Smooth Muscle and Cardiac Muscle
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
What are some differences between smooth muscle and skeletal muscle? (4)
Smooth muscle is not striated
Smooth muscle is involuntary
Myofilaments in smooth muscle are not organized into sarcomeres nor myofibril
Myofilament in smooth muscle are anchored in place via dense bodies
Myosin light chain phosphatase (MLCP) is always active. But during contraction, intracellular Ca++ is high, which leads to the activation of myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) (see figure). How does this initiate crossbridge cycling?
A. By moving tropomyosin to uncover myosin binding sites on actin
B. By activating troponin
C. By dephosphorylating myosin
D. By phosphorylating myosin
D. By phosphorylating myosin
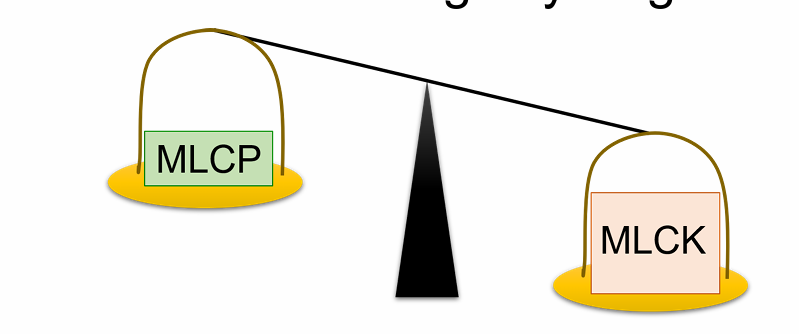
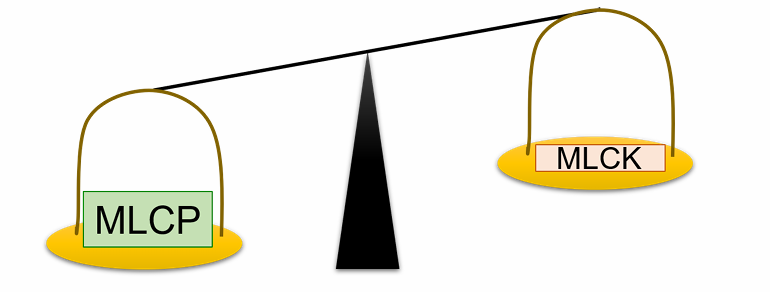
During relaxation, intracellular Ca++ is low, which leads to the inactivation of myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) (see figure). How does this stop crossbridge cycling?
A. By enabling a net phosphorylation of myosin
B. By activating myosin light chain phosphatase
C. By moving tropomyosin to cover myosin binding sites on actin
D. By inhibiting troponin
E. By enabling a net dephosphorylation of myosin
E. By enabling a net dephosphorylation of myosin
How does the contractile process differ between smooth muscle and skeletal muscle?
Cross-bridge cycling is essentially the same
But, in smooth muscle, the thin filaments lack troponin
How does the length tension relationship in smooth muscle compare to skeletal muscle?
The length tension curve is similar, but there is a much wider range of fiber length where significant force is generated in smooth muscle
Think about the urinary bladder or the stomach

Mechanisms for the rise in [Ca++]i in smooth muscle (3)(2)(2)(2)
Ligand- or Voltage-Gated Ca²⁺ Channels
→ Open in response to neurotransmitters or membrane depolarization
→ Ca²⁺ enters from outside the cellIP₃-Mediated Ca²⁺ Release from SR
→ Hormone/neurotransmitter binds GPCR → activates Gq → IP₃ produced
→ IP₃ binds to SR receptor → Ca²⁺ released from sarcoplasmic reticulumMechanically Gated Ca²⁺ Channels
→ Activated by stretch of the cell membrane
→ Ca²⁺ enters from extracellular space
How does the source of Ca++ for contraction in smooth muscle compare to that in skeletal muscle?
