geos120 exam 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/128
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:49 PM on 2/16/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
129 Terms
1
New cards
geoscience
earth science, especially geology
2
New cards
earth science
broader field encompassing geology, biology, chemistry, physics, astronomy, meteorology, etc.
3
New cards
geology
scientific study of earth (past, present, and future)
4
New cards
geological triad
geology=study of…
* earth materials
* processes and resulting
* sedimentary structures/landforms
* earth materials
* processes and resulting
* sedimentary structures/landforms
5
New cards
limestone (CaCO3)
what is the official state rock of Tennessee?
6
New cards
agate
what used to be the official state rock of Tennessee and was removed b/c it was not a rock?
7
New cards
tums (limestone)
what geologic material is used to alleviate acid stomach?
8
New cards
kaopectate
what geologic material is used to alleviate diarrhea?
9
New cards
surface processes
floods, landslides, soil erosion, and beach erosion are examples of..
10
New cards
internal processes
volcanoes and earthquakes are examples of..
11
New cards
landforms and structures
valleys and mountains are examples of..
12
New cards
experimental sciences
independent of time of occurrence
13
New cards
historical sciences
time plays a critical role in process
14
New cards
mississippi floodplain
which one is marked out?
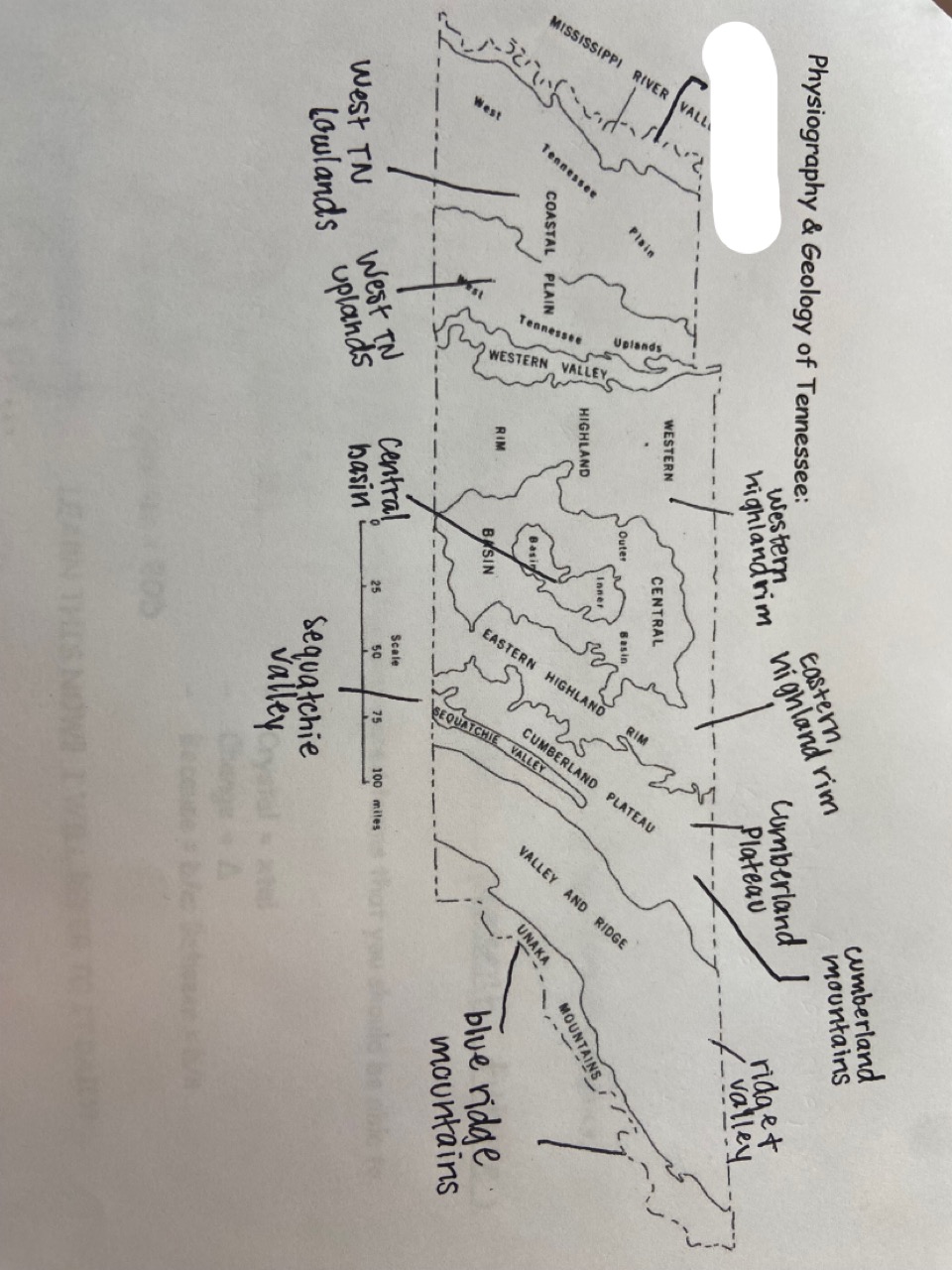
15
New cards
western highland rim
which one is marked out?
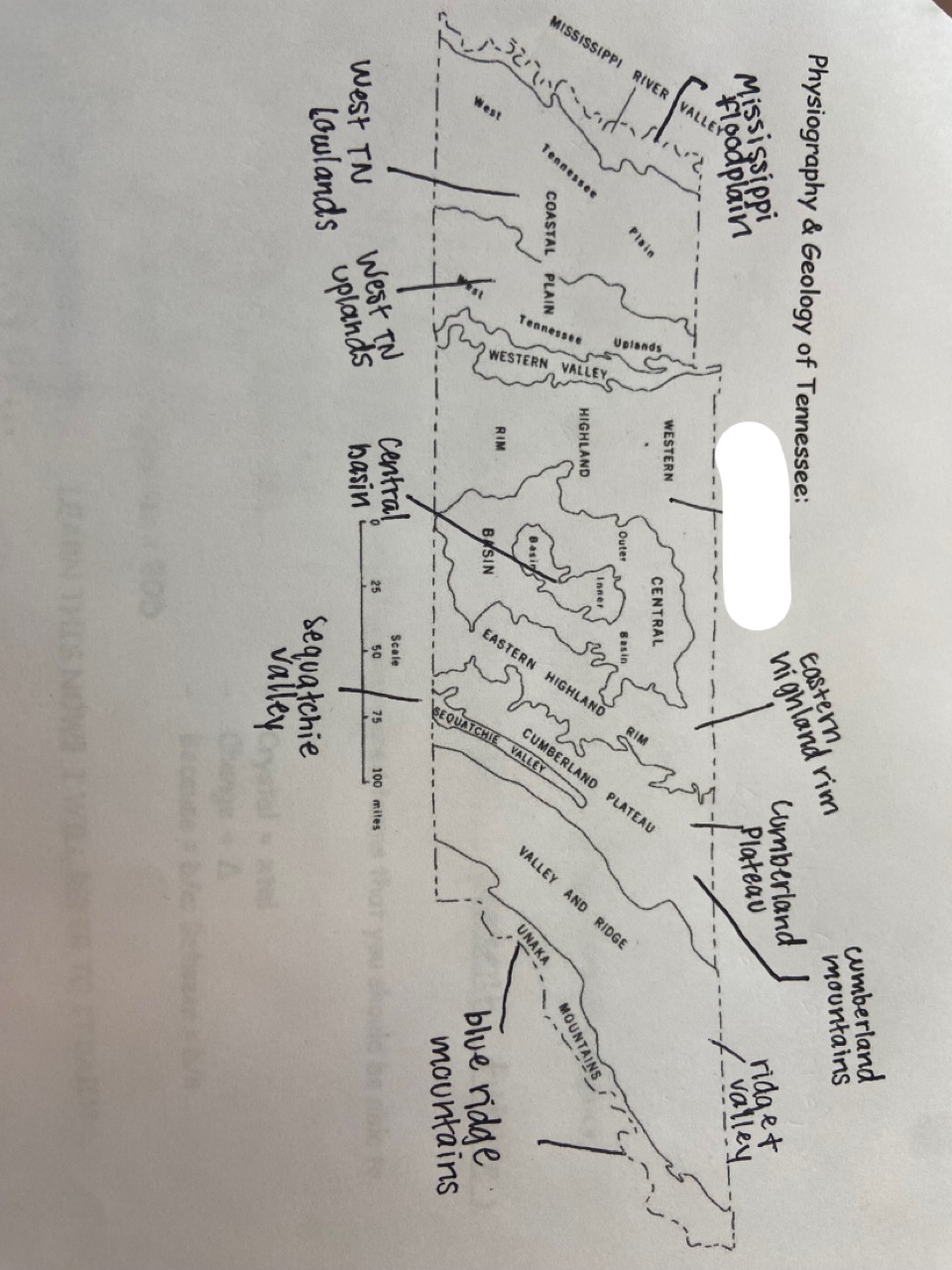
16
New cards
eastern highland rim
which one is marked out?
