Unit 4 Marathon: Quizlet 3 (Human Body Systems)
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
circulatory system
the organs and tissues involved in circulating blood and lymph through the body
heart
A hollow, muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body.
aorta
Largest artery in the body that carries blood away from the left ventricle of the heart
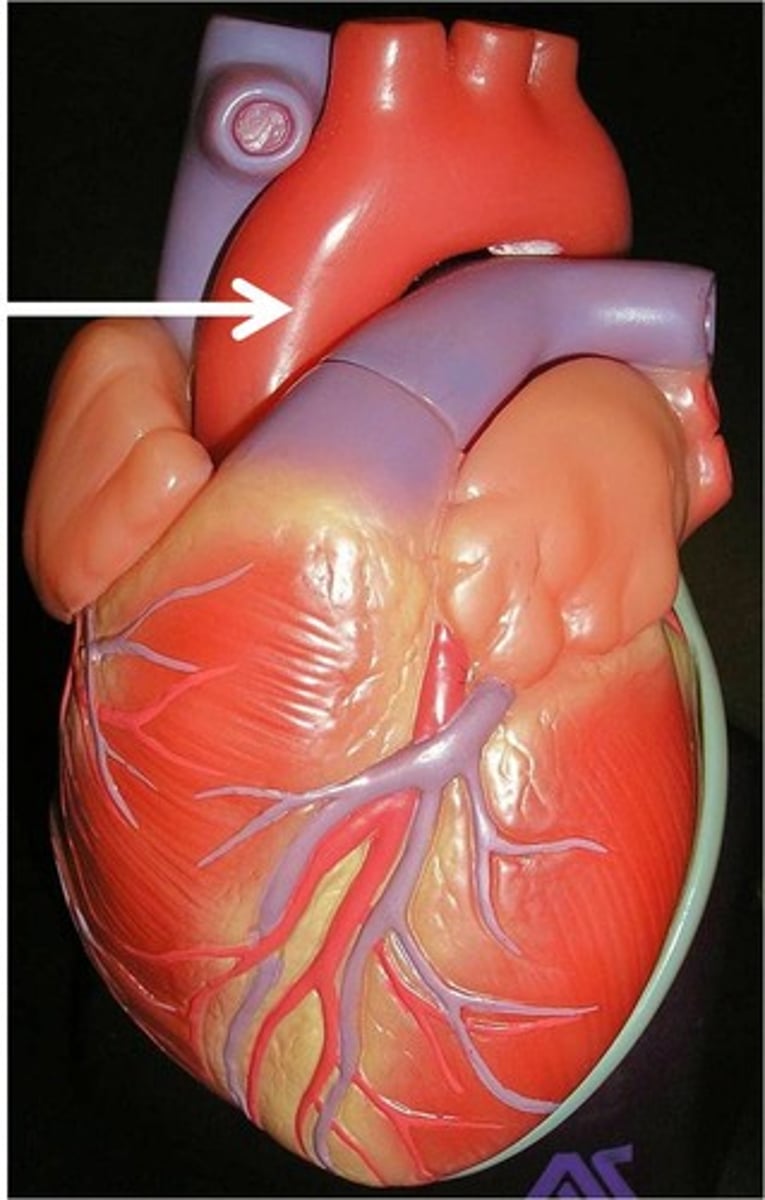
superior vena cava
A vein that is the second largest vein in the human body and returns blood to the right atrium of the heart from the upper half of the body.
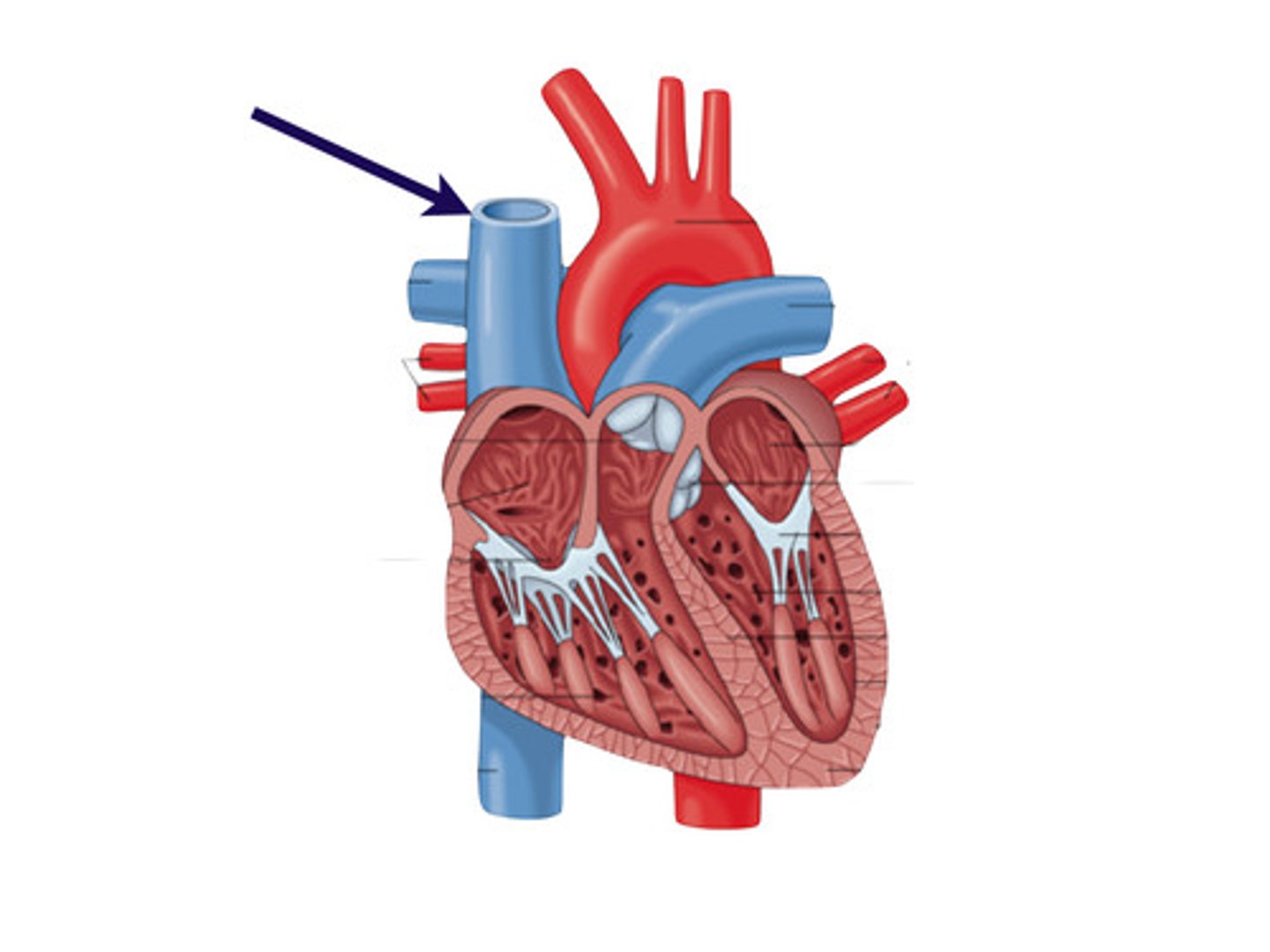
inferior vena cava
