B3: Organisation and the digestive system
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
Cells
Basic building blocks of all living organisms
Tissue
Group of cells with similar structure + function
Organs
Group of tissues working tog for a specific function
Organ systems
Groups of organs working tog to perform a specific function
Organisms
A number of organ systems working tog
Put into order of size
Organ systems
Cells
Organs
Organisms
Tissues
Cells
Tissues
Organs
Organ systems
Organisms
Types of tissue in the stomach involved in the digestion of food
Muscular
Glandular
Epithelial
Role of tissues in the stomach
Muscular- churns food
Glandular- releases enzymes
Role of the 3 types of tissue
What do specialised cells have?
Adaptations to help them carry out their functions
Adaptations of muscle cells
Can contract (get shorter)
Contain special protein fibres that can change their length
Have lots of mitochondria
Provide energy needed for contraction
Main nutrients in food
Carbohydrates (starch)
Protein
Lipids (fats)
Why do the 3 main nutrients in food need to be digested?
Too large to be absorbed into the BS
What happens during digestion?
Large food molecules broken down into small molecules by enzymes
SM can be absorbed into the BS
What acid does stomach contain and what is its function?
HCl
Helps enzymes digest proteins
How does the churning action of stomach muscles turn food into a fluid to aid digestion?
Increases SA for enzymes to digest
What chemicals are released from the pancreas into the SI?
Enzymes
Continue digestion of starch + protein
Start digestion of lipids
What chemicals are released from the liver into the SI?
Bile
Speeds up digestion of lipids
Neutralises stomach acid released from stomach
Digestive system
Organ system in which several organs work tog to digest + absorb food
How are the products of digestion used by the body?
To build new carbohydrates, lipids, proteins
What is the glucose produced from digestion used in?
Respiration
What do enzymes do?
Catalyse chemical reactions
Enzymes
Large protein molecules with an active site
Biological catalysts that catalyse specific reactions in living organisms
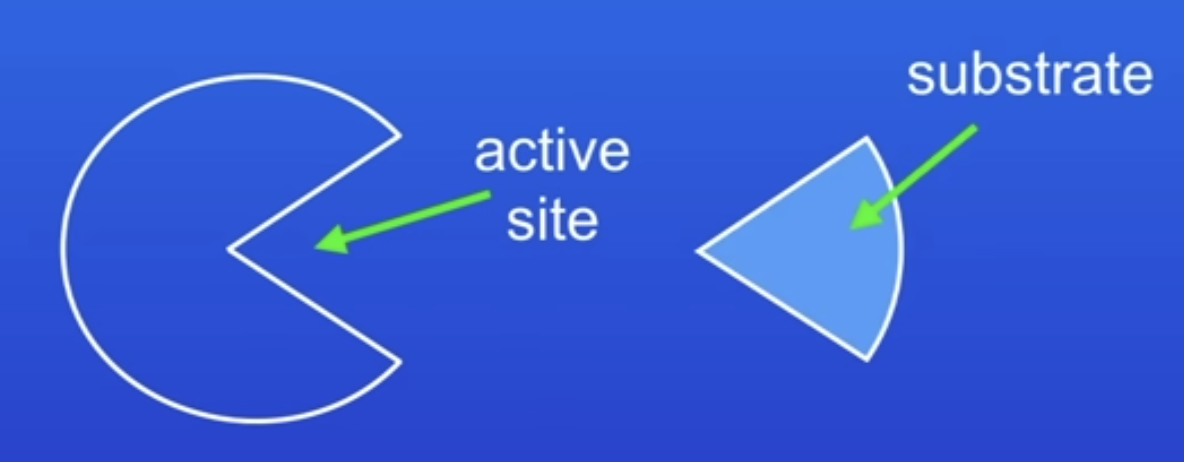
How are enzymes able to catalyse specific reactions in living organisms?
Due to the specific shape of their active site
Active site
Where substrate attaches to
Substrate
Molecule enzyme breaks down
Specific to 1 enzyme
For an enzyme to catalyse a reaction, the substrate must…
Fit perfectly into the active site
How does an enzyme catalyse a reaction?
Substrate binds to specific AS
Enzyme breaks down substrate into products

Catalyst
Increase the rate of chemical reactions w/o being used up / chemically changed
What happens if a substrate doesn’t fit into an active site
Enzyme can’t break down the substrate

Enzymes are…
Specific
What is meant by ‘enzymes are specific‘?
Substrate must fit perfectly into the AS (for reaction to be catalysed)
Lock and key theory
Enzymes in the digestive system + what they help break down
Protease- proteins
Lipase- lipids
Carbohydrase- carbohydrates
Amylase- starch
Where is protease found?
Stomach
Pancreatic fluid
SI
What do digestive enzymes do?
