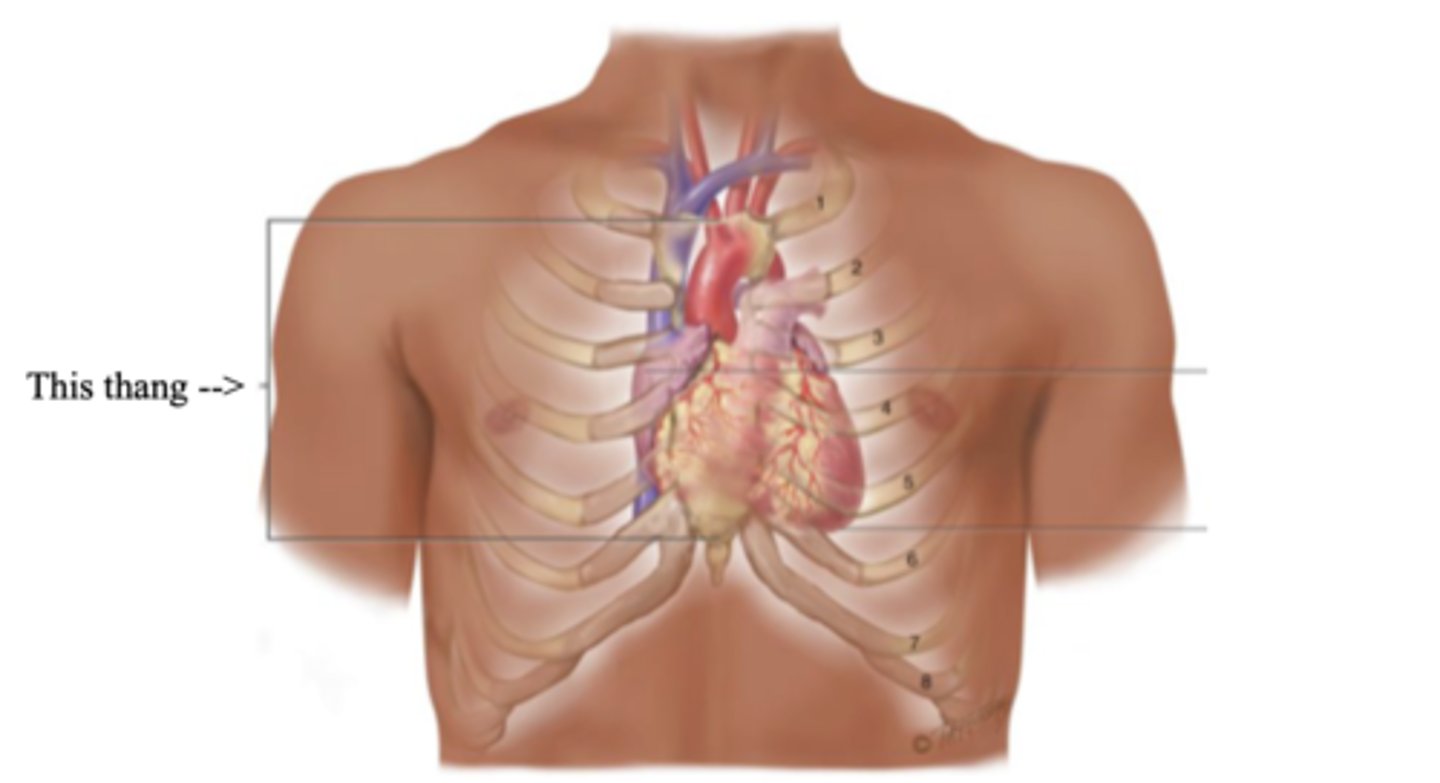
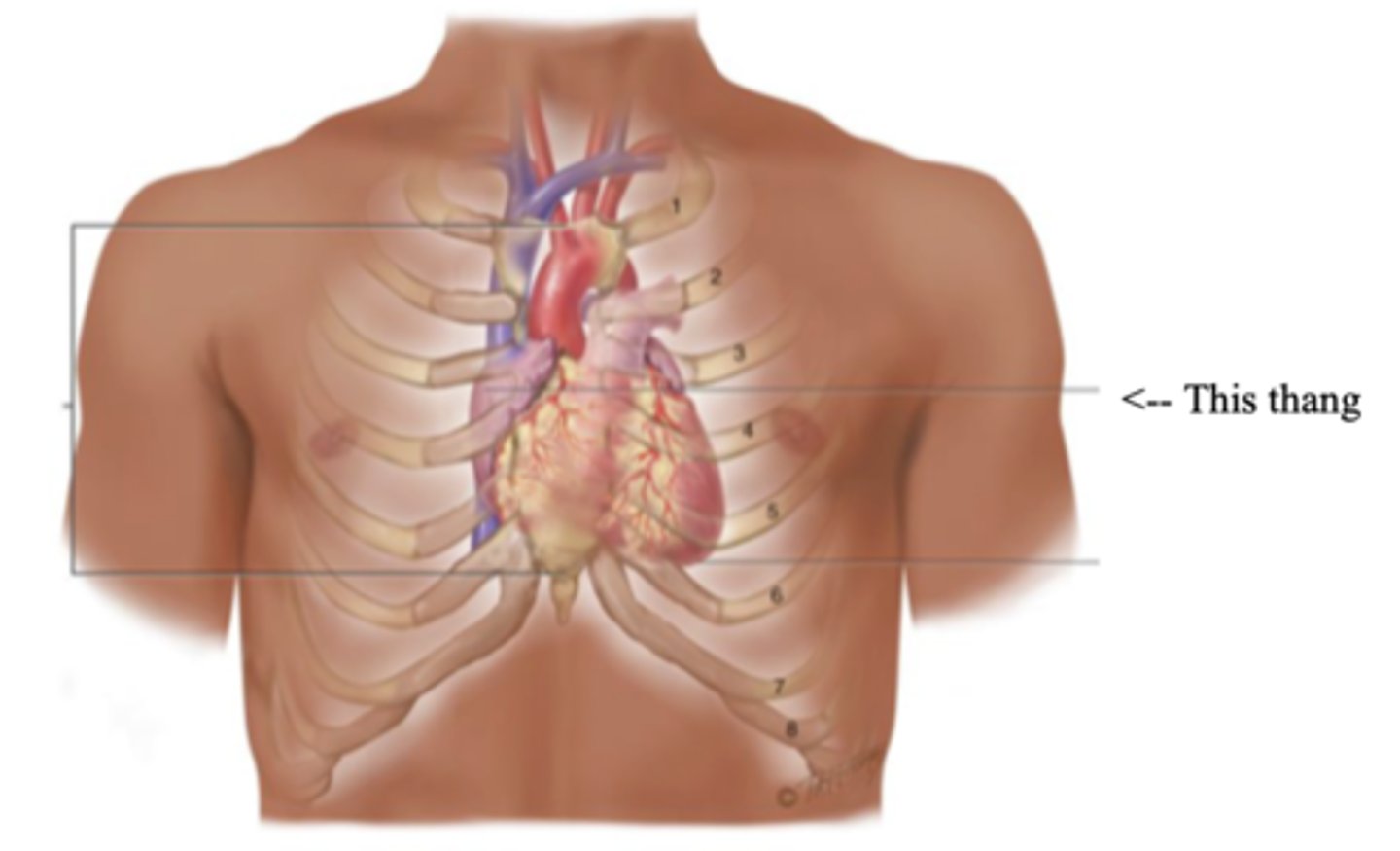
Precordium
The area on the anterior chest overlying the heart and great vessels
Mediastinum
The space located between the lungs where the heart is found
Apex (Heart)
The bottom part of the heart which points down to the left
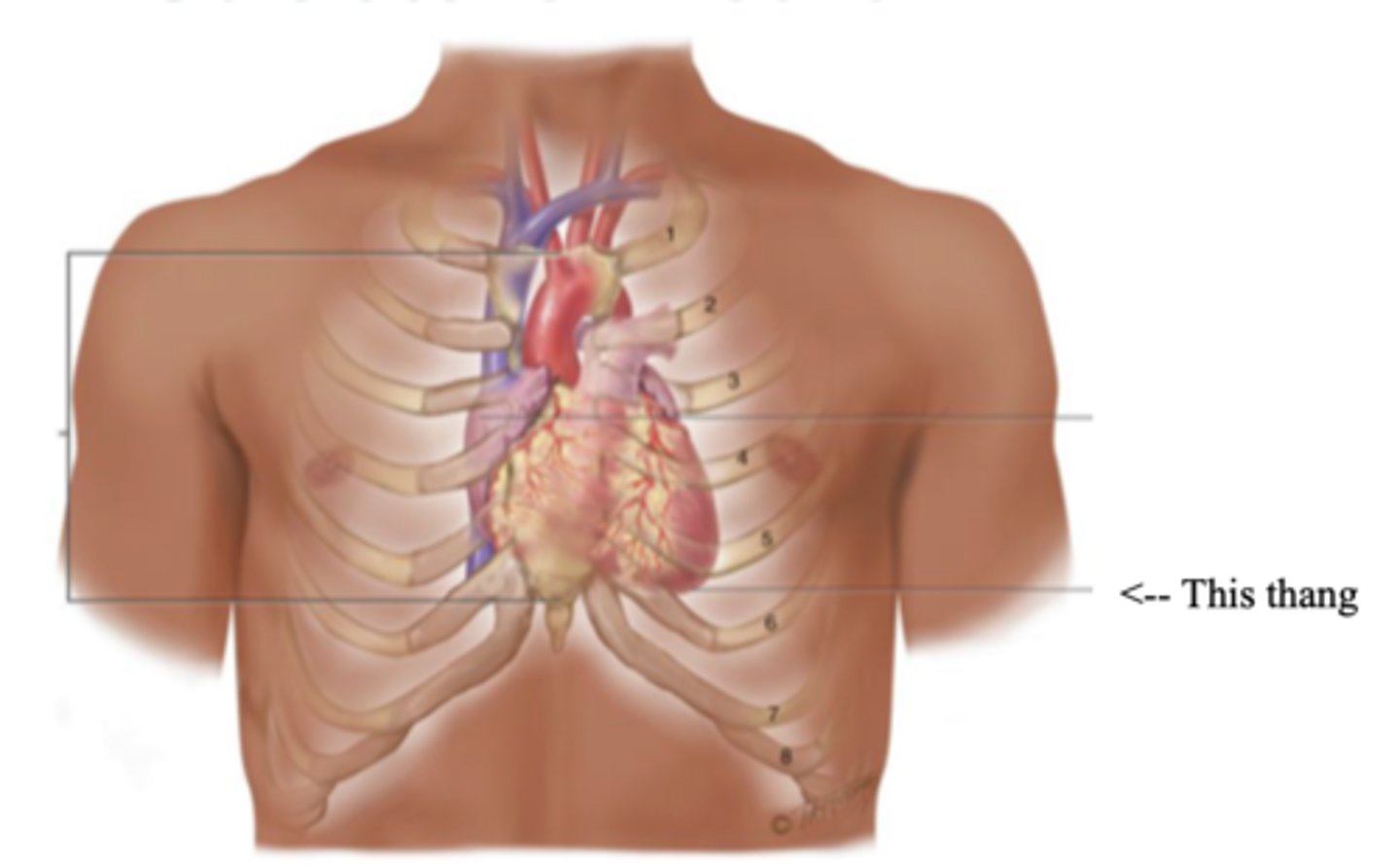
Base (Heart)
The top broader part of the heart
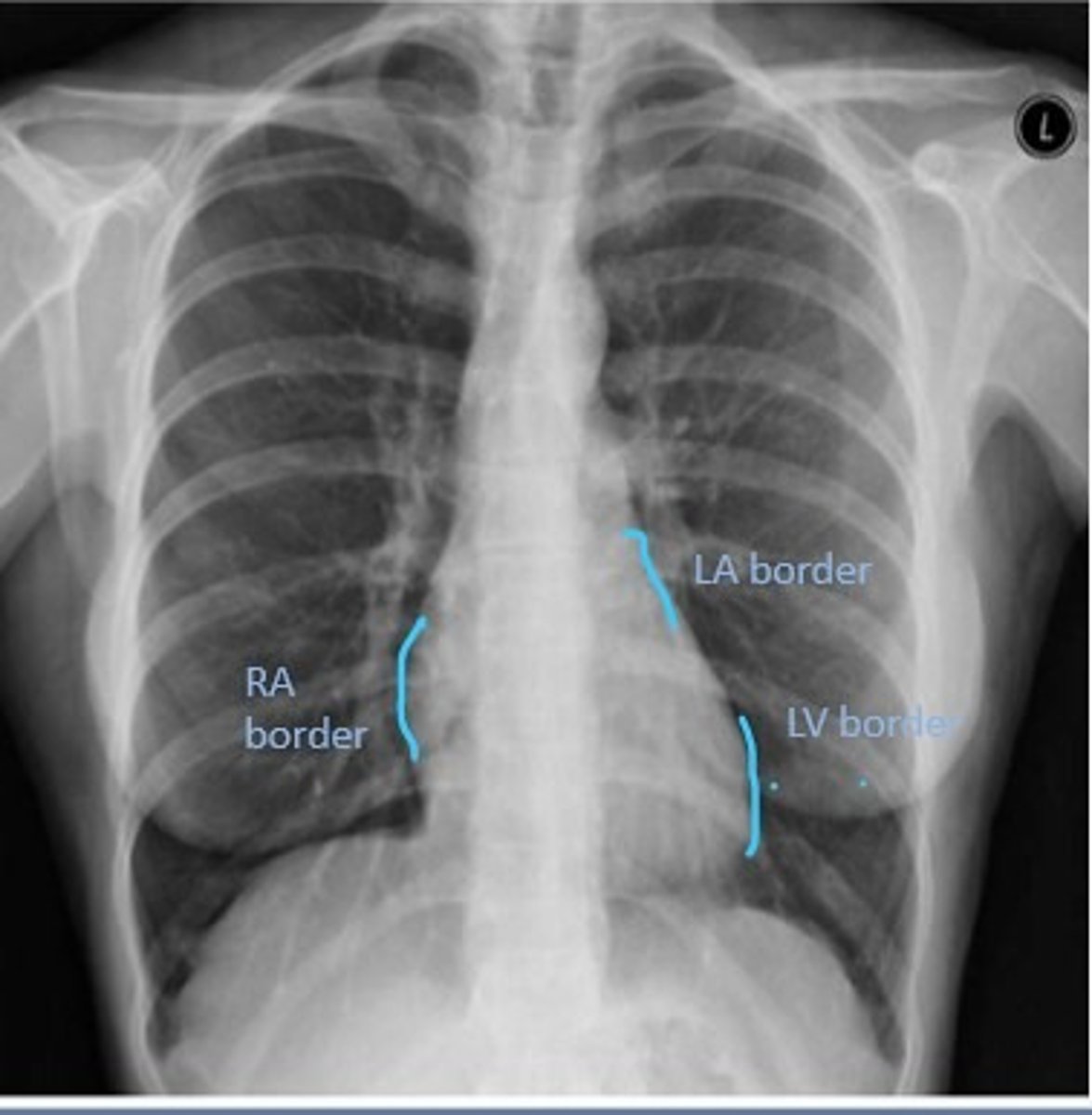
Right Cardiac Border
An area formed by the right atrium
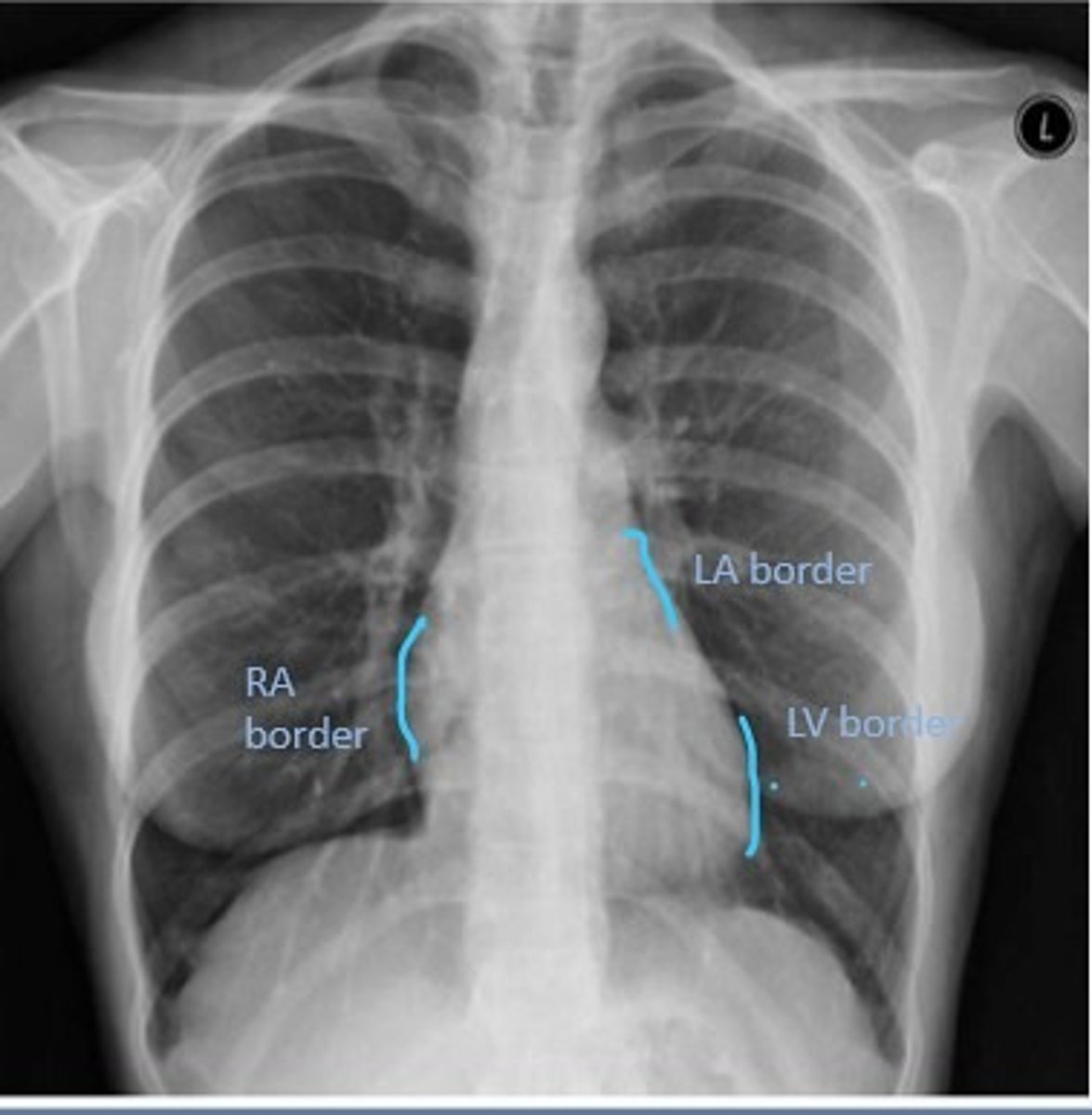
Left Cardiac Border
An area formed by the left ventricle
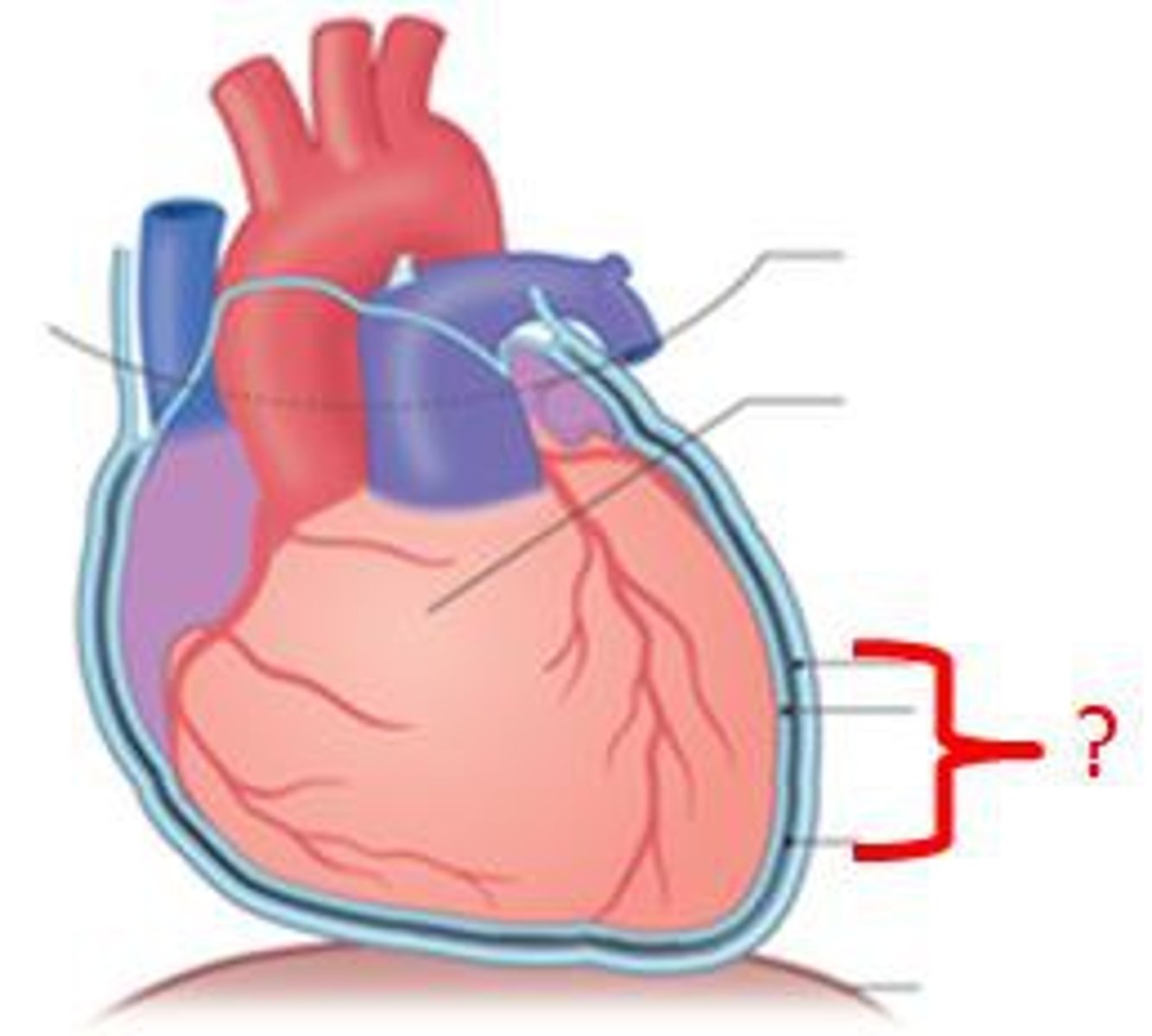
3 Layers of the Heart Wall
- Pericardium
- Myocardium
- Endocardium
Pericardium
Membrane surrounding the heart
Anatomy of the Heart
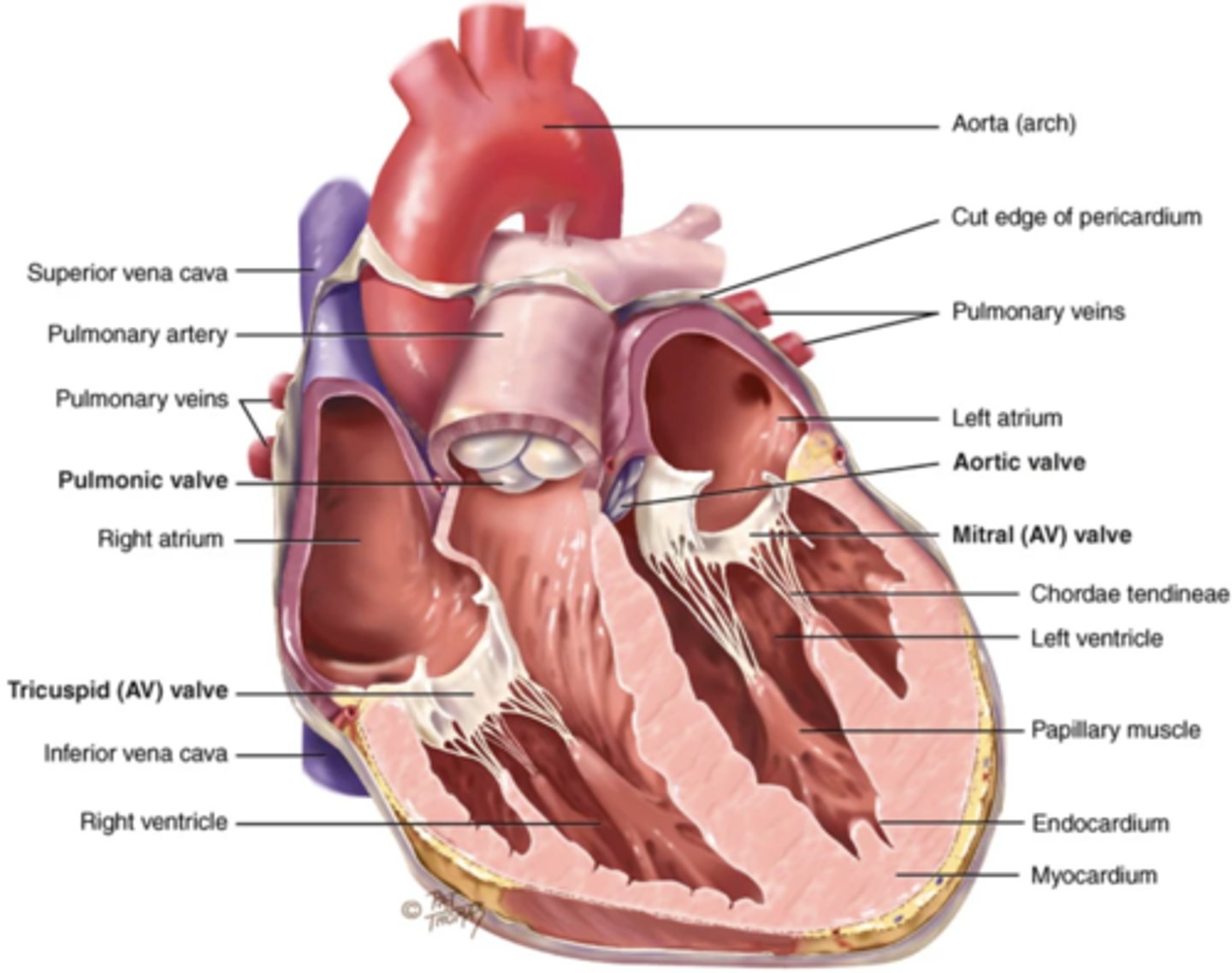
Myocardium
The muscular wall of the heart; does the pumping
Endocardium
The thin layer of endothelial tissue that lines the inner surface of the heart chambers and valves
2 Types of Chambers in the Heart
- Atrium
- Ventricles
Atrium (2)
A thin-walled reservoir for holding blood, located at the upper chamber of the heart