A vein that is the largest vein in the human body and returns blood to the right atrium of the heart from bodily parts below the diaphragm.
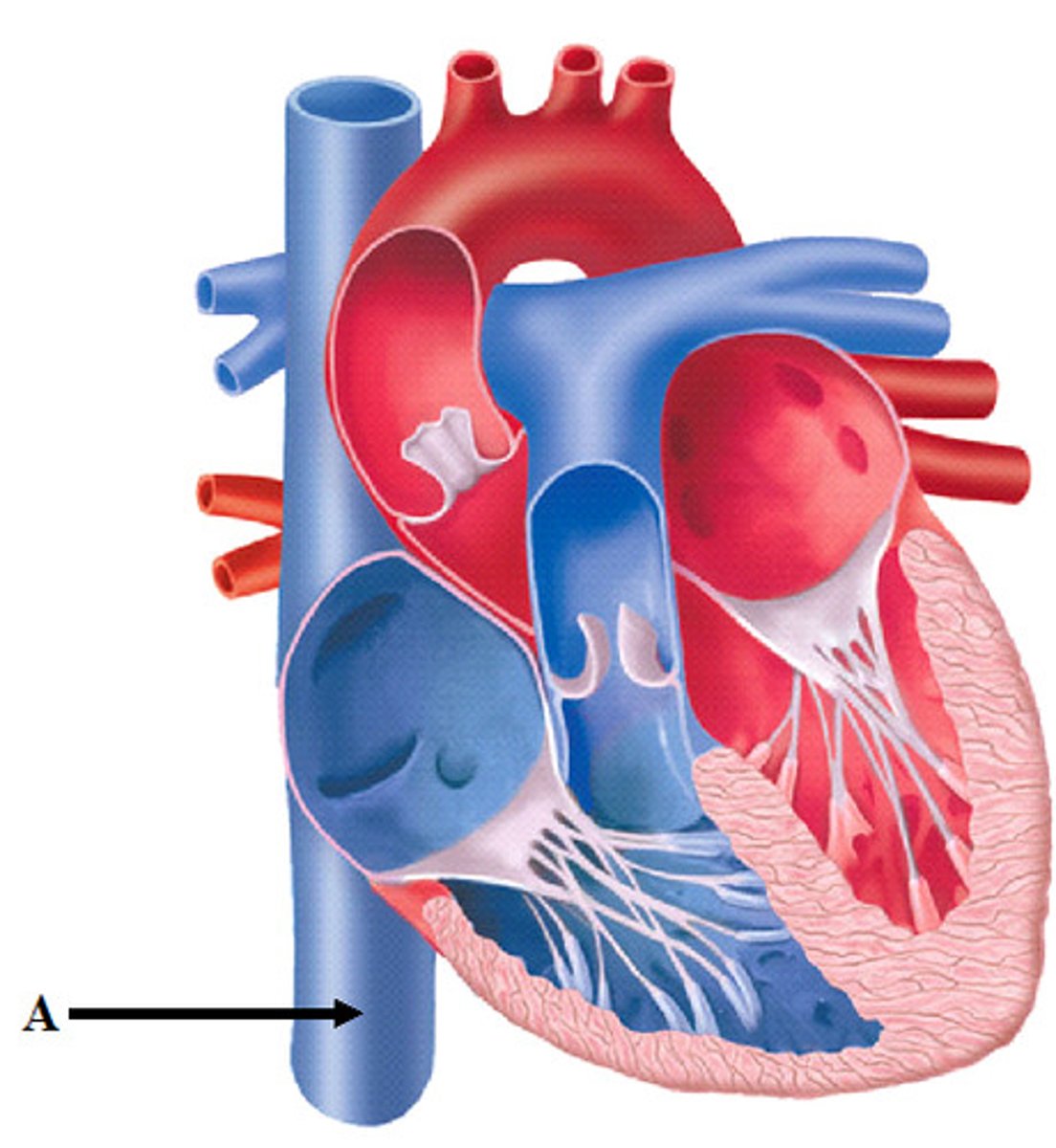
pulmonary veins
Deliver oxygen rich blood from the lungs to the left atrium
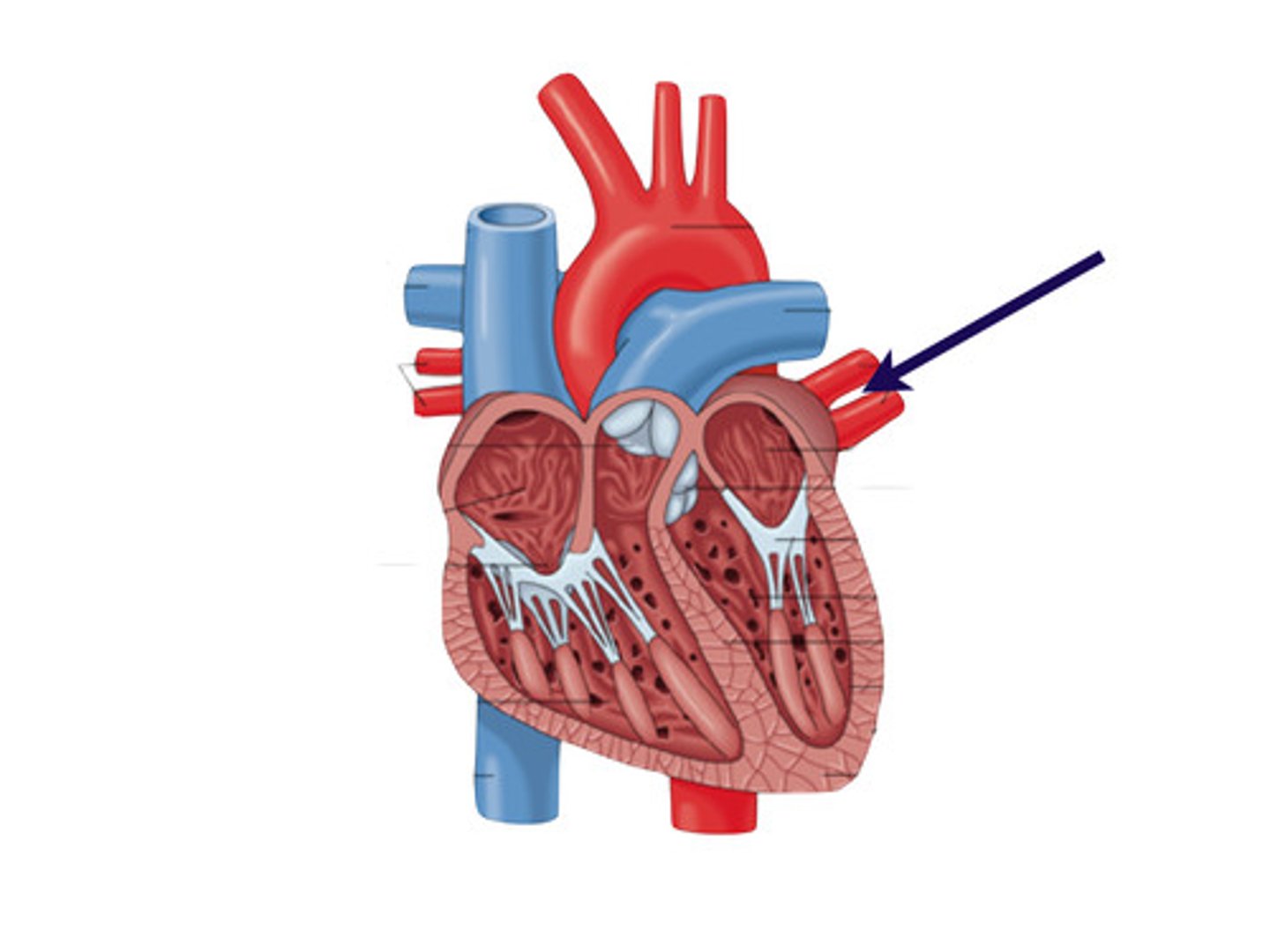
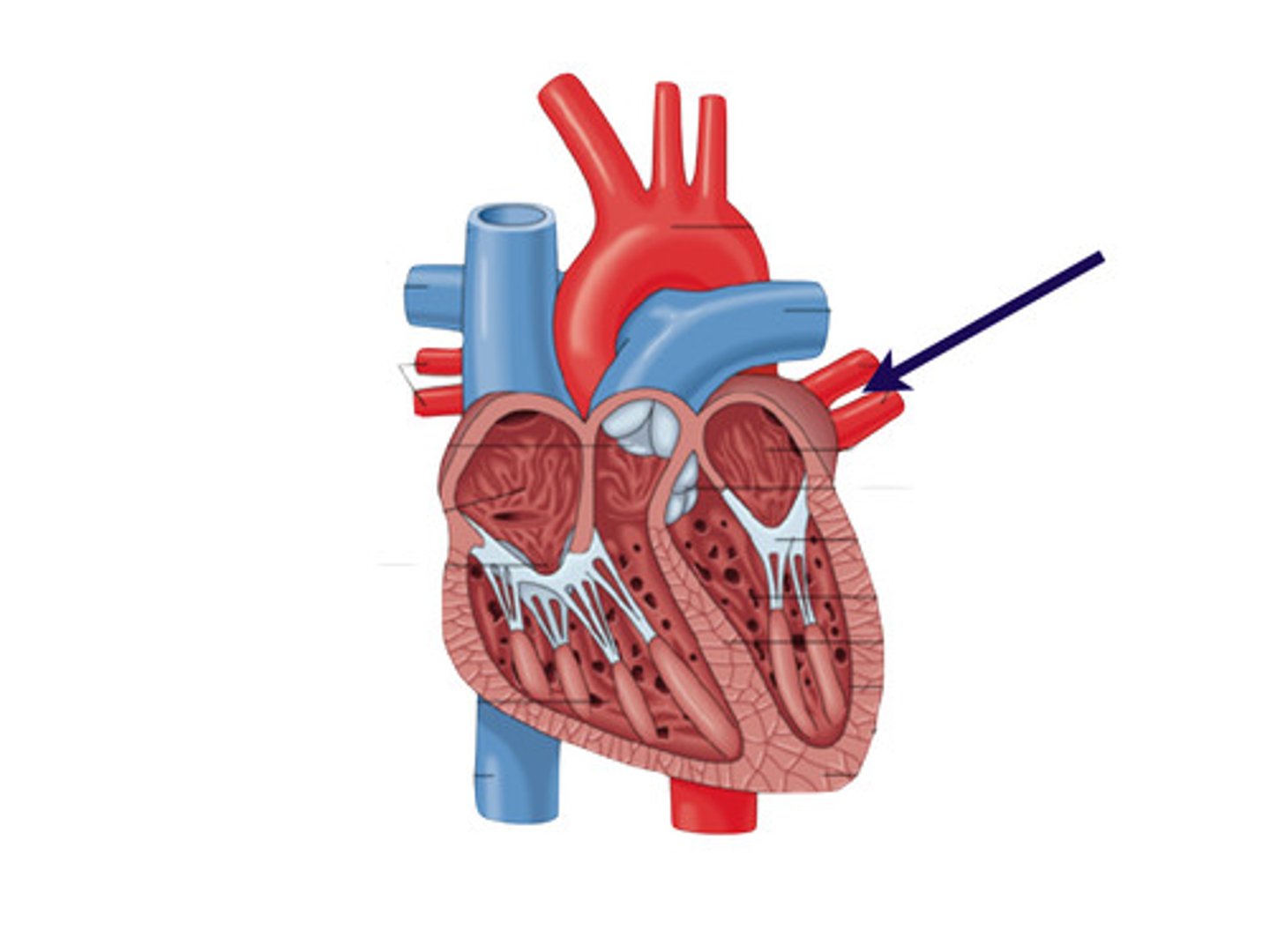
pulmonary arteries
carry deoxygenated blood out of the right ventricle and into the lungs
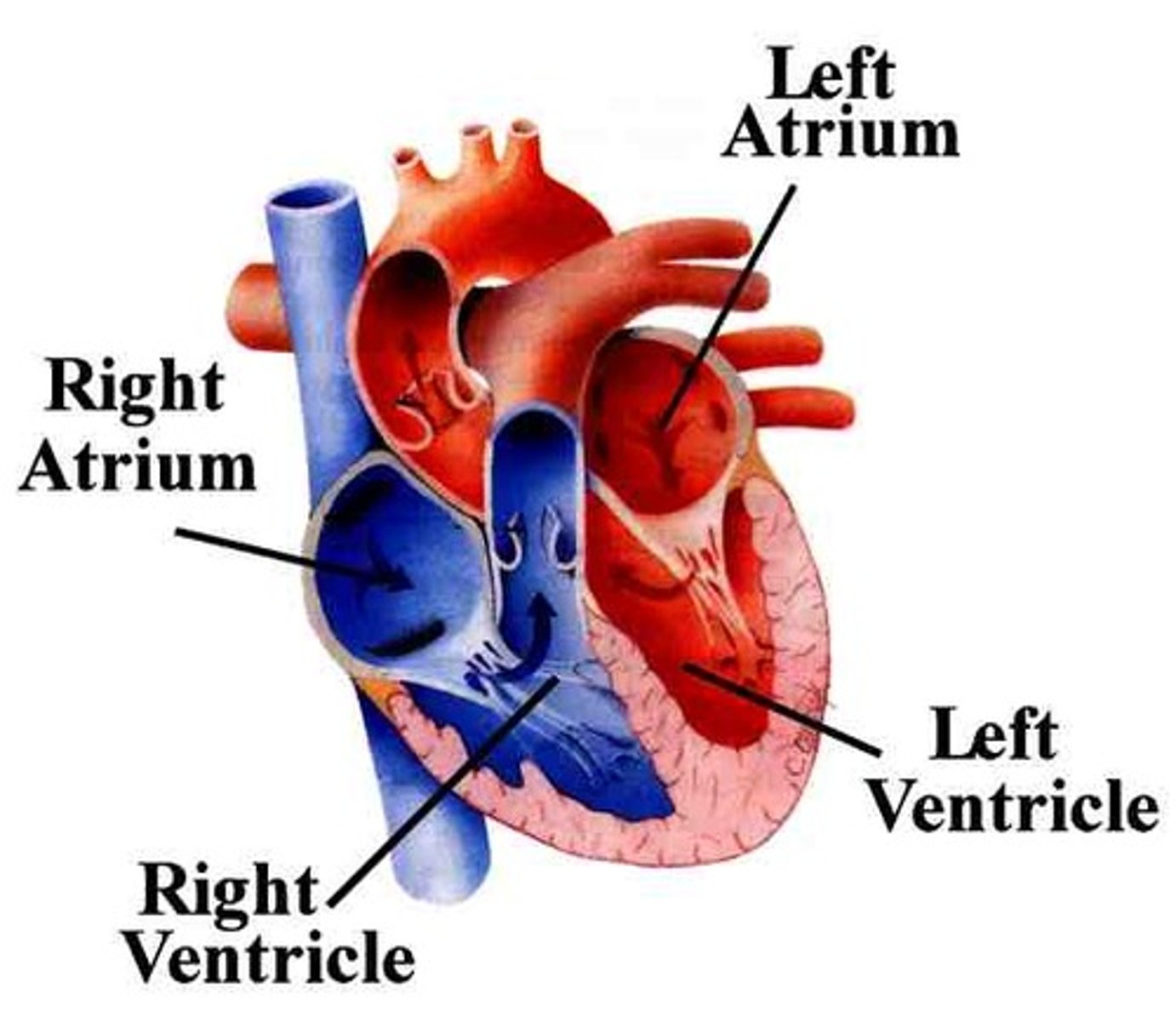
atria (right and left)
the two upper chambers of the heart (singular is atrium)
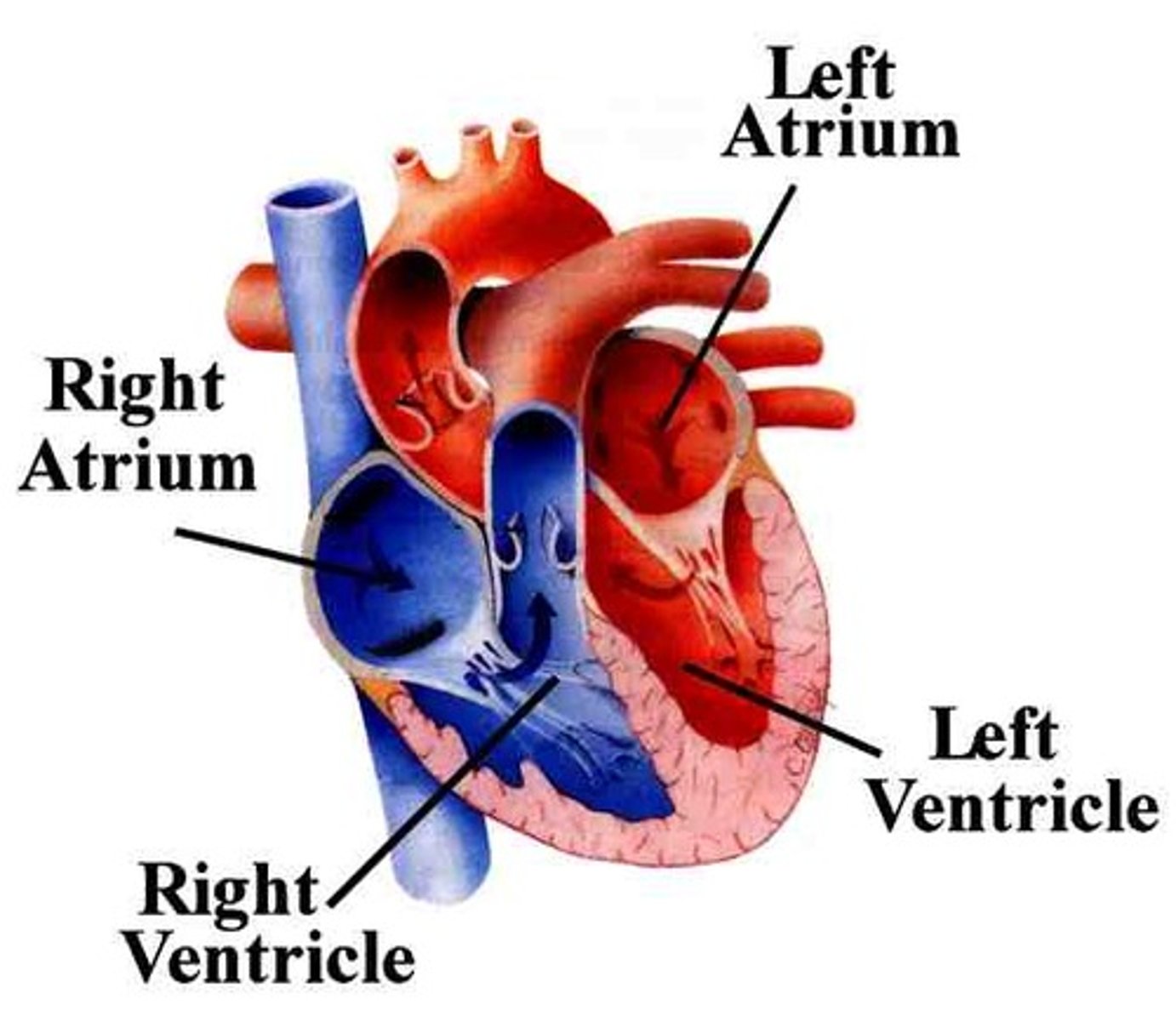
ventricles (right and left)
the two lower chambers of the heart
valves