Convert food into small soluble molecules that can be absorbed into the BS
Proteins
Long chains of AA
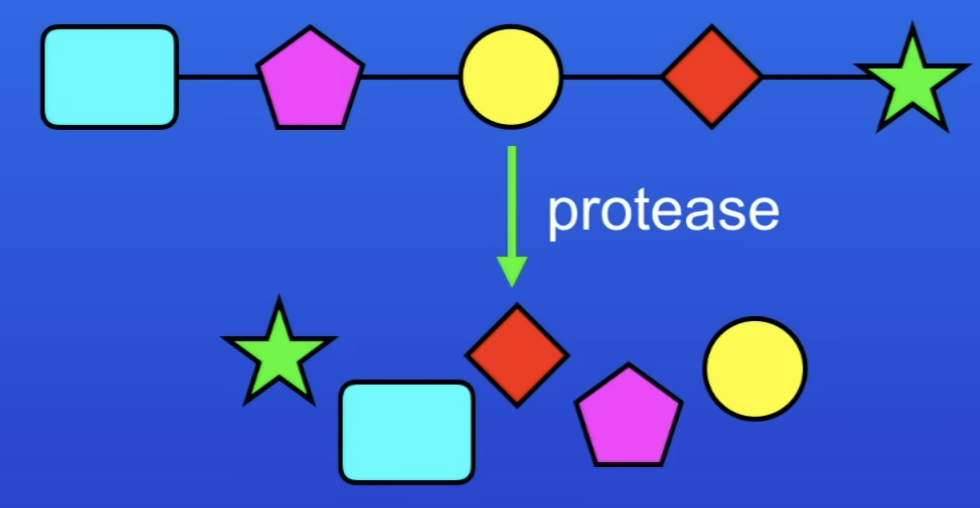
What happens when we digest proteins?
Protease enzymes convert protein back to individual AA
AA absorbed into BS + body cells
AA joined in a diff order to make human proteins
What is starch?
Carbohydrate
What is starch made up of?
Chain of glucose molecules
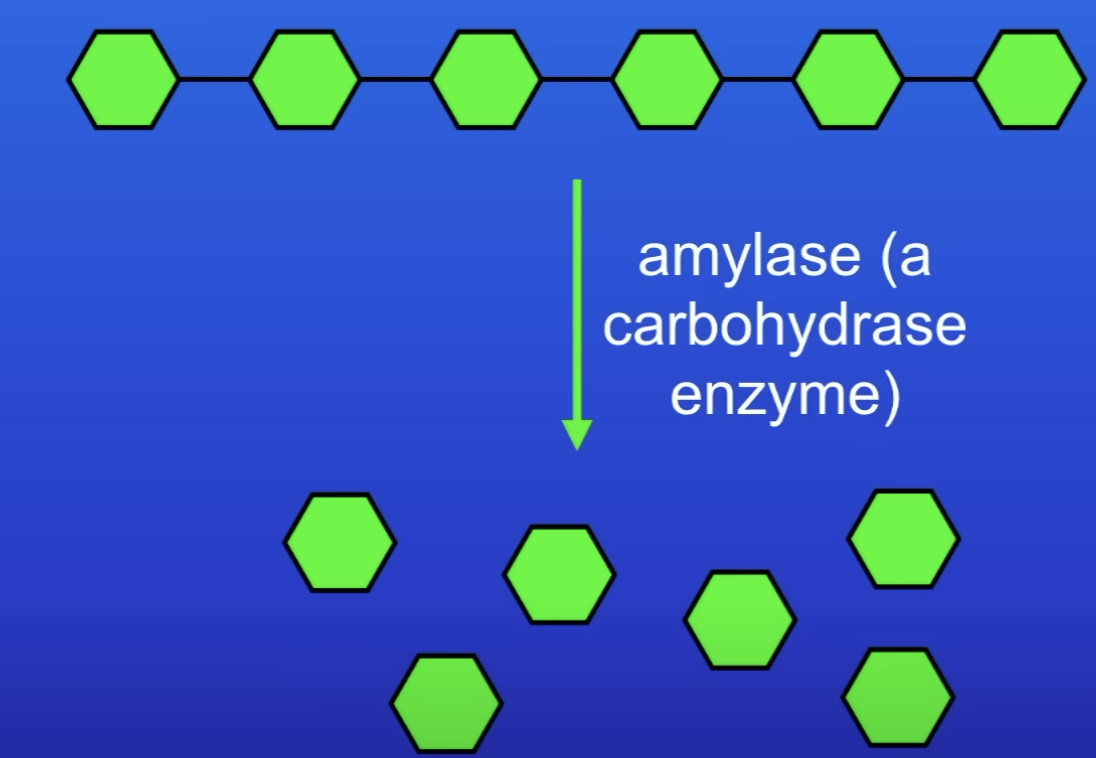
What is produced when carbohydrates like starch are digested?
Simple sugars
Where is amylase found?