Ventricle (2)
The thick walled muscular pumping chamber of the heart located at the bottom chamber of the heart
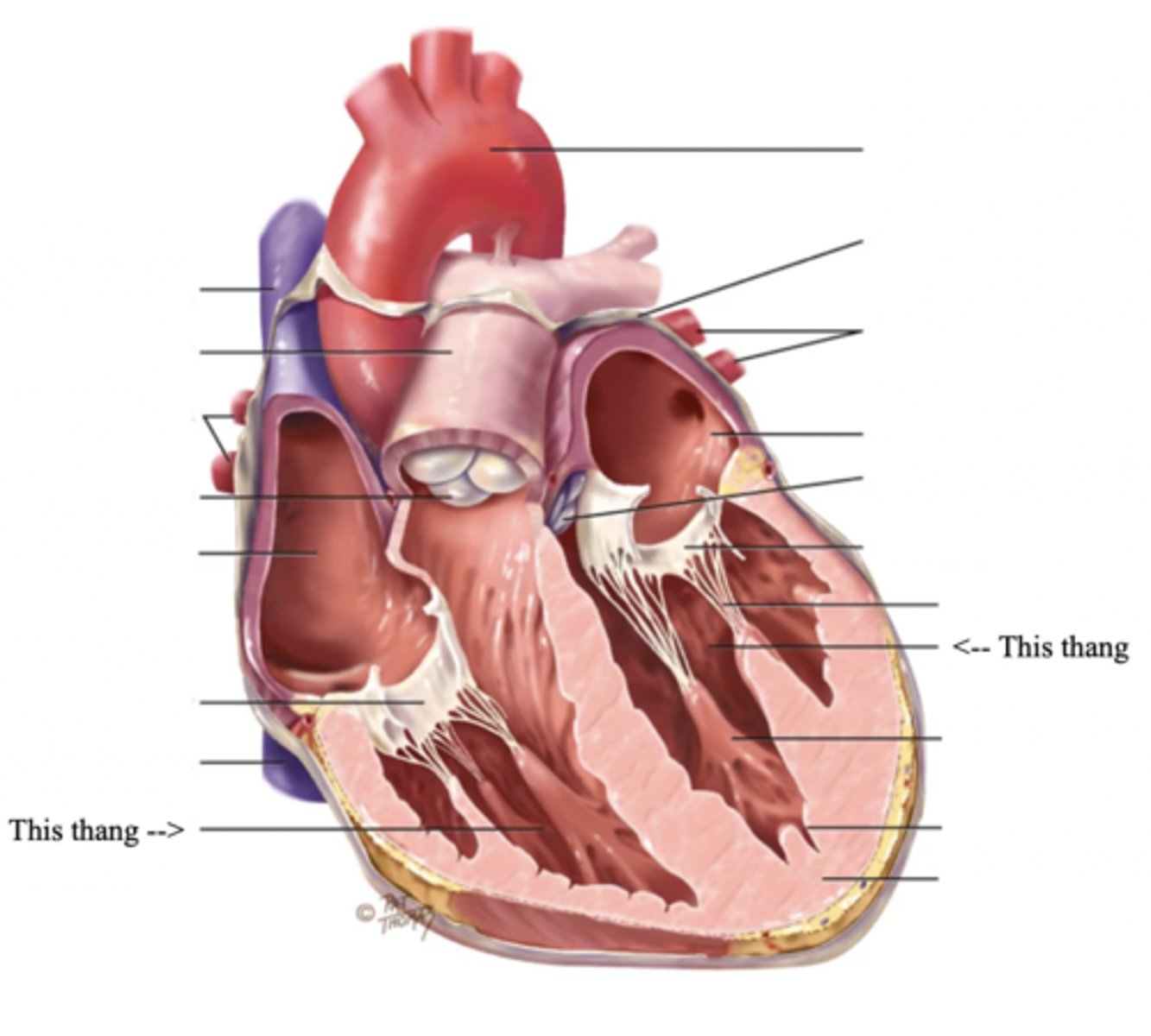
2 Main Types of Valves of the Heart
- Atrioventicular
- Semilunar
Atrioventricular Valves (AV) (2)
The valves that separate the atria and the ventricles
The 2 Atrioventicular Valves of the Heart
- Tricuspid
- Mitral
Tricuspid Valve
- The right AV valve separating the right atrium from the right ventricle
- Connected by 3 chordae tendinae
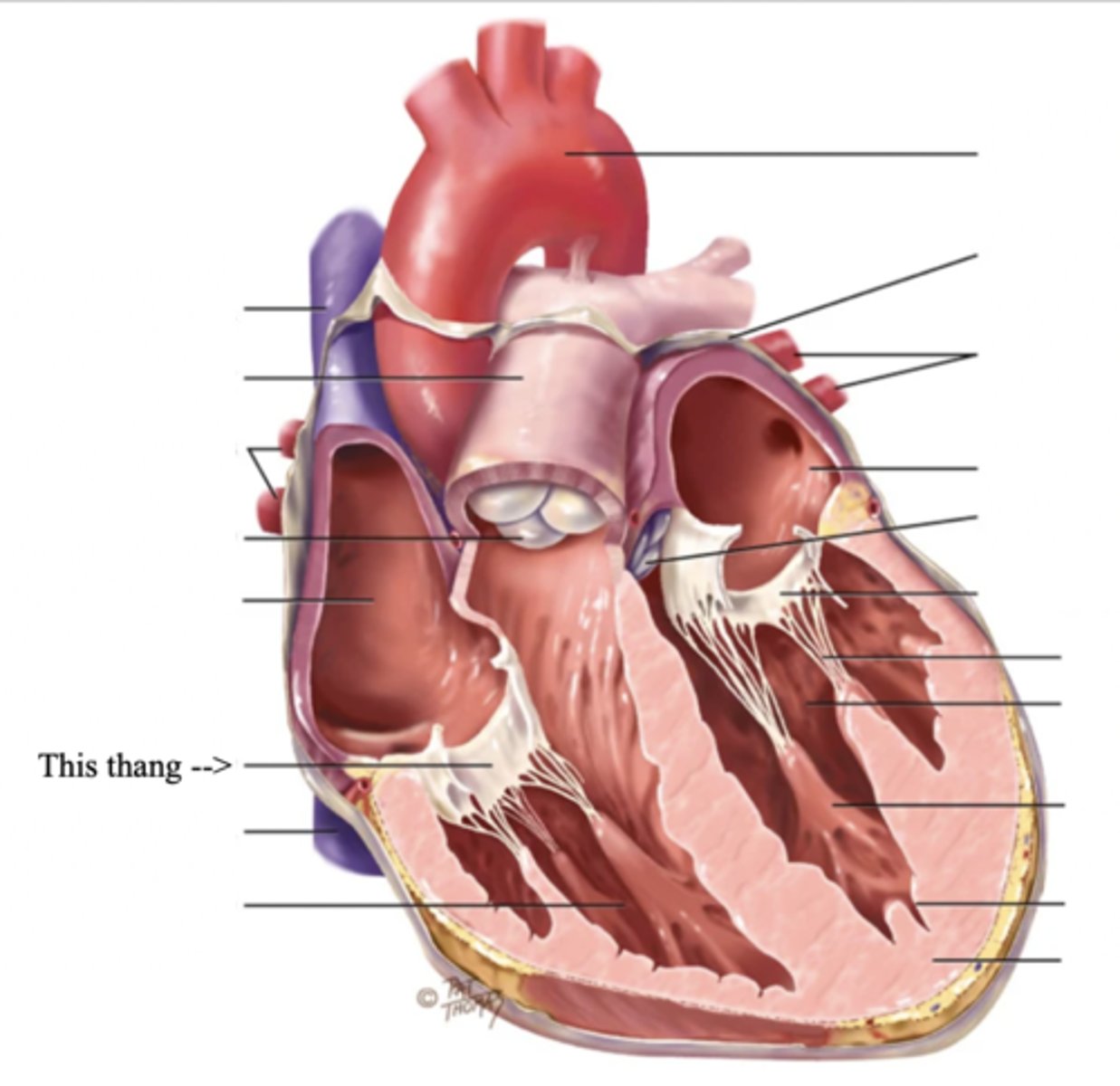
Mitral (Bicuspid) Valve
- The left AV valve separating the left atrium from the left ventricle
- Connected by 2 chordae tendinae
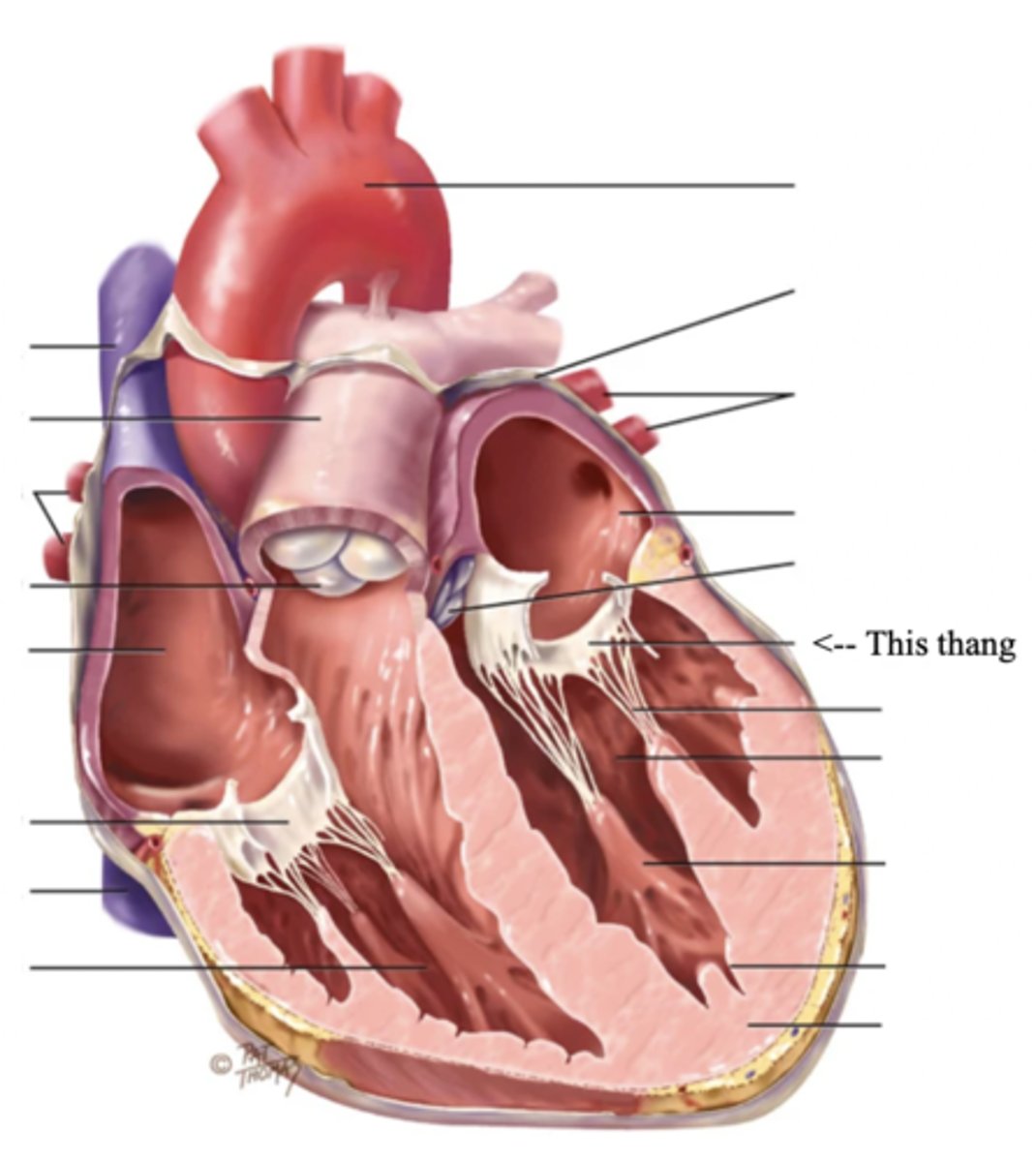
Chordae Tendinae
Fibers (heart strings) attatched to the tricuspid and mitral valve which pull it closed when papillary muscles contract, preventing back flow of blood
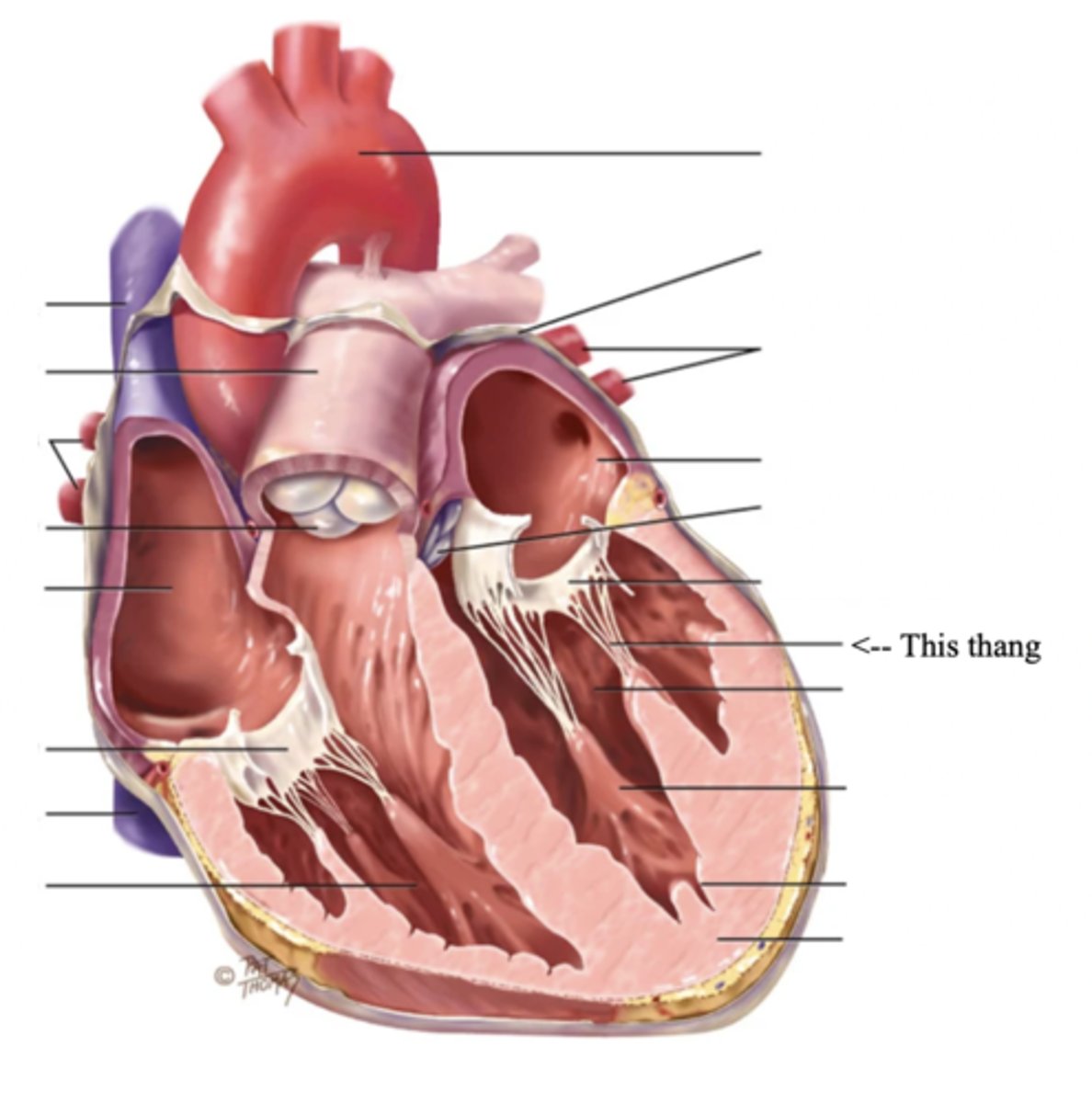
Semilunar Valves (SV) (2)
Valves located between the ventricles and the pulmonary arteries and aorta
The 2 Semilunar Valves of the Heart
- Pulmonic
- Aortic
Pulmonic Valve
The SV valve of the right side of the heart