Smooth needs Extracellular Ca++ and SR Ca++
Skeletal just needs SR Ca++
A person has 2 energy drinks and their blood pressure goes up because a substance in the energy drink causes an increase in intracellular Ca++ in arterial smooth muscle and contraction. They then have 5 more energy drinks and their blood pressure goes way up, partly because there is a greater increase in arterial smooth muscle contraction. How did this happen?
A. There was a greater increase in intracellular Ca++ in the muscle cells
B. Like skeletal muscle, there was more recruitment of muscle fibers
A. There was a greater increase in intracellular Ca++ in the muscle cells B
The increased force of contraction with smooth muscle cell steps (3)(1)
Graded increases in intracellular Ca++ →
Recruit more cross-bridges
Greater tension generated
or any muscle the strength of contraction depends on the rise of Ca++ concentration
Some smooth muscle cells will be contracted most of the time Or
Or exhibit smooth muscle tone
How blood vessles are contracted
Always Slightly contracted
How the lower esophageal sphincer is contracted
Unless eating, it is contracted keeping the sphincter closed
Which division of the peripheral nervous system causes contraction or relaxation of smooth muscle?
Autonomic nervous system
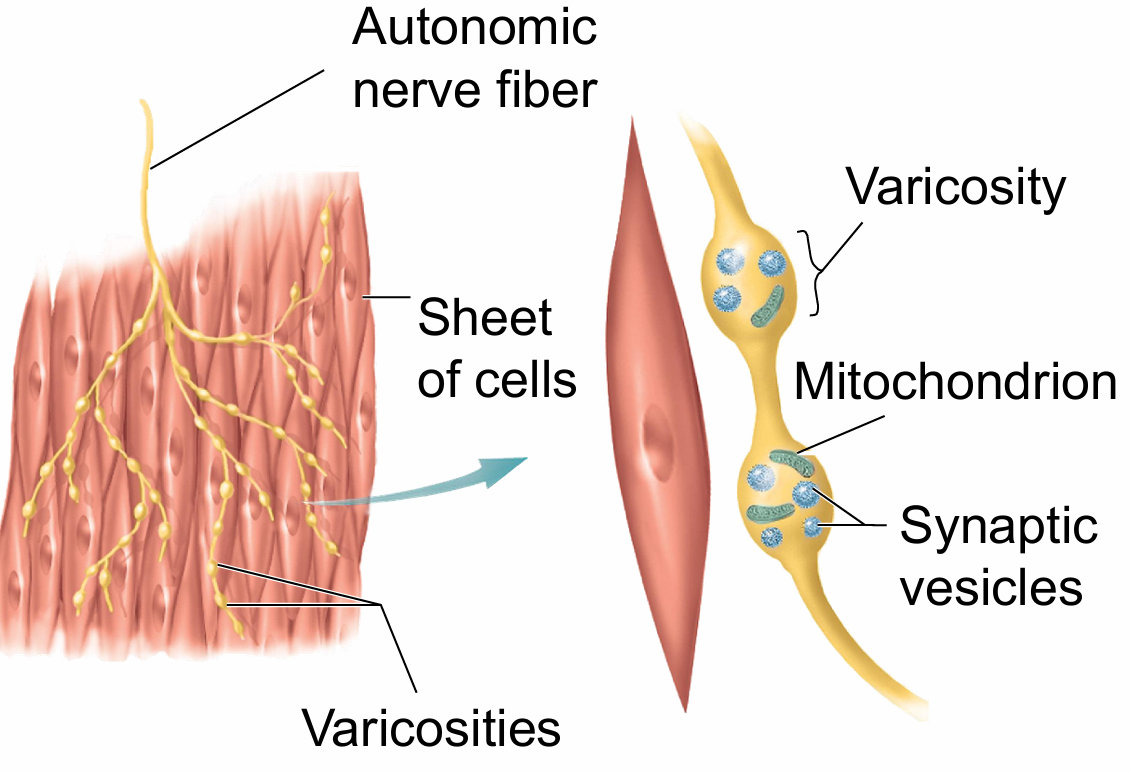
Label parts of innervation of smooth muscles by ANS
What neurotransmitter is released from Most postganglionic sympathetic neurons?