Saliva
Pancreatic fluid
Structure of lipids
1 molecule of glycerol attached to 3 molecules fatty acids
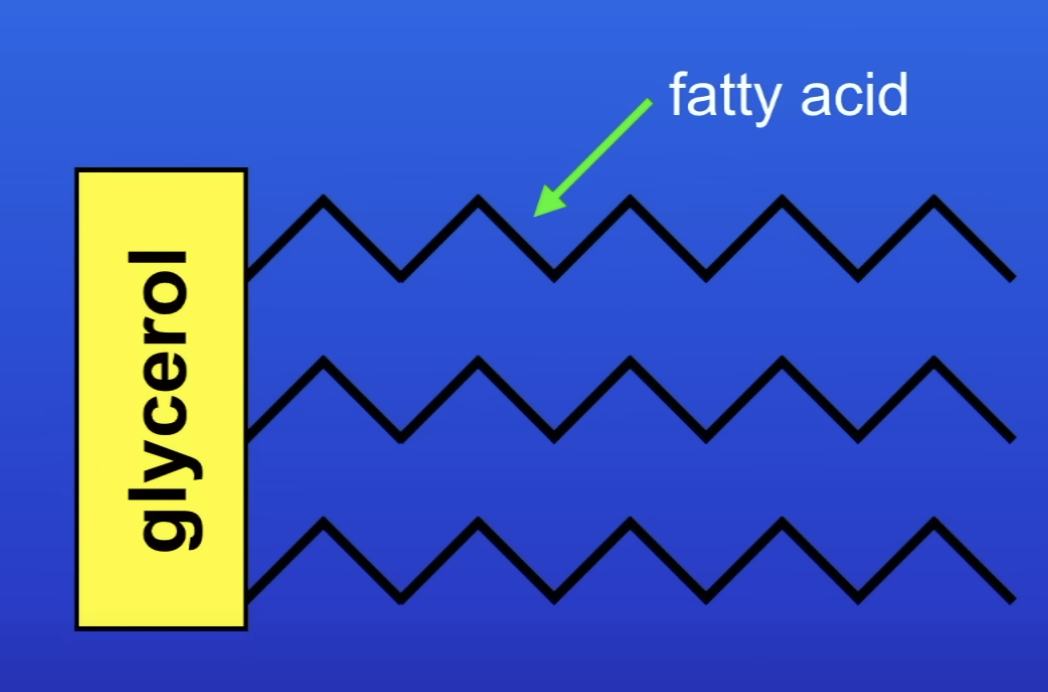
What does lipase break down / digest lipid molecules into?
Glycerol
Fatty acids
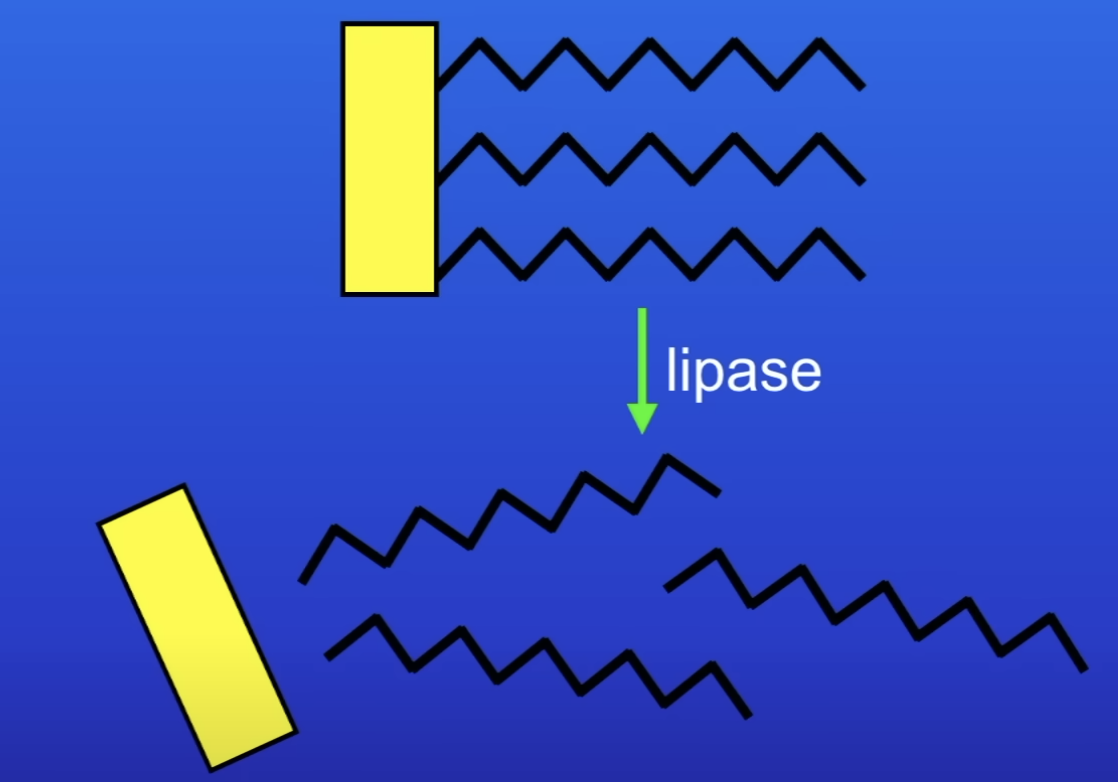
Where is lipase found?
Pancreatic fluid
SI
What do these enzymes break down these molecules into?
Carbohydrase
Amylase
Protease
Lipase
Carbohydrase- carbohydrates- simple sugars
Amylase- starch
Protease- proteins- AA
Lipase- lipids- glycerol + fatty acids
Amylase
Carbohydrase which breaks down starch
Where is bile made + stored?