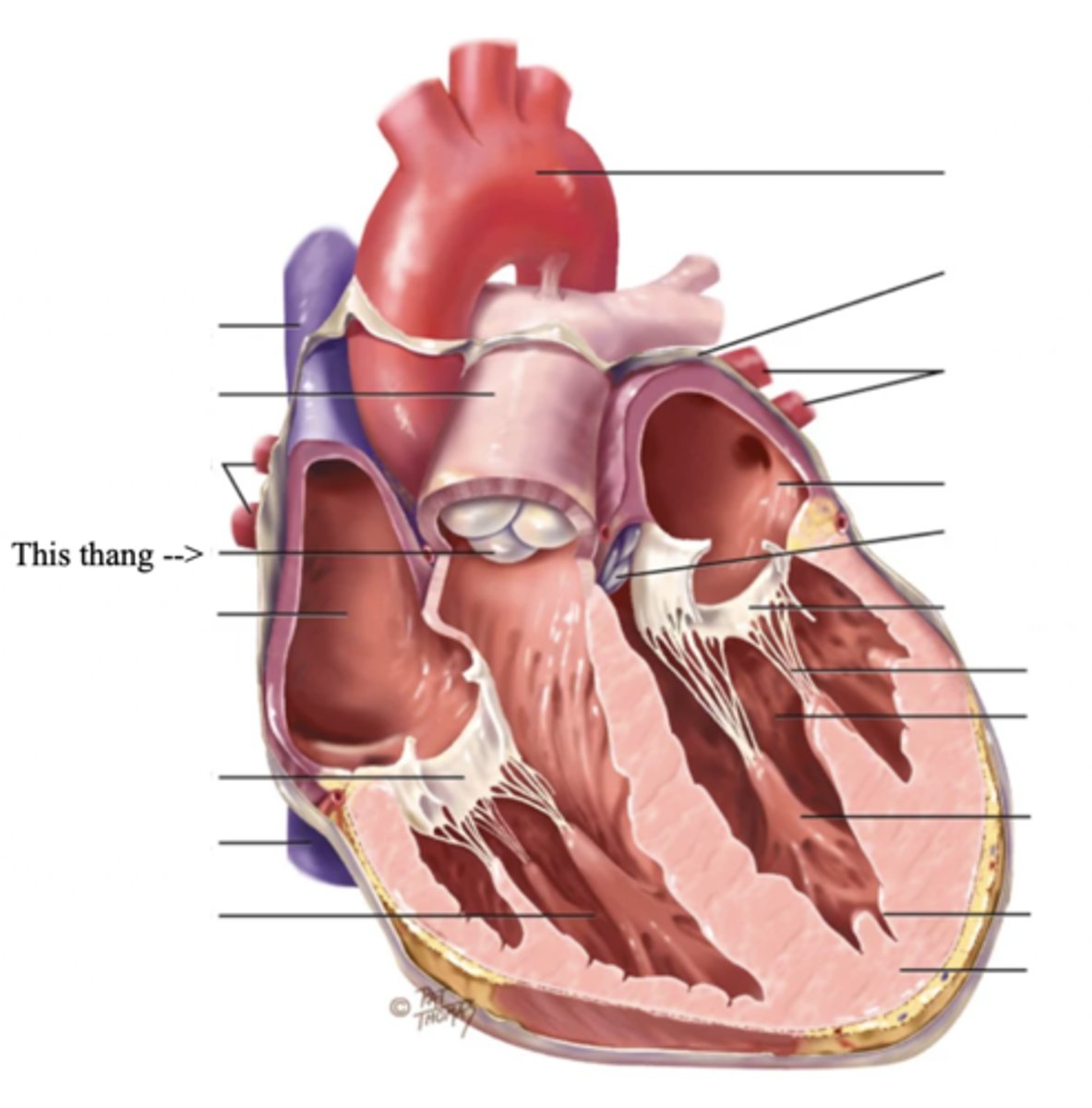
Aortic Valve
The SV valve of the left side of the heart
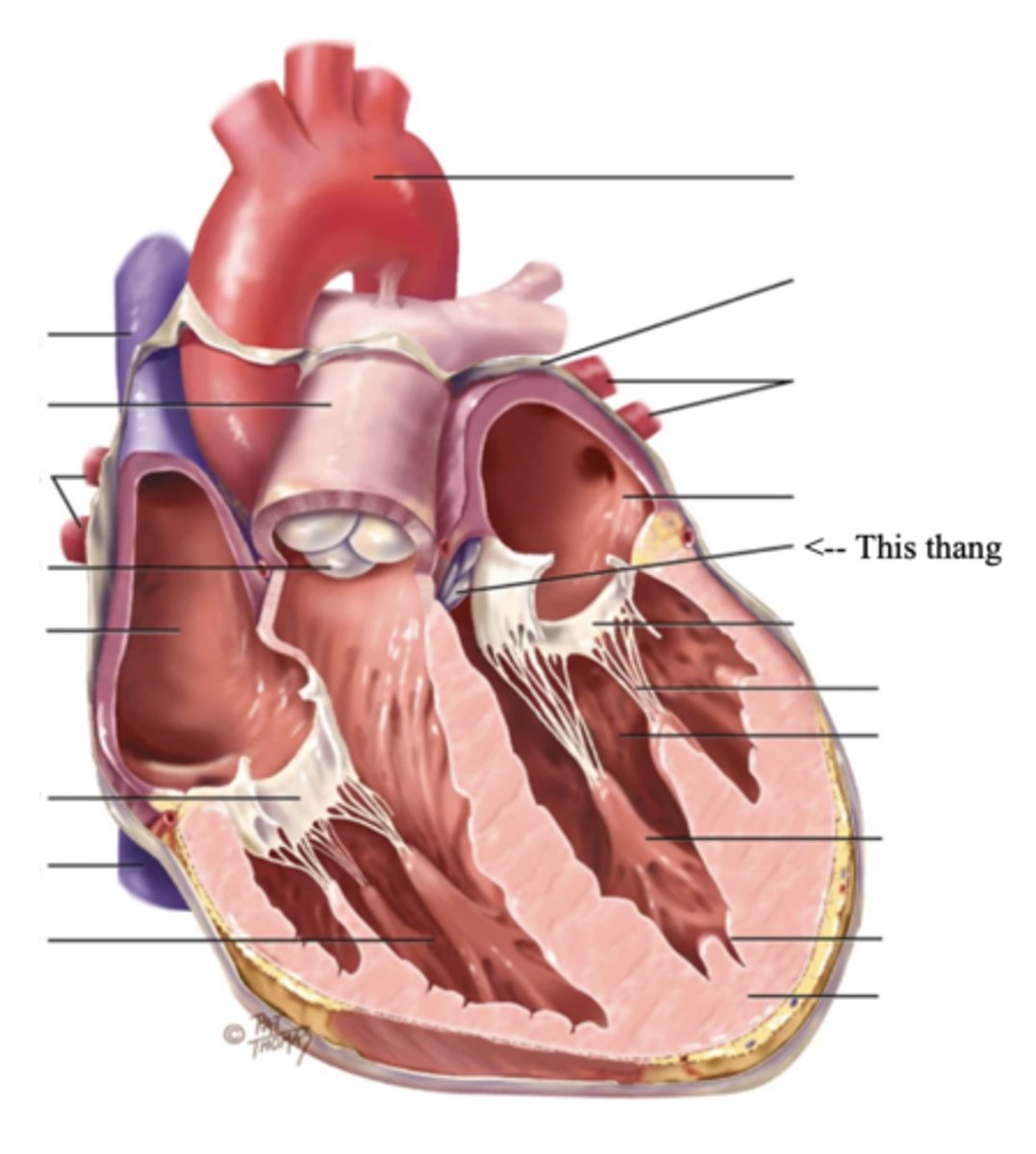
The 4 Great Vessels of the Heart
- Superior/inferior venae cavae
- Pulmonary artery
- Pulmonary veins
- Aorta
Superior/Inferior Venae Cavae
The large veins that empty into the right atrium of the heart and return unoxygenated venous blood to the right side of the heart
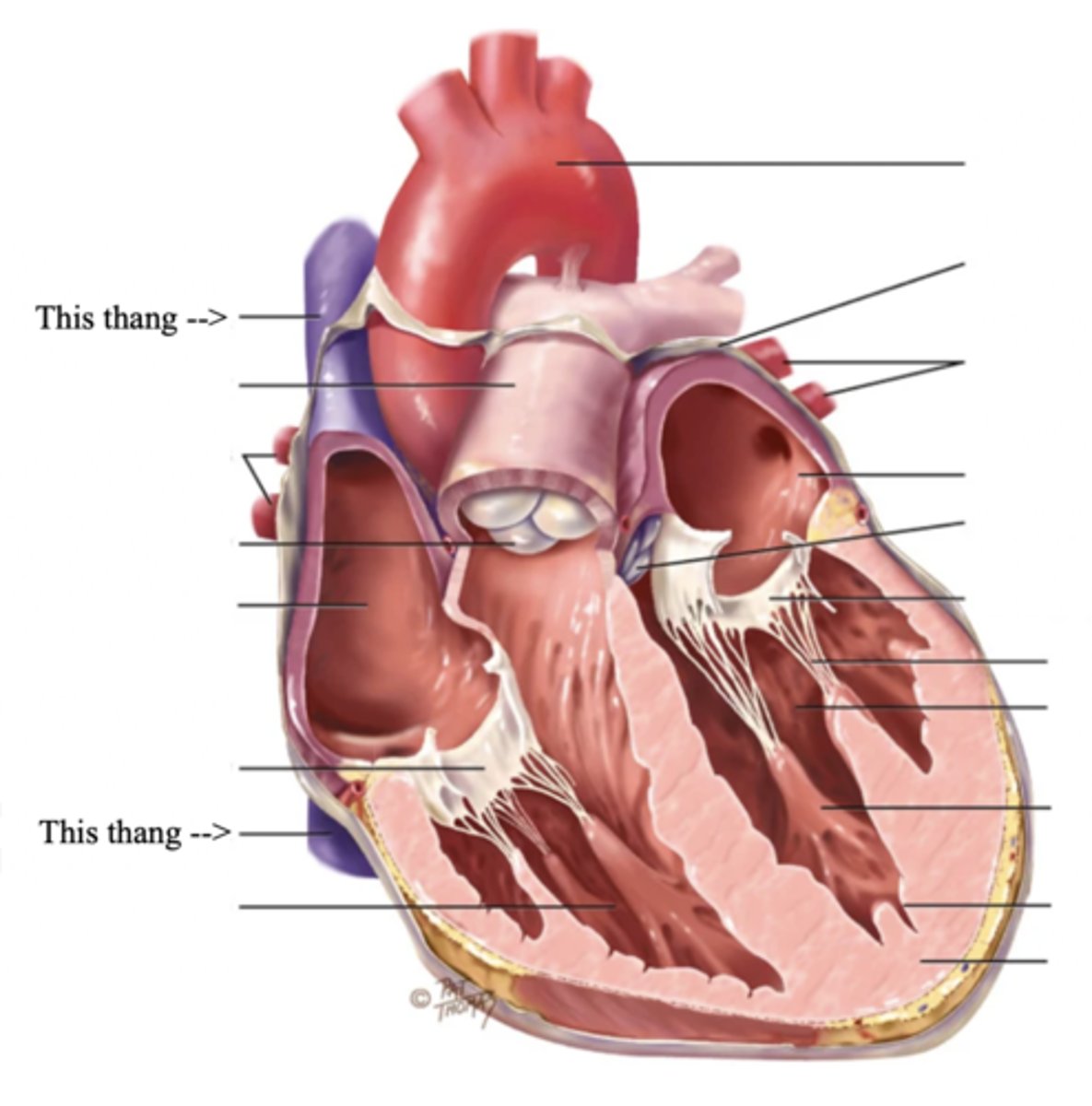
Pulmonary Artery
Artery carrying oxygen-poor blood from the heart to the lungs
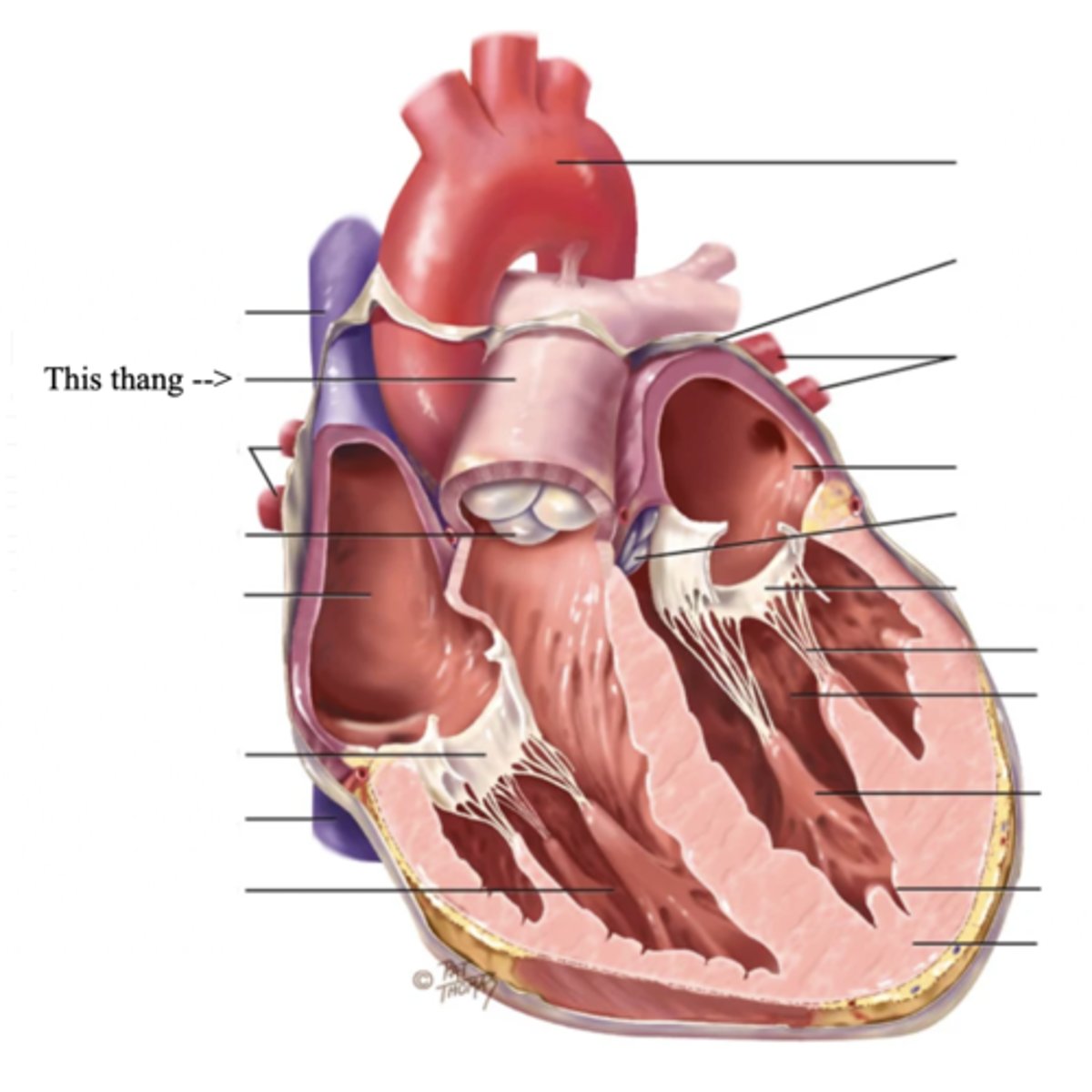
Pulmonary Veins
Veins carrying oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart
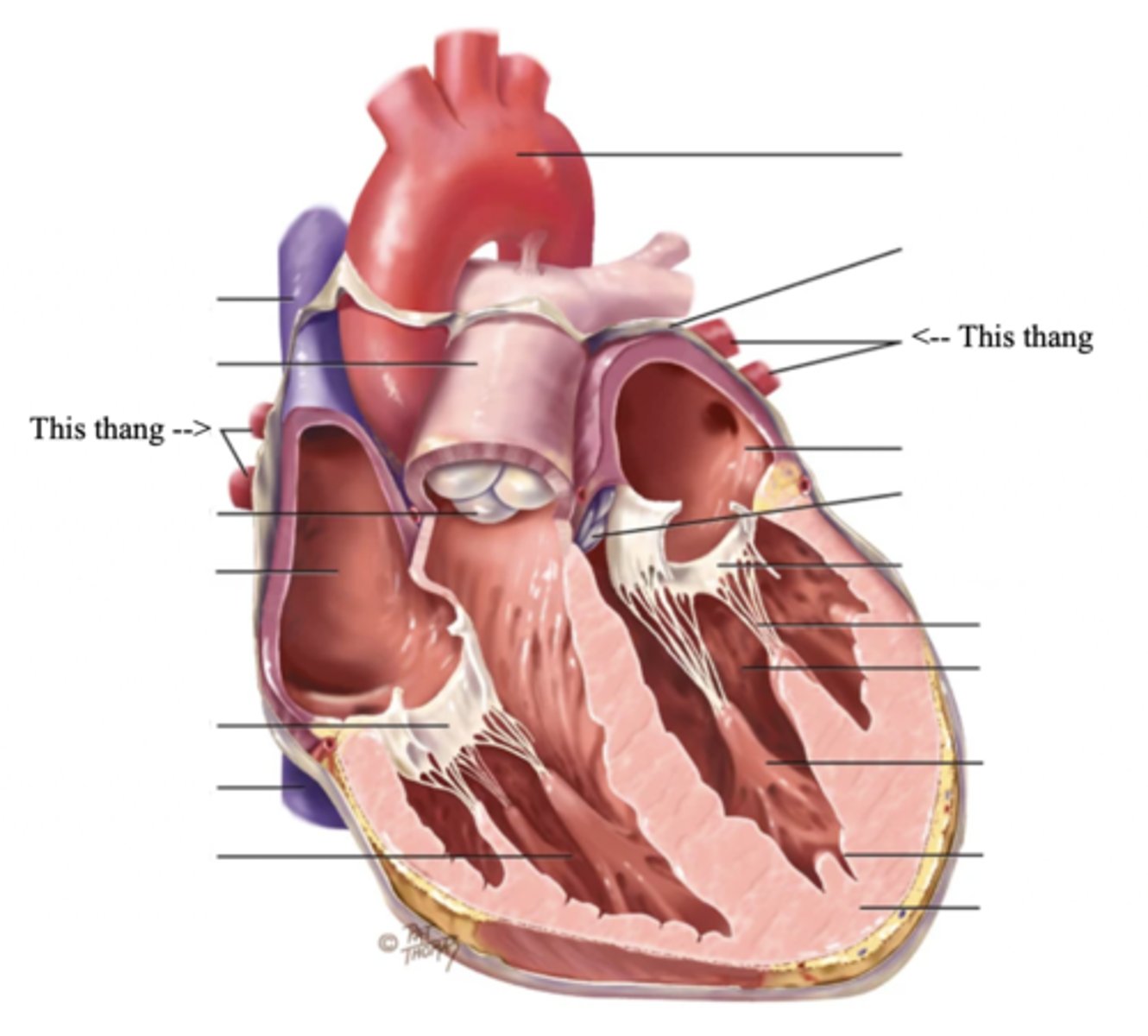
Aorta
The largest artery in the body which carries oxygenated blood from the heart throughout the body
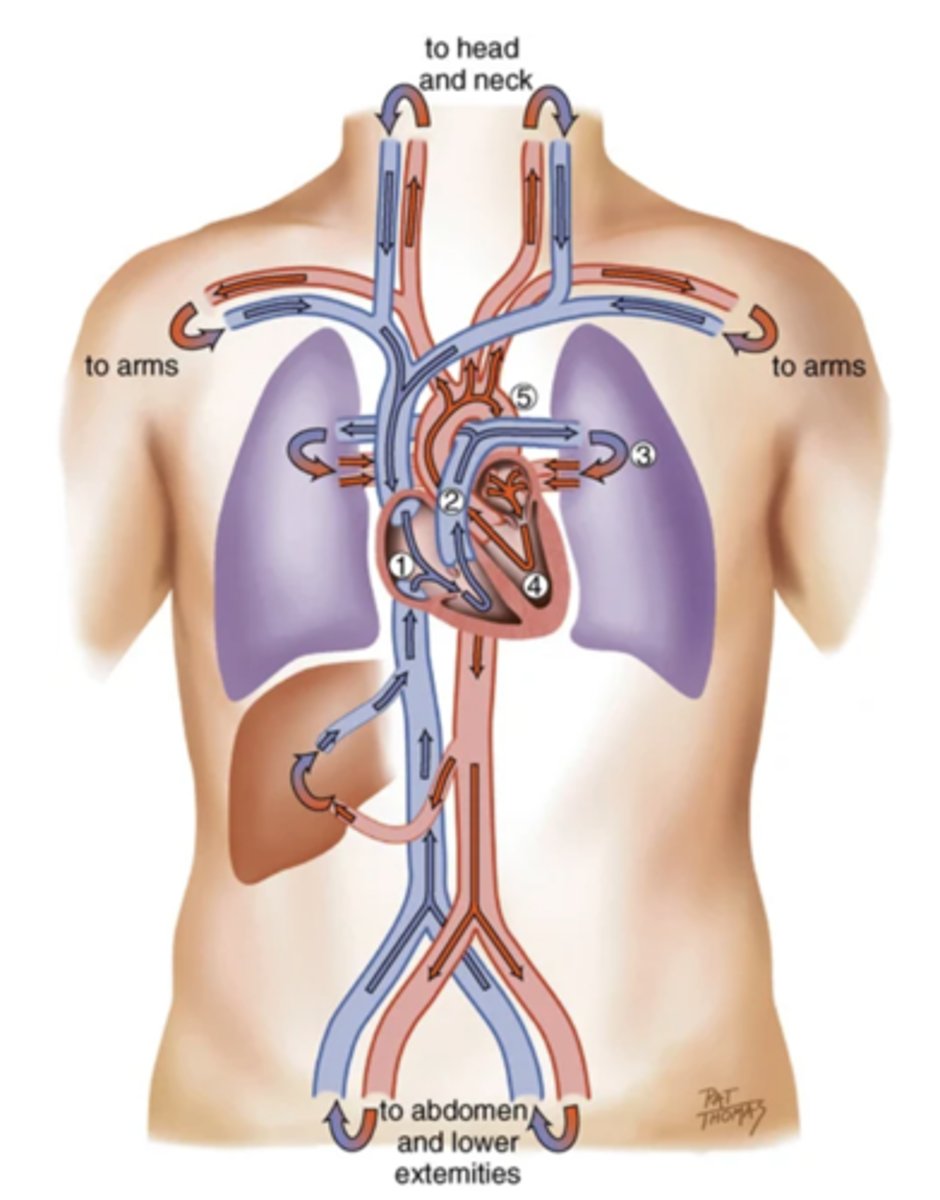
Blood Flow
Cardiac Cycle
A complete heartbeat consisting of contraction and relaxation of both atria and both ventricles
2 Phases of the Cardiac Cycle
- Diastole
- Systole
Diastole
The phase of the cardiac cycle where the ventricles relax and fill with blood (relaxation)
Systole