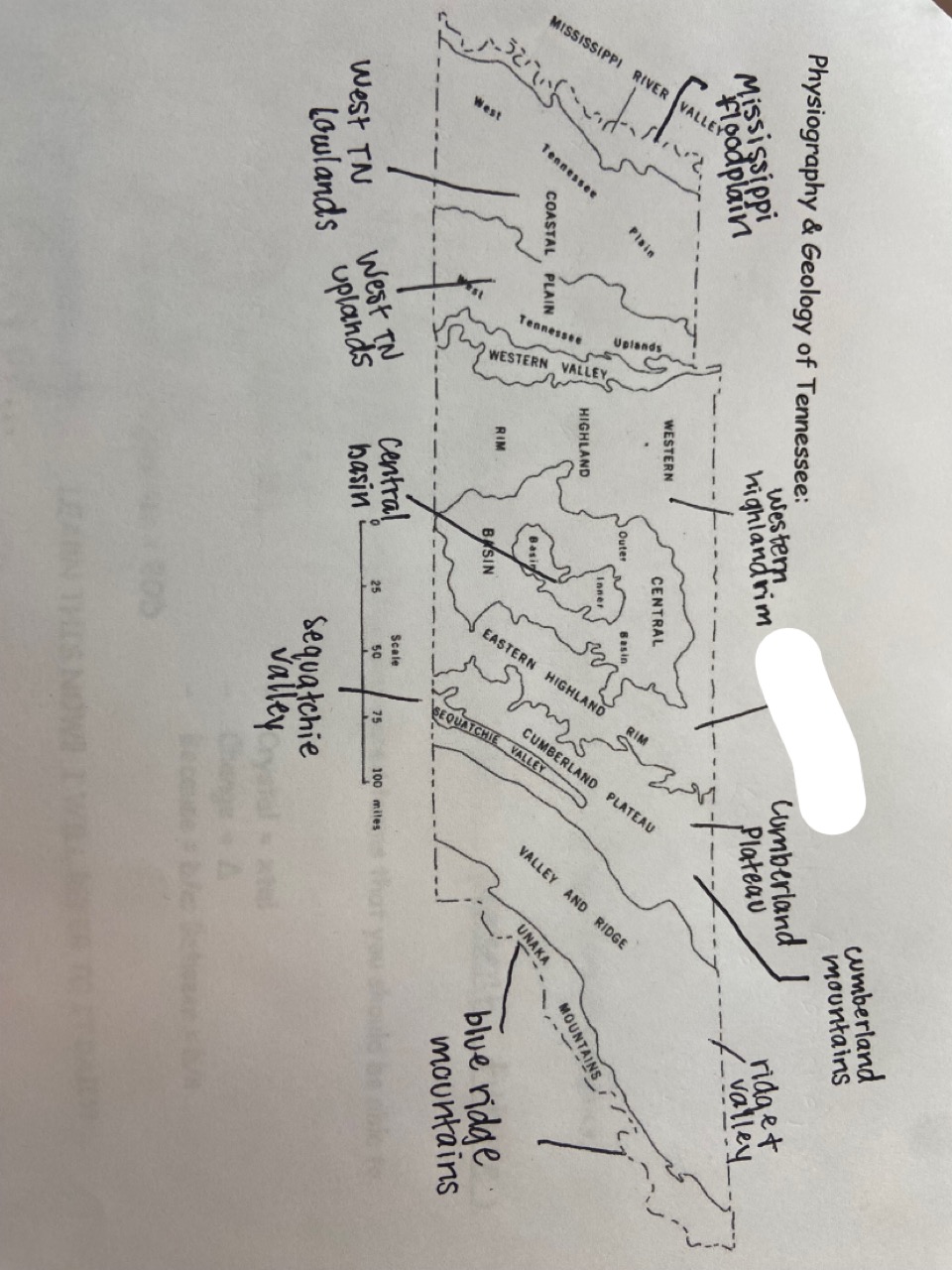
17
New cards
cumberland plateau
which one is marked out?
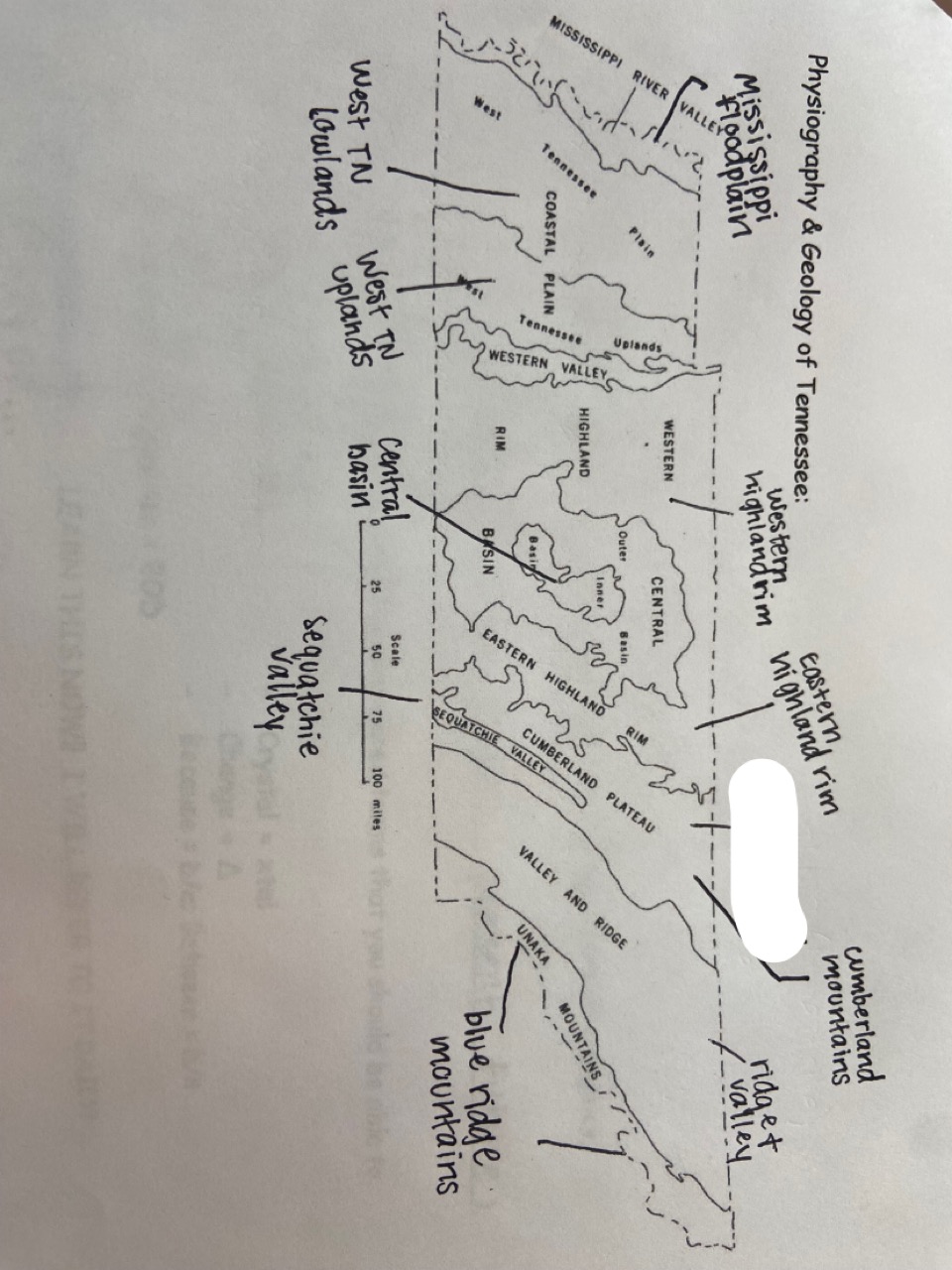
18
New cards
cumberland mountains
which one is marked out?