Made in liver
Stored in gall bladder
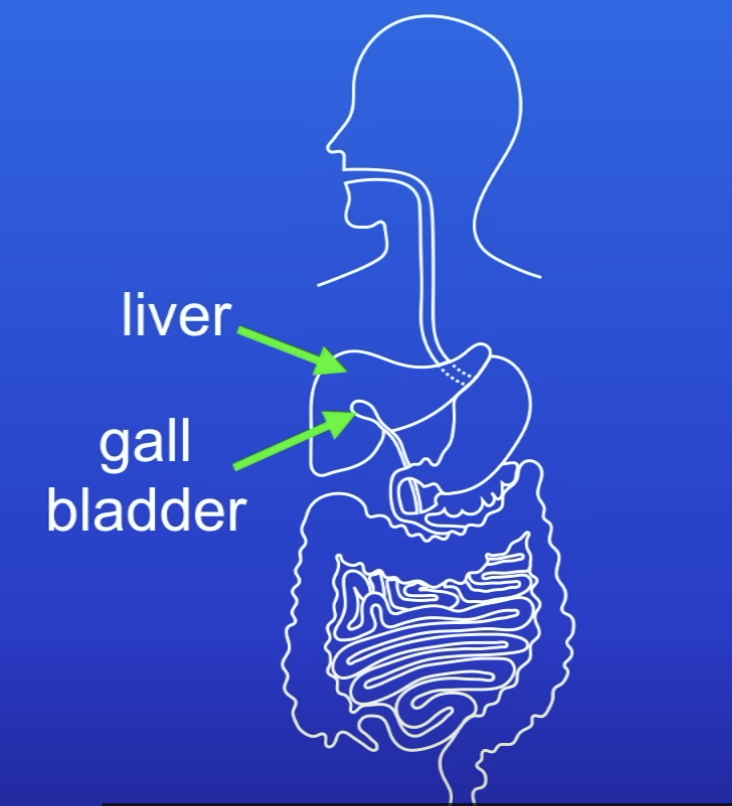
Bile
What does bile help?
Speed up digestion of lipids
Is bile an enzyme?
No
What does bile do to lipids?
Bile emulsifies lipids
How does bile speed up the digestion of lipids?
It converts large lipid droplets into smaller ones
Increases SA of lipid droplets
Which increases rate of lipid break down by lipase
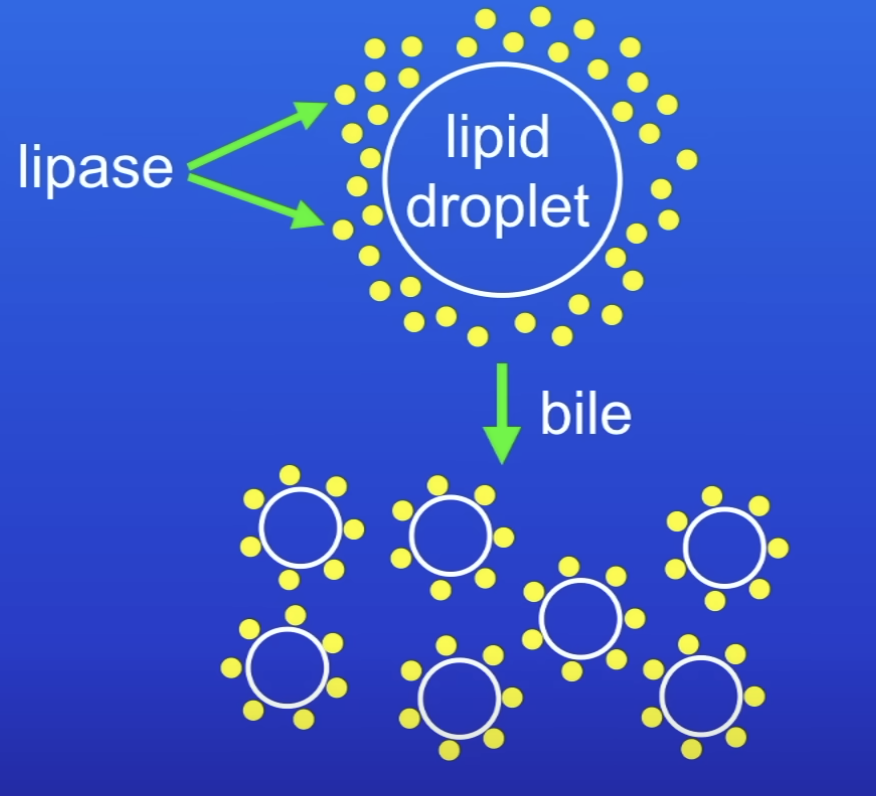
What does bile emulsifying lipids do?
Increases SA of lipid droplets
Which increases rate of lipid break down by lipase
Is bile acid or alkaline?
Alkaline
Bile is alkaline- what does this allow it to do?
Can neutralise stomach acid, creating alkaline conditions in SI
What does bile emulsify fats to form?
Small droplets which increases the SA
What helps increase the rate of fat breakdown by lipase?
Alkaline conditions
Large SA
Factors that affect enzyme action
Temp
pH
What happens to enzyme activity as temp increases (not exceeding optimum)?