The phase of the cardiac cycle where blood is pumped from the ventricles and fills the pulmonary and systemic arteries (contraction)
Steps of Diastole
1.) Ventricles relax
2.) AV valves open
3.) Higher atrial pressure causes passive ventricular filling (early/protodiastolic filling)
4.) The atria contracts and pushes the last amount of blood into the ventricles (atrial systole)
Steps of Systole
1.) High ventricular pressure causes AV valves to close
2.) Ventricles contract, increasing ventricular pressure
3.) SV valves suddenly open, resulting in a quick ejection of blood
4.) SV valves close once ventricular pressure falls below aortic pressure
The 4 Heart Sounds
- S1
- S2
- S3
- S4
3 multiple choice options
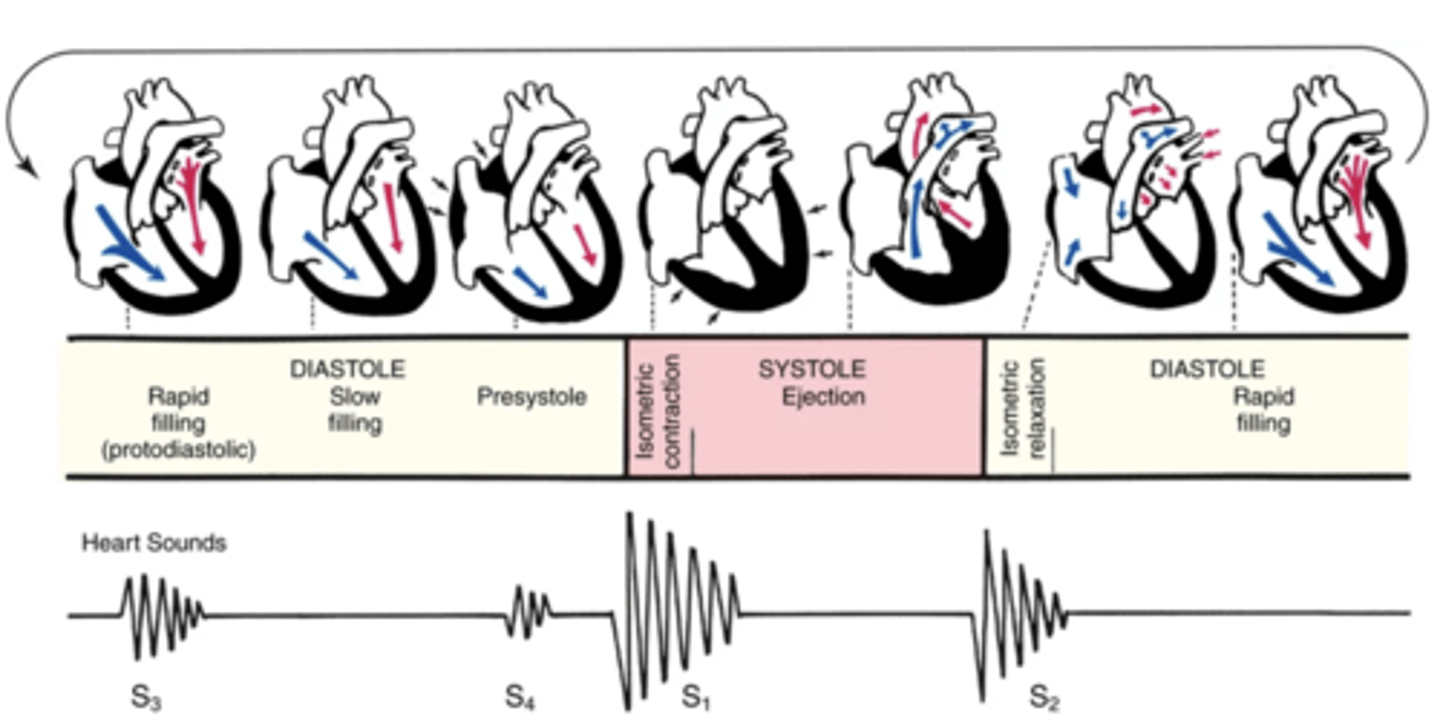
S1
The first heart sound that occurs with the closure of the AV valves, beginning systole
S2
The second heart sound that occurs with the closure of the SV valves, ending systole
S3
The third heart sound that sometimes occur when the ventricles are resistant to filling during protodiastole
S4
The fourth heart sound that sometimes occur when the ventricles are resistant to filling during the end of diastole (presystole/atrial systole)
