Neuro Block 3
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/109
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:00 PM on 11/6/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
1
New cards
motor cortex
part of frontal lobe for planning, initiating, and directing voluntary movements; located in the precentral gyrus; stimulation of neurons causes movements
2
New cards
brainstem centers
parts of brain that control basic movements and posture
3
New cards
basal ganglia
collection of nuclei in the forebrain that control the initiation and termination of voluntary movements (force of movements); receive input from cerebral cortex and provide output to upper motor neurons of the cortex and brainstem
4
New cards
cerebellum
part of brain involved in sensory motor coordination of ongoing movement; topographical organization; important for: balance, coordinated, learned motor skills, accuracy and error correction of movement
5
New cards
upper motor neurons
motor neurons that span from the motor cortex to interneuron circuits in the brainstem or spinal cord; do not leave CNS and do cross the midline; influence lower motor neurons indirectly via spinal interneurons (some do terminate directly); contribute to voluntary movement
6
New cards
lower motor neurons
motor neurons that span from cranial nerve nuclei or spinal cord to muscle; leave the CNS and do not cross over the midline; somata located in the ventral horn of the spinal cord; project to muscles and cause them to contract
7
New cards
alpha motor neurons
lower motor neurons that project to extrafusal muscle fibers (muscle contraction)
8
New cards
beta and gamma motor neurons
lower motor neurons that project to muscle spindles (spindle tension)
9
New cards
motor unit
one alpha motor neuron and all its postsynaptic muscle fibers
10
New cards
neuromuscular junction (NMJ)
consists of the presynaptic boutons of the the motor neuron and the postsynaptic end plate of the muscle fiber
11
New cards
end plate
region on a muscle fiber where a motor axon terminates; specialization of the postsynaptic muscle fiber with membrane "pockets"
12
New cards
junctional folds
pockets in the membrane of the postsynaptic muscle fiber
13
New cards
end plate potential (EPP)
depolarization due to neurotransmitter release that occurs at the "end plate"; graded in proportion to the amount of Ach released
14
New cards
short-term plasticity
a temporary increase or decrease in the EPP amplitude that depends on the firing rate of the alpha motor neuron
15
New cards
mini EPP (mEPP)
smallest end plate potential that can be recorded from one vesicle
16
New cards
myasthenia gravis
autoimmune disease of the NMJ in which the body produces abnormal antibodies that attack and degrade or destroy the AChRs on skeletal muscle; lack of working receptor sites causes the muscle weakness (result of decreased force of muscle contraction); first line treatment is drugs that inhibit the enzyme (acetylcholinesterase) that breaks down acetylcholine at the NMJ
17
New cards
compound action potential
a signal recorded from a nerve trunk made up of numerous axons; result of summation of many action potentials from the individual axons in the nerve trunk
18
New cards
proprioceptors
receptors in the muscles and joints that provide sensory input from the muscles to the spinal cord
19
New cards
muscle spindles
comprised of muscle fibers and sensory afferents; intrafusal fibers receive gamma-motor neuron inputs from the spinal cord; stretching the muscle stretches the intrafusal muscle fibers; activates mechanoreceptors in the sensory afferents causing action potentials that are relayed to the spinal cord
20
New cards
golgi tendon organ reflex
protective circuit that causes the muscle to relax if it is overloaded; sensory inputs activate local neurons that inhibit motor neurons of the same muscle causing muscle relaxation
21
New cards
medial local circuit neurons
neurons that project over many spinal cord segments as well as bilaterally to coordinate left/right and upper/lower body movement as well as posture
22
New cards
lateral local circuit neurons
neurons that project to fewer segments and unilaterally to coordinate fine, independent muscle movements (i.e. finger movements on one hand)
23
New cards
pyramidal decussation
corticospinal tract fibers cross the midline at the level of the medulla
24
New cards
lateral corticospinal tract
projection of upper motor neurons from cerebral cortex down the spinal cord for distal musculature; 90% of descending projections; decussation at the medulla
25
New cards
anterior corticospinal tract
projection of upper motor neurons from brainstem down the spinal cord for proximal musculature; 10% of descending projections; decussation at level where the axons synapse onto lower motor neurons in the ventral horn
26
New cards
superior colliculus
controls movements that orient eyes, head and body toward sensory stimuli
27
New cards
vestibular nuclei
controls reflexive changes in posture and reflexive eye movements
28
New cards
reticular formation
controls anticipatory changes in posture
29
New cards
medial white matter
made up of vestibulospinal, reticulospinal and colliculospinal tracts; coordinates multiple muscle groups by running the full length of the spinal cord and projecting mainly to interneurons rather than directly to lower motor neurons
30
New cards
somatotopic organization
different regions of motor cortex control different parts of the body, such that the body can be "laid out" across the cortex; disproportionate amounts of cortex devoted to different body parts relates to specialization of function: grabbing, tuning, running, etc; largely preserved throughout the descending motor pathways