Increases (reaction gets faster)
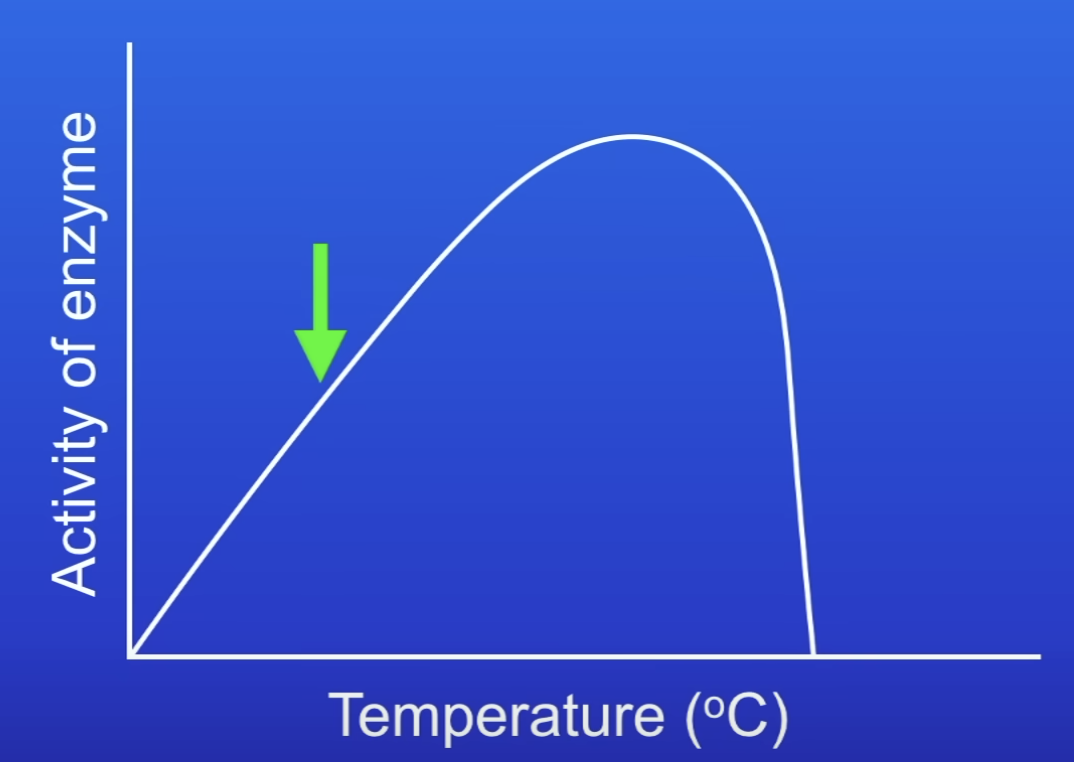
Why does enzyme activity increase as temp increases (not exceeding optimum)?
Enzyme + substrate moving faster
→ more collisions per s betw substrate + AS
Optimum temperature
Temp at which the enzyme is working at the fastest possible rate
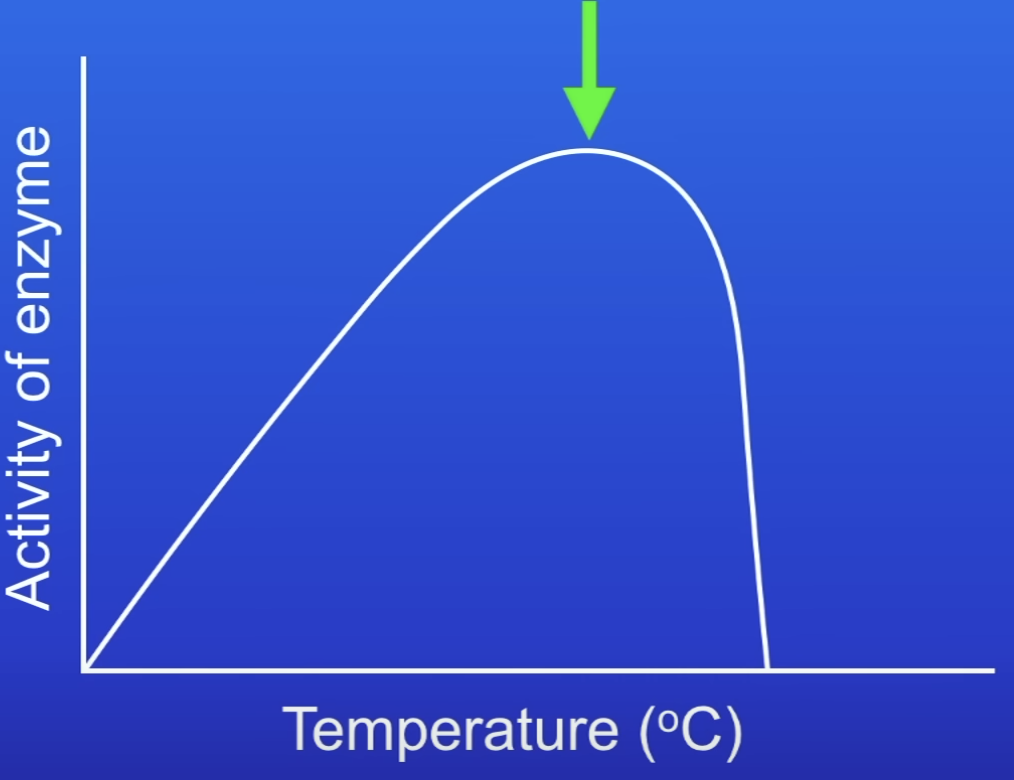
What happens at the optimum temperature
Max frequency of successful collisions between the substrate + AS
Optimum temp for human enzymes
37 °C
What happens to enzyme activity as temp increases beyond the optimum?
