Neuronal Injury
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Characteristics of the CNS - complex interactions
Neurotransmitters
Receptors
Genes
Environment
Characteristics of the CNS - different pathways for damage
Apoptosis
Necrosis
Infection
Ischemia
Trauma - brain and spinal cord
Chemical/toxicity
Radiation
Nutritional deficiency
Genetic influences
Apoptosis
Programmed
Not associated with an
Normal process that helps to regulate
This process can be excessive in times of
Can occur regardless of the _____ of CNS damage
Increase w/
Programmed cell death
Not associated with an inflammatory response
Normal process that helps to regulate overproduction of cells
This process can be excessive in times of CNS damage
Can occur regardless of the type of CNS damage
Increase w/ stroke, result of ischemic processes, neurodegenerative diseases (might be genetic in nature), traumatic injuries, drug related disorders
Necrosis
Cellular _____
F
Cell d_____
Release of
These materials start to encroach on
Always
is associated w/
Cellular swelling
Water enters the cell and causes cell membranes to rupture
Fragmentation
Cell disintegration
Release of cytotoxic materials
These materials start to encroach on neighboring cells causing damage there
Always pathological
is associated w/ an inflammatory response
Comparison of necrosis and apoptosis
Necrosis
Apoptosis
Cell size |
Nucleus |
Plasma membrane |
Cellular contents |
Adjacent inflammation |
Physiologic or pathologic |
Necrosis
Enlarged (swelling)
Pykinosis karyorrhexis karyolysis
Disrupted
Enzymatic digestion; may leak out of cell
Frequent
Invariably pathologic (culmination of irreversible cell injury)
Apoptosis
Reduced (shrinkage) |
Fragmentation into nucleosome-size fragments |
Intact; altered structure, especially orientation of lipids |
Intact; may be released into apoptotic bodies |
No |
Often physiologic, means of eliminating unwanted cells; may be pathologic after some forms of cell injury, especially DNA damage |
Excitotoxicity
how the body responds to
Excitatory _______ _______ ______ are activated
Calcium ions enter cells → activation of ________ ________ → release of _______ → damage to ___________ cells
This process leads to _______ _______ _______ (oxidative stress) → _______
Increase in oxidative stress is a secondary complication in diseases such as
how the body responds to necrosis
Excitatory amino acid receptors are activated
Calcium ions enter cells → activation of intracellular function → release of excitotoxins → damage to neighboring cells
This process leads to free radical formation (oxidative stress) → apoptosis
Increase in oxidative stress is a secondary complication in diseases such as Alzheimer’s,Parkinson’s, and ALS
Glial cells
Macroglia (from nerve cells; most populous)- when thinking about neurological disorders that impact the brain tissue directly, most of the time we’re thinking about the impact they have on the microglial cells
Astrocytes
Oligodendrocytes
Schwann cells
Microglia (immune cells)
immune function
modulate inflammatory process
have macrophage properties + it will be the release of those materials that will be damaging to the surrounding cells