Flaps of tissue that open and close to allow the flow of blood in one direction only. There are valves in the heart and in veins
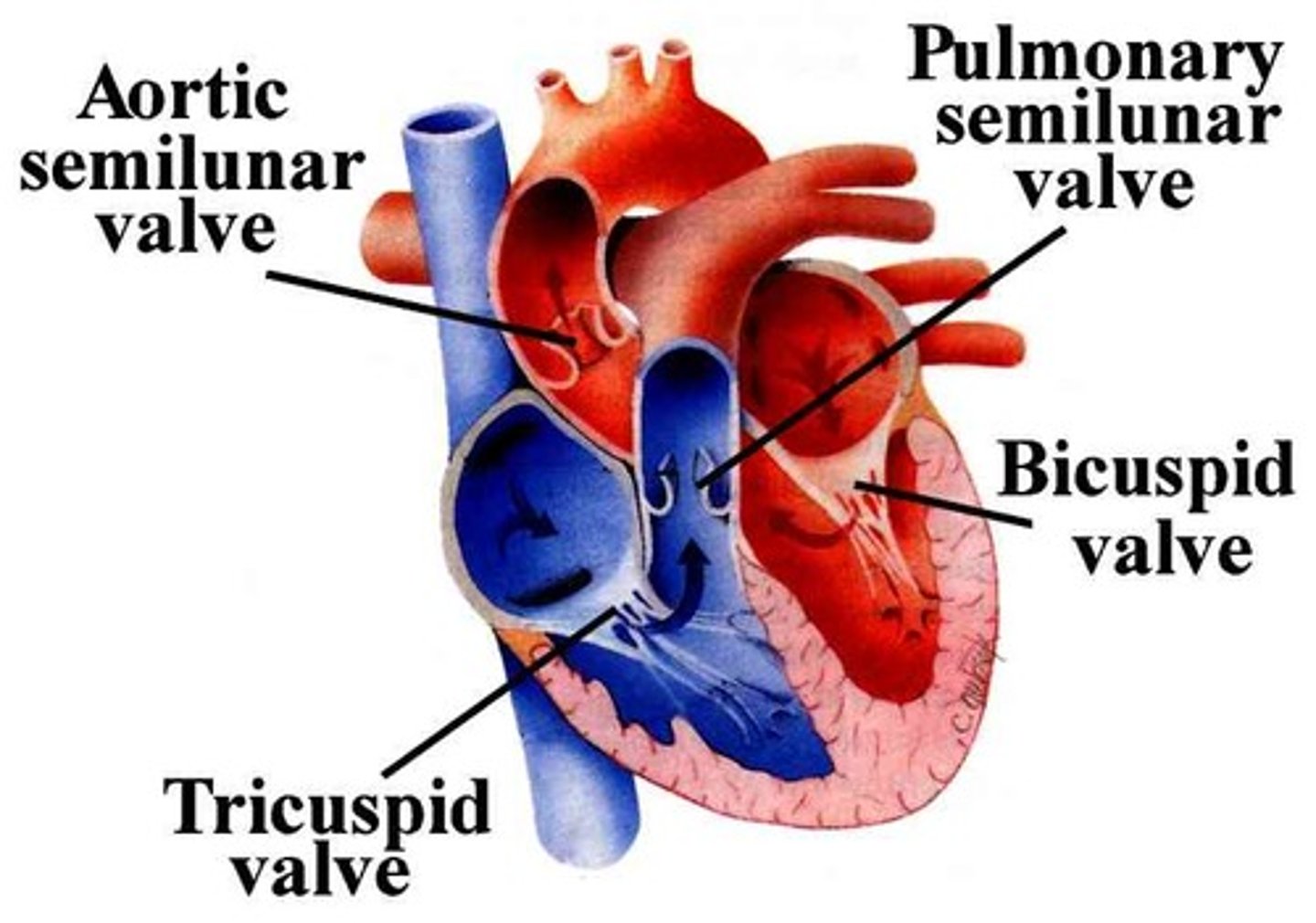
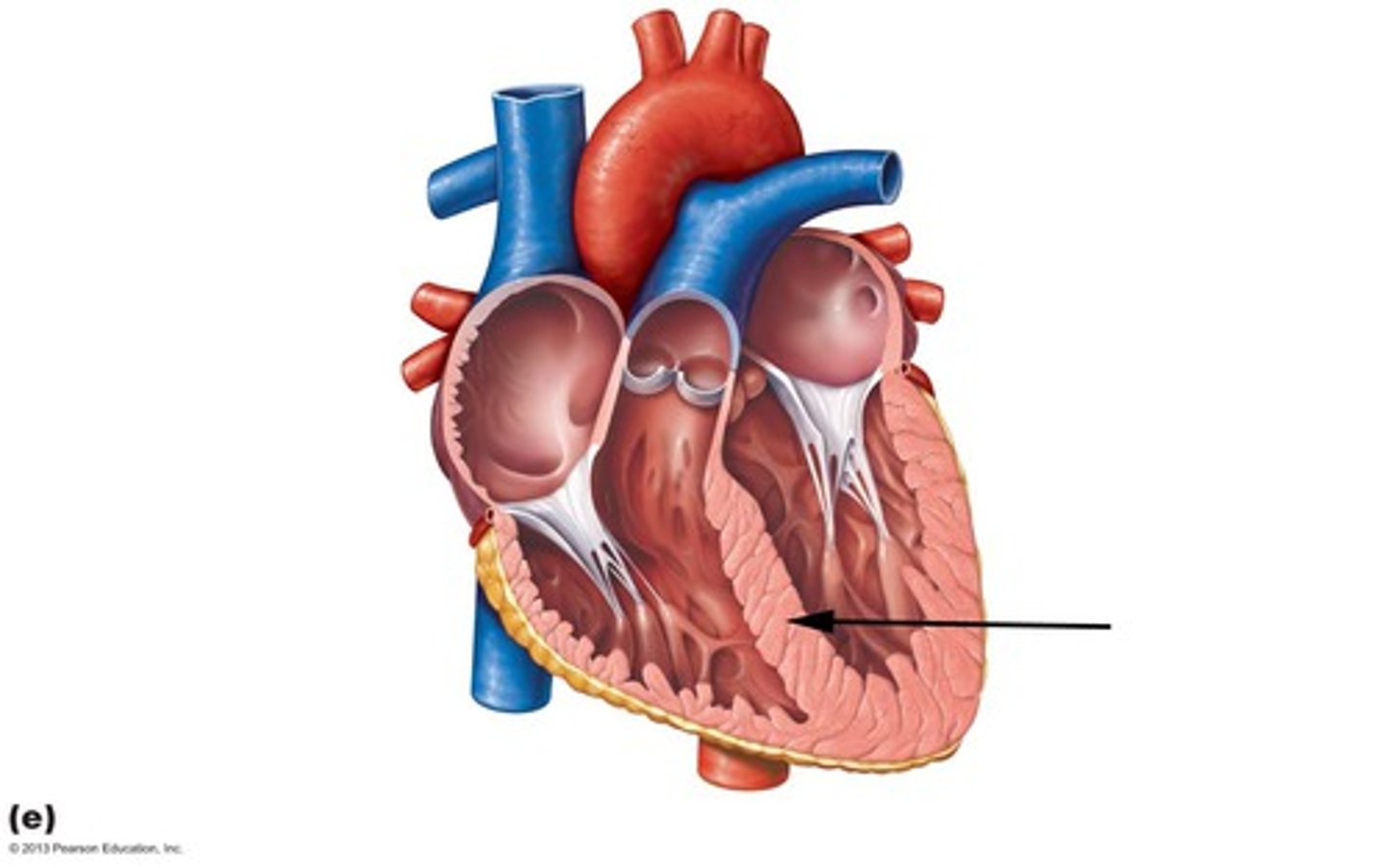
septum
Divides the right and left chambers of the heart
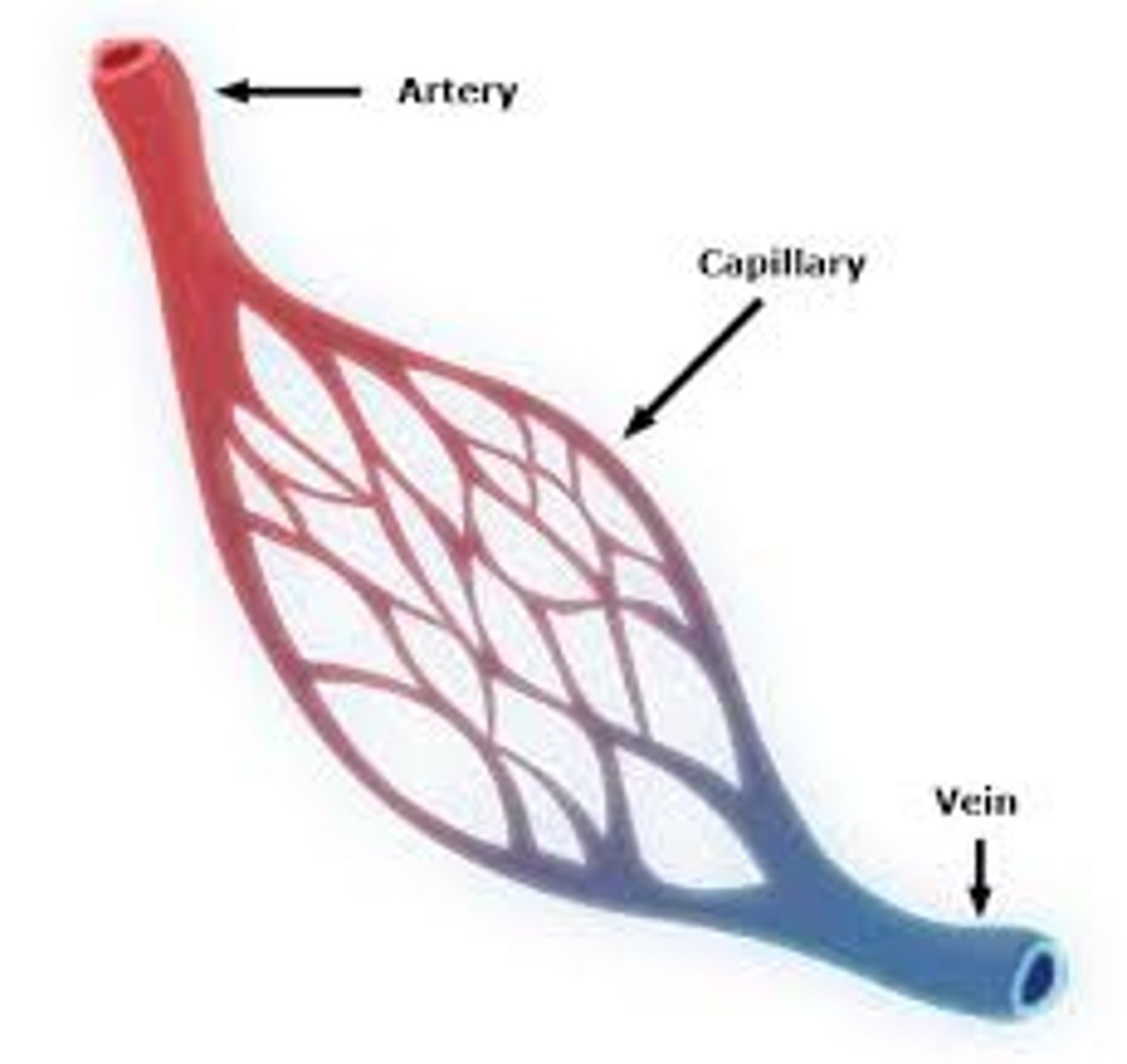
arteries
Blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart
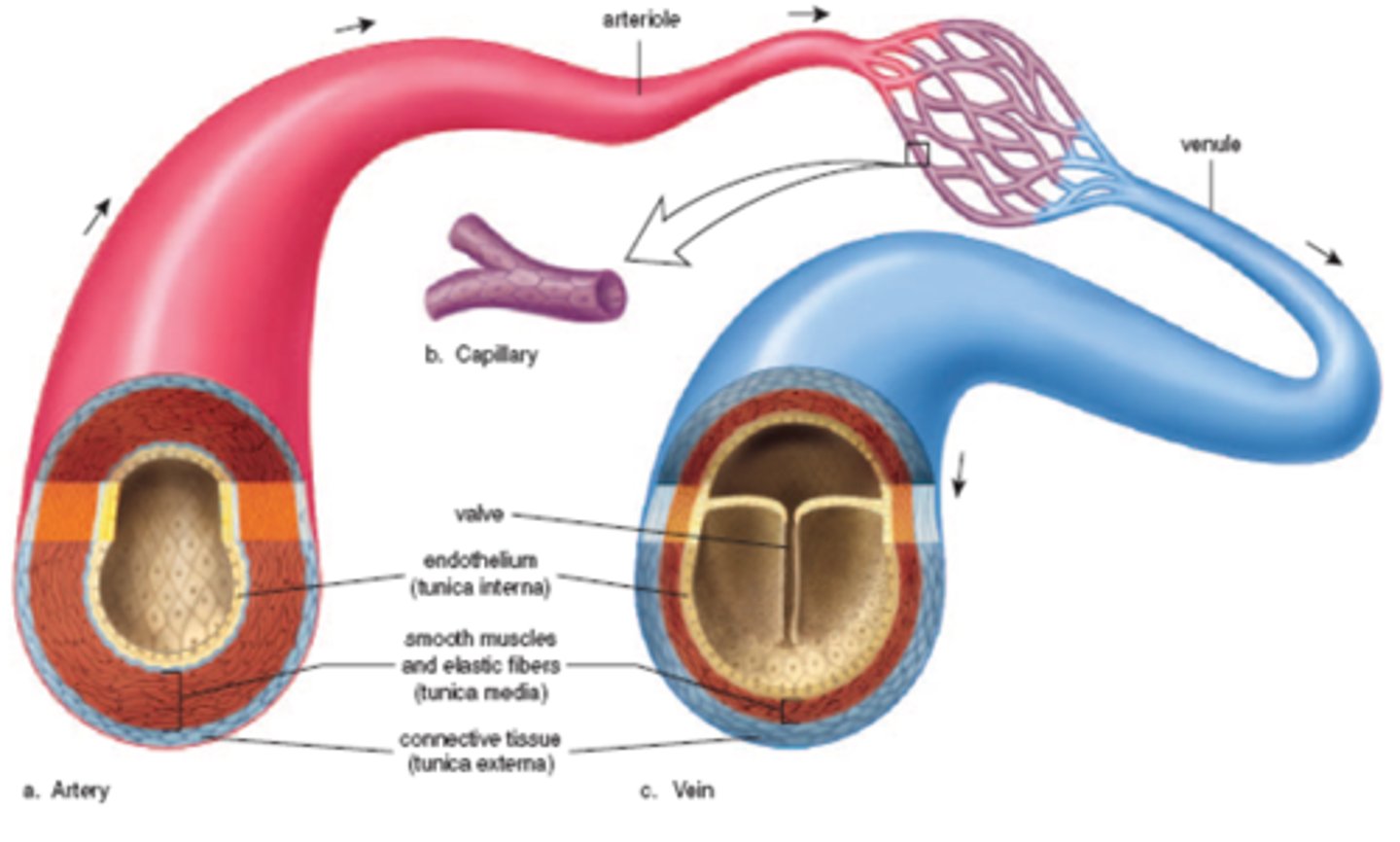
veins
Blood vessels that carry blood back to the heart
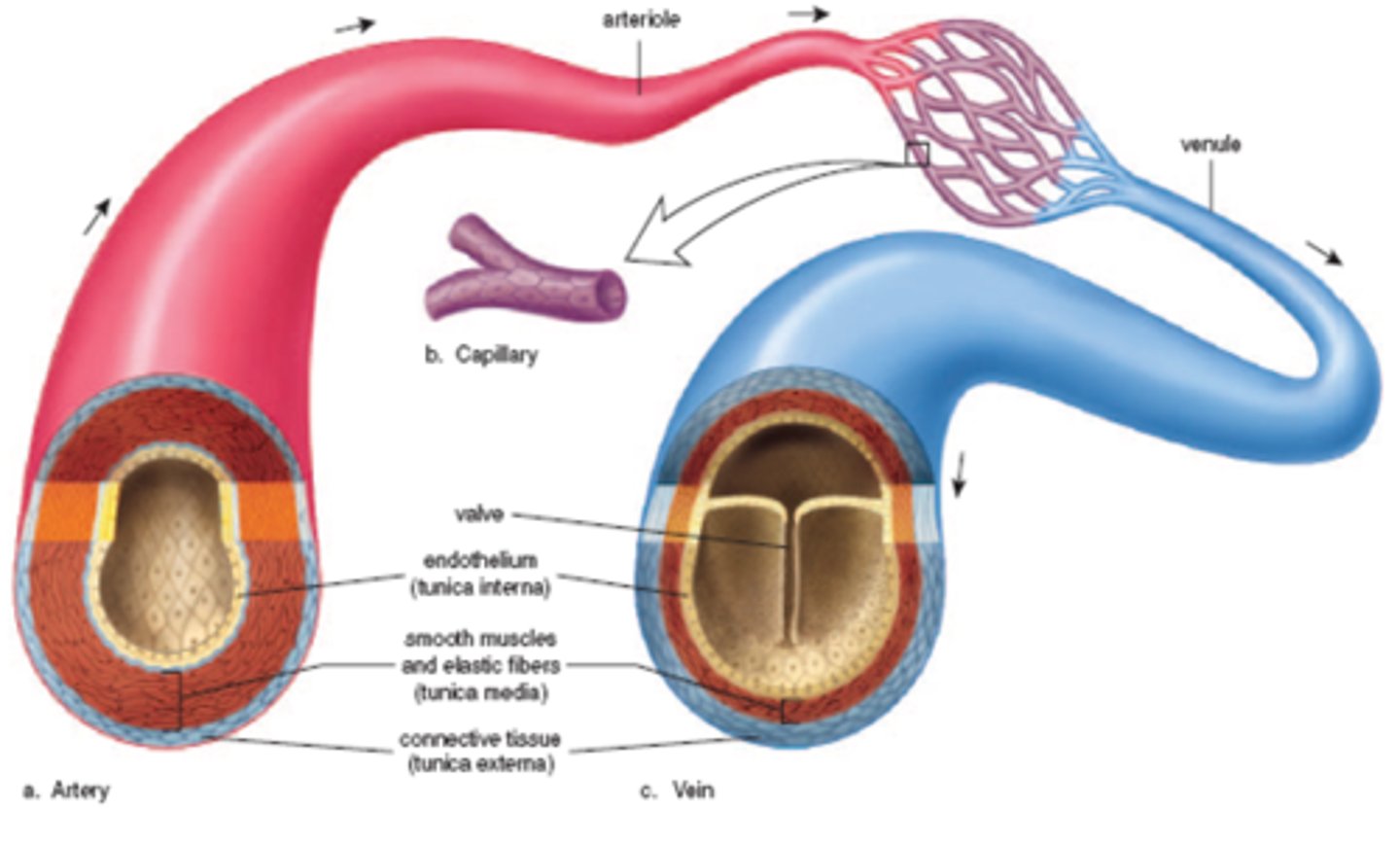
capillaries
Smallest blood vessels that bring oxygen and nutrients to cells and carry carbon dioxide and wastes away. Connect arteries and veins.
