Psychology Exam 4
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/178
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:11 PM on 12/9/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
179 Terms
1
New cards
self-concept
knowledge about and perceptions of ourselves
2
New cards
existential self
most basic part of our self-concept; knowledge that one is separate and distinct from others
3
New cards
when does existential self develop?
develops around 18-24 months
4
New cards
the rouge test
test used to identify a child's existential self; if makeup is put on a child's forehead, children 18-24 months will wipe the makeup off when looking in a mirror as they can separate themselves from others; children under 18 months will look behind the mirror to find the child with makeup;
5
New cards
categorical self (public self)
understanding that we each have specific properties; describing our physical or psychological characteristics
6
New cards
private self
one's inner self; not immediately known by others; things we only know about ourselves that others may not realize
7
New cards
theory of mind
understanding that people have unique beliefs, desires, and intentions; develops around the age of 4; assessed using false-belief tasks
8
New cards
self-discrepancy theory
states that comparing actual self to ideal or ought self results in negative feelings
9
New cards
actual self
who we actually are
10
New cards
ideal self
who we could be; person we could be if we reach our full potential
11
New cards
ought self
the person we think we should be
12
New cards
discrepancy between actual self and ideal self
this discrepancy will result in feelings of unhappiness, disappointment, dissatisfaction, or self-dislike
13
New cards
discrepancy between actual self and ought self
this discrepancy will result in feelings of fear, anxiety, personal inadequacy, or alienation
14
New cards
self-esteem
the extent to which we value ourselves
15
New cards
social comparisons
evaluations of ourselves based on comparisons to others
16
New cards
downward social comparison
comparing our lives to people who are doing worse in life; increases self-esteem
17
New cards
upward social comparison
comparing our lives to people who are doing better in life; decreases self-esteem
18
New cards
personality
stable and enduring pattern of thoughts, emotions, and behaviors
19
New cards
psychodynamic theory
unconscious motives influence personality
20
New cards
humanistic theory
potential for growth and personal fulfillment; reaching our full potential
21
New cards
trait theory
personality is explained by characteristics
22
New cards
social-cognitive theory
personality is explained by how we think; how social factors influence personality
23
New cards
created the psychodynamic theory
Sigmund Freud
24
New cards
Sigmund Freud's main belief
believed that unconscious forces determine behavior/personality
25
New cards
3 structures of the mind
unconscious, conscious, and preconscious
26
New cards
unconscious mind
reservoir of mostly unacceptable thoughts, feelings, and memories
27
New cards
conscious mind
everything that we are aware of
28
New cards
preconscious mind
information outside of awareness but accessible; bringing in information outside of awareness to focus
29
New cards
conflict between the different structures of the mind results in our ...
...personality
30
New cards
3 structures of personality
id, superego, ego
31
New cards
id
completely unconscious; survive, reproduce, aggress; operates on the Pleasure Principle
32
New cards
superego
moral compass; "Conscience;" how we ought to behave
33
New cards
ego
deals with the id's demands in realistic ways; operates on the reality principle to minimize tension/anxiety brought up between the id and superego
34
New cards
conflicts between the id and superego creates ...
... anxiety
35
New cards
repression
type of defense mechanism; pushes unacceptable id urges back into the unconscious and out of awareness
36
New cards
denial
type of defense mechanism; smokers may refuse to believe that smoking is bad for their health
37
New cards
displacement
type of defense mechanism; shifting aggressive or sexual impulses toward less threatening targets; a boss may yell at you at work, but you go home and yell at loved ones
38
New cards
sublimation
type of defense mechanism and form of displacement; shifting aggressive or sexual impulses toward socially appropriate targets; boxer takes out aggressive impulses on other boxers
39
New cards
projection
type of defense mechanism; disguise our own threatening impulses by attributing them to others
40
New cards
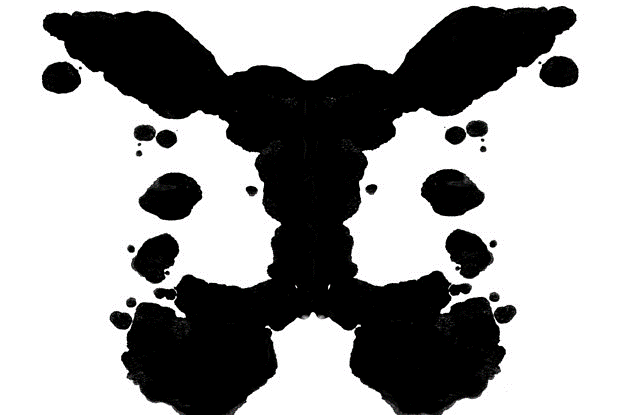

Rorschach Inkblot Tests
type of projective test; client is asked to describe what they see to understand unconscious thoughts or feelings
41
New cards
Thematic Apperception Test
type of projective test; client is asked to describe the scenario of the image to understand their thoughts through what they are projecting
42
New cards
oral stage
first 18 months; pleasure center = mouth; children will constantly put objects into their mouth for pleasure
43
New cards
anal stage
18-36 months; pleasure focus on bowel movement; children get pleasure from controlling their bowel; potty training
44
New cards
phallic stage
3-6 years; pleasure center = genitals
45
New cards
Oedipus complex
castration anxiety motivates boys to identify with their father; facilitates the superego
46
New cards
Electra complex
girls have no castration anxiety so they have weaker superegos; Freud believed females were morally inferior and had penis envy
47
New cards
latency stage
6 years-puberty; psychic time-out
48
New cards
genital stage
adolescence-adulthood; sexual pleasure shifts to people outside of the home; socially appropriate targets
49
New cards
Freud's Psychosexual Theory
conflicts arise at each Psychosexual Stage; if unresolved, we fixate our pleasure-seeking energy at that stage; if deprived at the oral stage, may continue to seek oral gratification; thumb sucking, smoking, biting nails, oral sex, etc.