31
New cards
Betz cells
large pyramidal neurons of the primary motor cortex that synapse directly on spinal cord interneurons and lower motor neurons for the hand
32
New cards
motor homunculus
body map in primary motor cortex; electrical stimulation of the surface of the brain maps locations that elicit specific muscle contractions; body regions that require fine motor control (hands/face) have a lot of cortical representation compared to areas that don't require such fine control
33
New cards
accessory motor areas
higher order parts of brain required for more complicated tasks; more intense stimulation is required than for M1
34
New cards
plasticity
motor maps can change as a result of learning and in response to damage
35
New cards
Purkinje cells
main target in cerebellum from inputs; release GABA to inhibit neurons of the cerebellar nuclei
36
New cards
climbing fibers
cell bodies located in inferior olive (inferior olivary nuclei); axons project to Purkinje cells and deep cerebellar nuclei; have strong excitatory control over Purkinje cells
37
New cards
mossy fibers
cell bodies located in pons and spinal cord; excite granule cells in cerebellar cortex and neurons in the deep cerebellar nuclei
38
New cards
granule cells
excitatory neurons; stimulated by the mossy fibers; axons form the parallel fibers, which excite Purkinje cells
39
New cards
long term motor learning
ability to modify motor programs with practice in order to improve the effectiveness and efficiency of movements
40
New cards
deep cerebellar nuclei
cells that receive inhibitory input from the cerebellar cortex; sole source of output from the cerebellum
41
New cards
dentate nucleus
deep cerebellar nucleus from lateral cortex of cerebrocerebellum; projects to the thalamus (and then motor cortex) for motor planning
42
New cards
interposed nuclei
deep cerebellar nuclei from intermediate cortex of spinocerebellum
43
New cards
fastigial nucleus
deep cerebellar nucleus from vermis of spinocerebellum; projects to the brainstem upper motor neurons for motor execution
44
New cards
cerebellar peduncles
axon bundles that connect the cerebellum to the rest of the brain
45
New cards
superior peduncle
cerebellar peduncle connected to the midbrain that carries cerebellar output; axons leaving the cerebellum; output to the thalamus which projects to motor cortex (body movements) and output to the superior colliculus (eye movements); decussation level for ascending inputs from the cerebellum to the cortex
46
New cards
middle peduncle
cerebellar peduncle connected to pons that carries cerebellar input; axons entering the cerebellum; decussation level for descending input from the cortex via the pons; projects to cerebrocerebellum;
47
New cards
inferior peduncle
cerebellar peduncle connected to medulla that carries input and output; input from vestibular nuclei and spinal cord, output to the vestibular nuclei
48
New cards
cerebral peduncles
axon bundles carrying cortical movement information to the pons, which then sends this information to the cerebellum through the middle *cerebellar* peduncle; NOT cerebellar peduncles but still an important pathway in the cerebellar circuit
49
New cards
cortical pathway
pathway in and out of cerebellum that selects efficient motor programs (motor planning); impairment can cause difficulties producing skilled sequences of learned movements, such as playing a musical instrument
50
New cards
spinal cord pathway
pathway in and out of cerebellum involved in error correction for proximal and distal muscle movements•; impairment can cause uncoordinated movements of proximal muscles or distal muscles
51
New cards
ataxia
lack of voluntary coordination of muscle movements
52
New cards
dysmetria
overshoot or undershoot target
53
New cards
intention tremor
irregular movement that worsens as movement approaches target; impairment of Purkinje synapses that underlie cerebellar degradation
54
New cards
spinocerebellar ataxia
errors in smoothness and direction of targeting movements; includes dysmetria and intention tremors; caused by genetic disorders
55
New cards
vestibular pathway
pathway in and out of cerebellum that controls muscles used in balance of the body and reflexive eye movements; impairment can cause inability to stand upright and not maintain the direction of gaze or uncoordinated eye movements
56
New cards
nystagmus
eyes drift from target and then jump back to it
57
New cards
corticostriatal pathway
sensory and motor input from multiple cortical regions to the caudate and putamen
58
New cards
nigrostriatal pathway
dopaminergic input from substantia nigra pars compacta to the caudate and putamen; SNc provides dopaminergic input to the corpus striatum, which excites the direct pathway, inhibits the indirect pathway
59
New cards
globus pallidus
receives input from the putamen and caudate; contains external and internal divisions; one of the main outputs from the basal ganglia to other parts of the brain; inhibits the thalamus (important for body movements) and therefore motor cortex
60
New cards
substantia nigra pars reticulata
receives input from the caudate; inhibits the superior colliculus (important for eye/head movements)
61
New cards
striatum
part of basal ganglia containing caudate nucleus and putamen
62
New cards
medium spiny neurons
GABAergic inhibitory neurons in the basal ganglia that receive input from cortex and SNc and inhibit neurons in the Globus Pallidus (GP) & SNr; do not fire action potentials easily, require many cortical inputs; fire action potentials before movement; code a "decision to move toward a goal" rather than movement itself.