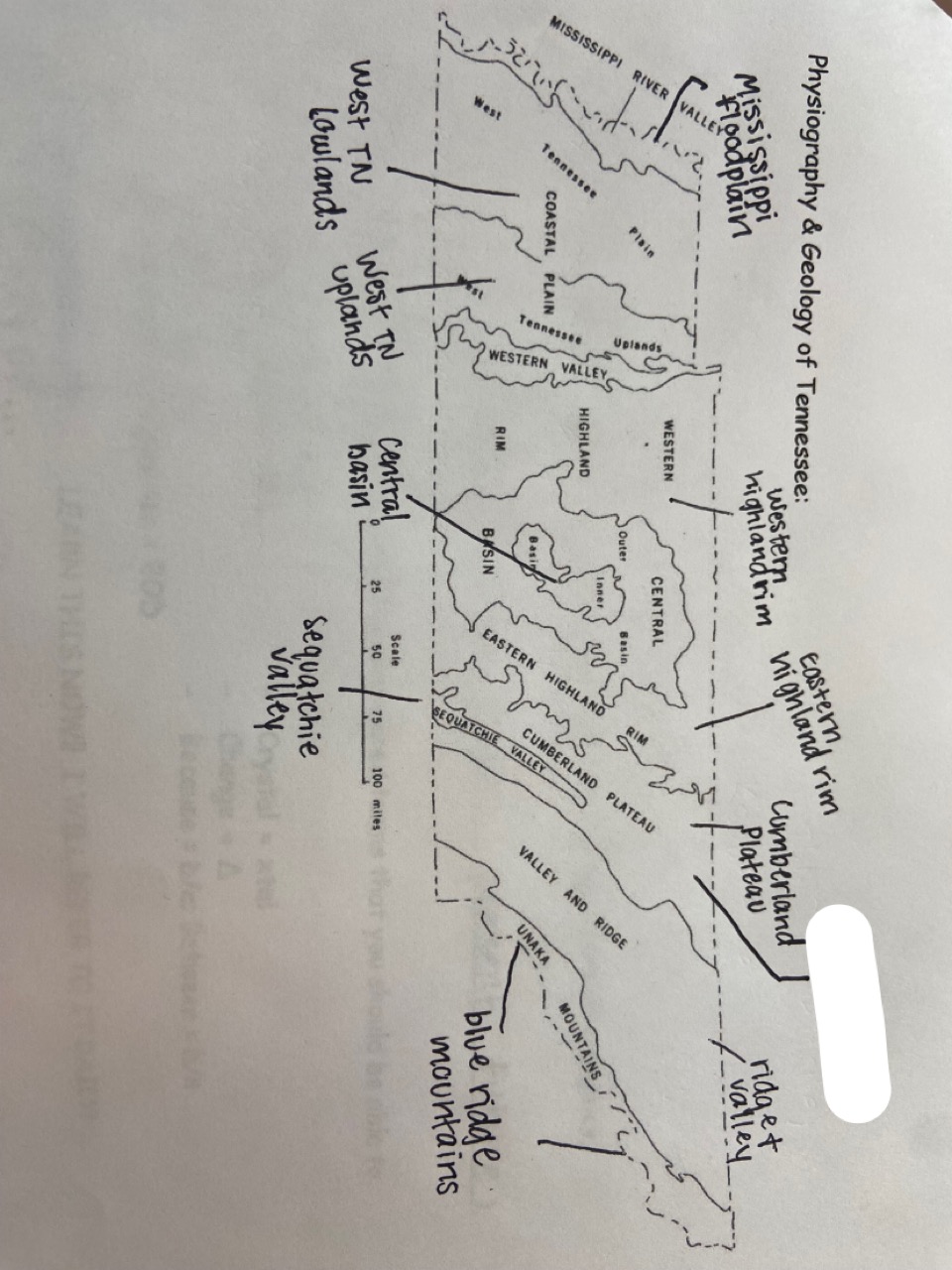
19
New cards
ridge and valley
which one is marked out?
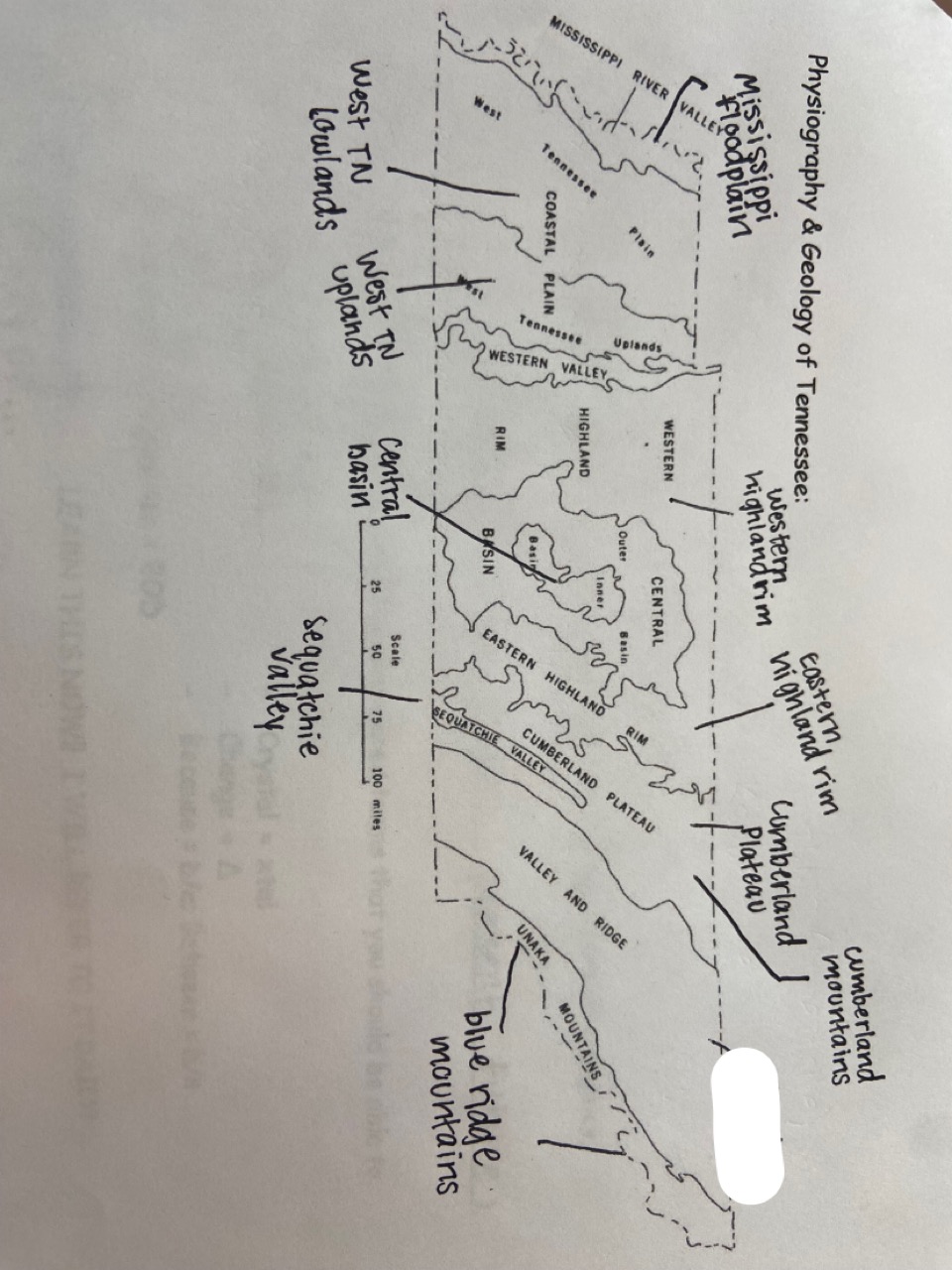
20
New cards
west tn lowlands
which one is marked out?