Rule with Stroke Volume Regarding Respiration
moRe to the Right
Less to the Left
3 multiple choice options
Murmurs
Blowing or swooshing sound from turbulent blood flow
Causes of Murmurs
- Increased velocity
- Decreased viscosity
- Structural defect
4 Characteristics of Heart Sounds
- Frequency (Pitch)
- Intensity (Loudness)
- Duration
- Timing
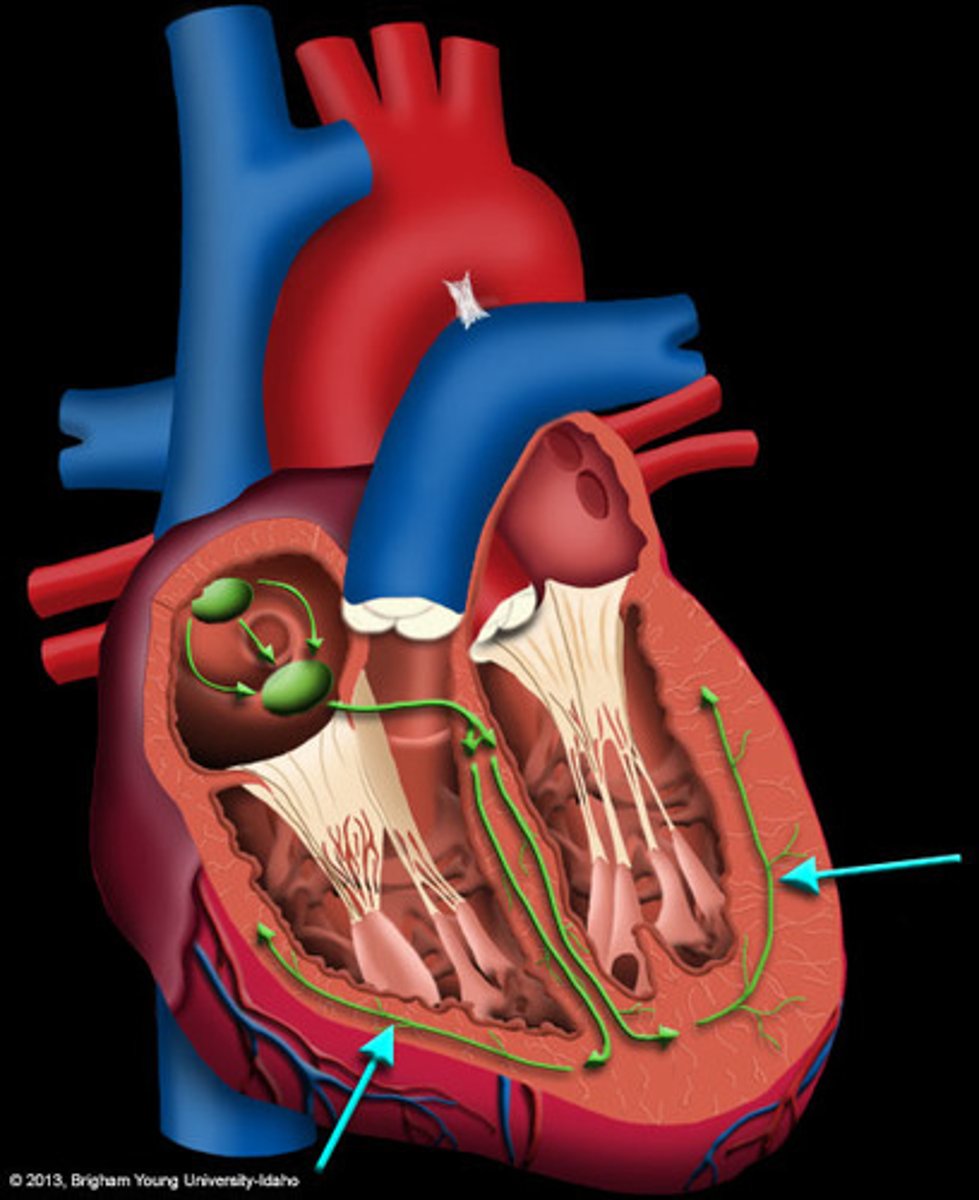
4 Parts of the Heart's Conduction System
- Sinoatrial (SA) node
- Atrioventricular (AV) node
- Bundle of His
- Purkinje fibers
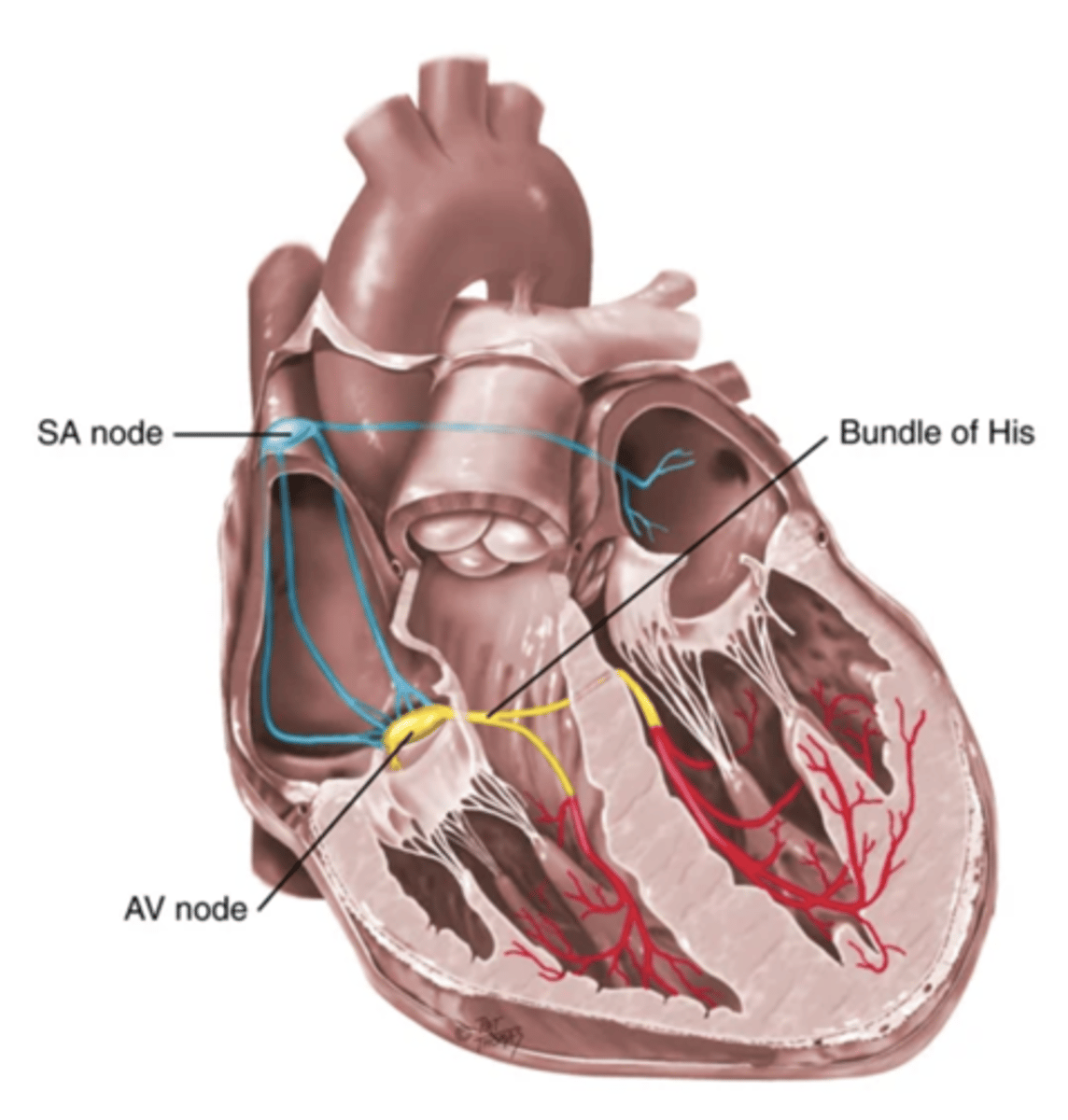
Sinoatrial (SA) Node
Pacemaker of the heart conduction system, located at the right atrium (light blue)
Atrioventricular (AV) Node
The part that relays electrical impulses from atria into the bundle of his in the heart's conduction system; delayed slightly (yellow)
Bundle of His
Part of the heart's conduction system that transmits the cardiac impulse from the atrioventricular node to the purkinje fibers (red)
Purkinje Fibers
Fibers in the ventricles that transmit impulses to the right and left ventricles, causing them to contract