63
New cards
global pallidus neurons
each one receives input from ~ 100 medium spiny neurons; required to ensure initiation of the correct motor plan; inhibited by GABA from MSNs
64
New cards
disinhibition
2 sequential inhibitions lead to activation of the pathway
65
New cards
direct pathway
cortical input to the basal ganglia excites MSNs in the Caudate and Putamen which inhibit neurons in the Globus Pallidus or Pars Reticulata and disinhibit the thalamus or superior colliculus to promote movement
66
New cards
indirect pathway
counteracts the direct pathway to terminate movement or suppress unwanted movements by increasing the inhibitory influence of the internal globus pallidus
67
New cards
hyperdirect pathway
counteracts the direct pathway to modulate movement through the subthalamic nucleus
68
New cards
D1
excitatory (depolarizing) dopaminergic receptors in the striatal neurons of the direct pathway; increase disinhibition of the thalamus, allowing movements to occur
69
New cards
D2
inhibitory (hyperpolarizing) dopaminergic receptors in the striatal neurons of the indirect pathway; prevent inhibition of the thalamus, allowing movements to occur
70
New cards
Parkinson's disease
loss of dopaminergic neurons in nigrostriatal pathway; symptoms occur when ~80% of SNc neurons are gone; death in 10-20 yrs and also dementia in later stages; symptoms include resting tremor, rigidity, loss of voluntary movement, shuffling gait, and disturbed posture; caused by genetic susceptibility, toxins, pesticides, and head trauma
71
New cards
hypokinetic symptoms
decreased voluntary movement
72
New cards
bradykinesia
slowed movements due to muscle rigidity
73
New cards
biogenic amines
dopamine(DA), norepinephrine (NE), epinephrine (Epi), serotonin (5-HT), histamine; involved in many behavioral functions; also found in the peripheral nervous system; can play a role in psychiatric diseases
74
New cards
dopamine
catecholamine involved in initiation of movement (basal ganglia) and motivation, reward, reinforcement (substantia nigra and ventral tegmental area); receptors are affected by cocaine and amphetamine; multiple types of receptors (D1-D5), all of which are metabotropic
75
New cards
vesicular monoamine transporter (VMAT)
transports monoamines into secretory vesicles using proton gradients; structure: twelve transmembrane domains; inhibitors: reserpine and tetrabenazine; regulations: trafficking, dimerization; includes VMAT2 and SLC18A2
76
New cards
Levodopa
dopamine precursor converted into dopamine in the brain and released by remaining dopamine neurons; used as Parkinson's disease treatment; issues are that necessary high doses cause nausea and vomiting and long-term, can cause involuntary movements and on/off period of drug working
77
New cards
carbidopa
enzyme that delays the conversion of levodopa to dopamine; does NOT cross the blood-brain barrier; allows more levodopa to get to the brain, so lower doses are required; produced a significant improvement in the treatment of PD; reduces nausea and vomiting associated with high doses of levodopa but other side effects are still present
78
New cards
Lewy body
abnormal circular structures with a dense core consisting of alpha-synuclein protein; found in the cytoplasm of nigrostriatal neurons in people with Parkinson's disease
79
New cards
alpha-synuclein
A protein normally found in the presynaptic membrane, where it is apparently involved in synaptic plasticity. Abnormal accumulations are apparently the cause of neural degeneration in Parkinson's disease.