Decreases to 0
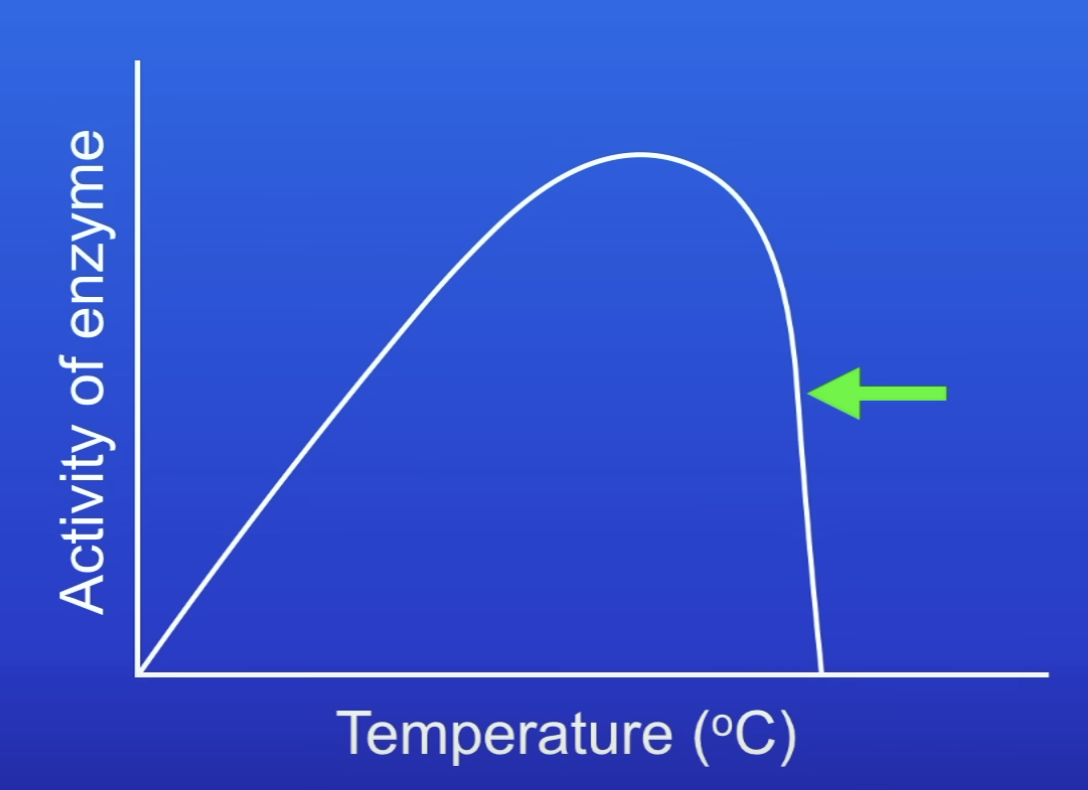
Why does enzyme activity become 0 after temp has been increased past the optimum?
At high temps, enzyme molecule vibrates + shape of AS changes
Substrate no longer fits perfectly into AS
AS has denatured
What is meant by the active site has denatured?
Substrate no longer fits perfectly into AS
Enzyme can’t catalyse the reaction

What happens when an enzyme is denatured?
Shape of AS changes
Optimum pH
Enzyme activity is maximum
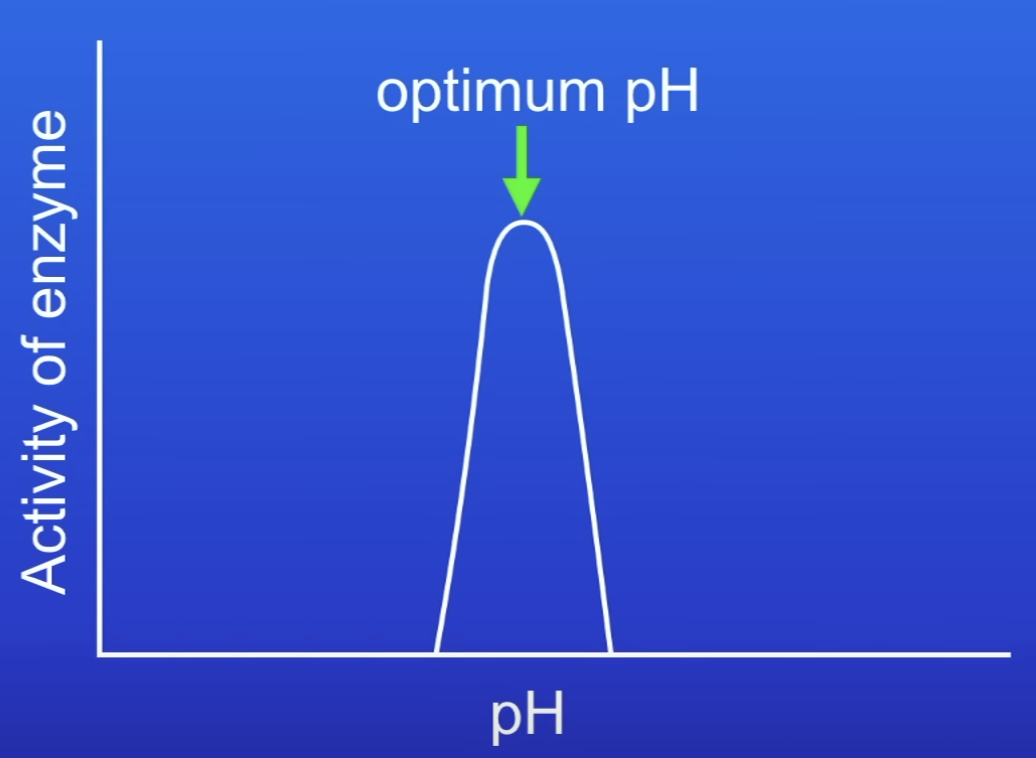
What happens to enzyme activity if PH is made more acidic or alkaline and why?