ECG Waves
- P wave
- P-R interval
- QRS complex
- Q-T interval
- T wave
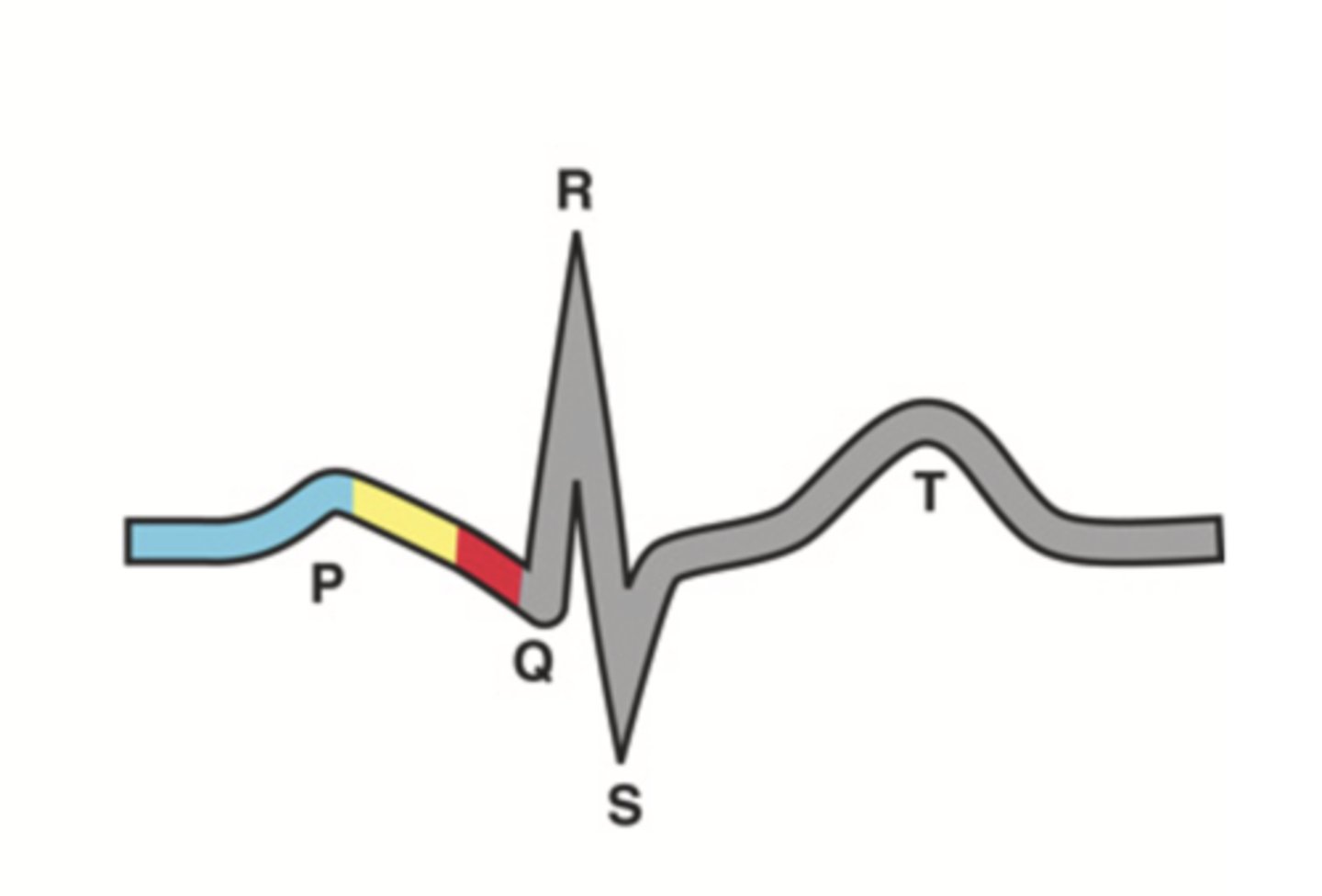
P Wave
Atrial depolarization
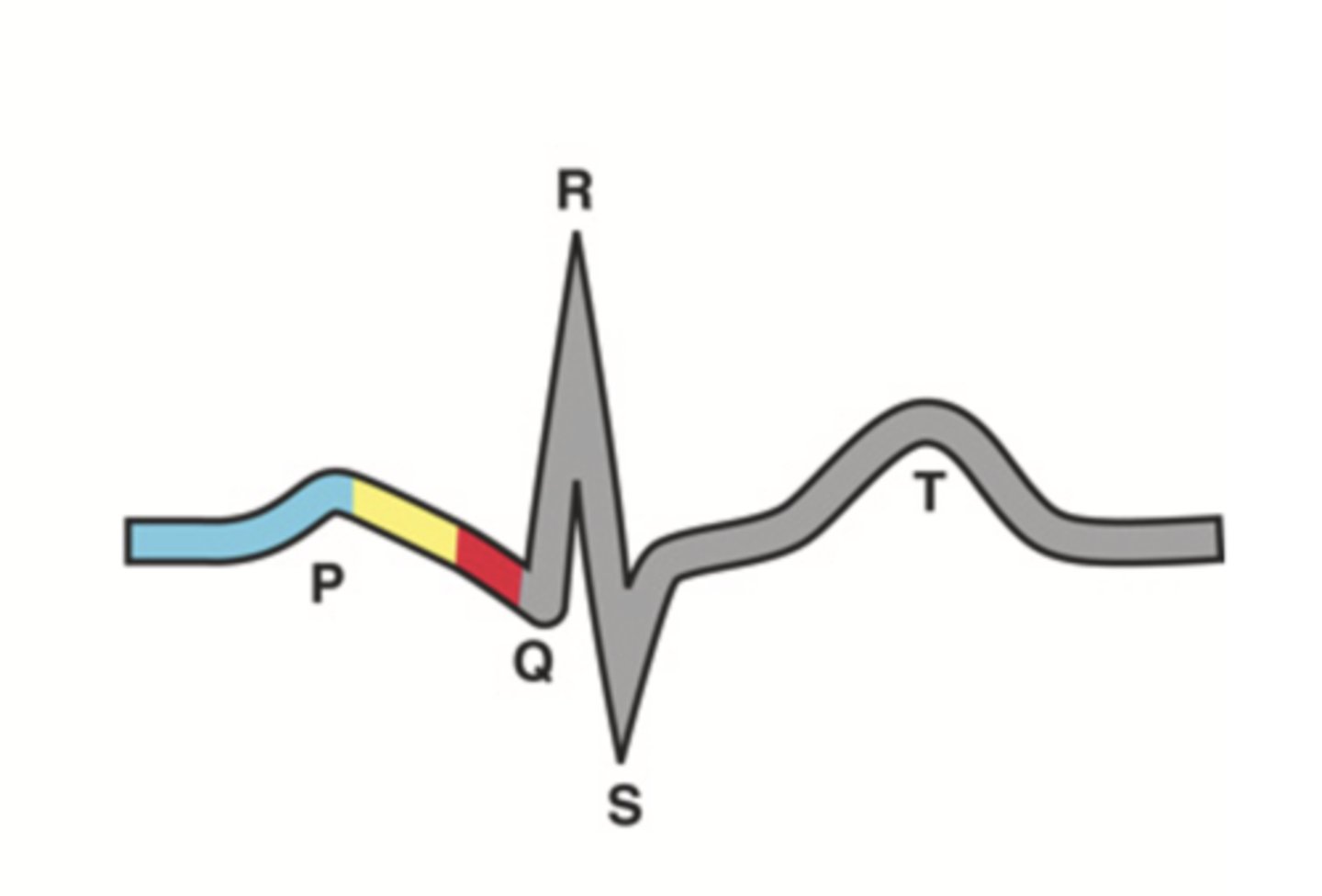
P-R Interval
Atrial contraction
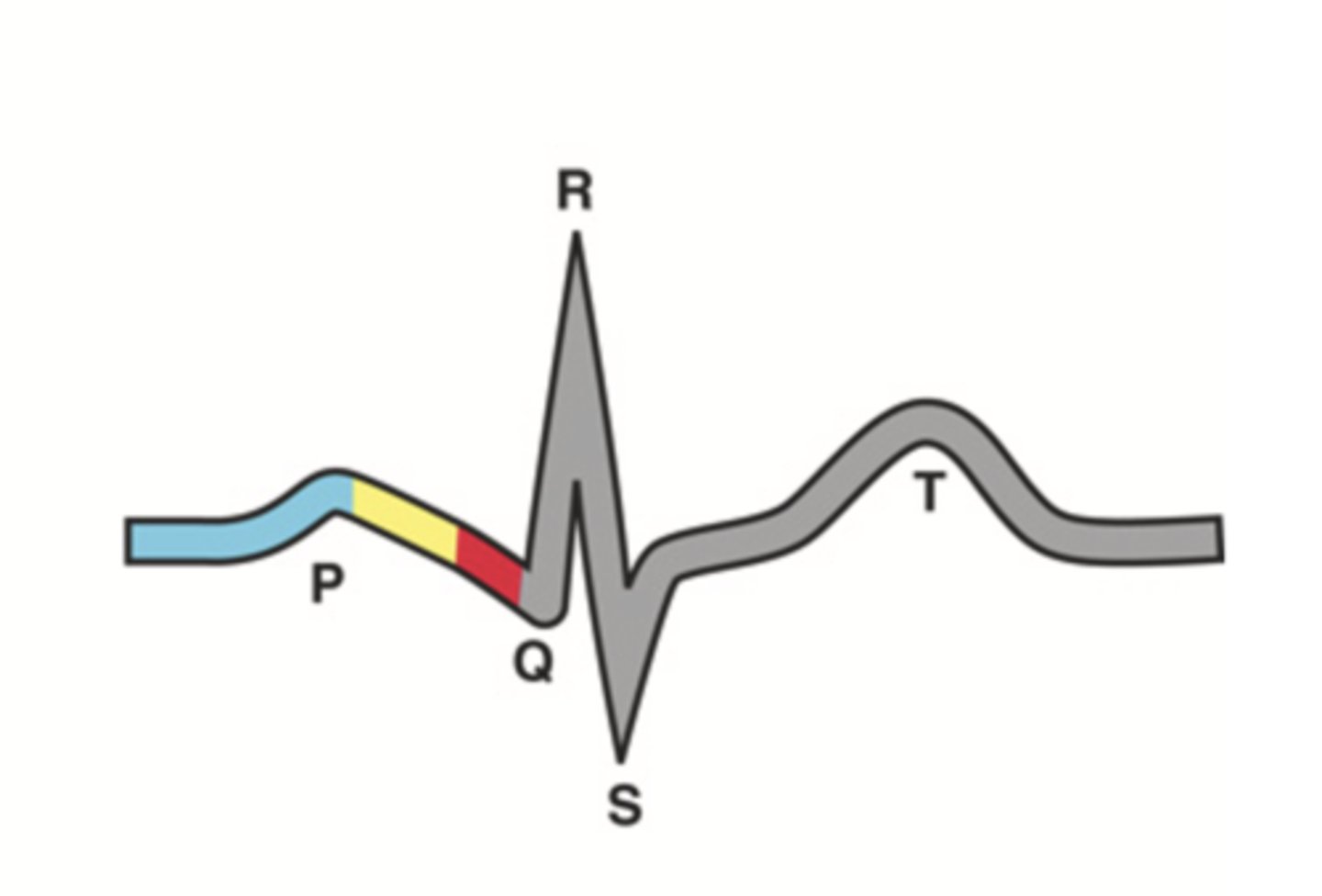
QRS Complex
Ventricular depolarization
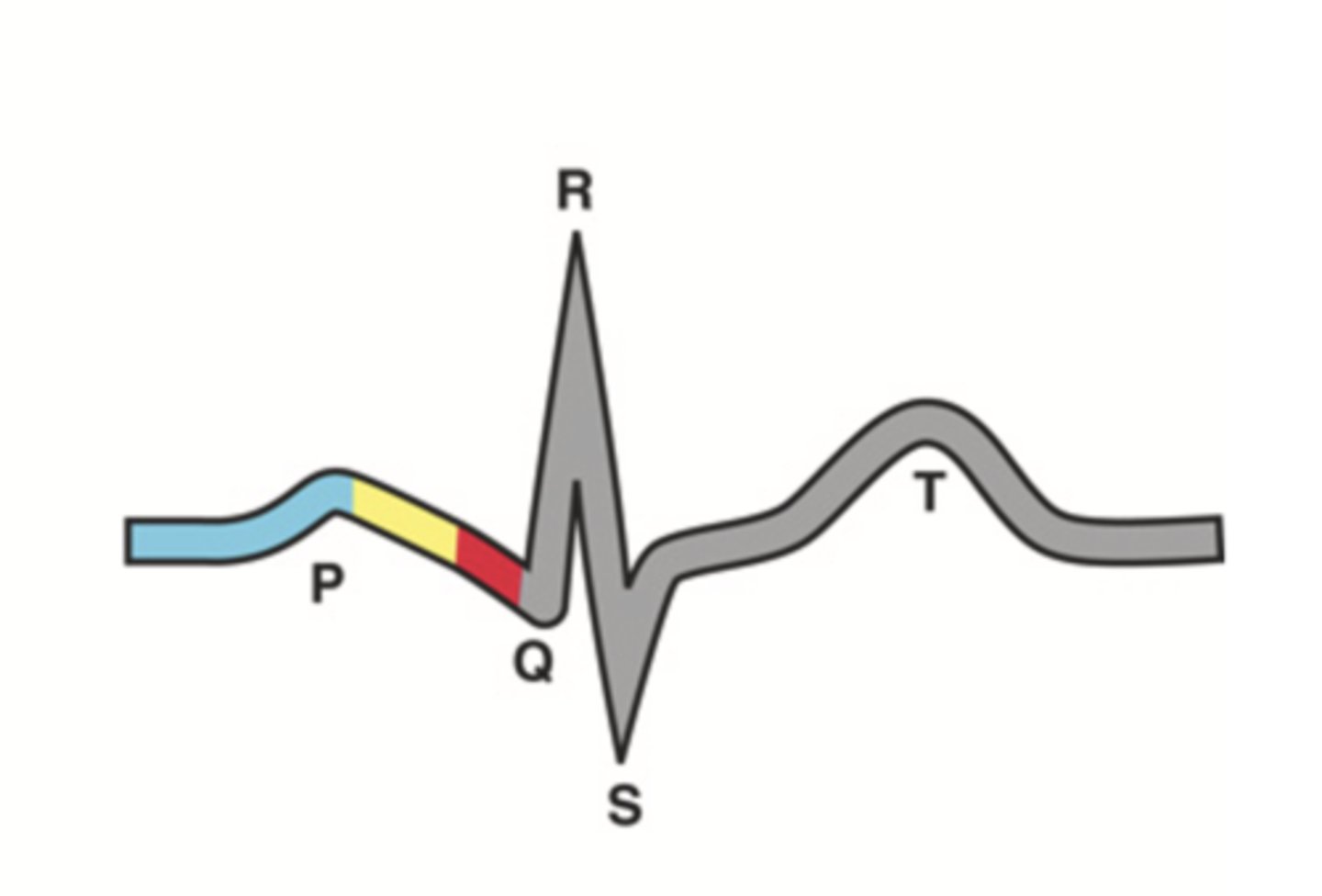
Q-T Interval
Ventricular contraction
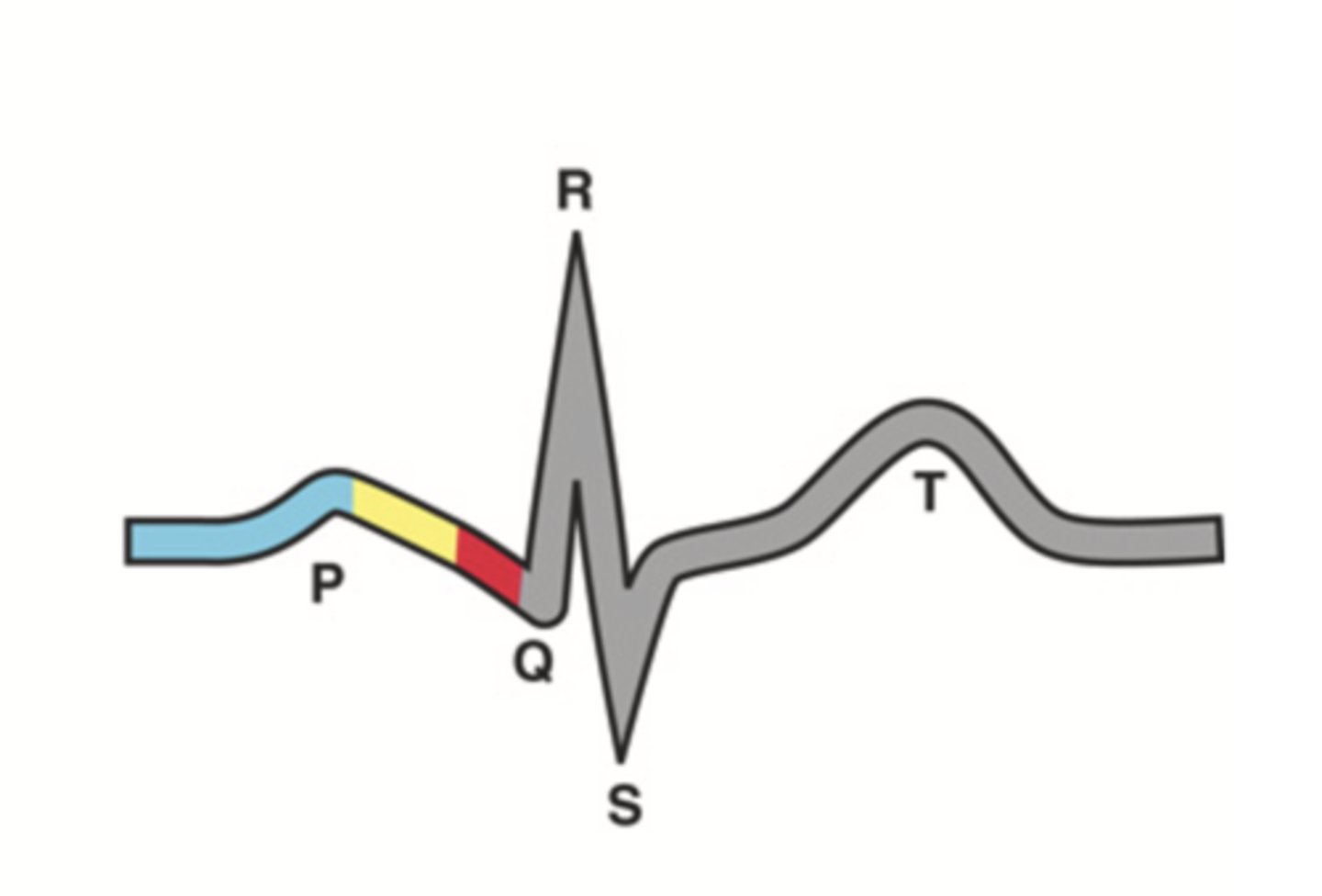
T Wave
Repolarization of ventricles
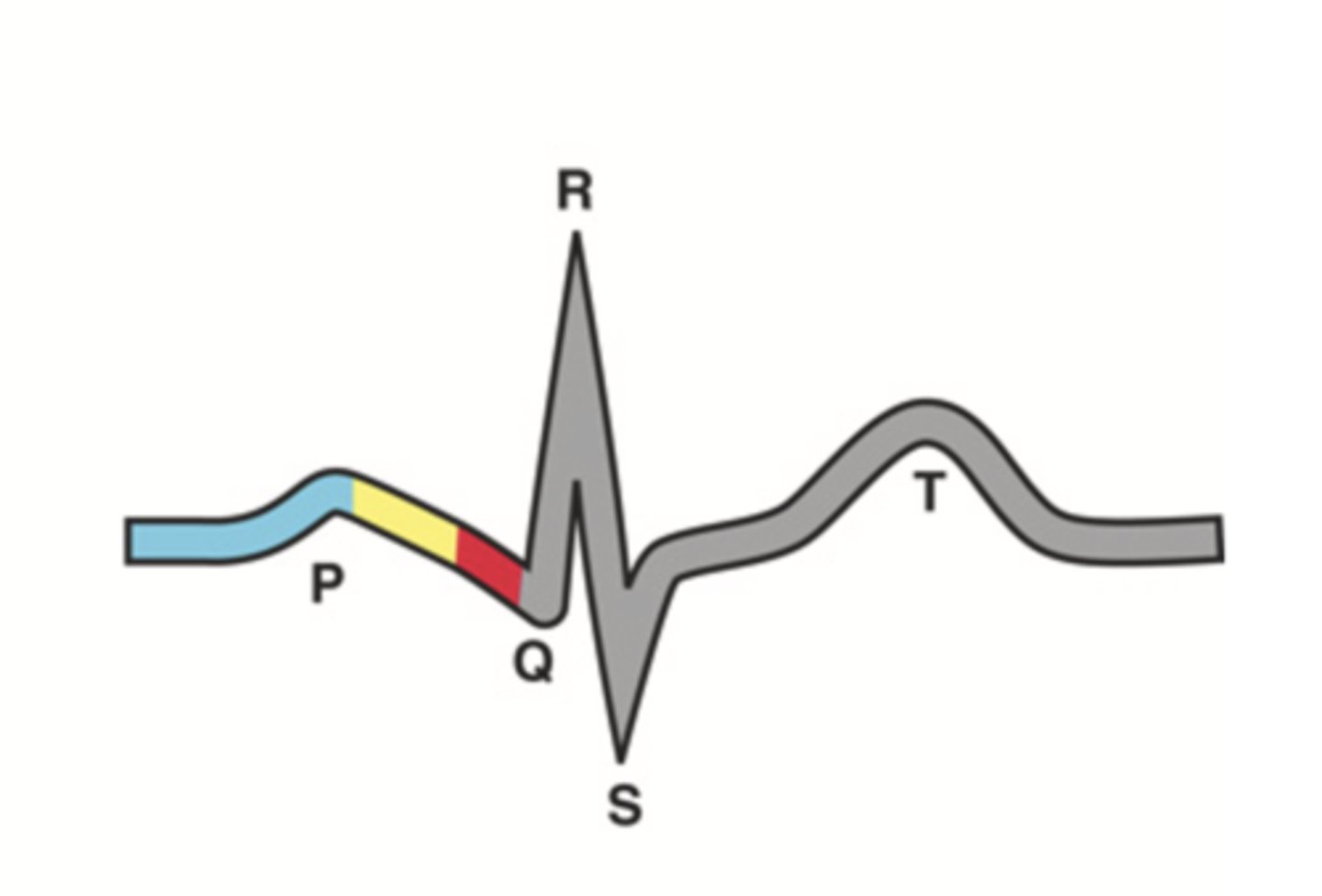
Stroke Volume
The volume of blood pumped out of the heart's left ventricle during each systolic cardiac contraction
Cardiac Output
Stroke volume x heart rate
Preload
The stretch at the end of diastole
Afterload
The ventricular pressure needed to overcome the high pressure in the aorta and open the aortic valve
2 Main Neck Vessels
- Jugular veins
- Carotid arteries
Jugular Veins
- One of the main neck vessels; carries unoxygenated blood to the superior vena cava
- Has 2 parts
- Provides information about activity of right side of heart
2 Parts of the Jugular Veins
- External
- Internal
External Jugular Veins
