CNS, brain structure, AP, synaptic transmission
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:12 PM on 4/9/24
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
1
New cards
What is the nervous system?
A network of cells that form the basis for our psychological experiences.
2
New cards
What is the CNS made up of?
Brain and spinal cord
3
New cards
What is the function of the CNS?
To control behaviour and regulate the body’s physiological processes like breathing.
4
New cards
What is the brain?
The centre of all consciousness and it deals with higher order thinking like memory.
5
New cards
What is the spinal cord?
A collection of nerve cells attached to the brain and run the length of the spinal column.
6
New cards
What is the function of the peripheral nervous system?
To transmit millions of neurons to and from the CNS.
7
New cards
What is the peripheral nervous system made up of?
Everything except the brain and spinal cord.
8
New cards
What are the 2 sub-divisions of the peripheral nervous system?
Autonomic nervous system
Somatic nervous system
Somatic nervous system
9
New cards
What is the autonomic nervous system responsible for?
Automatic responses like fight or flight.
10
New cards
What is the somatic nervous system responsible for?
Voluntary actions
11
New cards
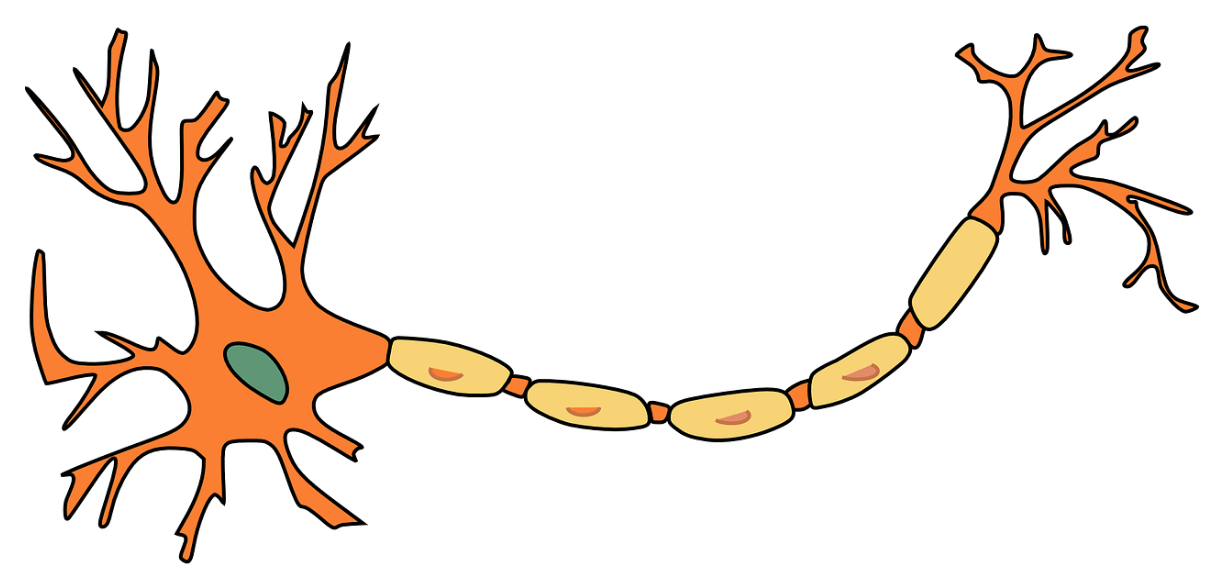
What structures is the neuron made up of?
Dendrite
Nucleus
Cell body
Axon
Myelin Sheath
Nodes of Ranvier
Axon terminal
Nucleus
Cell body
Axon
Myelin Sheath
Nodes of Ranvier
Axon terminal
12
New cards
What is the function of the dendrite?
To collect signals from other surrounding neurons
13
New cards
What is the function of the cell body?
To collect signals into one stronger signal
14
New cards
What is the function of the axon?
To carry the electrical nerve impulse down the length of the cell
15
New cards
What is the function of the myelin sheath?
Acts as insulation to speed up the conduction of the impulse and keep it travelling in one direction
16
New cards
What is the function of the nodes of Ranvier?
Gaps between the myelin sheath to speed up the impulse
17
New cards
What is the function of the axon terminal?
To pass on the impulse to the next neuron
18
New cards
What are the 4 lobes of the brain?
* Frontal lobe
* Temporal lobe
* Parietal lobe
* Occipital lobe
* Cerebellum
* Temporal lobe
* Parietal lobe
* Occipital lobe
* Cerebellum
19
New cards
What is the function of the frontal lobe?
* Higher order thinking
* Emotional control
* Decision making
* Emotional control
* Decision making
20
New cards
What is the function of the temporal lobe?
* Auditory info
* Memory
* Memory
21
New cards
What is the function of the parietal lobe?
* Sensory info
* Physical sensation e.g skin contact and movement
* Physical sensation e.g skin contact and movement
22
New cards
What is the function of the occipital lobe?
Visual info
23
New cards
What is the function of the cerebellum?
Co-ordinating motor movement e.g balance
24
New cards
What are action potentials?
Electrochemical impulses that travel along axons in one direction only, carrying information.
25
New cards
What is the resting membrane potential of a neuron?
\-70mV
26
New cards
What does the neurons negative resting membrane potential mean?
It is negatively charged compared to outside of the cell.
27
New cards
At what voltage is an action potential triggered?
\-55mV
28
New cards
What does the All-or-None principle state?
If a neuron doesn’t reach -55mV the action potential will not occur.
29
New cards
What happens after the neuron reaches -55mV?
The action potential sends an impulse along the axon towards the axon terminal where it carries on to the next neuron.
30
New cards
What does depolarisation mean?
Ions move in and out of the membrane causing it to become less negative.
31
New cards
What does repolarisation mean?
The membrane gets more negative.
32
New cards
What happens after repolarisation?
A refractory period of hyperpolarisation.
33
New cards
Describe the process of synaptic transmission.
* AP comes down the axon to the axon terminal
* A vesicle full of neurotransmitters releases them into the synaptic cleft
* Neurotransmitters drift across the gap and bind to a receptor
* AP is passed onto the next neuron
* Some of the neurotransmitters are degraded by enzymes, others are carried back to the pre-synaptic neuron by transporter proteins- called reuptake
* A vesicle full of neurotransmitters releases them into the synaptic cleft
* Neurotransmitters drift across the gap and bind to a receptor
* AP is passed onto the next neuron
* Some of the neurotransmitters are degraded by enzymes, others are carried back to the pre-synaptic neuron by transporter proteins- called reuptake
34
New cards
What are the 3 things that can happen to neurotransmitters in the synaptic cleft?
* Bind to a receptor
* Degraded by enzymes
* Carried back to the pre-synaptic neuron by transporter proteins (reuptake)
* Degraded by enzymes
* Carried back to the pre-synaptic neuron by transporter proteins (reuptake)
35
New cards
What are neurotransmitters?
Chemical messengers that act between the neurons in the brain. This allows the brain to process thoughts and memories.
36
New cards
What are synapses?
Gap between neurons
37
New cards
What mechanism do receptors work on?
Lock and key