blood
A connective tissue with a fluid matrix called plasma in which red blood cells, white blood cells, and cell fragments called platelets are suspended.
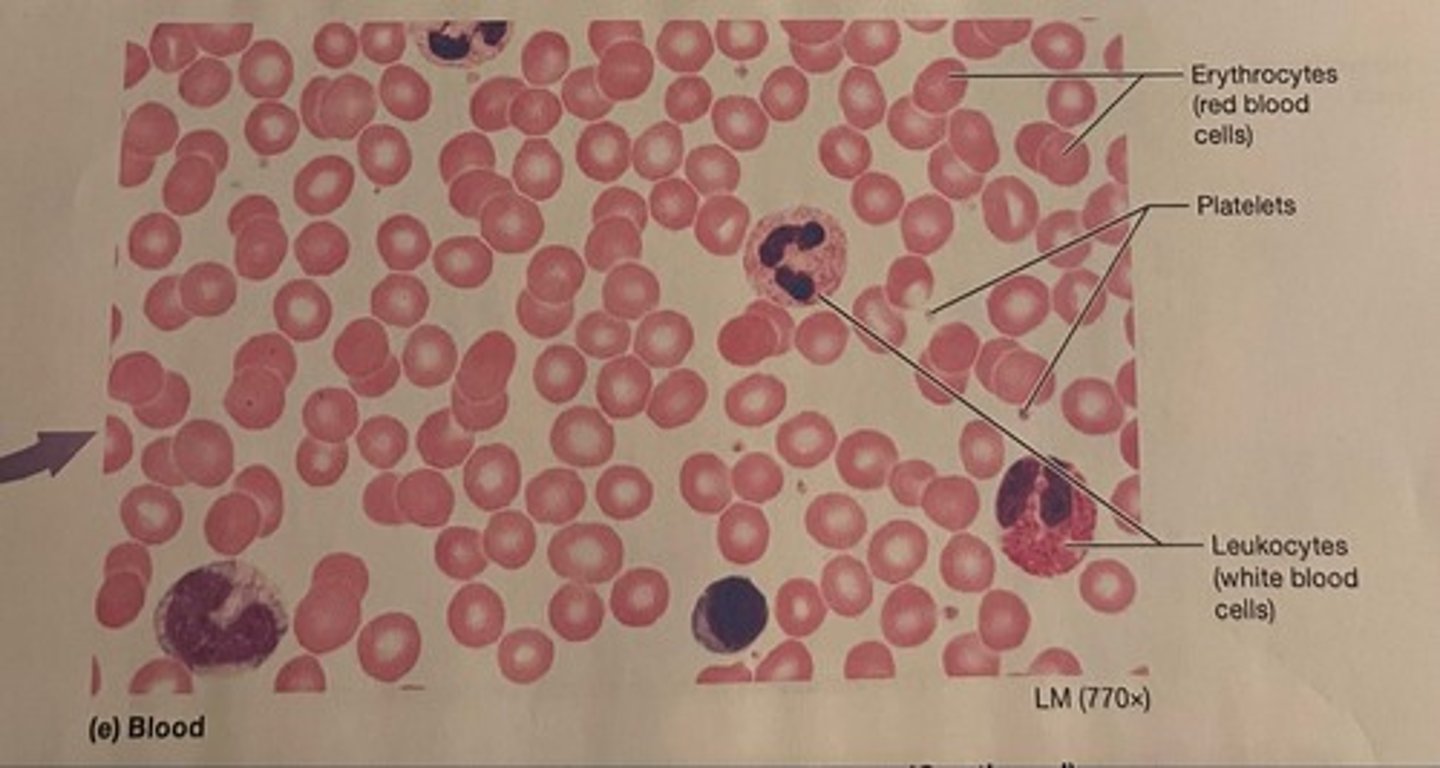
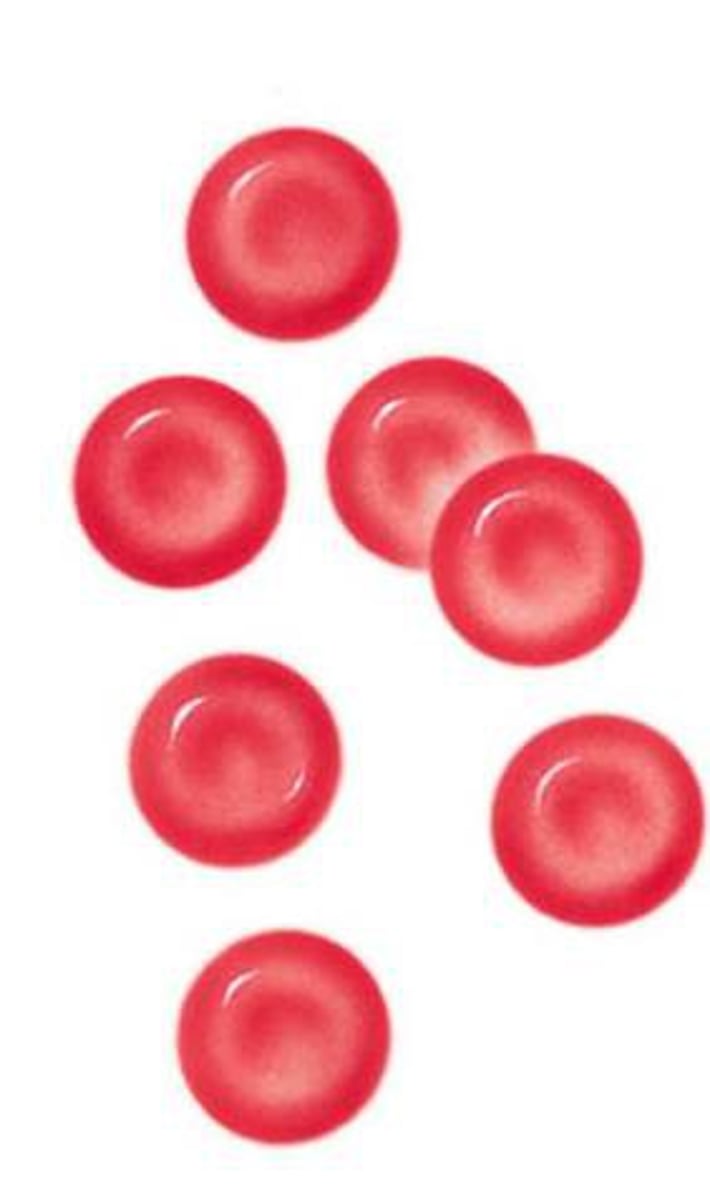
red blood cells
Blood cells that carry oxygen from the lungs to the body cells.
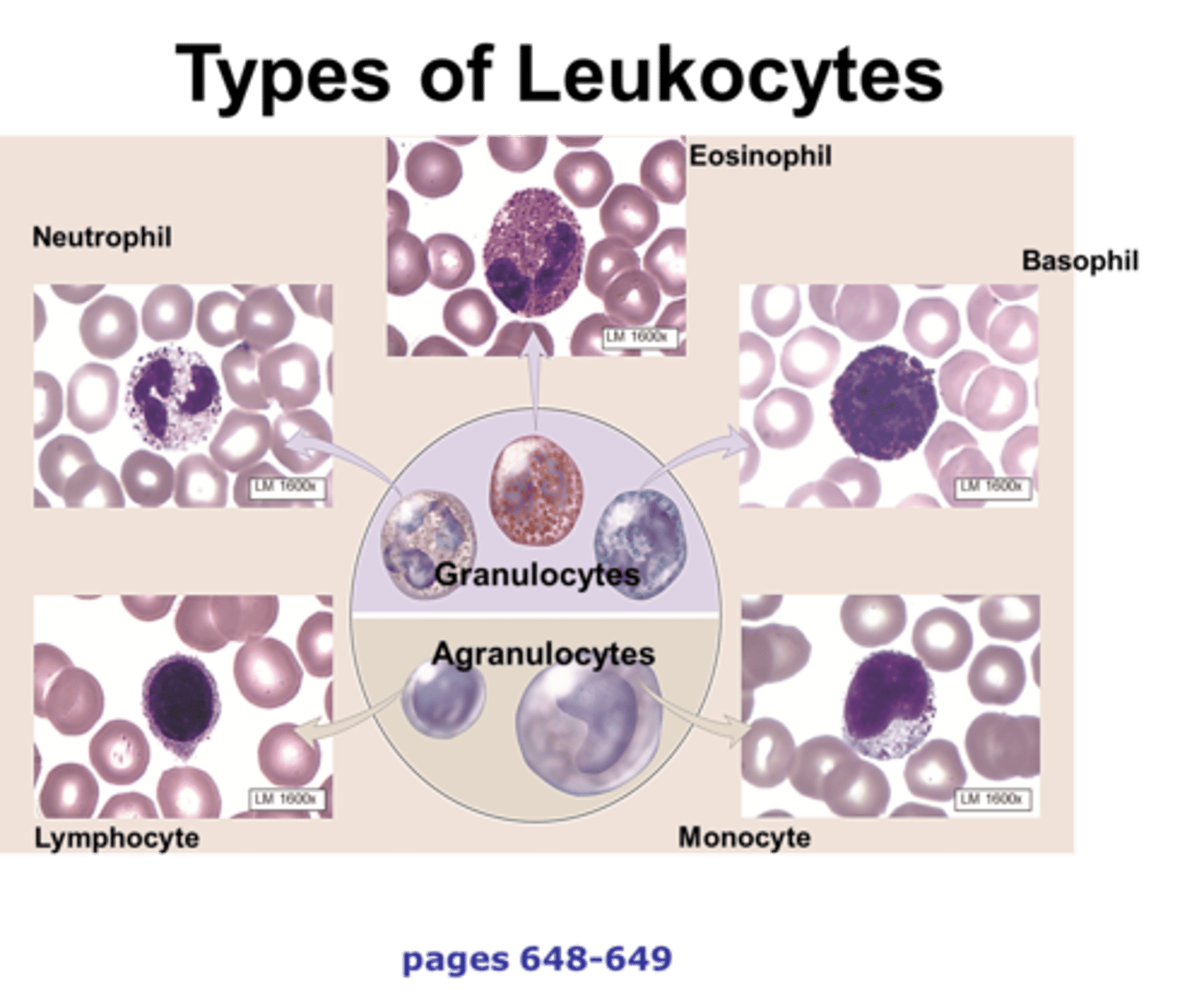
white blood cells
Blood cells that perform the function of destroying disease-causing microorganisms
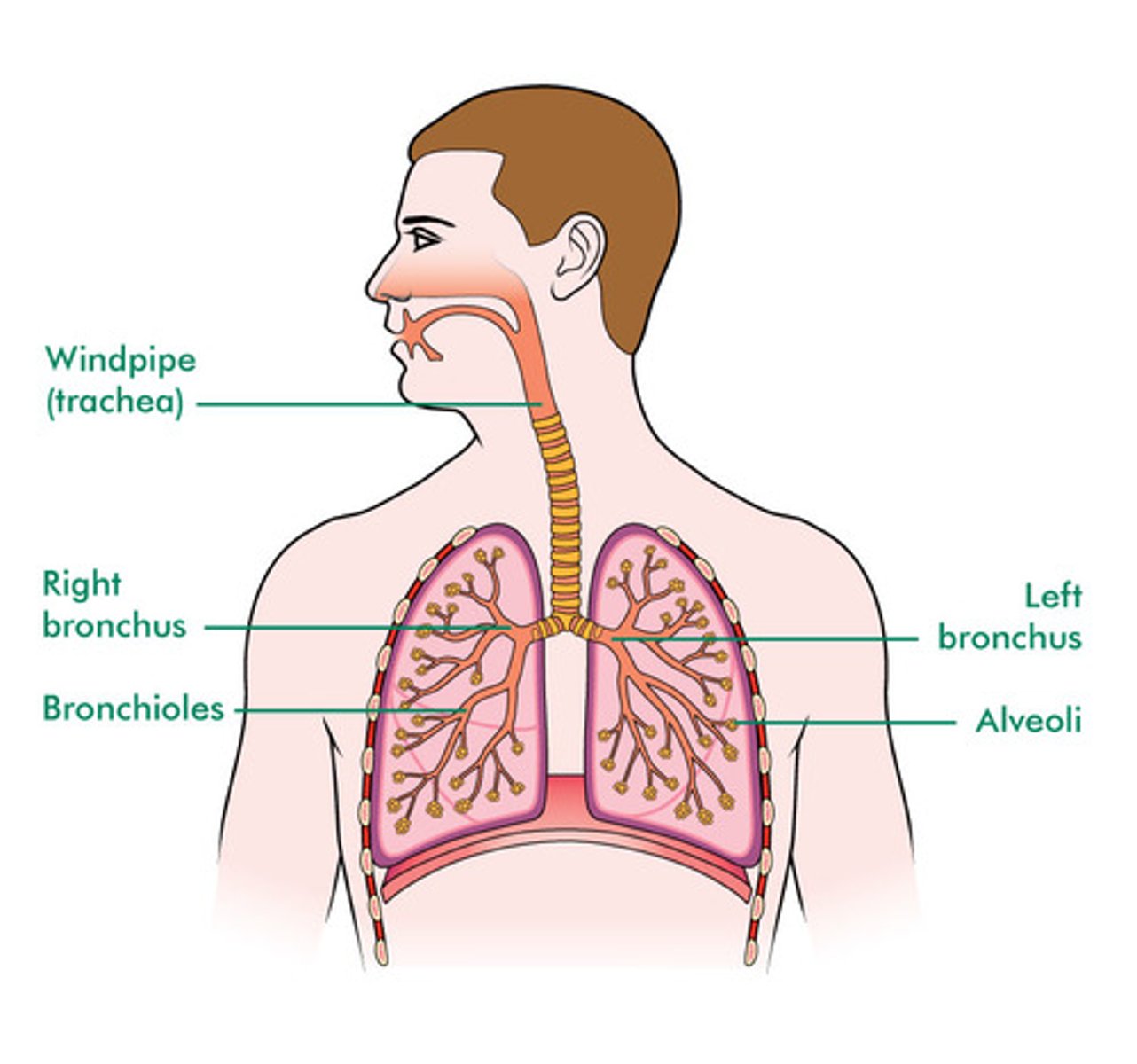
respiratory system
A system of organs, functioning in the process of gas exchange between the body and the environment, consisting especially of the nose, nasal passages, nasopharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs.