Norepinephrine (Sweat is exception)
What neurotransmitter is released from Postganglionic parasympathetic neurons?
Acetylcholine
Norepinephrine
Receptor it binds to on smooth muscle
Effect on smooth muscle (relax or contract?)
Receptor it binds to on smooth muscle - Alpha 1 Gq
Effect on smooth muscle (relax or contract?) - Contract
Epinephrine
Receptor it binds to on smooth muscle
Effect on smooth muscle (relax or contract?)
Receptor it binds to on smooth muscle - Alpha 1 Gq, Beta 2 Gs
Effect on smooth muscle (relax or contract?) - Contract, Relax
Acetylcholine
Receptor it binds to on smooth muscle
Effect on smooth muscle (relax or contract?)
Receptor it binds to on smooth muscle - M3 Gq
Effect on smooth muscle (relax or contract?) - Contract
What else can effect smooth muscle contraction or relaxation?
other hormones and local factors
Iris radial smooth muscle (pupillary dilator)
Activates Alpha 1 or Beta 2?
Contract or relax?
Activates Alpha 1 or Beta 2? - Alpha 1
Contract or relax? - Contraction
Bronchial smooth muscle
Activates Alpha 1 or Beta 2?
Contract or relax?
Activates Alpha 1 or Beta 2? - Beta 2
Contract or relax? - Relaxation
Mechanism of epinephrine-induced contraction and relaxation of smooth muscle Beta 2
Epinephrine binds to Beta 2
cAMP is increased
INACTIVATES MLCK
Mechanism of epinephrine-induced contraction and relaxation of smooth muscle Alpha 1
Epinephrine binds to alpha 1
Ca++ is increased
ACTIVATES MLCK
Another way to classify smooth muscle (2)
Single unit smooth muscle
Multiunit smooth muscle
Single unit smooth muscle
Feature
Hint
Examples
Feature - Contracts as one unit
Hint - Needs to undergo synchronous activity
Examples - GI tract urinary bladder
Multiunit smooth muscle
Feature
Hint
Examples
Feature - Cells respond independently
Hint - Oftentimes tonically contracted
Examples - Large arteries
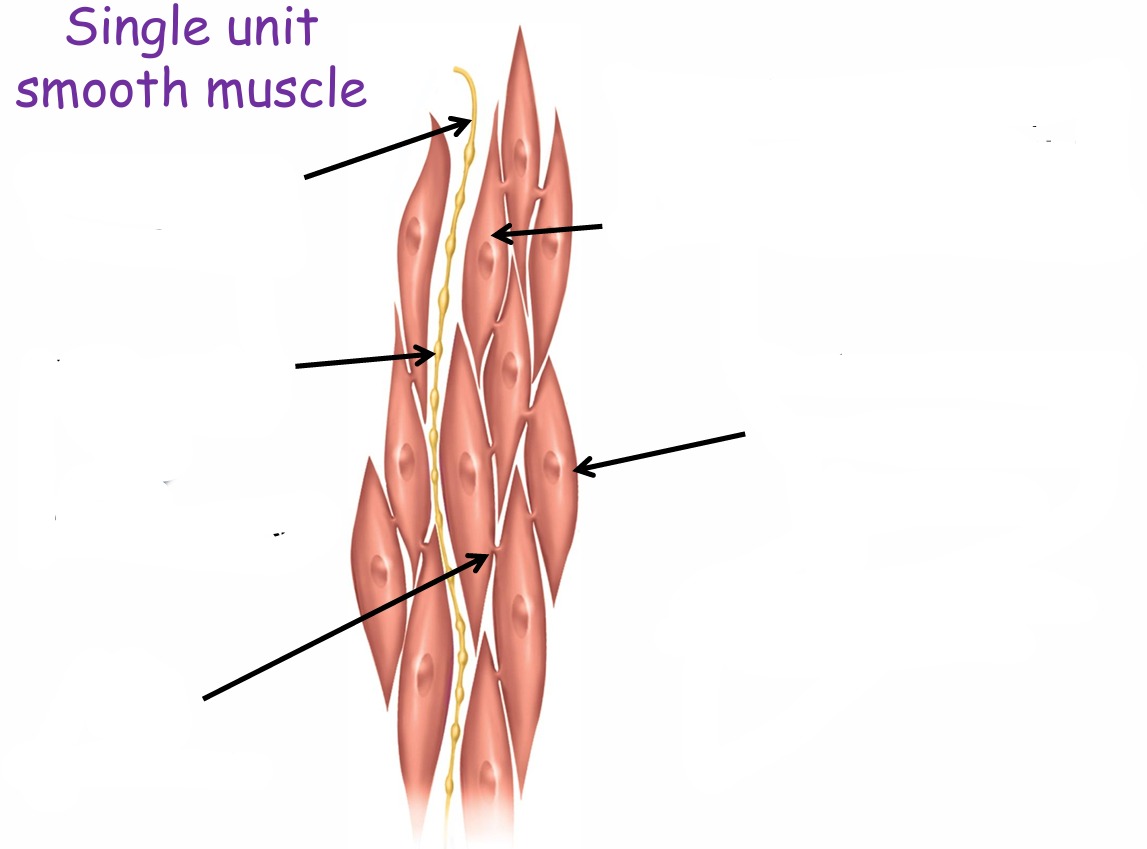
Label this single unit smooth muscle
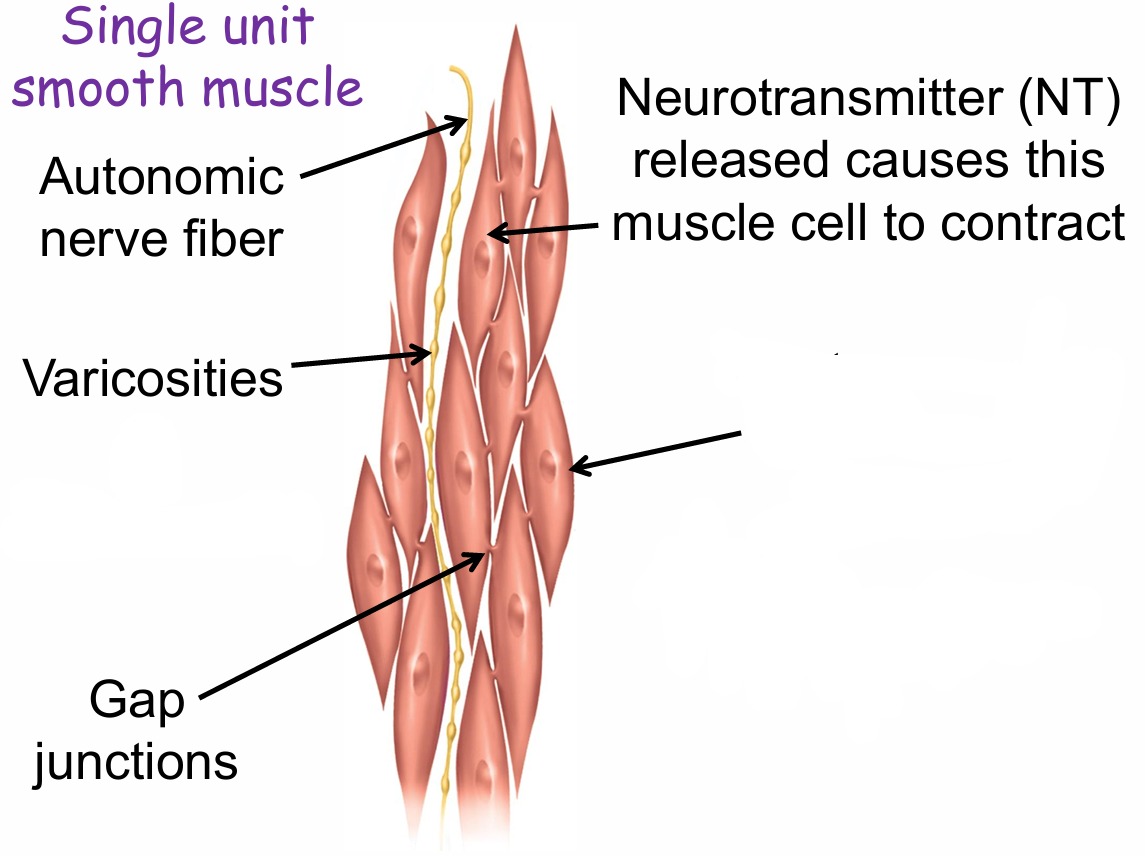
What do varicosities do?
