Chapter 2 flashcards HLST 3320
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 12:17 AM on 9/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
1
New cards
Data modelling refers to the process of
creating a specific data model for a determined problem domain
2
New cards
Data modelling as an _________ , progressive process
Iterative
3
New cards
Data model
Is a simple representation of more complex real-world data structures
4
New cards
A problem domain
Is a clearly defined area within the real-world environment, with well-defined scope and boundaries, that is to be systemically addressed
5
New cards
An implementation-ready data model should contain at least the following components:
* A description of the data structure that will store the end-user data.
* A set of enforceable rules to guarantee the integrity of the data.
* A data manipulation methodology to support the real-world data transformations.
* A set of enforceable rules to guarantee the integrity of the data.
* A data manipulation methodology to support the real-world data transformations.
6
New cards
Database designers make use of _________ data-modelling constructs and powerful database design tools that diminish the potential for errors in database modelling
existing
7
New cards
Data models are a ________ tool
Communication
8
New cards
Why are data models important?
Because data is viewed in different ways by different people and you will be unlikely to create a good database without first creating and appropriate data model
9
New cards
A sound data environment requires an **____________________** based on an appropriate data model
overall database blueprint
10
New cards
When a good database blueprint is available, it does not matter that an applications programmer’s **______** of the data is different from that of the manager or the end user
view
11
New cards
Entity
is a person, place, thing, concept, or event about which data will be collected and stored
12
New cards
Attribute
is a characteristic of an entity
13
New cards
Relationship
describes an association among entities
14
New cards
What are the three different types of relationships
* 1:M or 1..\*
* M:N or \**..**
* 1:1 or 1..1
* M:N or \**..**
* 1:1 or 1..1
15
New cards
Relationships are
bidirectional
16
New cards
A constraint is
A restriction placed on the data
17
New cards
Why are constraints important?
They help ensure data integrity
18
New cards
Constraints are usually expressed in the form of _____
rules
19
New cards
Example of a constraint
A students GPA must be between 0.0 and 4.0
20
New cards
Business rule
is a brief, precise, and unambiguous description of a policy, procedure, or principle within a specific organization (anything that stores data)
21
New cards
What are business rules used for?
Business rules are used to define entities, attributes, relationships, and constraints
22
New cards
what is the main source of business rules?
The main **sources of business rules** are company managers, policy makers, department managers, and written documentation such as company procedures
23
New cards
Business rules are essential to database design due to the following reasons:
* It helps to standardize the company’s view of data
* It can be a communication tool between users and designers
* It allows the designer to understand the nature, role, and scope of the data
* It allows the designer to understand business processes
* It allows the designer to develop appropriate relationship participation rules and constraints and to create an accurate data model
* It can be a communication tool between users and designers
* It allows the designer to understand the nature, role, and scope of the data
* It allows the designer to understand business processes
* It allows the designer to develop appropriate relationship participation rules and constraints and to create an accurate data model
24
New cards
As a general rule, a noun in a business rule will translate into an ________ in the model, and a verb (active or passive) associating nouns will translate into an ____________ among the entities.
Entity, relationship
25
New cards
What does “a customer generates many invoices” tell you about the organization?
Customer and invoices are nouns therefore they are the entities and generate is the verb which demonstrates the relationship
26
New cards
**Entity names** should be descriptive of
the objects in the business environment and use technology that is familiar to the users
27
New cards
An attribute name should be
descriptive of the data represented
28
New cards
A proper naming convention can help make your model
Self-documenting
29
New cards
What is the first generation of data models?
File system
30
New cards
The second generation of the data models?
Hierarchal and network
31
New cards
The third generation of data models?
Relational
32
New cards
The fourth generation of data models
Object-oriented
33
New cards
What is the next generation of data models?
XML
34
New cards
Why was the hierarchal model developed?
The **hierarchical model** was developed in the 1960s to manage large amounts of data for complex manufacturing projects.
35
New cards
What is a segment?
A segment is the equivalent of a file system’s record type
36
New cards
Within the hierarchy, a higher layer is perceived as the ________ of the segment directly beneath it, which is called the ________.
Parent, child
37
New cards
Why was the network model created?
The **network model** was created to represent complex data relationships more effectively than the hierarchical model, to improve database performance, and to impose a database standard.
38
New cards
How is the network model different from the hierarchal model?
The network model allows a record to have more than one parent
39
New cards
What are the database concepts that emerged with the network model that are still used?
* schema
* Subschema
* Data manipulation language
* Data definition language
* Subschema
* Data manipulation language
* Data definition language
40
New cards
Schema
is the conceptual organization of the entire database as viewed by the database administrator.
41
New cards
Subschema
defines the portion of the database “seen” by the application programs that produce the desired information from the data within the database
42
New cards
Data management language (DML)
which defines the environment in which data can be managed and to work with the data in the database.