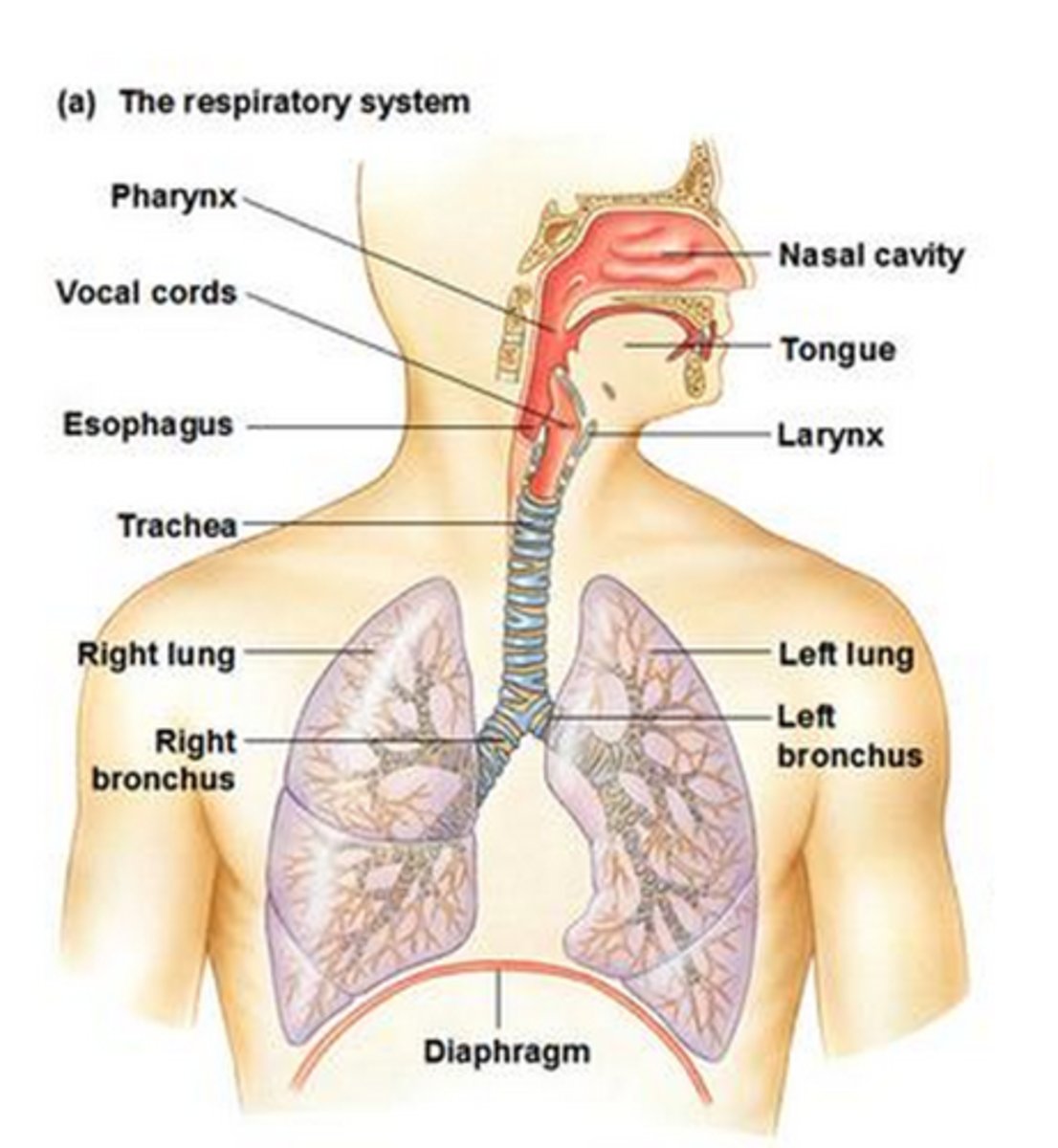
nose
Organ that takes in and releases air
pharynx
the membrane-lined cavity behind the nose and mouth, connecting them to the esophagus and trachea
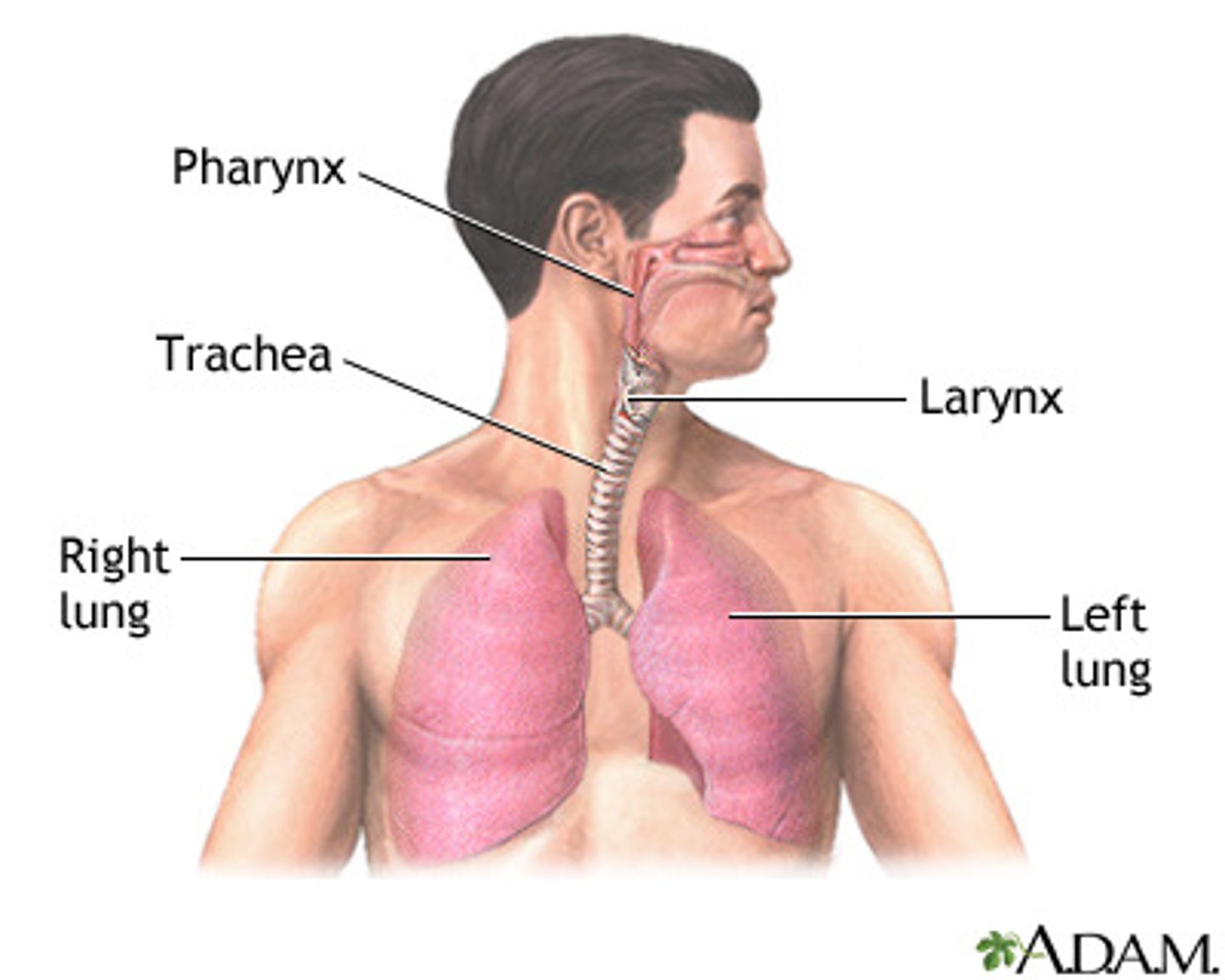
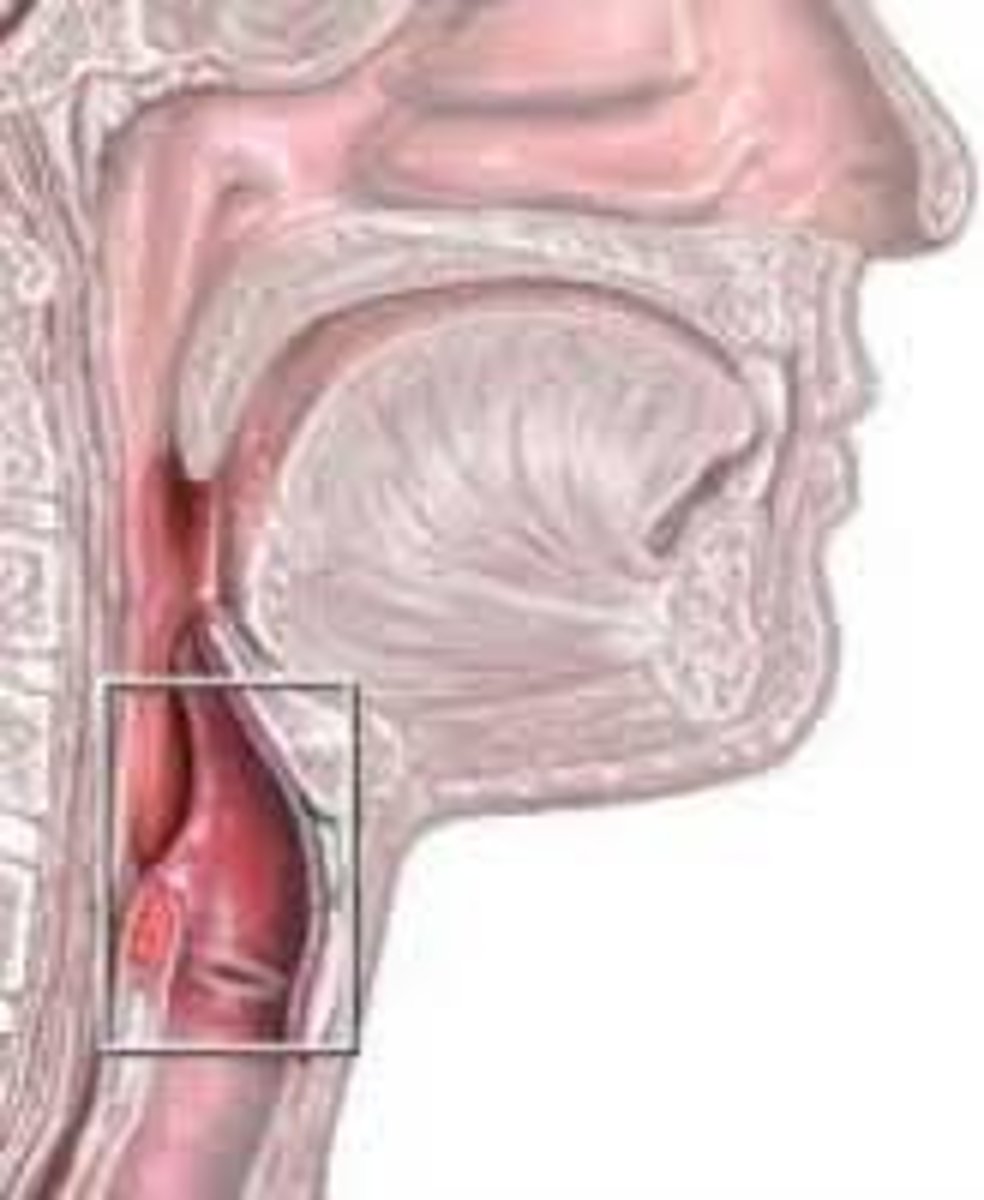
larynx
voice box; passageway for air moving from pharynx to trachea; contains vocal cords
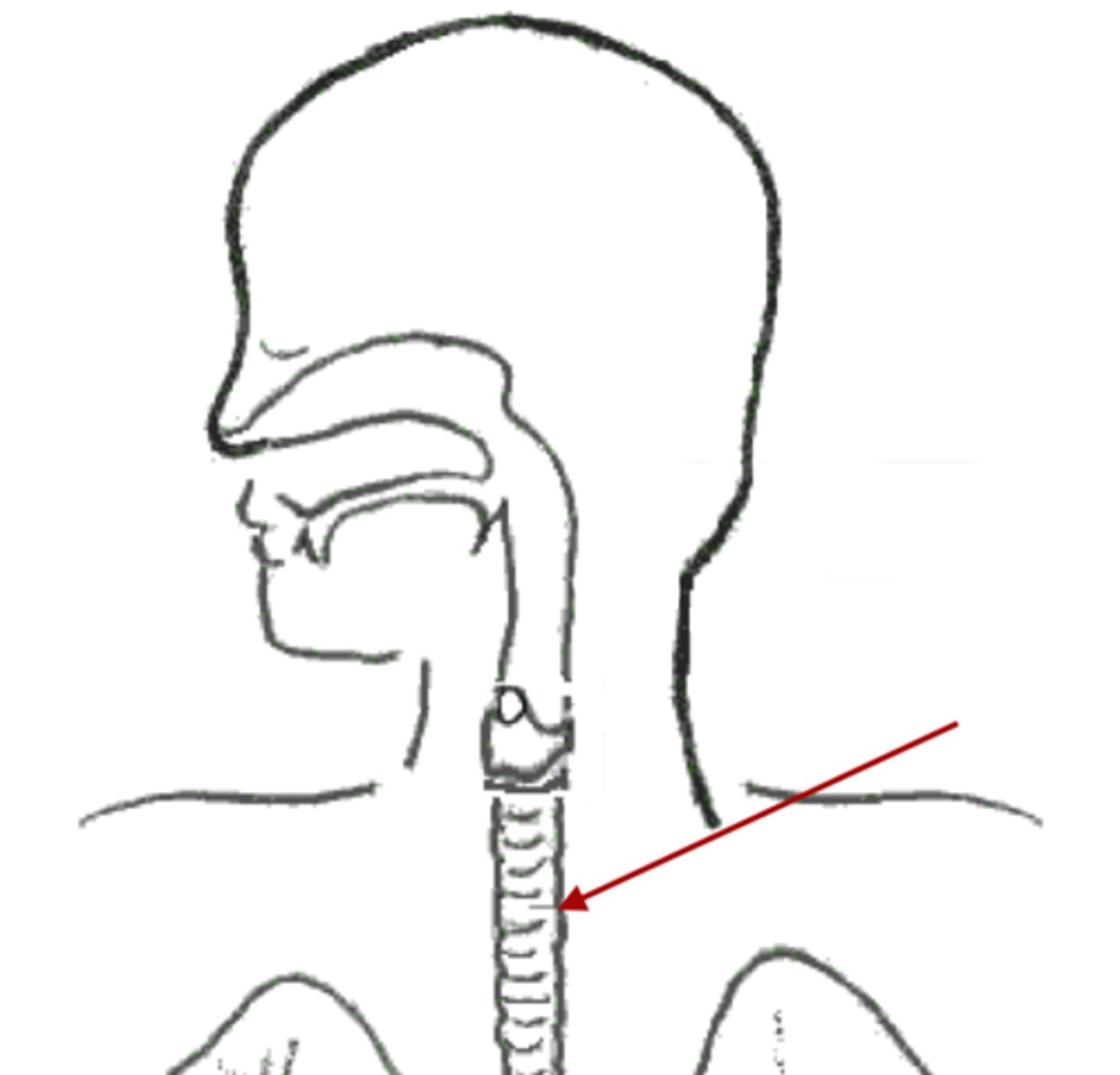
trachea
a large tube reinforced by rings of cartilage, extending from the larynx to the bronchial tubes and conveying air to and from the lungs; the windpipe.