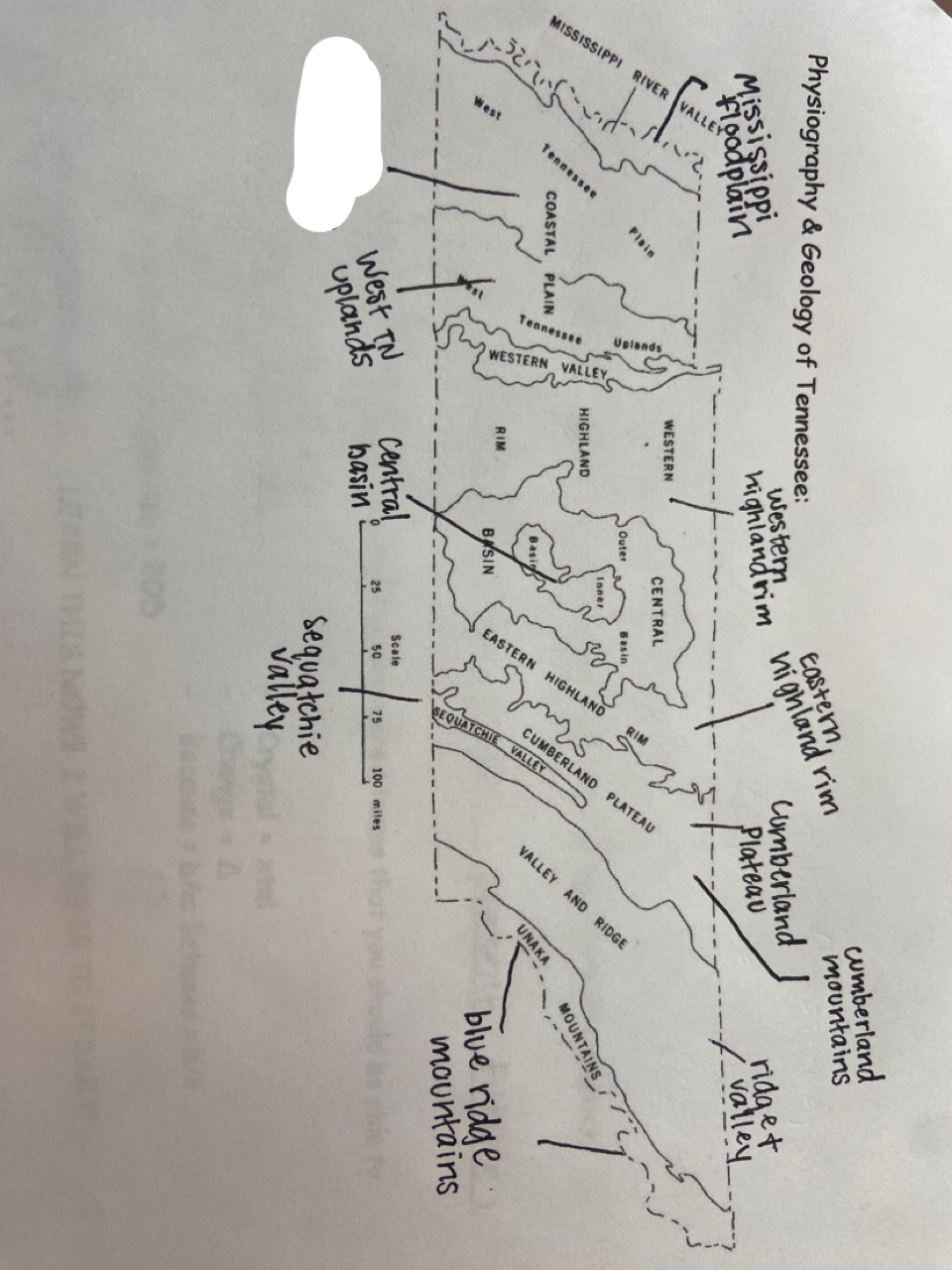
21
New cards
west tn uplands
which one is marked out?
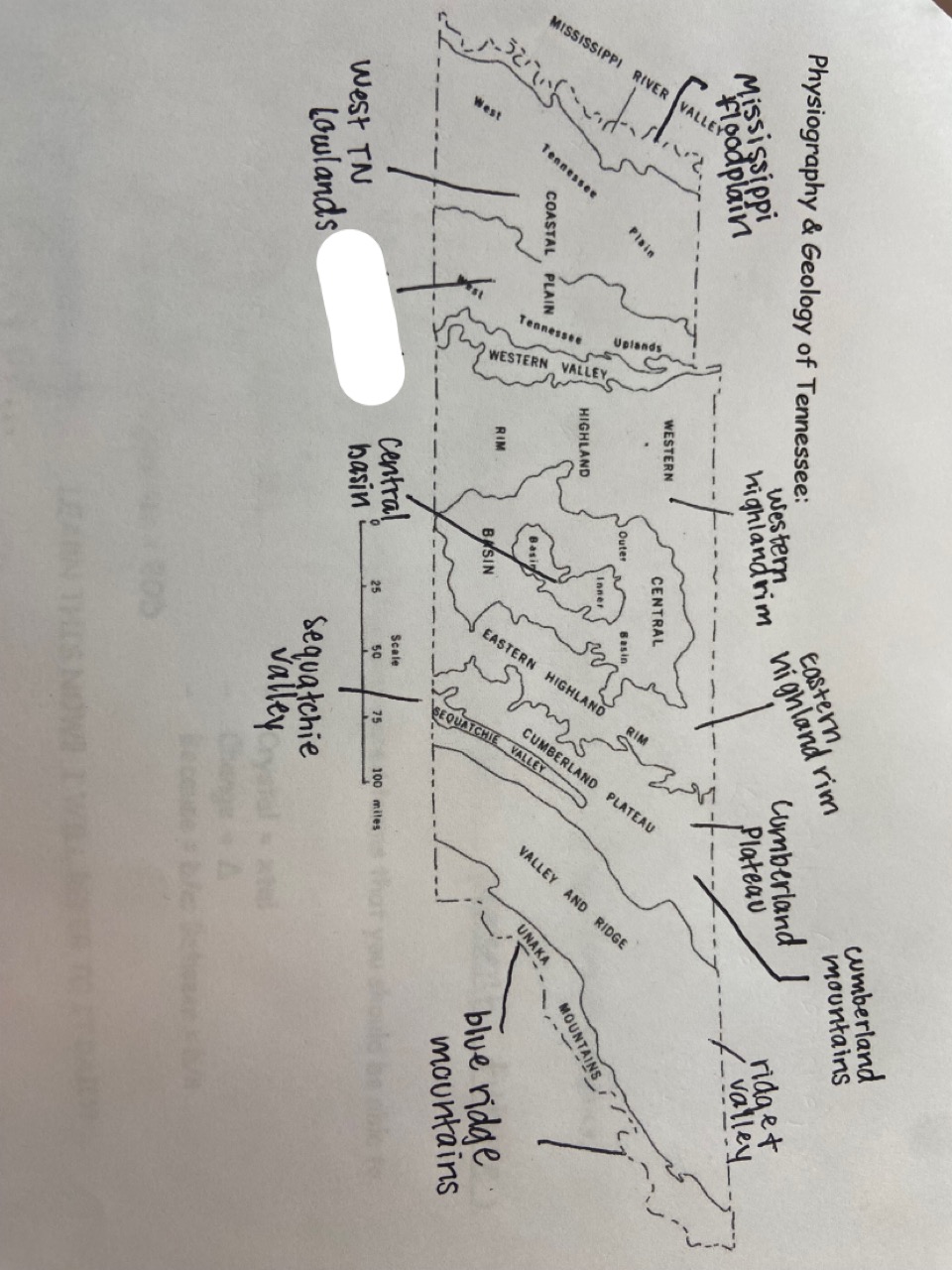
22
New cards
central basin
which one is marked out?