43
New cards
Data definition language (DDL)
enables the database administrator to define the schema components
44
New cards
What is the foundation of the relational model?
The relational models foundation is a mathematical concept known as relation
45
New cards
What is a relation?
sometimes called a table, is a matrix compose of intersecting rows and columns
46
New cards
Each row in a relation is called a _________.
tuple
47
New cards
Each column represents an
attribute
48
New cards
The relational data model is implemented through a very sophisticated
Relational database management system (RDBMS)
49
New cards
what is the relational database management system?
The RDBMS performs the same basic functions provided by the hierarchical and network DBMS systems as well as other functions that makes it easier to understand
50
New cards
What is the most important advantage of the RDBMS?
it can hide the complexities of the relational model from the user
51
New cards
What are the three parts of a SQL-based relational database application:
* the end user interface
* A collection of tables
* SQL engine
* A collection of tables
* SQL engine
52
New cards
the end-user interface
the interface allows the end user to interact with the data
53
New cards
A collection of tables
tables “present” the data to the end user in a way that is easy to understand
54
New cards
SQL Engine
the SQL engine executes all queries or data requests
55
New cards
Complex design activities require conceptual ______ to yield successful results
Simplicity
56
New cards
Entity relationship Model
was developed as a graphical tool in which entities and their relationships are pictured
57
New cards
An ER model is made of
* entity
* Attributes
* Relationships
* Attributes
* Relationships
58
New cards
An Entity relationship diagram
uses graphical representations to model database components
59
New cards
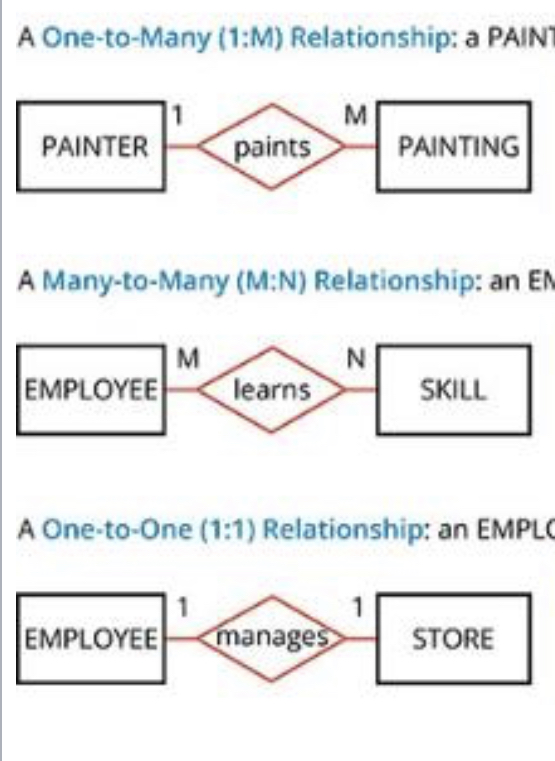
\
Chen’s notation
60
New cards
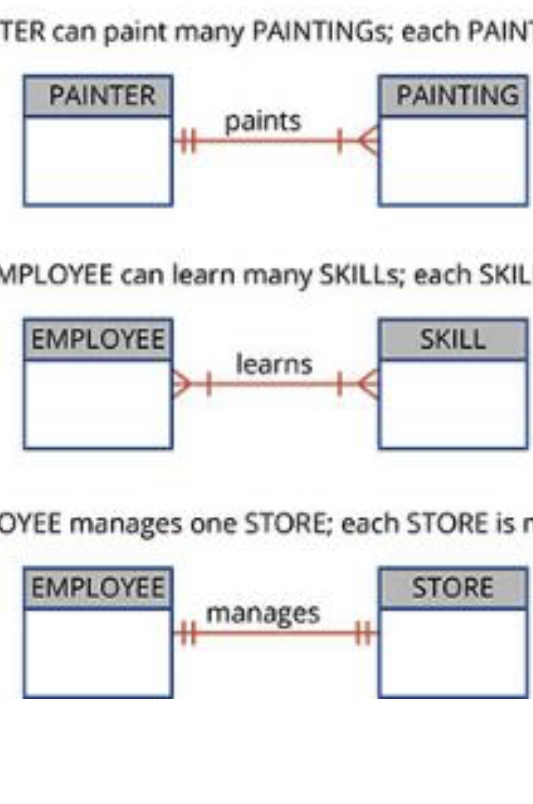
Crows foot Notation
61
New cards

UML Class
62
New cards
Why is the object-oriented data model needed
Increasingly complex real-world problems demonstrated a need for a data model that more closely represented the real world.