Drops to 0
AS denatures if conditions are too acidic or alkaline
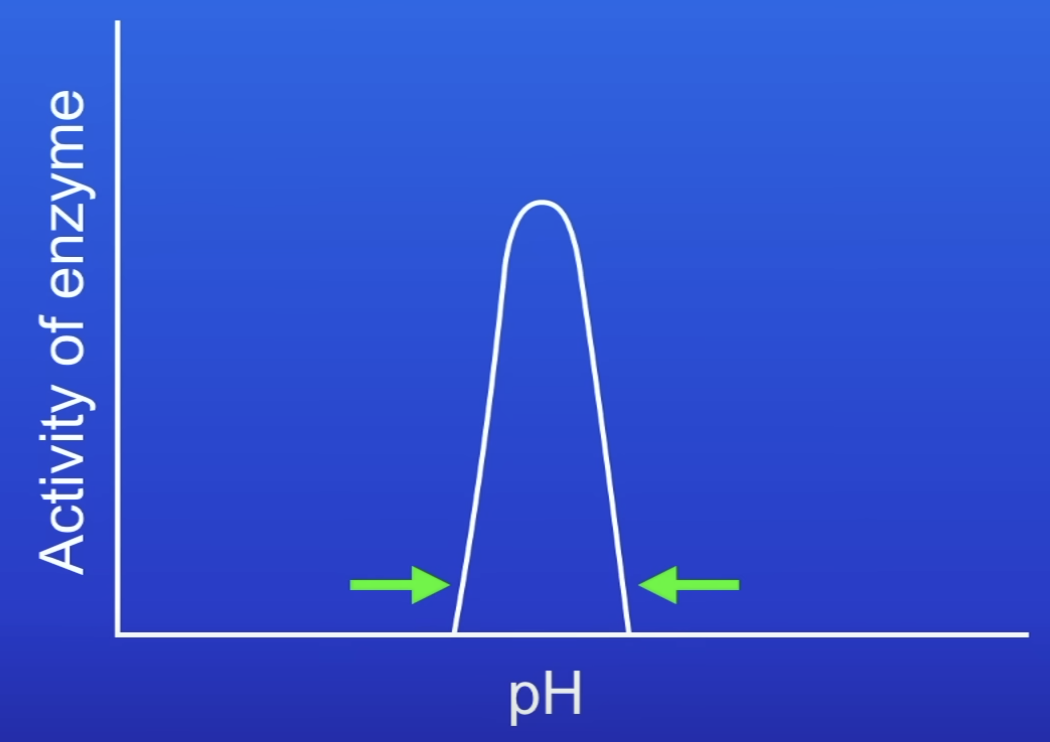
Each enzyme has a?
Specific optimum pH
What conditions to enzymes in the stomach work best at?
Acidic pH
Eg protease
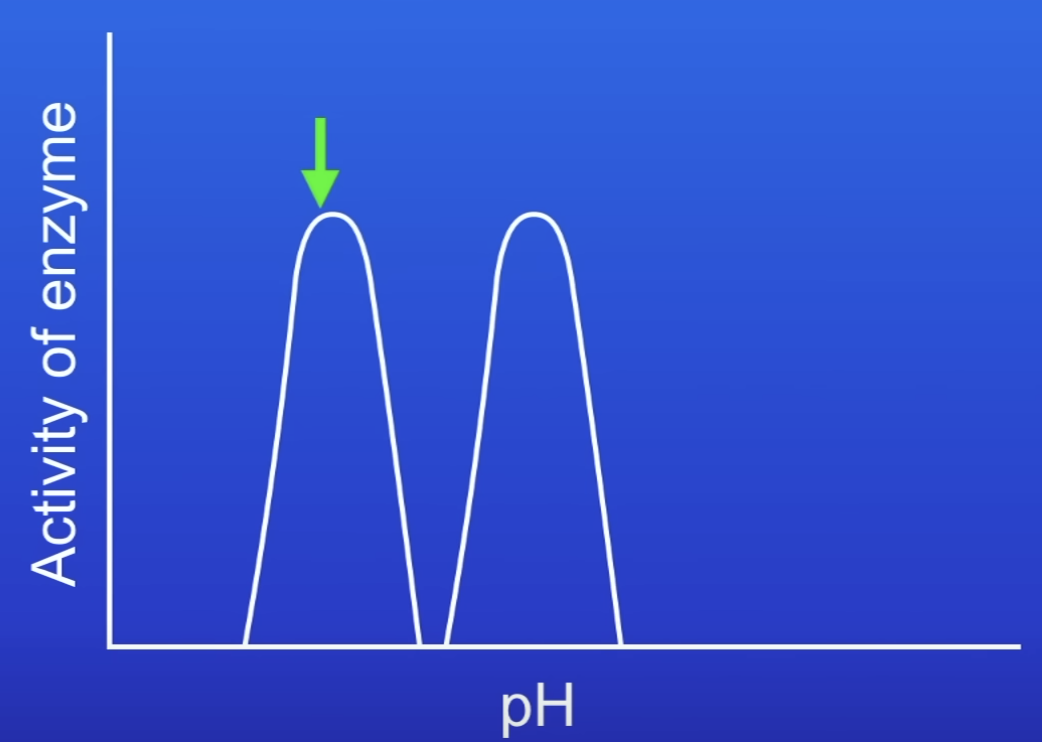
What conditions to enzymes in the small intestine work best at?