The more superficial jugular vein that lies lateral to the sternocleidomastoid and above the clavicle
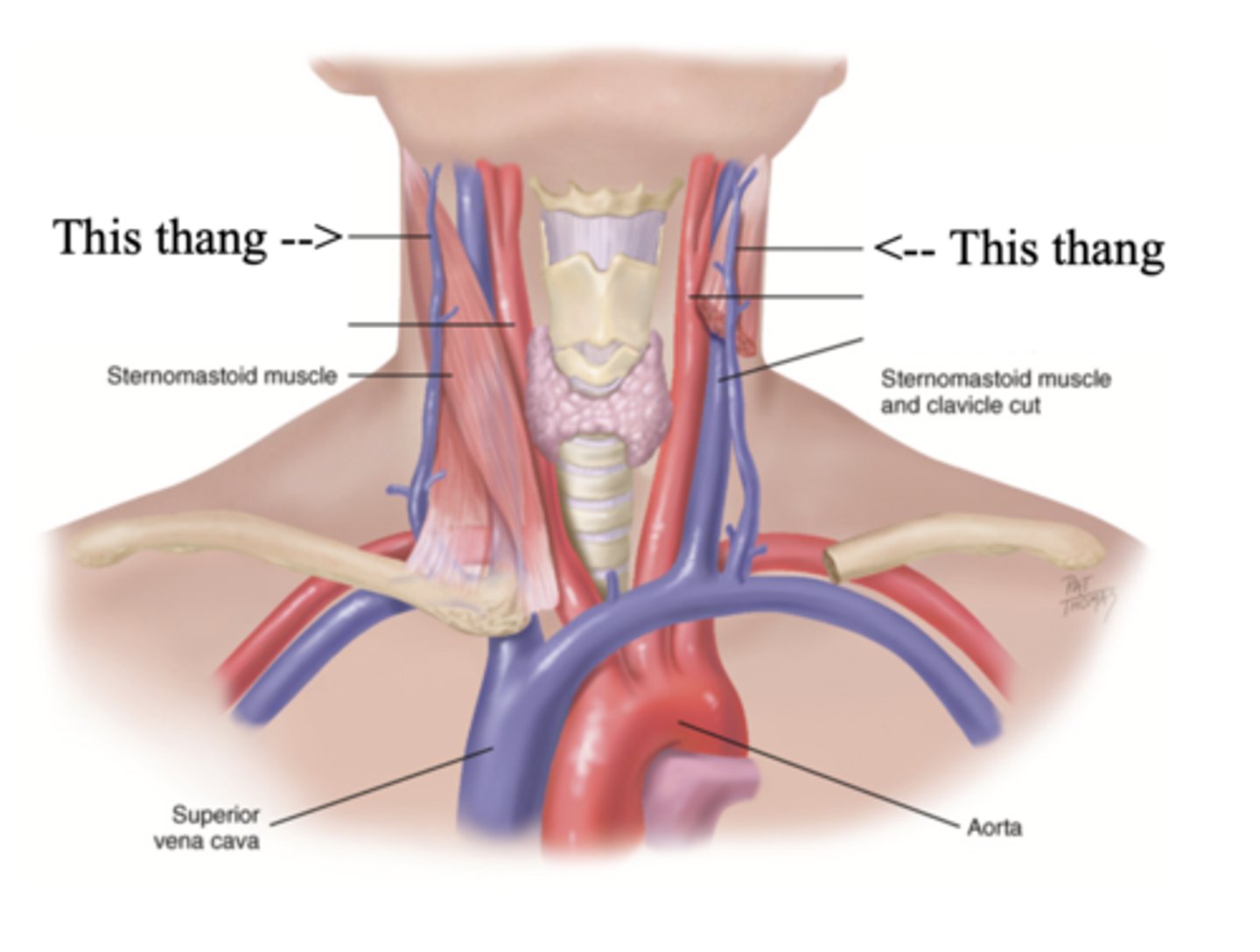
Internal Jugular Veins
The deeper jugular vein that lies medial to the sternocleidomastoid
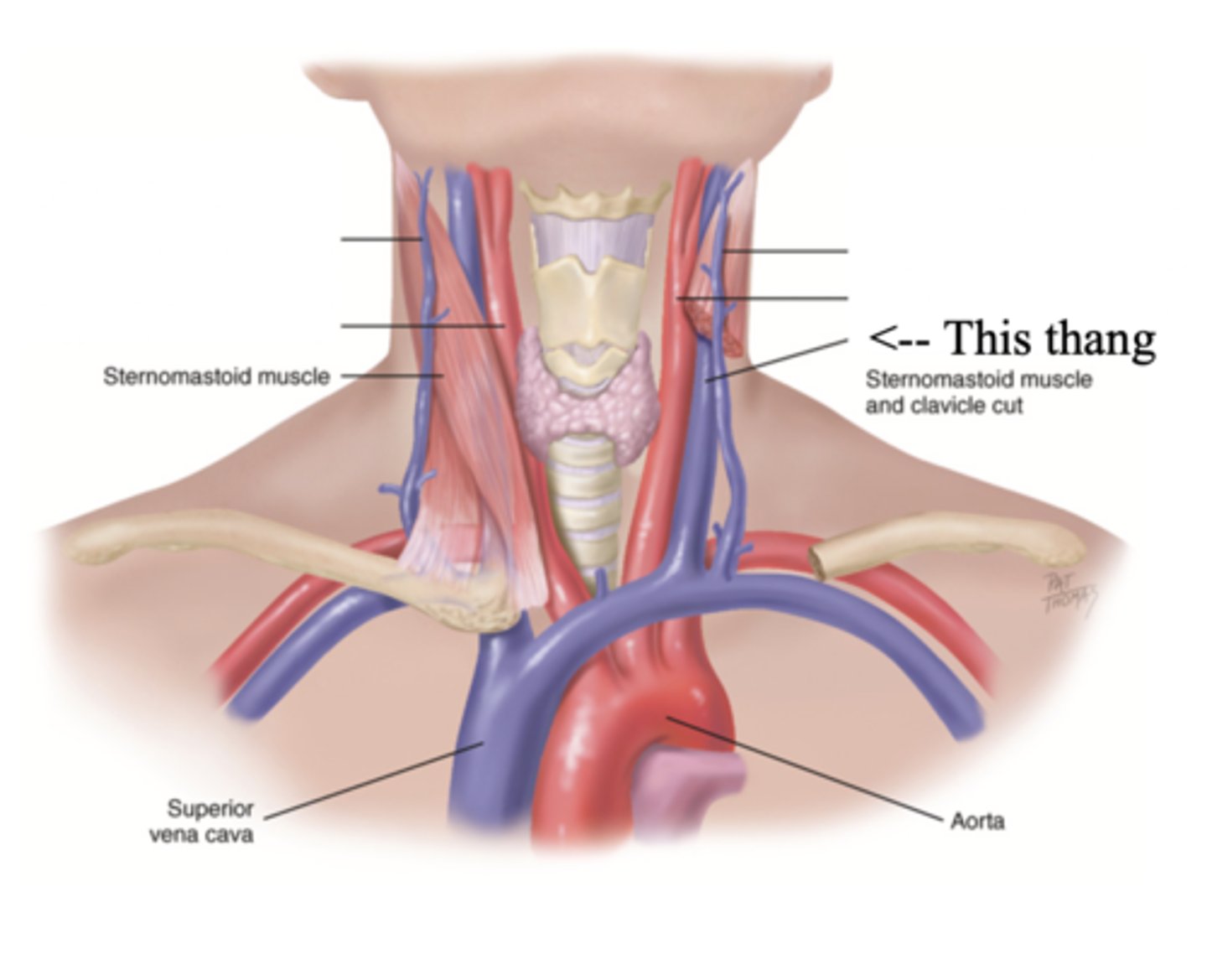
Carotid Arteries
The major neck vessel that carries oxygenated blood from the heart to the head
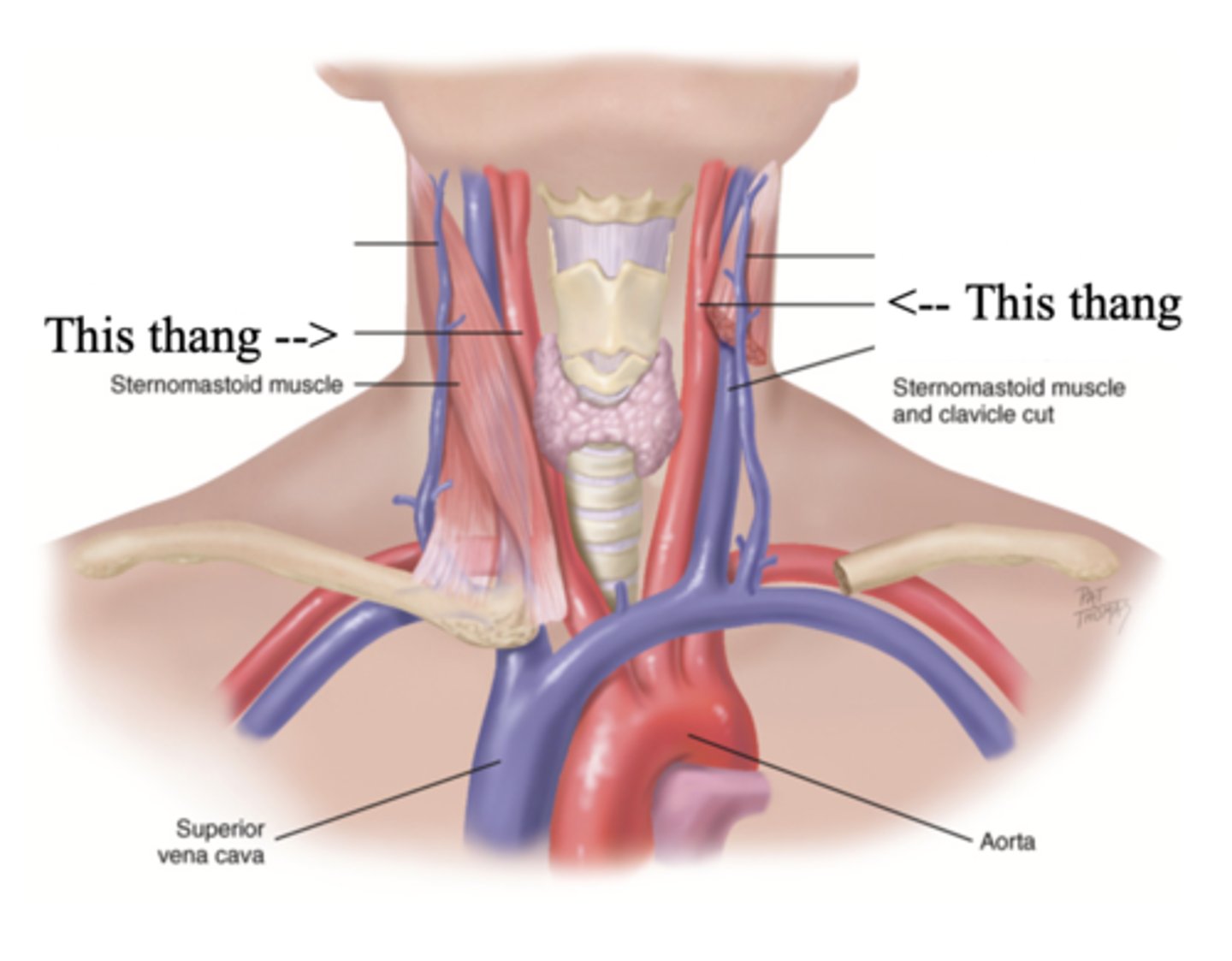
Main Differences Between Internal Jugular Veins and Carotid Arteries
- Internal jugular pulse more lower and lateral to sternocleidomastoid than the carotid pulse, which is higher and more medial
- Internal jugular pulse is more undulant and diffuse, while carotid pulse is more brisk and localized
- Internal jugular pulse varies with respiration
- Carotid pulse can be palpated
- Palpating internal jugular pulse will obliterate it
- Internal jugular pulse drops/disappears as the patient is brough to a sitting position
Developmental Heart Considerations for Infants and Children
- Heart is more horizontal until 7
- Lower BP and higher heart rate
- Innocent heart murmurs
Developmental Heart Considerations for Older Adults