older adults have heightened immune response → may be why we see an increase in prevalence of some neurological diseases such as Alzheimer’s, PD in the older population
Astrocytes
Most ______ brain cells
support ____
provide _____ to brain
Permeable to _____
Monitor and remove _____ and other _____
Can seal off ______ brain tissue
Most numerous brain cells
support NS
provide nutrition to brain
Permeable to potassium
Monitor and remove glutamate and other debris
Can seal off damaged brain tissue
Damage to astrocytes
Proliferative ______damage occurs
_______, _______ occur
Altered _______ expression in the setting of brain injury
Can be a site of ______ which can _______ surrounding ______ tissues and _______ structures
Proliferative neuronal damage occurs
Swelling, scarring occur
Altered genetic expression in the setting of brain injury
Can be a site of neoplasm which can compress surrounding neural tissues and vascular structures
Oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells
Oligodendrocytes =
Schwann cells =
Both help to produce the
Oligodendrocyte function is disrupted in demyelinating diseases such as
Oligodendrocytes = CNS
Schwann cells = PNS
Both help to produce the myelin sheath surrounding the axon
Oligodendrocyte function is disrupted in demyelinating diseases such as multiple sclerosis
Neurons (nerve cells)
DNA mutation can lead to
Abnormalities to
Drug ______ or ______
DNA mutation can lead to vulnerability to neurological disease
Abnormalities to gene structure
Drug toxicity or misuse
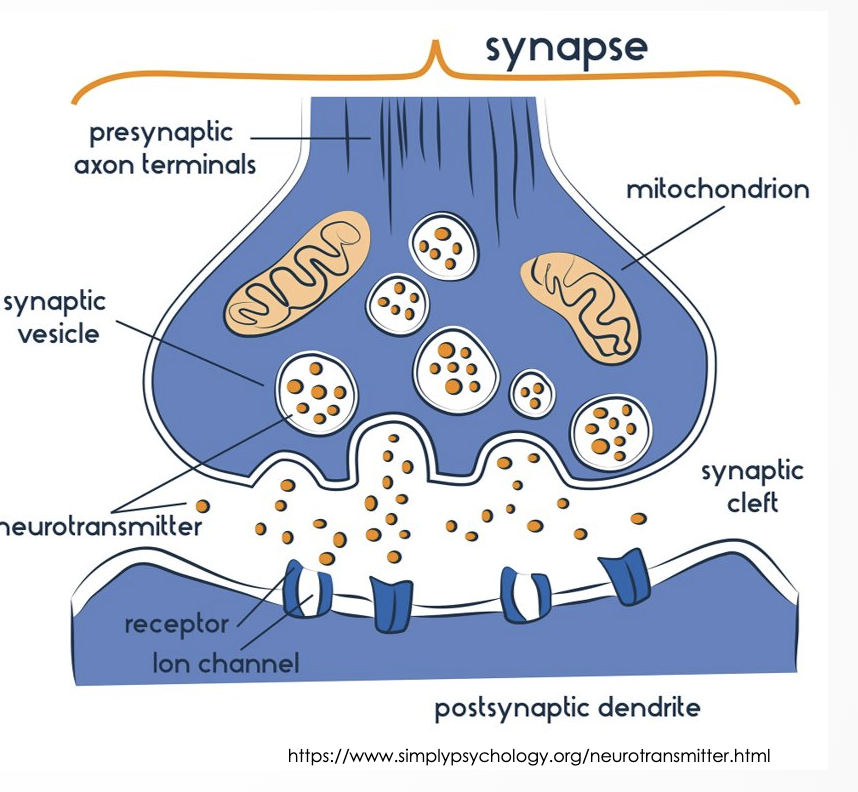
Neurotransmission
Depolarization of terminal causes _______ influx and opens channels in _______ neuron
Neurotransmitters are ______
Drugs will affect this process by
Depolarization of terminal causes sodium influx and opens channels in postsynaptic neuron
Neurotransmitters are released
Drugs will affect this process by blocking transmission, increase or decrease the release of neurotransmitters,allow for reuptake of neurotransmitter back into the presynaptic terminal, or change the properties of the membrane
Recovery from neurological injury- Peripheral nerve injury
New
Proliferation of
Microsurgical approximation may result in
New axonal sprouts
Proliferation of Schwann cells
Microsurgical approximation may result in reinnervation
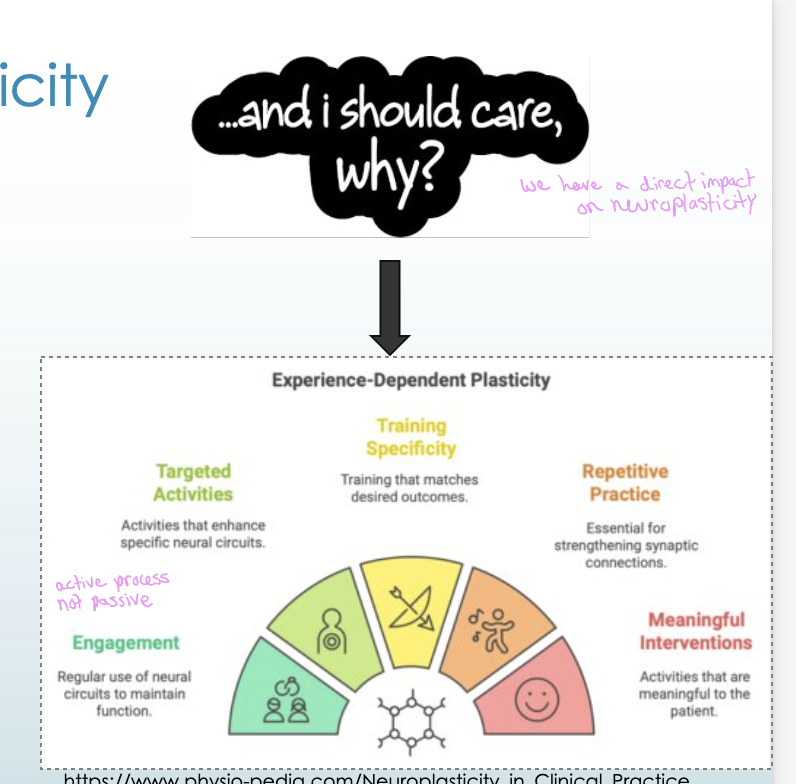
Neuroplasticity
Redistribution of
Alterations of
N______
I_____ S_____
R______
Redistribution of cortical mapping
Alterations of neural networks
Neurotransmitters
Individual synapses
Receptors
Factors that influence recovery
________ of the lesion
_______ of the lesion
Is the injury ______ or _______?
Was the injury _______ or _______
A____
E_____
B____ ____
E______ r_________
Location of the lesion
damage to brainstem will have devastating effects
Size of the lesion
Is the injury static or progressing?
Was the injury sudden (massive hemorrhage) or gradual (slow growing tumor)?
Age
older adults do not have the capacity to heal as much as younger populations
Environment
are they being appropriately stimulated in being asked to perform tasks that are going to help promote neuroplasticity
Brain health
Blood flow
Immune systems
Metabolism
Emotional regulation