Alkaline pH
Eg enzyme released fm pancreas into SI (lipase)
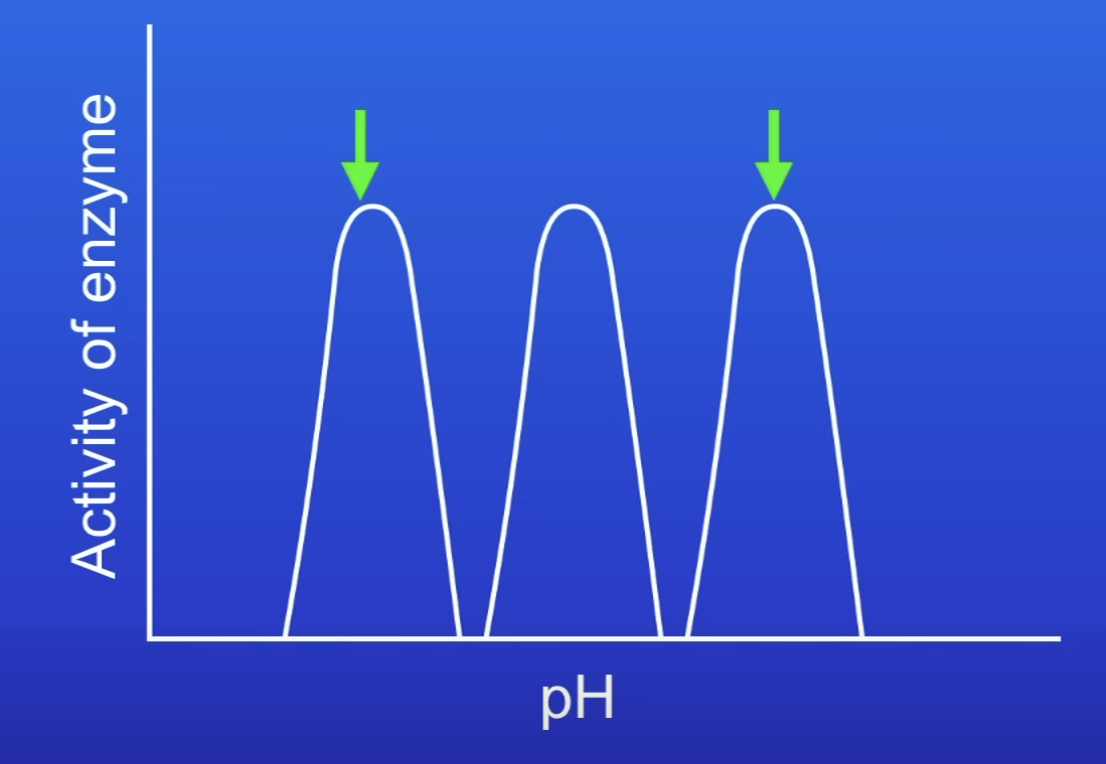
Are there different protease enzymes in the stomach and SI, and why?
Yes
Stomach- acidic
SI- alkaline
What are buffer solutions used for?
To control pH
Examples of carbohydrates
Starch
Sugars (glucose)
How to test for food groups + positive results
Starch
Glucose
Proteins
Lipids
Starch- iodine solution- blue-black
Glucose- benedict’s solution
Protein- biuret solution- purple/ lilac
Lipids- ethanol- white, cloudy emulsion
Positive + negative results to test for starch with iodine solution
Positive- orange changes to blue-black
Negative- no color change, IS remains orange
If glucose is present, what does the color of benedict’s solution tell us?
Approx amount of sugar present
Not exact amount
Positive + negative results to test for sugars (glucose) with benedict’s solution
Green (small amt)
Yellow (more)
Brick red (lots)
What sugars does the benedict’s test work for?
Reducing sugars (eg glucose)
Examples of non-reducing sugars
Sucrose
Positive + negative results to test for proteins with biurets solution
Biuret solution (blue) changes to purple/ lilac
Positive results to test for lipids with ethanol
Cloudy, white emulsion
When testing for flames with ethanol, why is it imp that no naked flames are present?
Ethanol is v flammable
What are digestive enzymes produced by?
Specialised cells in glands + lining of digestive system
What happens in the SI?
Products of digestion absorbed into the BS
How is the small intestine adapted for absorbing products of digestion?
Villi is / has:
V long
Lots of villi inside the SI
Microvilli on the surface of villi
V good blood supply (capillaries)
A thin membrane
What do the adaptations of the small intestine mean there is?
Rapid rate of diffusion
If a molecule can’t be absorbed by diffusion, how is it absorbed?
AT
In what conditions do protease enzymes in the stomach work best at?
Acidic
How does the stomach maintain a low pH for protease enzymes?
Releases HCl
In what conditions do enzymes in the pancreas + SI work best at?
Alkaline
Alkaline conditions provided by bile
Role of bile
Neutralises acid
Emulsifies fats
Purpose of HCl in the stomach
Provides optimum acidic pH for protease
Kills bacteria in the stomach
What does the thick layer of mucus produced by the stomach do?
Coats stomach walls- protects them from being digested by the acid + enzymes
What happens if someone develops a stomach ulcer?
Protective mucus is lost
Acid production may increase
Lining of stomach is attacked by acid + enzymes → painful
Why is bile not an enzyme?
Doesn’t break down fat molecules
It emulsifies fats into tiny droplets
What happens in the small vs large intestine?
Small- products of digestion absorbed into BS
Large- water absorbed into BS
Pancreas
Releases enzymes into SI
Does digestion take place in the pancreas?
No