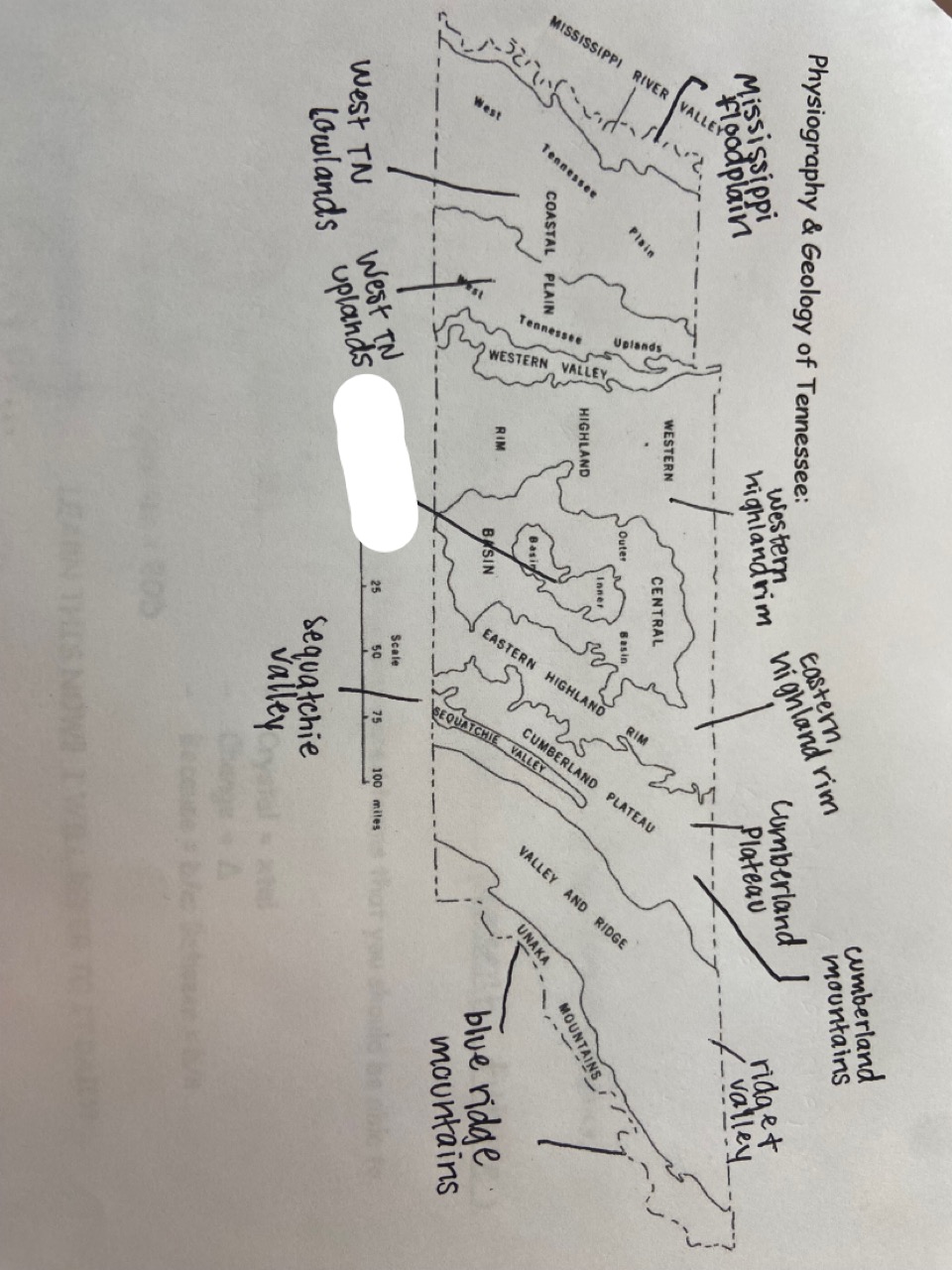
23
New cards
sequatchie valley
which one is marked out?
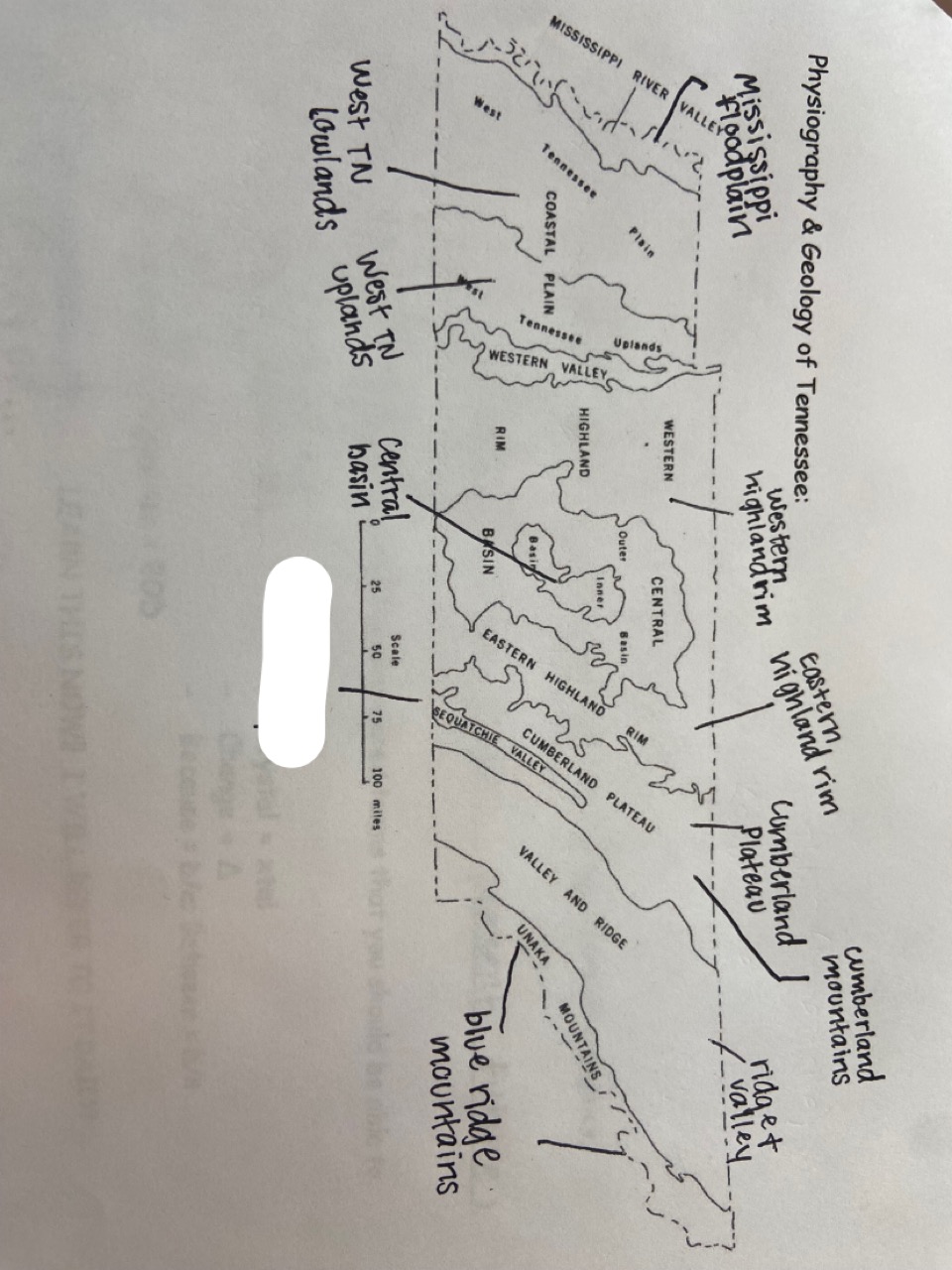
24
New cards
blue ridge mountains
which one is marked out?