50
New cards
criticisms of
Freud's theory
Freud's theory
too much focus on sex and aggression; theories are not testable and no empirical support; stops at adolescence
51
New cards
Freud's major contributions
introduced the importance of the unconscious; early childhood experiences can have long lasting implications; developed the "Free Association" technique
52
New cards
trait theory
more to personality than unconscious motives; our traits cause a person to behave the same in different situations
53
New cards
traits
stable and enduring thoughts and behaviors; causes a person to behave the same in different situations
54
New cards
Lexical Approach
psychologists went through dictionaries and picked out every word that could be used to describe a person; 18,000 words
55
New cards
factor analysis
grouped similar words together from the dictionaries
56
New cards
big five factors of personality
broad traits; describe the main dimensions of personality; measured on a continuum
57
New cards
conscientiousness
organized/disorganized, forgiving/unforgiving
58
New cards
agreeableness
generous/ruthless, helpful/uncooperative
59
New cards
neuroticism
anxious/calm, insecure/secure
60
New cards
openness
tolerant/intolerant, creative/conforming
61
New cards
extraversion
social/reserved, outgoing/"home-body"
62
New cards
self-report measures
asks people to voluntarily share information about themselves to assess traits
63
New cards
pros of self-report measures
easy to obtain; can be quick and effective; relatively inexpensive
64
New cards
cons of self-report measures
people are biased (social desirability); difficult to create good (reliable and valid) measures; people may not pay careful attention; typically don't take into consideration the situation
65
New cards
Fleeson's theory
typical individuals are likely to experience all levels of all traits in his/her everyday life
66
New cards
what changes who you are?
the interaction between nature and nurture; environmental events -> genes
67
New cards
psychological disorders
characterized by abnormal behaviors
68
New cards
abnormal behaviors must be ...
...deviant, maladaptive, and distressful
69
New cards
deviant
behaviors are different from the "norm"
70
New cards
maladaptive
behaviors interfere with one's ability to function
71
New cards
distressful
feelings of shame, guilt, despair, etc.
72
New cards
disorders are...
...maladaptive and distressful
73
New cards
DSM stands for
diagnostic & statistical manual of mental disorders
74
New cards
purpose of the DSM-5
used to identify and diagnose mental disorders
75
New cards
DSM list of criteria for diagnosis
these must be met prior to the diagnosis of an individual
76
New cards
controversies about DSM-5 criteria for ADHD
diagnostic criteria has been relaxed; age has been changed
77
New cards
controversies about DSM-5 criteria for Autism Spectrum Disorder
diagnosis for Asperger Syndrome has been dropped
78
New cards
controversies about DSM-5 criteria for Mild Neurocognitive Impairment
new diagnosis for adults experiencing cognitive decline even though intelligence and memory fades overtime for everyone
79
New cards
anxiety disorders
distressing, persistent anxiety; uncontrollable fear, motor tension (trembling), hyperactivity (racing heart), apprehension
80
New cards
generalized anxiety disorder
pathological and constant worry; difficult to concentrate; unable to identify the reason for the worry
81
New cards
panic disorder
anxiety -> panic attacks; intense dread and terror; chest pain, choking, dizziness
82
New cards
specific phobias
irrational, overwhelming, and persistent fear of a particular object; fear of that object/experience is disproportionate to the level of threat
83
New cards
obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
unwanted thoughts and/or actions; can become very time consuming; threatens normal functioning
84
New cards
medication
type of anxiety and depressive disorder treatment including anti-anxiety/anti-depressants; relapse rates are high; can be habit forming
85
New cards
cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
type of anxiety and depressive disorder treatment; taught how to identify problematic thoughts/behaviors; taught strategies to overcome these
86
New cards
depressive disorders
type of mood disorder where there is a constant lack of pleasure in one's life
87
New cards
major depressive disorder (MDD)
chronic fatigue, sense of worthlessness, reduced interest in the things that usually bring enjoyment; appetite and sleep disturbances
88
New cards
biological cause of MDD
a chemical imbalance can cause too few receptors for serotonin in the body causing this disorder
89
New cards
chemical imbalance
there are too few receptors for serotonin which causes a person to develop MDD; antidepressants typically include SSRIs
90
New cards
psychological causes of MDD
learned helplessness and rumination on negative thoughts can cause this disorder
91
New cards
learned helplessness
feelings of powerless and loss of control; when we try something and keep failing
92
New cards
mood disorders
can be characterized by feeling sad or depressed sometimes or emotional extremes
93
New cards
one extreme of mood disorders
depression
94
New cards
another extreme of mood disorders
mania
95
New cards
bipolar disorders
extreme mood swings from intense depression to overwhelming mania; as if we two selves; happy-go-lucky, risk-seeking self or the withdrawn, depressed self
96
New cards
bipolar I
must have at least one manic episode; may or may not have a major depressive episode
97
New cards
bipolar II
hypomanic and depressive episodes; still experiences a depressive state but not a full blown manic episode
98
New cards
hypomanic
mildly elevated moods
99
New cards
electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)
type of depressive disorder treatment; mild electrical current is passed through the brain to improve extreme depressive states
100
New cards
interpersonal therapy
type of depressive disorder treatment; helps people form relationships to seek out support