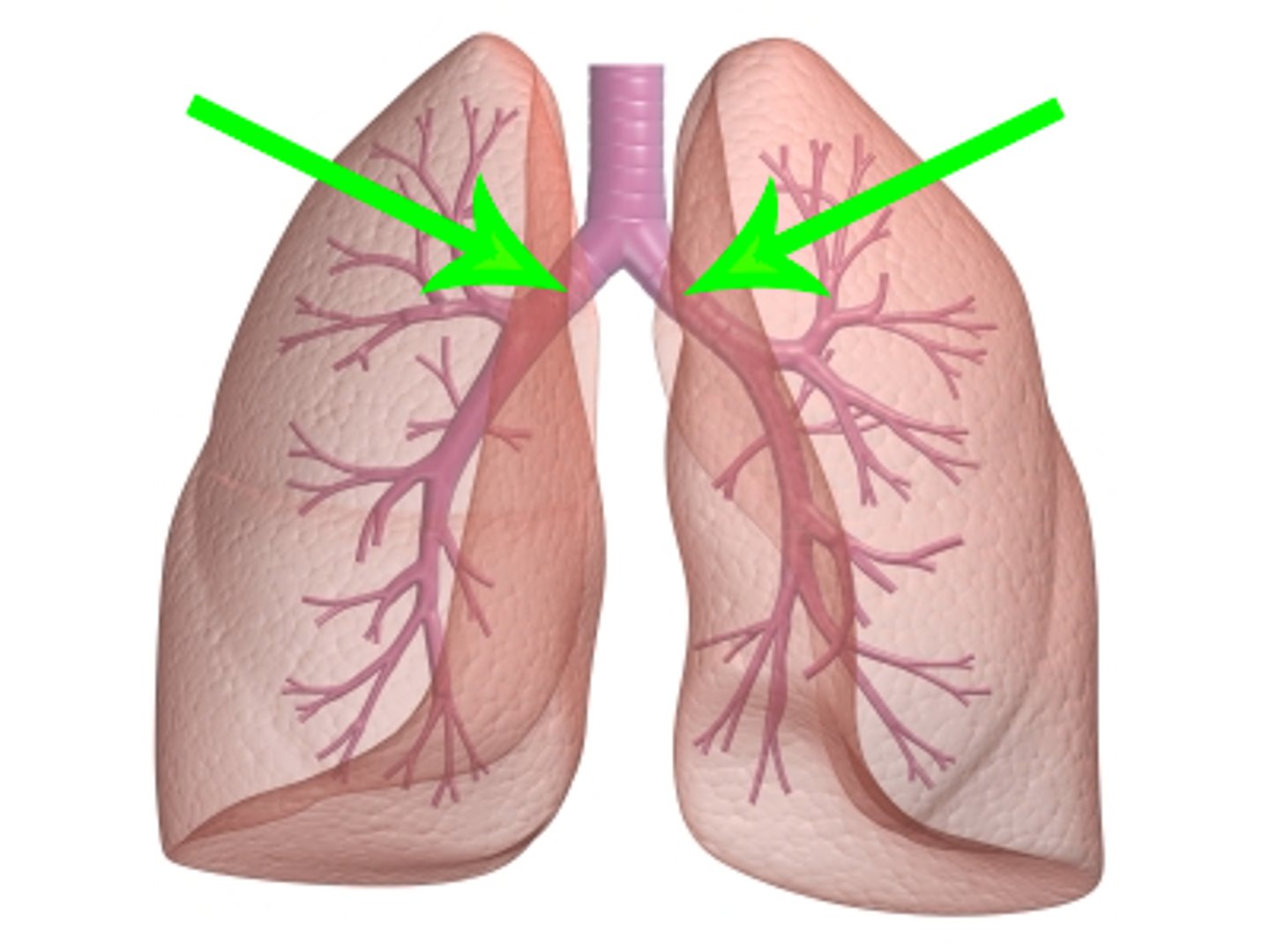
bronchi
The passages that direct air into the lungs (singular: bronchus)
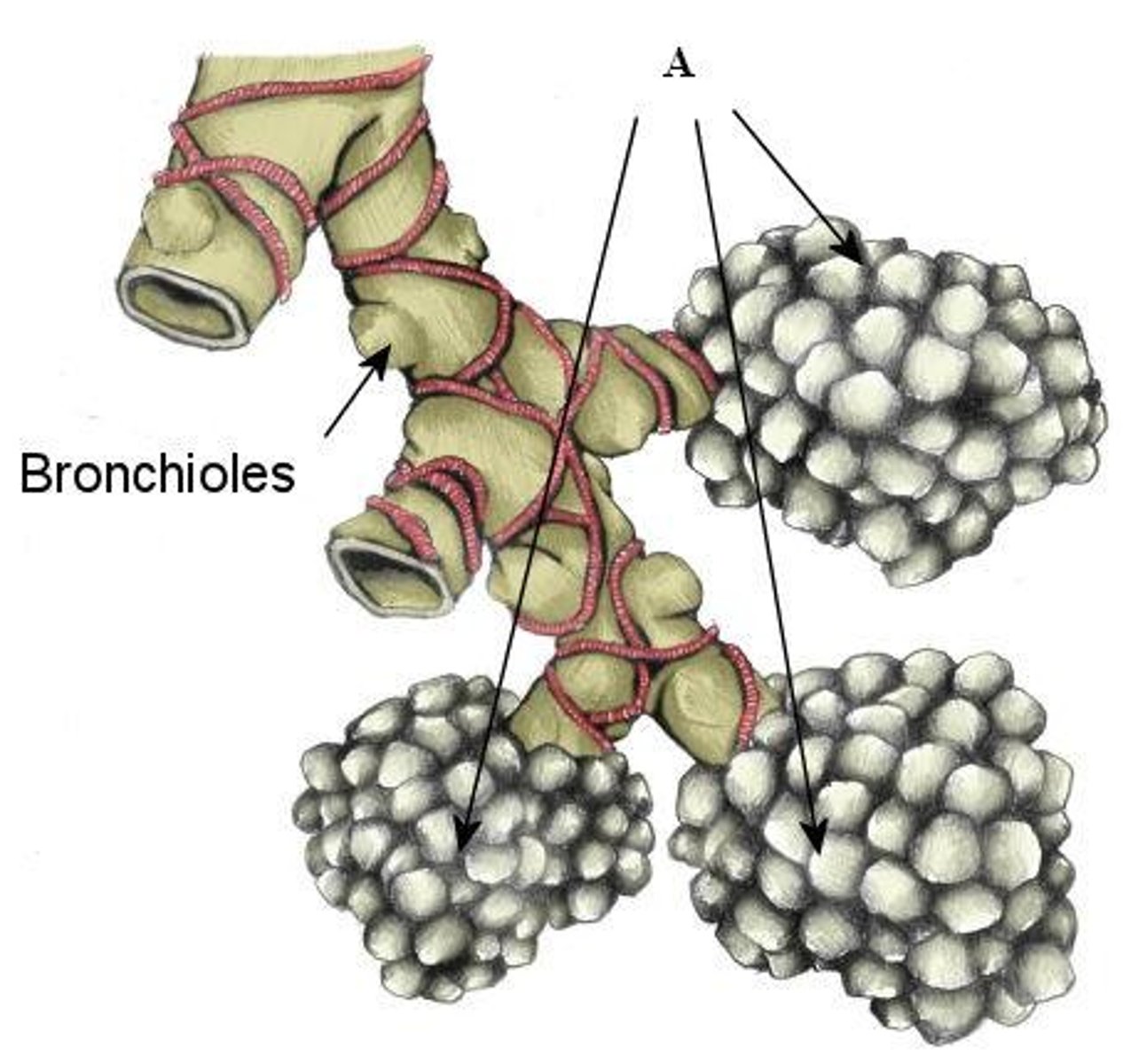
bronchioles
Smallest branches of the bronchi: Airways in the lungs that lead from the bronchi to the alveoli.
alveoli
tiny sacs of lung tissue specialized for the movement of gases between air and blood (singular: alveolus)
nervous system
the network of nerve cells and fibers that transmits nerve impulses between parts of the body.