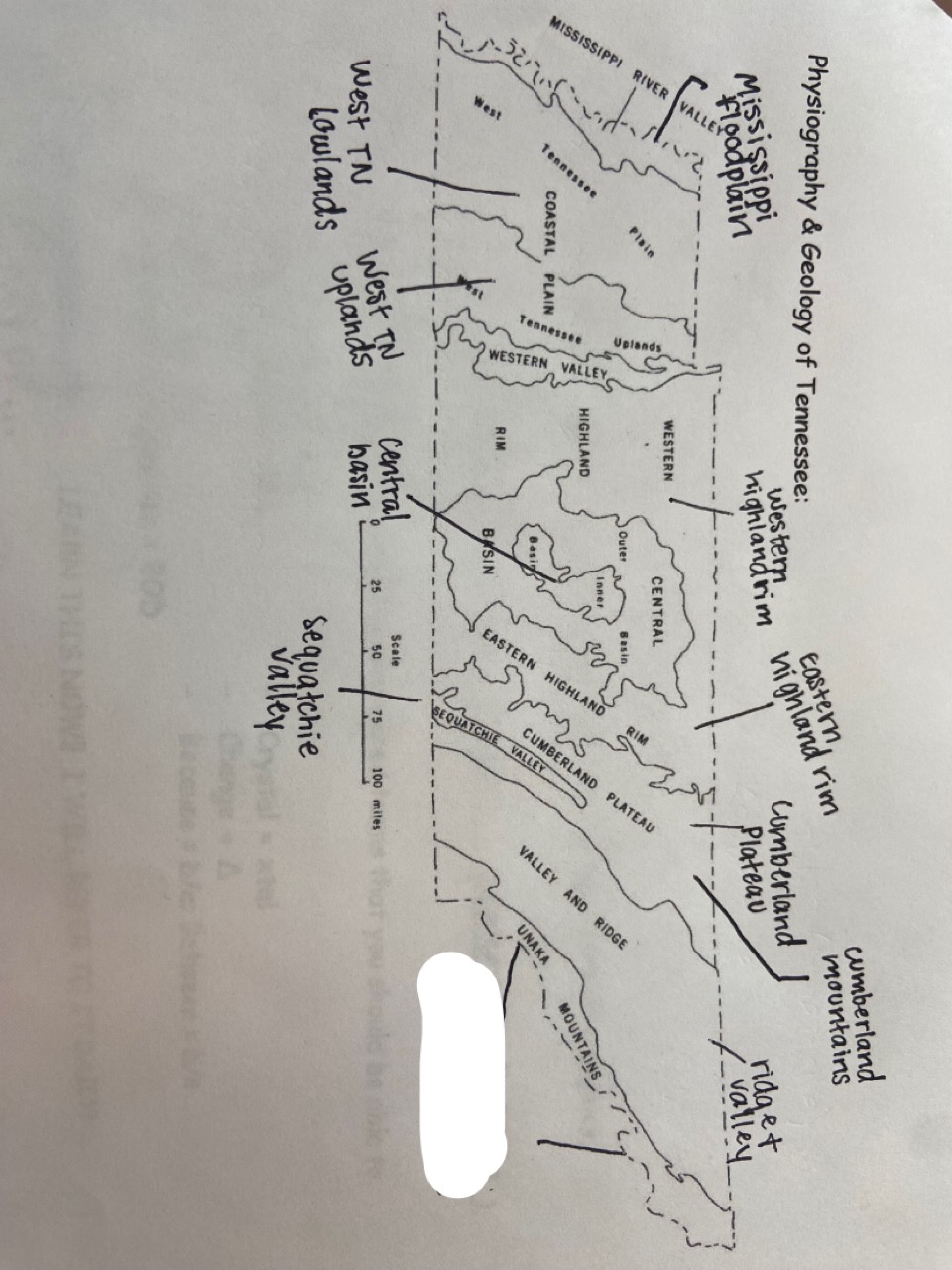
25
New cards
james hutton
“father of geology,” noted that the Hadrian’s Wall was thousands of years old even though there was virtually no soil development. Thus, soil development must be a slow and long-term process.
26
New cards
relative time
how old events or materials are in relation to other events or materials w/o numerical dates
27
New cards
absolute time
precise numerical dates assigned to events and materials
28
New cards
principle of natural causes
processes now operating or consistent w/ natural laws responsible for natural phenomena
29
New cards
principle of parsimony
explanations of geologic history should be as simple and direct as evidence indicates
30
New cards
principle of multiple working hypotheses
sound scientific investigations develop several parallel hypotheses to test simultaneously; avoid “shoe-horning” and identify most scientific sound hypotheses
31
New cards
principle of uniformitarianism
geologic record interpreted on geologic processes active today being same as operating in past unless the evidence indicates otherwise
32
New cards
principle of original horizontality
Steno’s 3 laws: strata originally deposited horizontal
33
New cards
principle of superposition
Steno’s 3 laws: in normal undistributed sequence of sedimentary rock, older layer is deposited on bottom, youngest on top
34
New cards
principle of lateral continuity
Steno’s 3 laws: strata can be traced laterally away in all directions unless they have (1) been eroded away (2) reach edge of depositional basin and “pinch out,” or (3) change character as a facies change
35
New cards
facies
aspects (what does it look like?); lateral change in rock or sediment type
36
New cards
principle of cross-cutting relationships
geologic features that cuts across another is younger than one it cuts
37
New cards
principle of inclusions (components)
inclusions always older than rocks they are included in
38
New cards
principle of metamorphism
metamorphic rocks always older than adjacent unmetamorphosed rocks
39
New cards
principle of biotic succession
fossils in sedimentary rocks occur in particular stratigraphic (vertical) order: predictable once original sequence is known
40
New cards
principle of fossil correlation
(nicholas steno) similar fossil assemblages are similar age and strata containing them are similar ages\`
41
New cards
principle of unconformities
planar surfaces separating successive strata and represent significant gaps in rocks sequences (“missing time”)
form due to:
* erosion of originally deposited material
* non-deposition
form due to:
* erosion of originally deposited material
* non-deposition
42
New cards
disconformity
what conformity type is shown?
