Plant classification and characteristics
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
absorbs water directly and stay near water sources.
Need water for their spores to travel and fertilize.
Gymnosperms use _____ to disperse pollen, Angiosperms use _________ to disperse pollen, and posses _____ that attract animals for dispersal of the _____ inside
wind, pollinators, fruits, seeds
seeds produced in cones that open and release seeds, usually dispersed by wind.
allows for the transport water and nutrients, enabling taller growth and wider habitat colonization.
posess vascular tissue and reproduce via spores. Angiosperms have flowers and seeds.
possess needle-like leaves with a waxy cuticle and have conical shapes to shed snow.
protect seeds and attract animals for long-distance dispersal when eaten
bryophytes
Non-vascular land plants evolved from green algae. Need to be near a water source for reproduction; absorbs water directly into their cells. aka mosses
seedless vascular plants
Vascular plants that evolved specialized tissue to grow taller and be farther from water sources. Reproduce using spores instead of seeds. aka ferns
gymnosperms
The first type of vascular plants to have seeds, producing "naked seeds" inside a cone that open and release seeds when conditions are optimal. The seeds are usually dispersed by the wind and end up close to the original plant. aka conifers/evergreens.
angiosperms
produce flowers, attracting insects for pollination. After fertilization, the flowers develop into fruits that enclose the seeds.
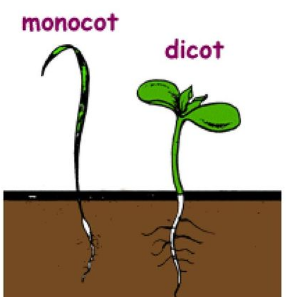
monocot characteristics
one cotyledon, parallel veins in leaves, scattered vascular bundles in stems, flower petals in multiples of 3
dicots
two cotyledons, net-like veins in leaves, ring arranged vascular bundles in stems, flower petals in multiples of 4 or 5
angiosperm types
monocots and dicots
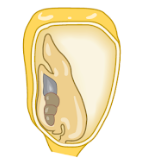
monocot cotyledon number
1
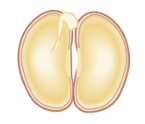
dicot cotyledon number
2
cotyledon
embryonic leaf; first leaves to appear from a germinating seed

monocot leaf venation
usually parallel

dicot leaf vein assortment
usually net-like; palmate or pinnate
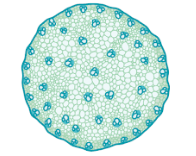
monocot vascular bundles in stems
scattered
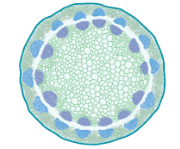
dicot vascular bundles in stems
arranged in a ring

monocot flower petal count
multiples of 3

dicot flower petal count
multiples of 4 or 5
monocot vascular bundles in roots
roots where vascular bundles are arranged in a ring formation
dicot vascular bundles in roots
roots where vascular bundles are arranged in a central cross or star formation