Geography unit B
1/43
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
where the ocean currents move cold water, rich in nutrients, from the ocean floor to the surface
plunging breaker
Breaks quickly with substantial force and wave energy is concentrated over a small area of the beach.
Surging breakers
Rush up a very steep beach without dissipating much energy in the beach layer known as swash.
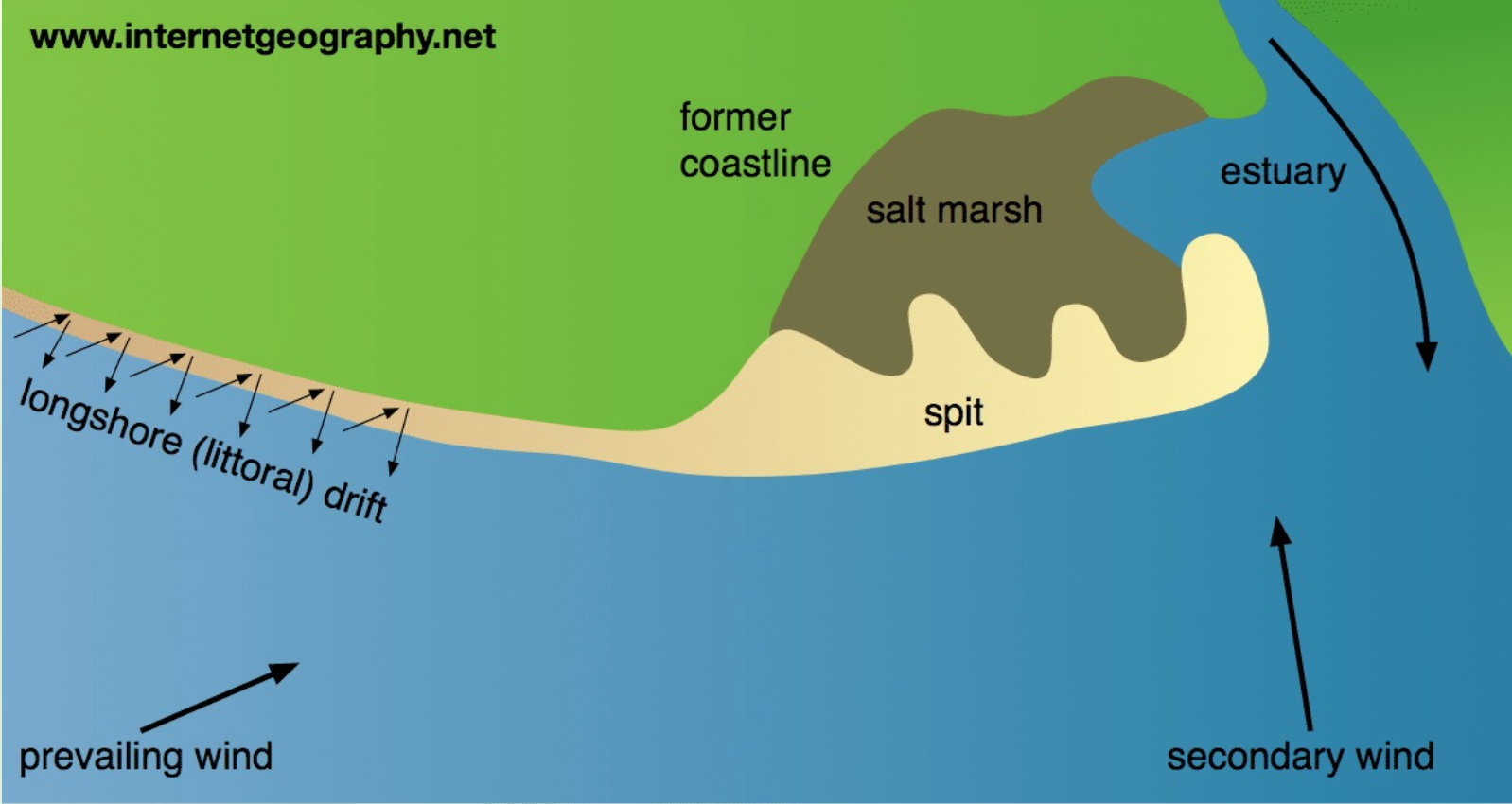
tombolo
spit joining the mainland to an island
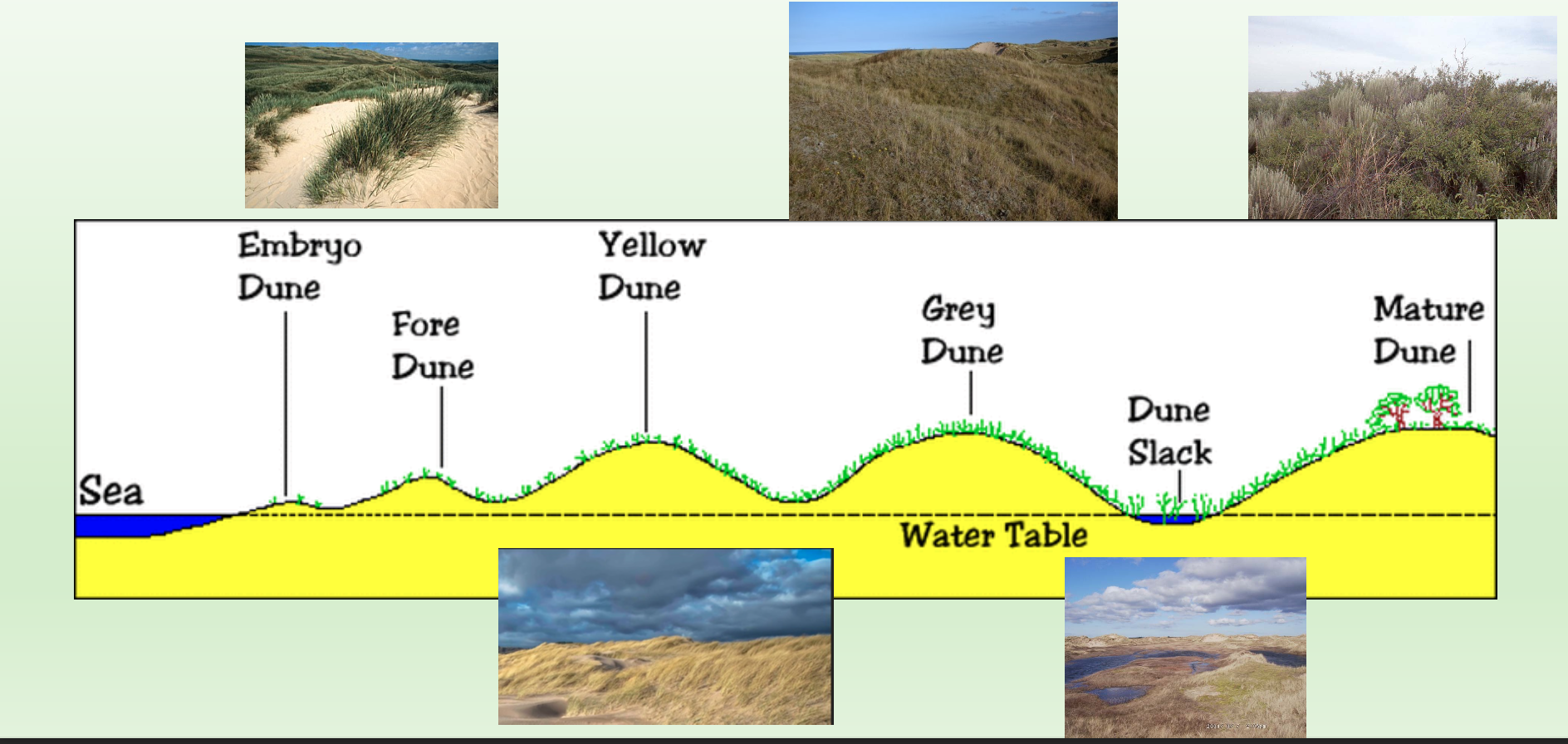
Sand dunes formation
Sand dunes are small ridges or hills of sand found at the top of a beach, above the reach of the waves, sand is deposited by the wind around an object such as a rock, forming embryo dunes
oceanic conveyor belt
a constantly moving system of deep ocean circulation driven by temperature.
Upwelling
deep cold nutrient water rising on the surface
Thermohaline circulation
the conveyor belt- transfer of energy by deep sea currents, cold water sink and moves towards the equator
thermocline
layer between surface warm water and deep cold water.
halocline
change in water salinity levels as the depth change
EEZ
exclusive economic zones- prescribed by UN that a state has speacial rights regarding exploration and use of marine resources
Subaerial weathering
weathering of caves and large sedinments caused due to waves.
isostatic
local sea level change- the height of the land rises or falls depending on pressure out on by ice.
fetch
the stretch of ocean water over which wind was blown
coral reefs
underwater ecosystem characterised by reef building corals
Mangroves
shrub that grow in costal saline water
concordant coast
ocean infiltration and erosion of soft material
discordant coast
when the bands of different rock types run perpendicular to the coast
gabion
wire meshcages filled with pebbles
groyne
wooden barriers constructed at right angles
revetments
traditionally been wooden slatted barriers constructed towards the rear of beaches to protect the base of cliffs
sea walls
built in front of cliffs to protect against waves
downwelling
occurs when surface water becomes more dense and sinks to the bottom
onceanic carbon cycle
photosynthesis, turns carbon dioxide into organic material, this carbon sinks to the bottom causing upper part to have low carbon concentration.