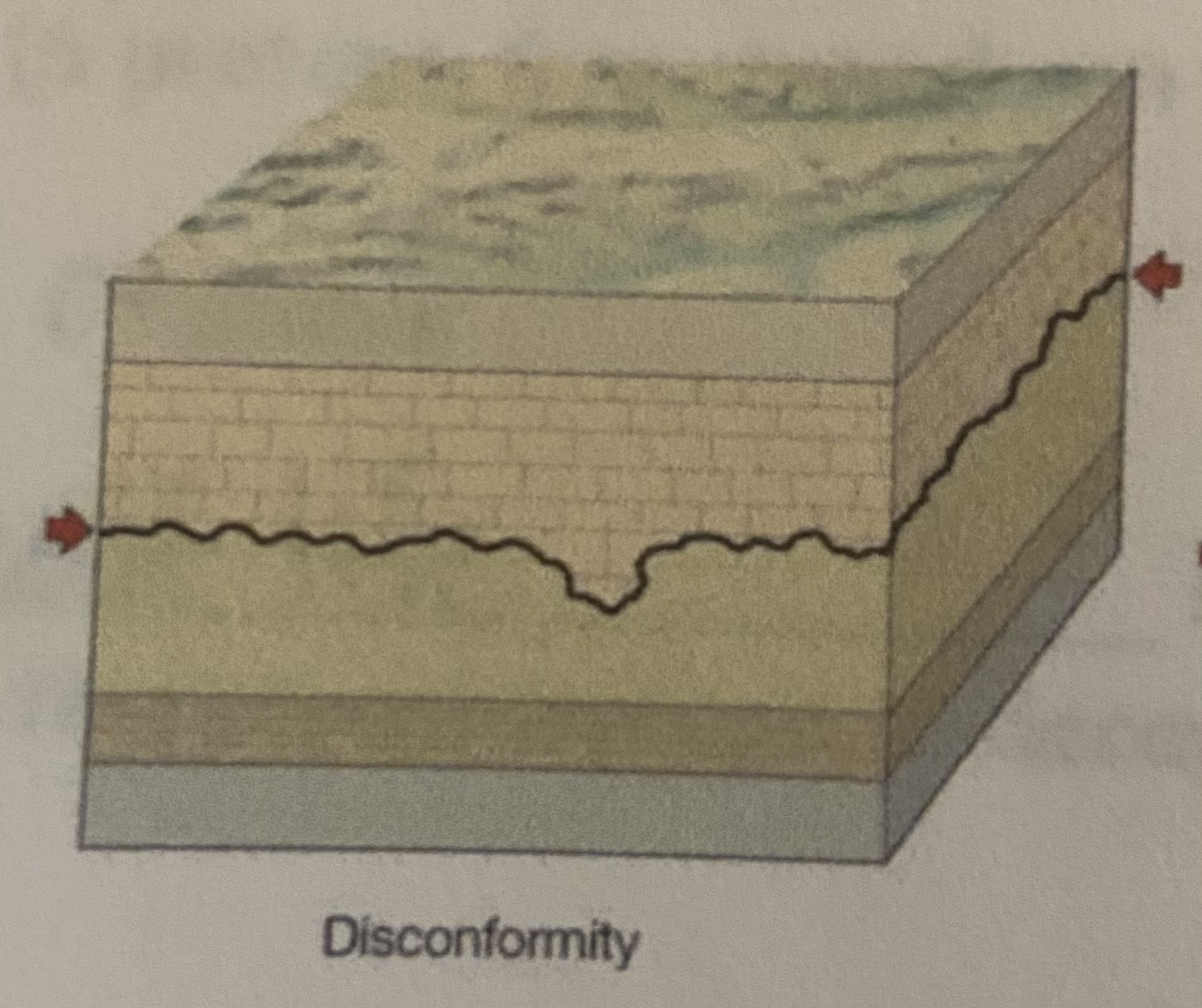
43
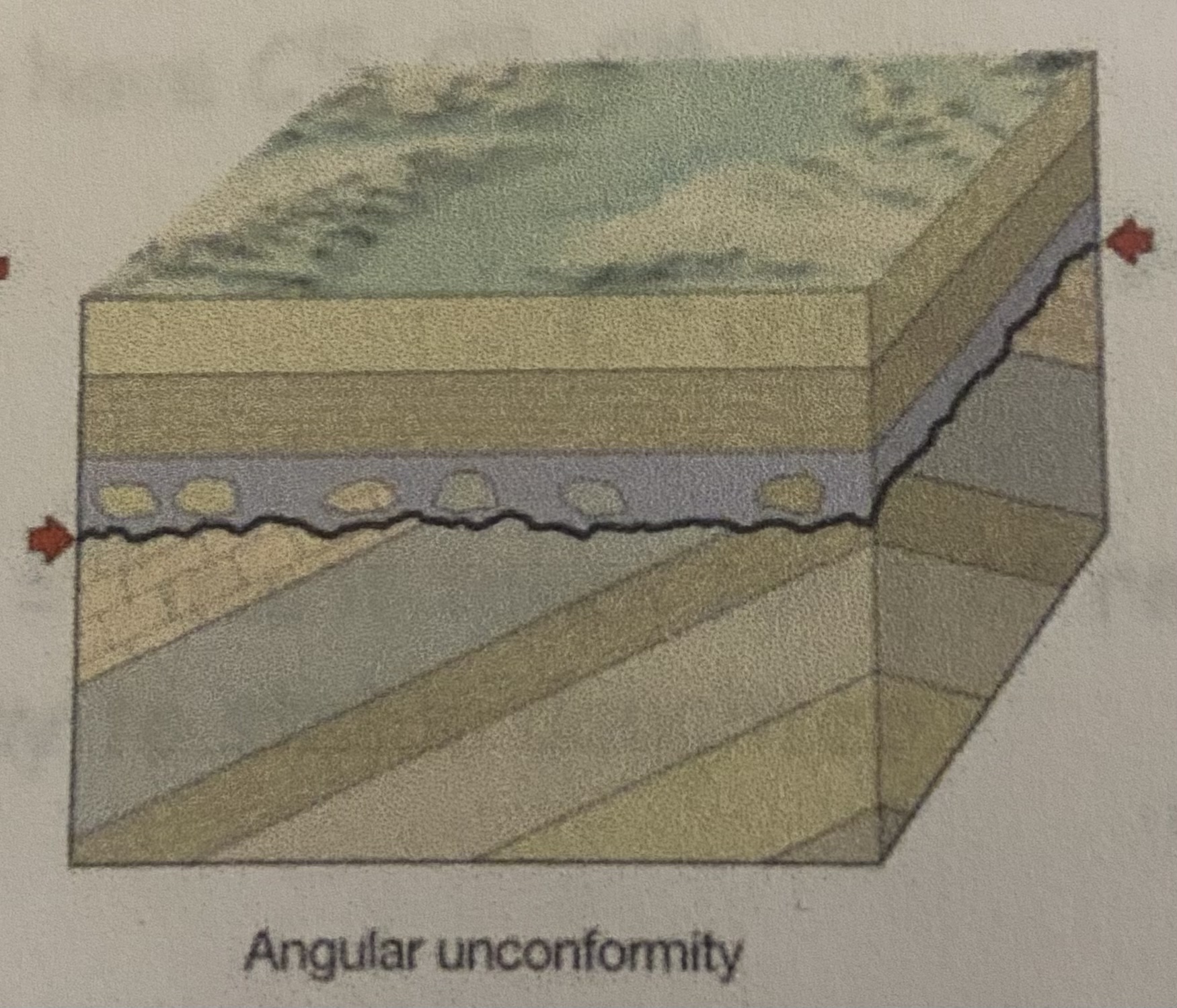
New cards
angular uncomformity
what conformity type is shown?