- Arteries stiffen, increasing systolic pressure
- Risk for cardiovascular diseases
- Orthostatic hypotension
Foramen Ovale
A hole that connects the two atria in the fetal heart
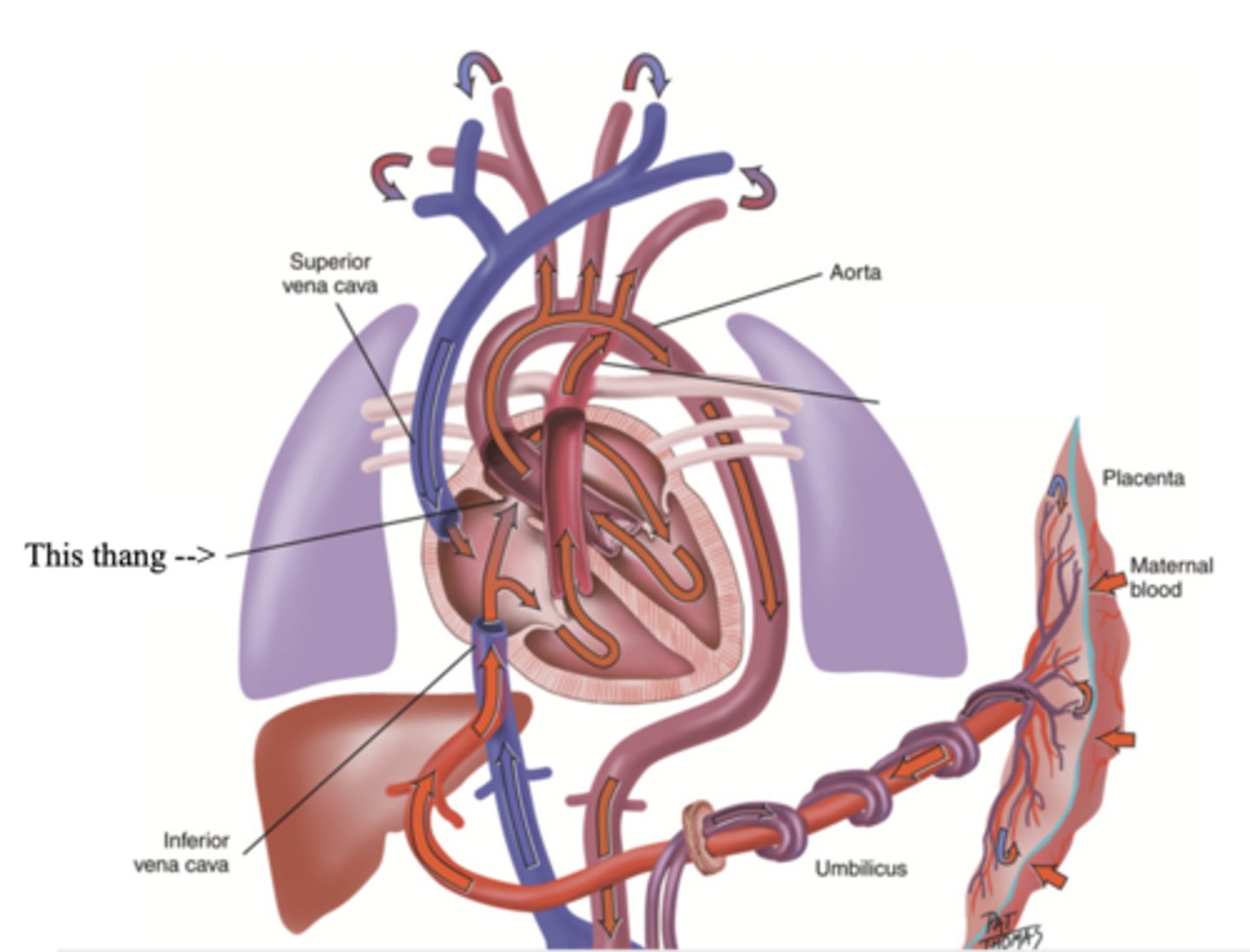
Ductus Arteriosus
A blood vessel in a fetus that bypasses pulmonary circulation by connecting the pulmonary artery directly to the ascending aorta
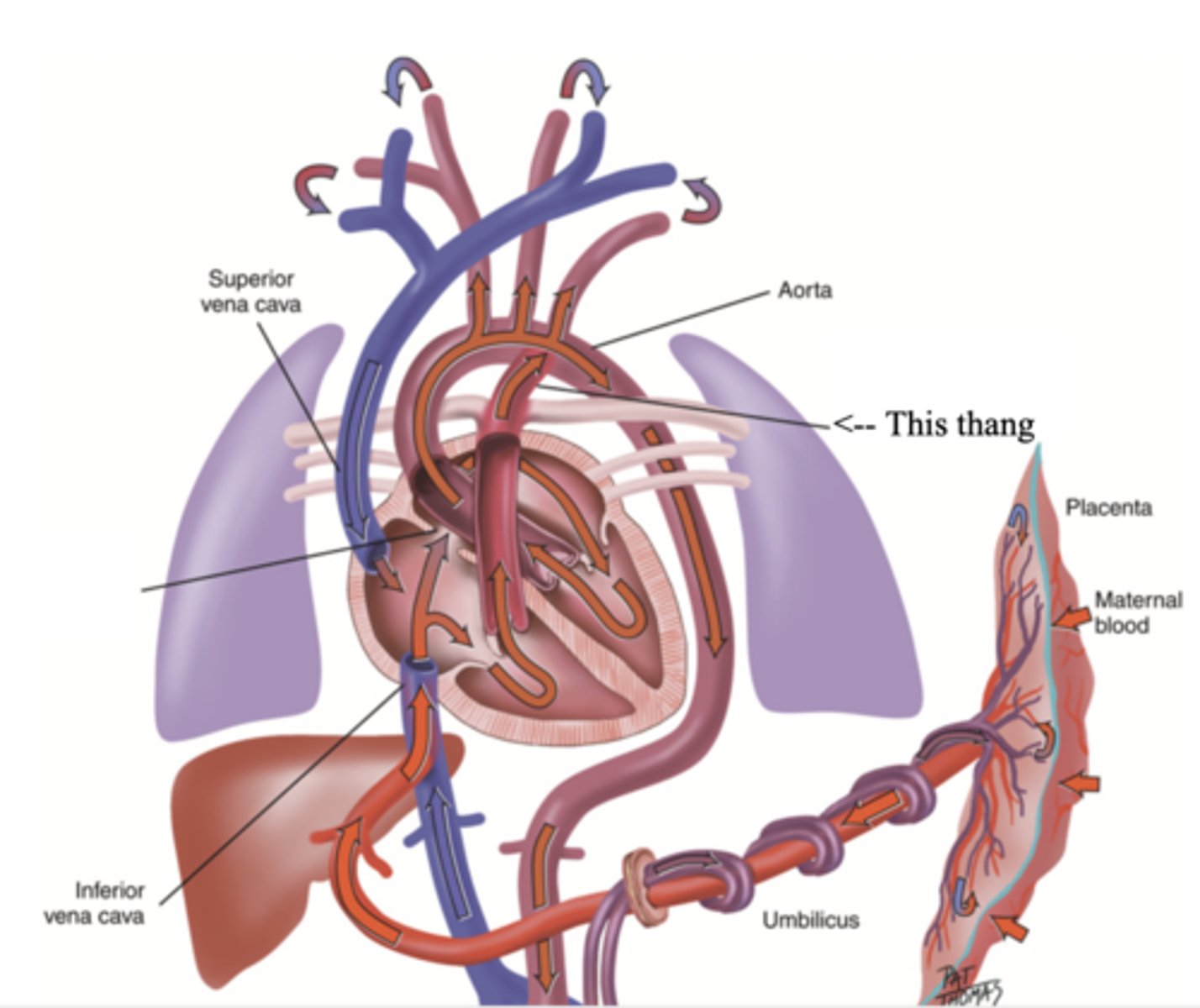
Developmental Heart Considerations for Pregnant Women
- Increase in blood volume
- Increase in stroke volume
- Increase in cardiac output
3 multiple choice options
Subjective Data to Assess for the Heart
1.) Chest pain
2.) Dyspnea
3.) Orthopnea
4.) Cough
5.) Fatigue
6.) Cyanosis or pallor
7.) Edema
8.) Nocturia
9.) Cardiac history
10.) Family cardiac history
11.) Personal habits (cardiac risk factors)
Major Risk Factors for Heart Disease
- Stroke
- High blood pressure
- Smoking
- High cholesterol levels
- Obesity
- Physical inactivity
- Diabetes
Orthopnea
The need to assume a more upright position to breathe
OLD CARTS
- Onset
- Location
- Duration
- Character
- Alleviating/aggravating factors
- Radiation
- Treatment
- Severity