80
New cards
MPTP
neurotoxin that induces Parkinson's disease; precursor to MPP+; model is selective, mitochondrial, only mouse, and no pathology (apoptosis)
81
New cards
deep brain stimulation
implantation of an electrode into areas of the basal ganglia (particularly GPi and STN); stimulation overrides abnormal patterns of basal ganglia activity; requires brain surgery, expensive; may exacerbate depression / emotional symptoms and cause symptoms in those you have not had them previously
82
New cards
brain tissue transplant
fetal tissue, genetically engineered cells that produce dopamine transplanted to patients with Parkinson's disease; still in experimental stage, controversial
83
New cards
Dementia with Lewy Bodies (DLB)
motor symptoms of Parkinson's disease plus orthostatic hypotension, cognitive decline, hallucinations, loss of abstract thinking, fluctuating alertness; pathology: Lewy body inclusions, loss of dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra; treatment: no cure, similar treatments as PD for motor symptoms, cognitive symptoms improve with medications used in Alzheimer's
84
New cards
hypokinetic disorders
Parkinsonism, apraxia, catatonia, gait disorders, stiff persons, etc
85
New cards
hyperkinetic disorders
tremor, dystonia, chorea, tics, myoclonus, etc.
86
New cards
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
disease caused by death of upper and lower motor neurons; motor symptoms- muscle weakness, tripping, dropping items, fatigue, slurred speech, muscle cramps; end stage impacts the muscles responsible for breathing which leads to ventilator use; protein inclusions in cell bodies and axons of degenerating neurons
87
New cards
superoxide dismutase
mutation of this gene causes 20% of familial ALS cases
88
New cards
Riluzole
ALS medication that extend the amount of time before ventilation support is needed and it can extend survival by a few months
89
New cards
Dexpramipexole
ALS treatment in its phase III clinical trial; slowed disease progression; increases mitochondrial efficiency
90
New cards
Huntington's disease
autosomal dominant genetic disorder that causes neurodegeneration of striatum; insufficient tonic output from the GP permits unwanted, excessive movements; motor symptoms- lack of coordination, unsteady gait, chorea; cognitive symptoms- executive functioning such as planning, abstract thinking, rule acquisition; connection between the caudate and the GPe is degenerated
91
New cards
huntingtin
Poly-Q repeat (CAG nucleotide repeat that codes for the amino acid glutamine) in the N-terminus of this protein causes Huntington's disease; healthy if < 36 repeats and symptomatic if > 40 repeats
92
New cards
Tetrabenazine
treatment for chorea that depletes stores of monoamines by reversing the vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2) on vesicles
93
New cards
tremor
involuntary rhythmic, oscillatory movements; alternating or synchronous contractions of antagonist muscles
94
New cards
essential tremor
autosomal dominant nerve disorder characterized by uncontrollable shaking, or "tremors," in different parts and on different sides of the body; hands, arms, head, larynx, tongue, and chin (rarely lower body) affected; true cause not understood but thought that the responsible abnormal electrical brain activity is processed through the thalamus
95
New cards
homeostasis
active regulation of the body to create a balanced internal environment controlled by the different nuclei of the hypothalamus
96
New cards
infundibulum
stalk that connects the pituitary gland to the hypothalamus
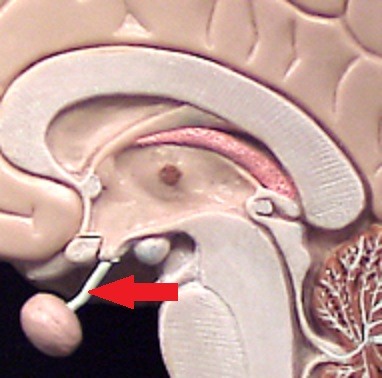
97
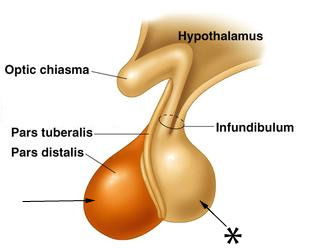
New cards
posterior pituitary
extension of the hypothalamus
98
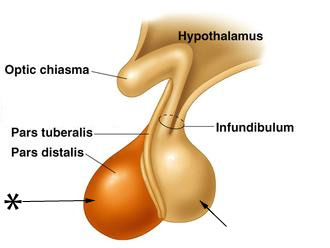
New cards
anterior pituitary
true endocrine gland of epithelial origin
99
New cards
sympathetic stress system
fast response to stress, synaptic signaling and release of epinephrine and norepinephrine
100
New cards
HPA axis stress system
slow response to stress, hormonal signaling and release of cortisol through adrenal glands