44
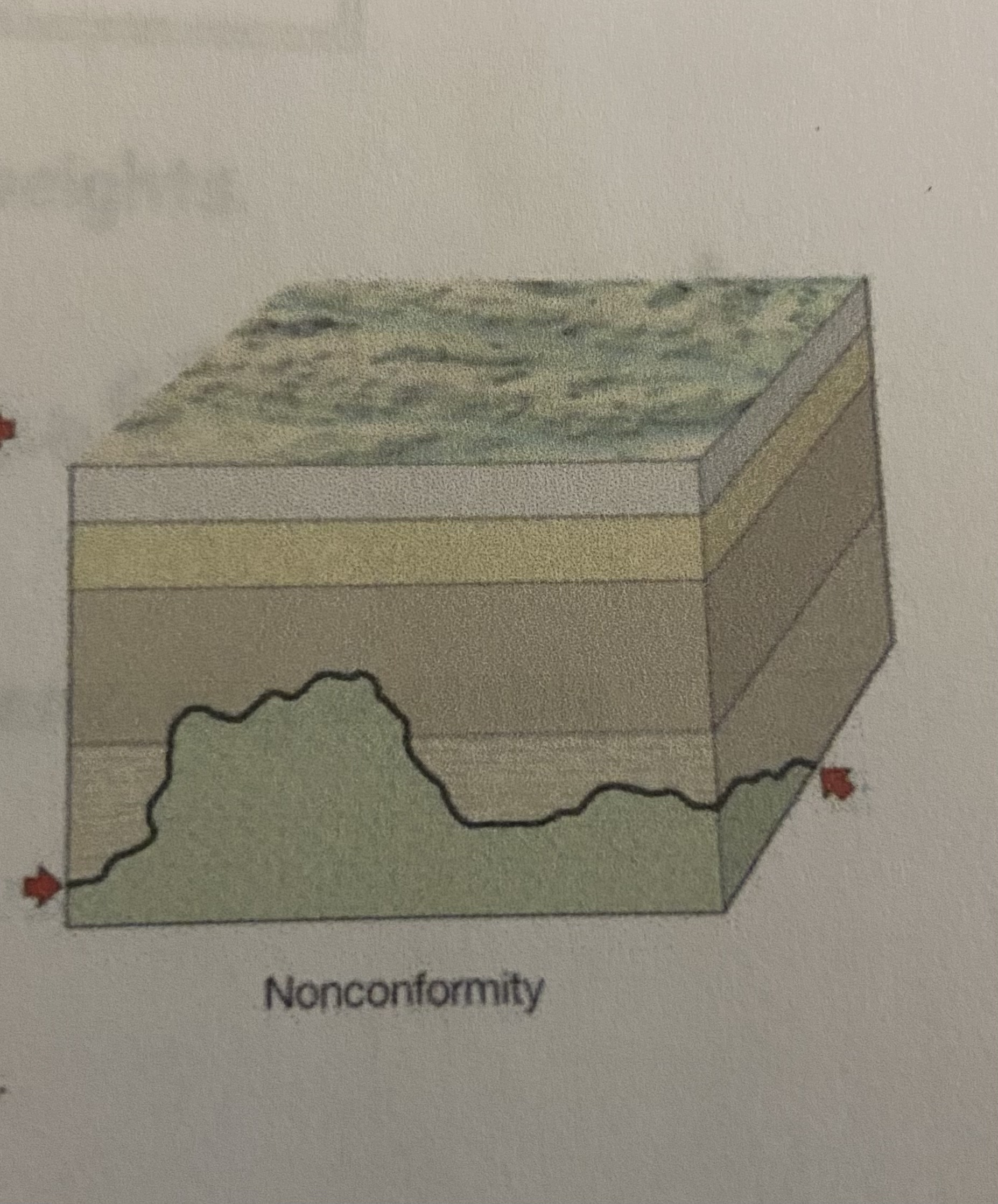
New cards
nonconformity
what conformity type is shown?
45
New cards
radiometric
science of dating and determining numeric time of events in earth history (13 methods)
46
New cards
absolute time
methods to determine numerical intervals of geologic time in units of years
47
New cards
isotope
same element with different # of atomic weights
48
New cards
half life
time it takes for 1/2 of remaining unstable radioactive parent isotope to decay to stable daughter
49
New cards
age of rock
what formula is (# half-lives passed) \[number of years/one half-life\]?
50
New cards
5730
one half-life is how many years?
51
New cards
direct sampling
when earth delivers to us
52
New cards
volcanic eruptions
“earth vomits” magma erupts
53
New cards
diatremes and kimberlite pipes
“earth belches” deep gas and magma (source of all diamonds)
54
New cards
55
New cards
ophiolites
slices of ocean crust pushed on land
56
New cards
petrology
experimental studies
57
New cards
6000 km
how far is it to the center of earth?
58
New cards
deepest mine
3\.6 km @ S. Afr. Au Mine
59
New cards
deepest drilled hole
12\.3 km @ Kola, Siberia
60
New cards
seismology
what is the most useful remote sensing?
61
New cards
seismic waves
earthquake produced by sudden rupture of rock or slip along a fault
62
New cards
primary body wave
* compression waves
* fastest traveling
* push me/pull me
* fastest traveling
* push me/pull me
63
New cards
secondary body wave
* shear waves
* slowest traveling
* moves only through solids
* up and down
* slowest traveling
* moves only through solids
* up and down
64
New cards
seismology
what can tell us about earth’s interior
* liquid vs solid state - p vs s waves
* density of material - speed of wave travel
* rock type - based upon density in speed of wave
* boundary changes - changes in velocity and direction of wave
* thickness - time of travel
* liquid vs solid state - p vs s waves
* density of material - speed of wave travel
* rock type - based upon density in speed of wave
* boundary changes - changes in velocity and direction of wave
* thickness - time of travel
65
New cards
reflection
wave bounces off boundary beneath material of contrasting density
66
New cards
Refraction
wave bends at boundary
67
New cards
outer core
through what layer do P waves slow down?
68
New cards
inner core
through what layer do P waves speed up?
69
New cards
continental drift
“pattern” (wegener - 1915)
70
New cards
sea floor spreading
“mechanism” (hess - 1960s)
71
New cards
iron
what geological phenomena did magnetometers discover?
72
New cards
symmetrical
is the pattern of magnetic stripping random or symmetrical about MOR?
73
New cards
beneath eastern mediterranean sea
where is the oldest ocean crust? (340 mil)
74
New cards
mid ocean ridges
where is the youngest ocean crust?
75
New cards
john tuzo wilson
canadian geologist, proposed tectonic plates, interact in three ways along boundaries
76
New cards
divergent boundary
new ocean crust created at spreading centers and displaces old crust laterally
77
New cards
convergent boundary
subduction zone; 3 primary types
* andean (ocean-continent)
* island arc type (ocean-ocean)
* collision (continent-continent)
* andean (ocean-continent)
* island arc type (ocean-ocean)
* collision (continent-continent)
78
New cards
wilson cycle
opening and closing of oceans; life cycle of oceans
79
New cards
“ring of fire and shaking”
active tectonic boundary
80
New cards
whole mantle convection
mantle made of one big cell
81
New cards
two mantle convection cells
higher and lower part had own convection cell
82
New cards
complex model
shallow and deep convection cells with irregular pathways
83
New cards
slab pull model
denser, colder plate sinks at subduction zone, pulls rest of plate behind it
84
New cards
ridge push model
(mantle convection) hotter mantle material roses beneath divergent boundaries, cooler material sinks at subduction zones
85
New cards
combined model
moving plates, EQs, and volcanic eruptions are due to earth’s loss of internal heat
86
New cards
geomorphology
study of surface processes and landforms
87
New cards
surface water
fluvial (rivers), lacustrine (lakes), and paludal (swamps)
88
New cards
infiltration capacity
what determines amount of surface water?
89
New cards
drainage basins
land area contributing H2O to river or stream
* consist of interconnected network of streams in area
* consist of interconnected network of streams in area
90
New cards
divide
imaginary line separating drainage basins
91
New cards
dendritic
tree-like branching tributaries
* most common drainage pattern
* most common drainage pattern
92
New cards
radial
streams diverge from center point
* typical streams on volcanoes
* typical streams on volcanoes
93
New cards
rectangular
streams bend at right angles
* bedrock fractures perpendicular to each other
* bedrock fractures perpendicular to each other
94
New cards
trellis
parallel running main stream and short perpendicular tributaries
* follow folds and faults in bedrock
* ex. appalachian valley and ridge
* follow folds and faults in bedrock
* ex. appalachian valley and ridge
95
New cards
ephemeral
stream type: only flow when raining
96
New cards
intermittent
stream type: flow only at certain time of year (rainy season, snow melts)
97
New cards
perennial
stream type: flow continuously throughout the year
98
New cards
headwaters
upstream origination point; v-shaped
99
New cards
mouth
end point of river/stream into ocean or lake; wide meanders w/ floodplain
100
New cards
floodplain
area on either side of stream or river where alluvium accumulates during floods