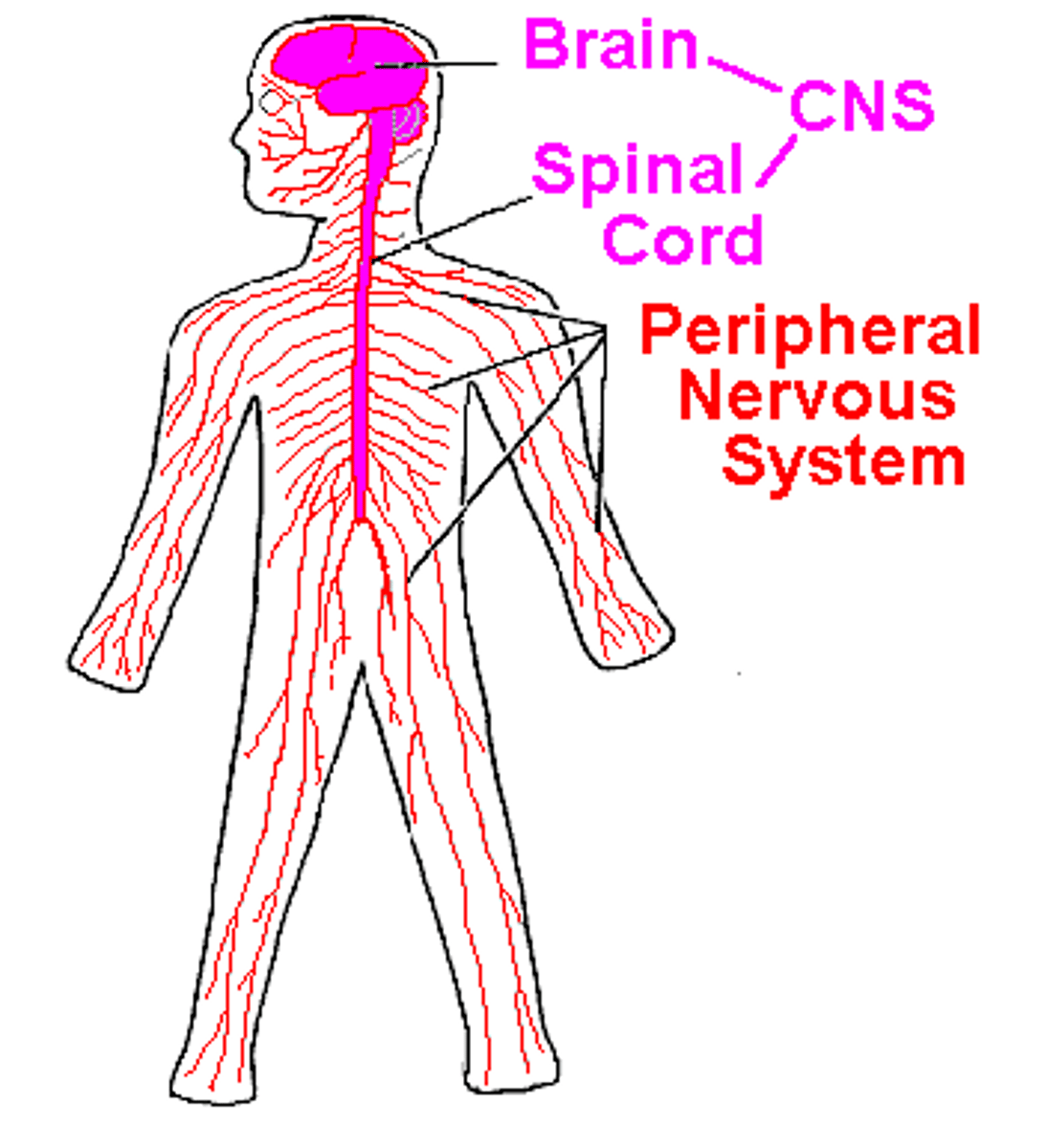
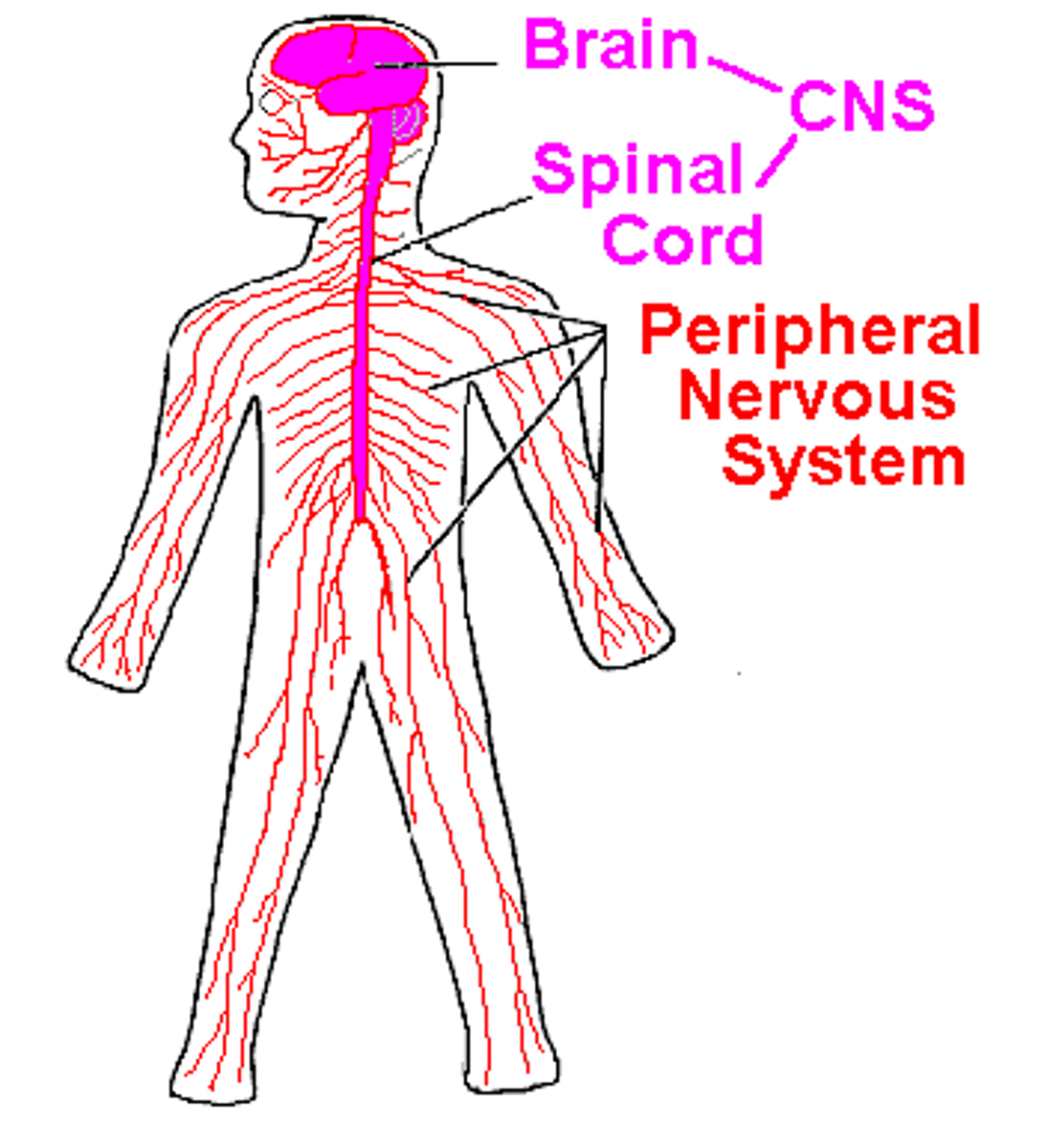
central nervous system (CNS)
brain and spinal cord
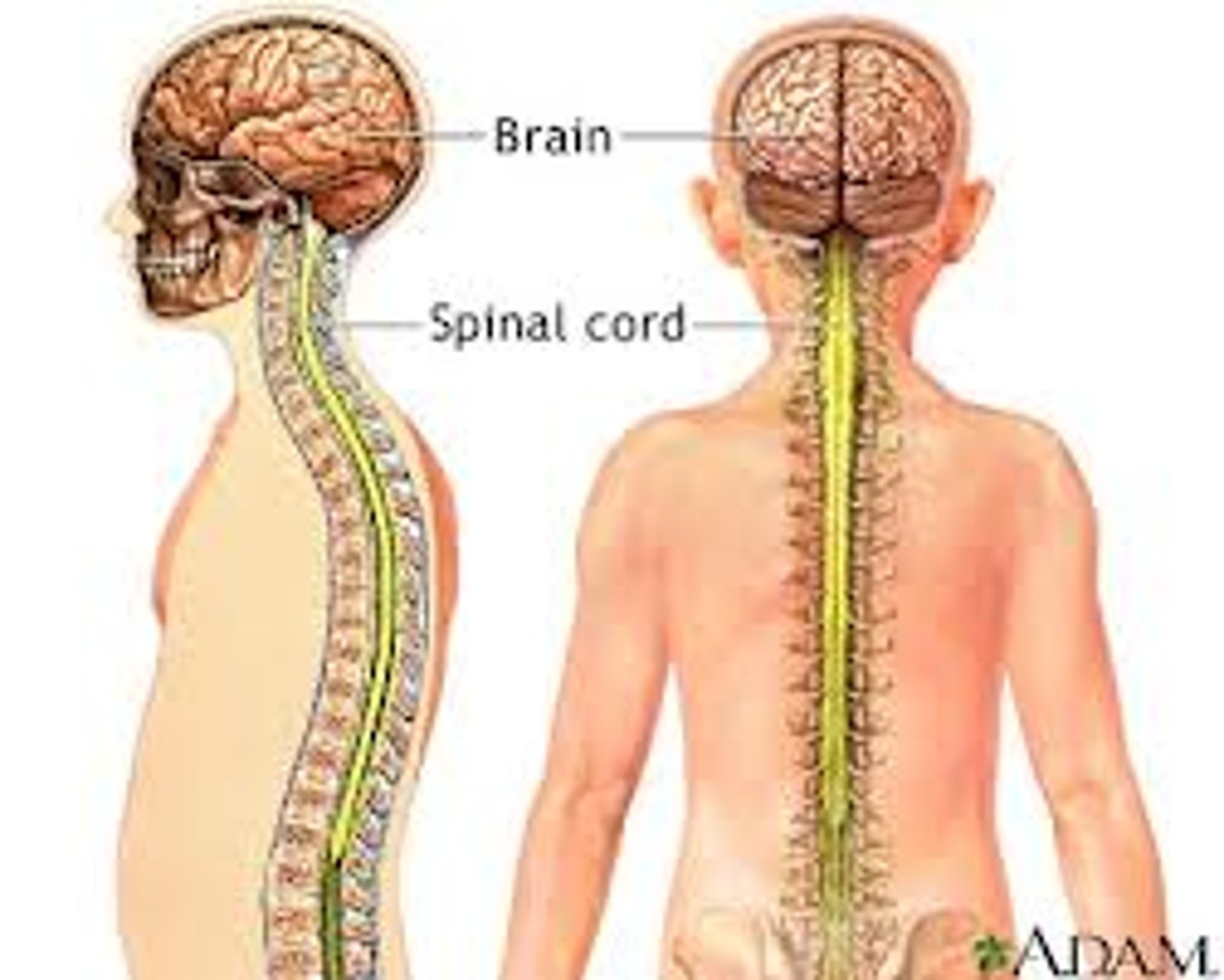
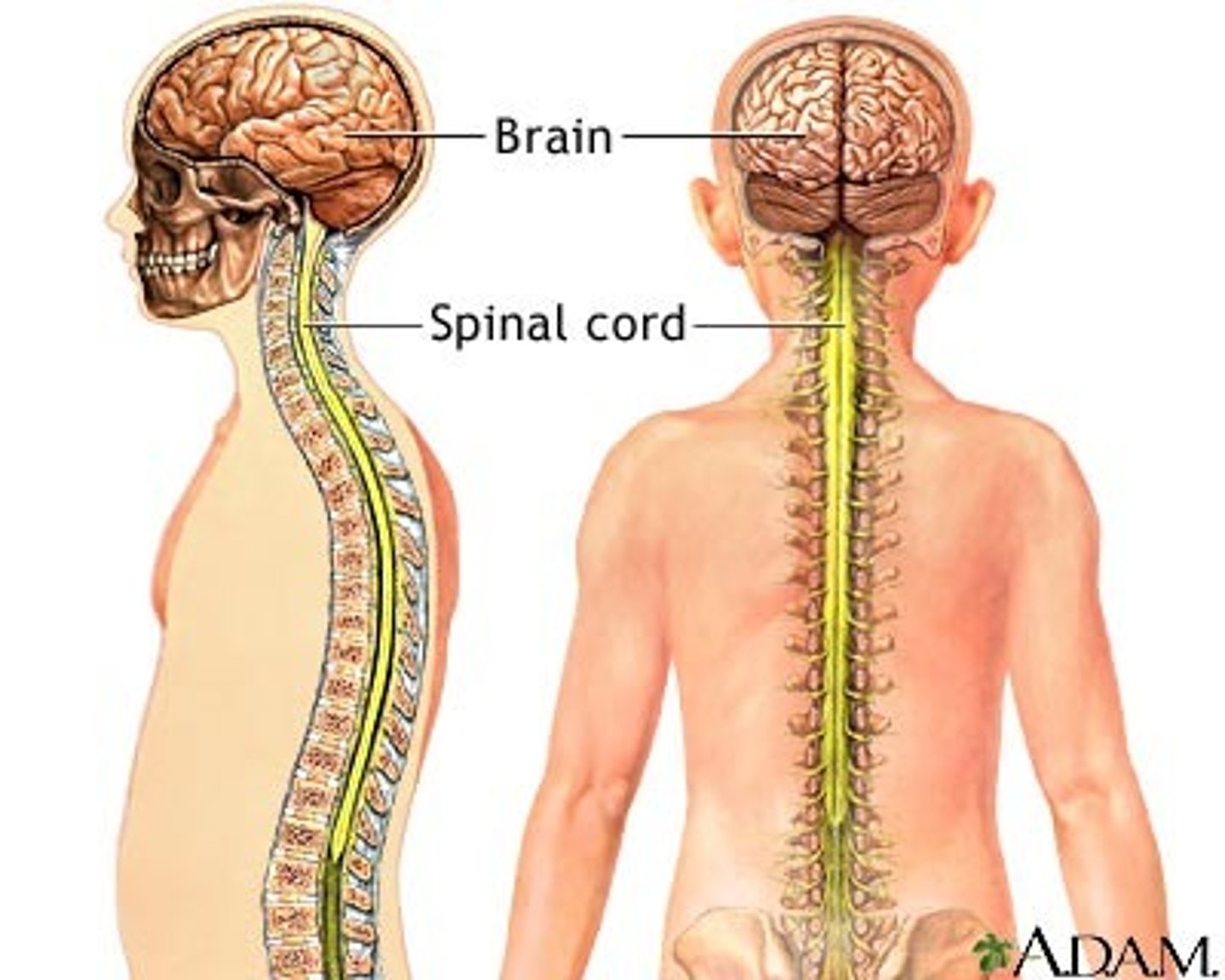
brain
The mass of nerve tissue that is the main control center of the nervous system
spinal cord
Nerves that run up and down the length of the back and transmit most messages between the body and brain
peripheral nervous system
the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system to the rest of the body
somatic nervous system
the division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the body's skeletal muscles
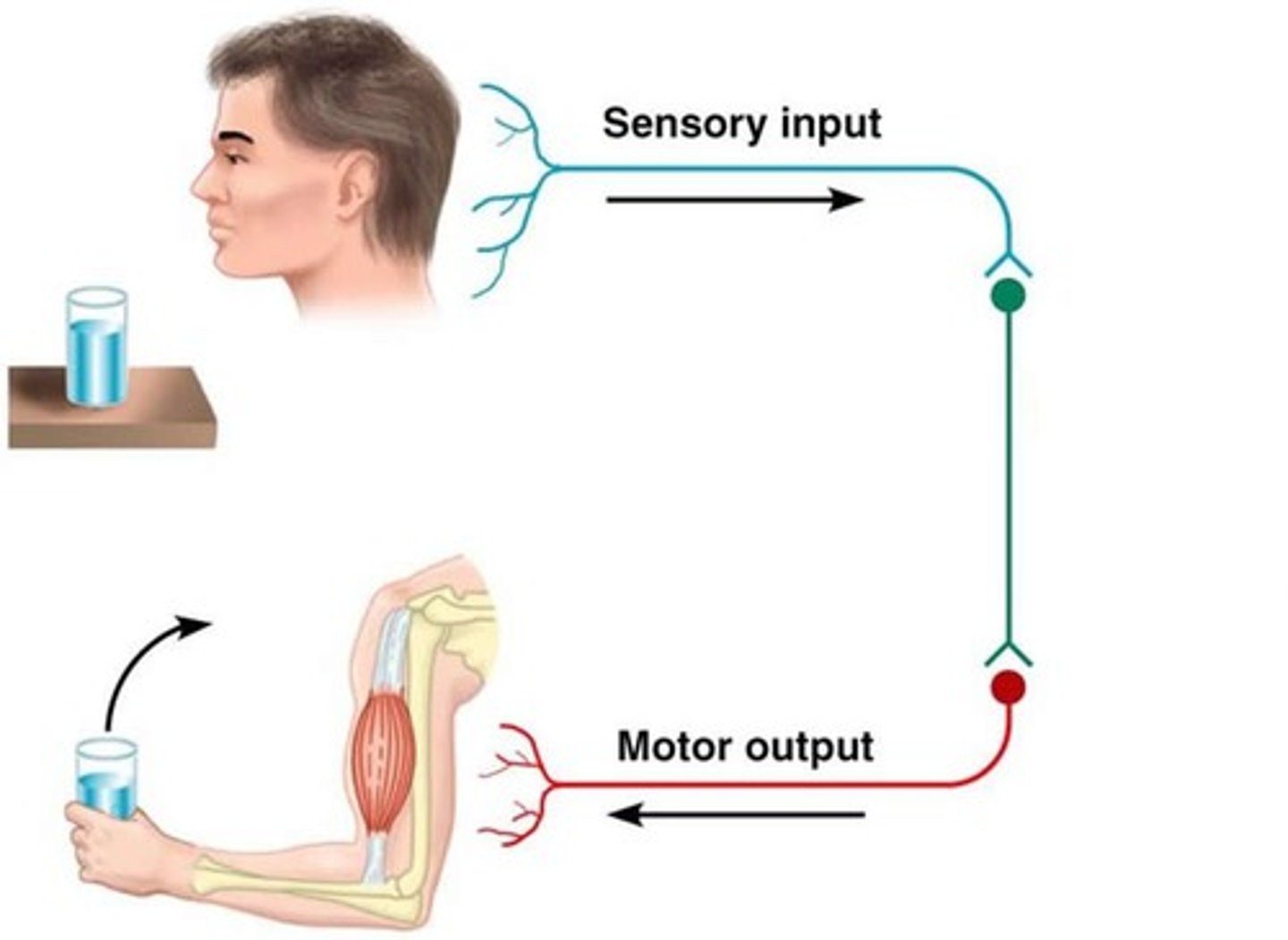
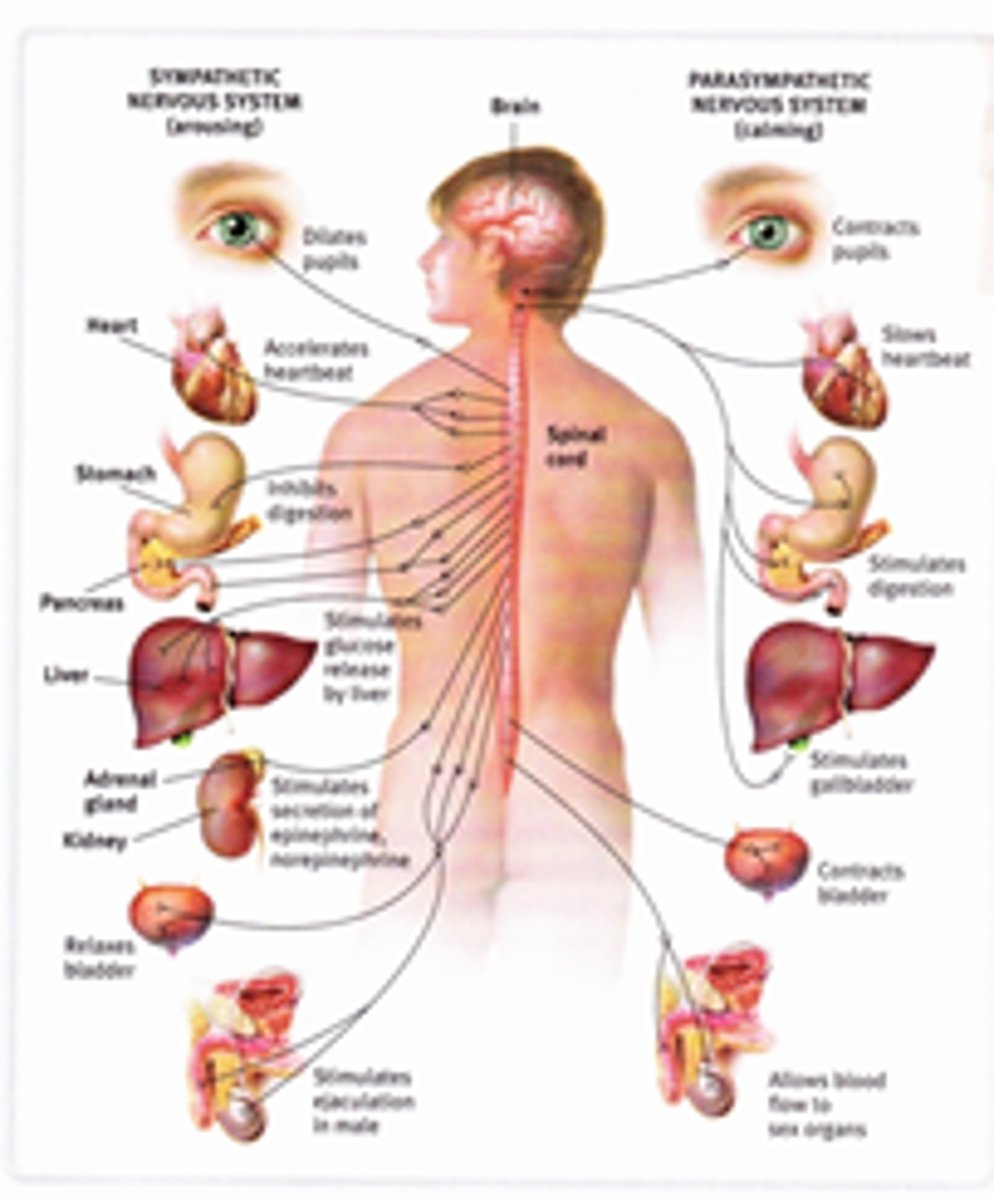
autonomic nervous system