63
New cards
In the **object-oriented data model (OODM)**, both data and its relationship are contained in a single structure known as an
Object
64
New cards
The OODM is said to be a **semantic data model** because
Semantic indicates meaning
65
New cards
The object oriented data model is based on the following components:
* object
* Attributes
* Class
* Class hierarchy
* Inheritance
* Attributes
* Class
* Class hierarchy
* Inheritance
66
New cards
An object in an OODM is an
abstraction of a real-world entity
67
New cards
Attributes in an OODM describes
the properties of an object
68
New cards
A class in an OODM is
a collection of similar objects with shared structure and behaviour
69
New cards
What does a classes method represent in an OODM?
A class’s **method** represents a real-world action such as finding a selected PERSON’s name, changing a PERSON’s name, or printing a PERSON’s address
70
New cards
What is a class hierarchy
The **class hierarchy** resembles an upside-down tree where each class has only one parent
71
New cards
What is the inheritance?
**Inheritance** is the ability of an object within the class hierarchy to inherit the attributes and methods of the classes above it
72
New cards
Object-oriented data models are typically depicted using **__________________** class diagrams
Unified Modelling language (UML)
73
New cards
What is the UML?
is a language based on OO concepts that describes a set of diagrams and symbols that can be used to graphically model a system.
74
New cards
What are UML class diagrams?
UML class diagrams are used to represent data and their relationships within the larger UML object-oriented system’s modeling language
75
New cards
The **extended relational data model (ERDM)** adds many of the OO model’s features within the ________ relational database structure
simpler
76
New cards
A DBMS based on the ERDM is often described as an
object/relational database management system (O/R DBMS)
77
New cards
What is the Extensible Markup Language (XML)
has emerged as a standard for the efficient and effective exchange of structured, semistructured, and unstructured data
78
New cards
Why is the OR DBMS successful?
The success of the O/R DBMSs can be attributed to the model’s conceptual simplicity, data integrity, easy-to-use query language, high transaction performance, high availability, security, scalability, and expandability
79
New cards
Internet of things
is a web of Internet-connected devices exchanging and collecting data
80
New cards
What is big data
refers to a movement to find new and better ways to manage large amounts of web- and sensor-generated data and derive business insight from it
81
New cards
A basic characteristic of Big Data databases can be described
The 3 V’s, volume, velocity, variety
82
New cards
what are some of the most frequently used big data technologies?
* Hadoop
* Hadoop distributed file system (HDFS)
* Mapreduce
* NoSQL
* Hadoop distributed file system (HDFS)
* Mapreduce
* NoSQL
83
New cards
What is Hadoop?
is a Java-based, open-source, high-speed, fault-tolerant distributed storage and computational framework
84
New cards
What is Hadoop distributed file system
is a highly distributed, fault-tolerant file storage system designed to manage large amounts of data at high speeds
85
New cards
What is MapReduce?
is an open-source application programming interface (API) that provides fast data analytics services
86
New cards
What is NoSQL?
is a large-scale distributed database system that stores structured and unstructured data in efficient ways
87
New cards
What are the general characteristics of NoSQL databases
* They are not based on the relational model and SQL
* They support highly distributed database architectures
* They provide high scalability, high availability, and fault tolerance
* They support very large amounts of sparse data
* They are geared toward performance rather than transaction consistency
* They support highly distributed database architectures
* They provide high scalability, high availability, and fault tolerance
* They support very large amounts of sparse data
* They are geared toward performance rather than transaction consistency
88
New cards
What did the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) Standards Planning and Requirements Committee (SPARC) do?
defined a framework for data modeling based on degrees of data abstraction
89
New cards
What are the 3 levels of data abstraction?
* external, conceptual, and internal
90
New cards
What is the external model?
is the end users’ view of the data environment
91
New cards
What does end user mean?
The term end users refers to people who use the application programs to manipulate the data and generate information
92
New cards
What is an external schema?
an external schema is a specific representation of an external view
93
New cards
What are the important advantages of the use of external views that represent subsets of the database?
* It is easy to identify specific data required to support each business unit
* It makes the designer’s job easy by providing feedback about the model’s adequacy
* It helps to ensure security constraints in the database design
* It makes application program development much simpler
* It makes the designer’s job easy by providing feedback about the model’s adequacy
* It helps to ensure security constraints in the database design
* It makes application program development much simpler
94
New cards
What does the conceptual model represent?
The **conceptual model** represents a global view of the entire database by the entire organization
95
New cards
What is the conceptual schema the basis for?
it is the basis for the identification and high-level description of the main data objects
96
New cards
What is the most widely used conceptual model?
the ER model
97
New cards
What is the conceptual model independent of?
it is independent of both software and hardware
98
New cards
What is software independence?
means that the model does not depend on the DBMS software used to implement the model
99
New cards
What is hardware independence?
means that the model does not depend on the hardware used in the implementation of the model.
100
New cards
What are the advantages of the conceptual model?
* It provides a bird’s-eye view of the data environment that is easy to understand
* The conceptual model is independent of both software and hardware
* The conceptual model is independent of both software and hardware