Releases NT
What causes this muscle cell to contract?
Electrical impulse that passes through the gap junction
The versatility of smooth muscle/ functions (3)
Keeps blood vessels partially constricted at all times
Contracts and relaxes in response to a large variety of signals
In sphincters, it remains contracted which keeps the sphincter closed for a long period of time and only transiently relaxes
It can be relaxed for a long time, and then contract strongly in response to stimuli, such as in the esophagus or urinary bladder
What do intercalated disks contain (2)
Gap junction
Adhesion proteins
What is cardiac muscle?
Involuntary
Striated
Contains myofilaments
Myofilaments are organized in sarcomeres
What is the purpose of the gap junctions in the intercalated disks?
Electrical synapse
Electrical impulse (that causes contraction) spreads or conducts from one cell to the next ensuring
Ensures that each chamber of the heart contracts as one unit
Similar to skeletal muscle → cardiac muscle has
T tubules and an extensive sarcoplasmic reticulum
NOT Tubules in smooth muscle
Membrane depolarization causes
Causes an increase in intracellular Ca++
What are the steps of E-C coupling in cardiac muscle? (6)
Depolarization
→ Action potential depolarizes the cardiac cell membrane.L-type Ca²⁺ Channel Opens
→ Voltage-gated channel allows Ca²⁺ (trigger calcium) to enter from outside.Ryanodine Receptor Activation
→ Trigger Ca²⁺ binds to ryanodine receptors on the SR (Ca²⁺-induced Ca²⁺ release).Ca²⁺ Release from SR
→ SR releases more Ca²⁺ into the cytoplasm (Ca²⁺ spark).↑ Intracellular [Ca²⁺]
→ Multiple sparks increase overall Ca²⁺ concentration.Contraction
→ Ca²⁺ binds troponin → cardiac muscle contracts.
Ca++ then binds to troponin and there is cross bridge cycling, the same as skeletal muscle But…Since all cardiac myocytes are involved in contraction with each heartbeat, how can the force of contraction be increased?
Something (like norepinephrine) causes A greater increase in intracellular Ca++
This recruits more cross-bridges (only about 30% are used at rest) to increase tension and force
How does excitation-contraction coupling in cardiac muscle compare to skeletal muscle?
C. Similar except that both calcium influx and calcium release from the SR are important for contraction
D. Very different, it is more like smooth muscle
E. Exactly the same
C. Similar except that both calcium influx and calcium release from the SR are important for contraction
How does Ca++ exit the cytoplasm of the cardiac muscle cell and facilitate relaxation? (4)(2)(2)(2)
Ca²⁺-ATPase (SERCA)
→ Pumps Ca²⁺ back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR)
→ Uses ATPCa²⁺-ATPase (PMCA)
→ Pumps Ca²⁺ out of the cell membrane
→ Uses ATPNa⁺/Ca²⁺ Exchanger (NCX)
→ Exchanges 1 Ca²⁺ out for 3 Na⁺ in
→ Driven by Na⁺ gradient (no ATP)Result: Decrease in intracellular [Ca²⁺] → Cardiac muscle relaxation