A subdivision of the peripheral nervous system. Controls involuntary activity of visceral muscles and internal organs and glands.
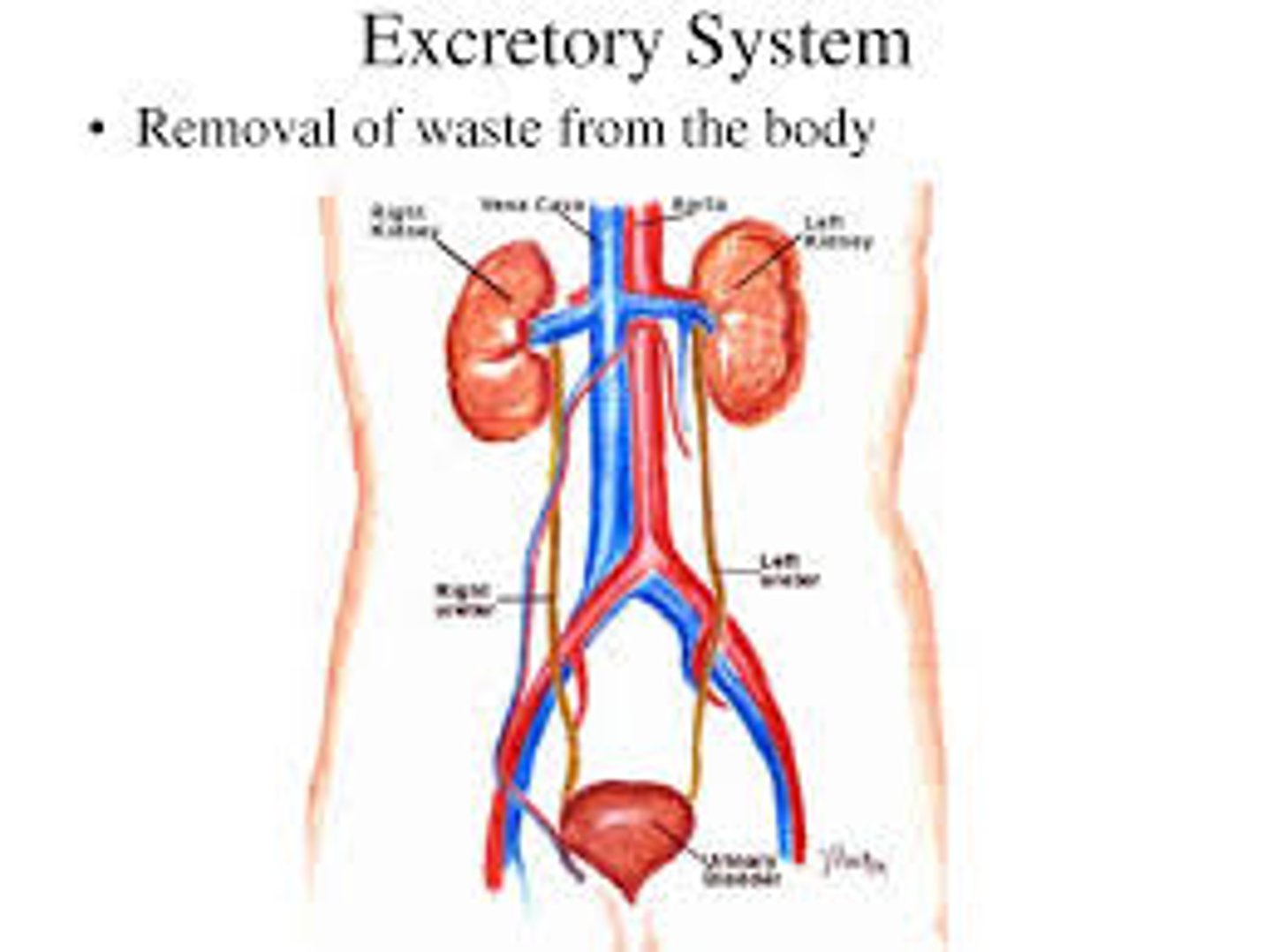
excretory system
the system that removes waste from your body and controls water balance
skin and the excretory system
largest organ system of the body; helps the excretory system to rid the body of waste and regulates body temperature and water balance
lungs and the excretory system
excrete carbon dioxide during respiration
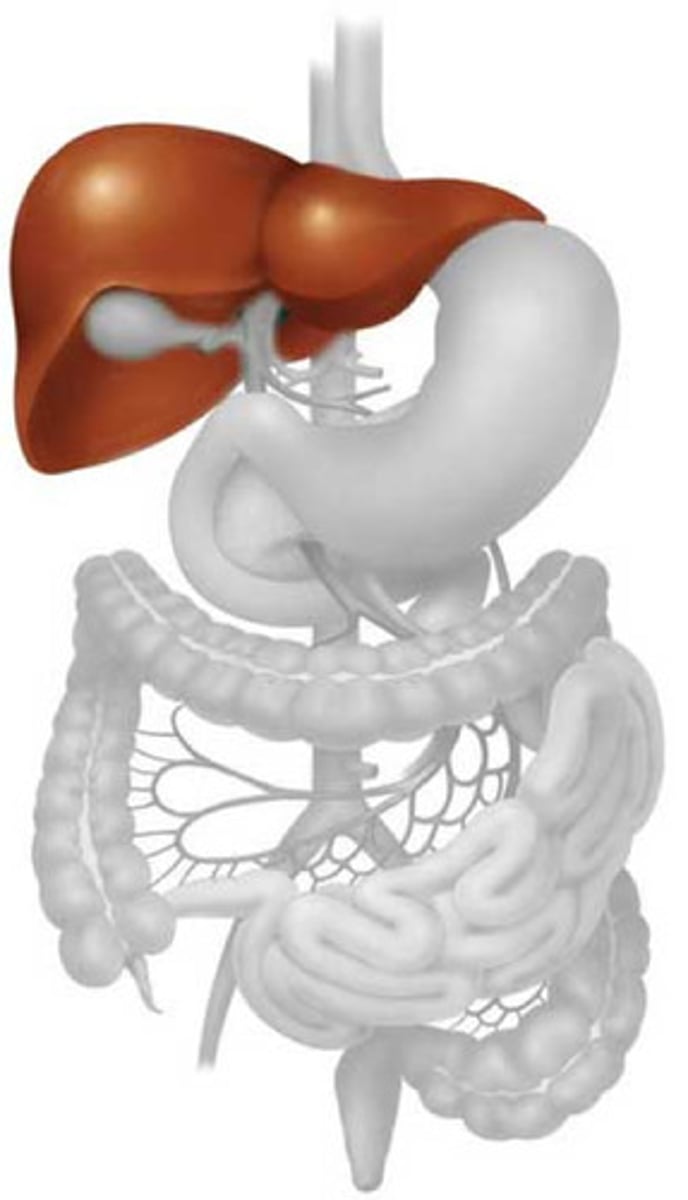
liver and excretory system
breaks down excess amino acids in bloodstream into nitrogen compound, which is then converted into urea and filtered, released by kidneys; also breaks down poisons such as alcohol to be excreted
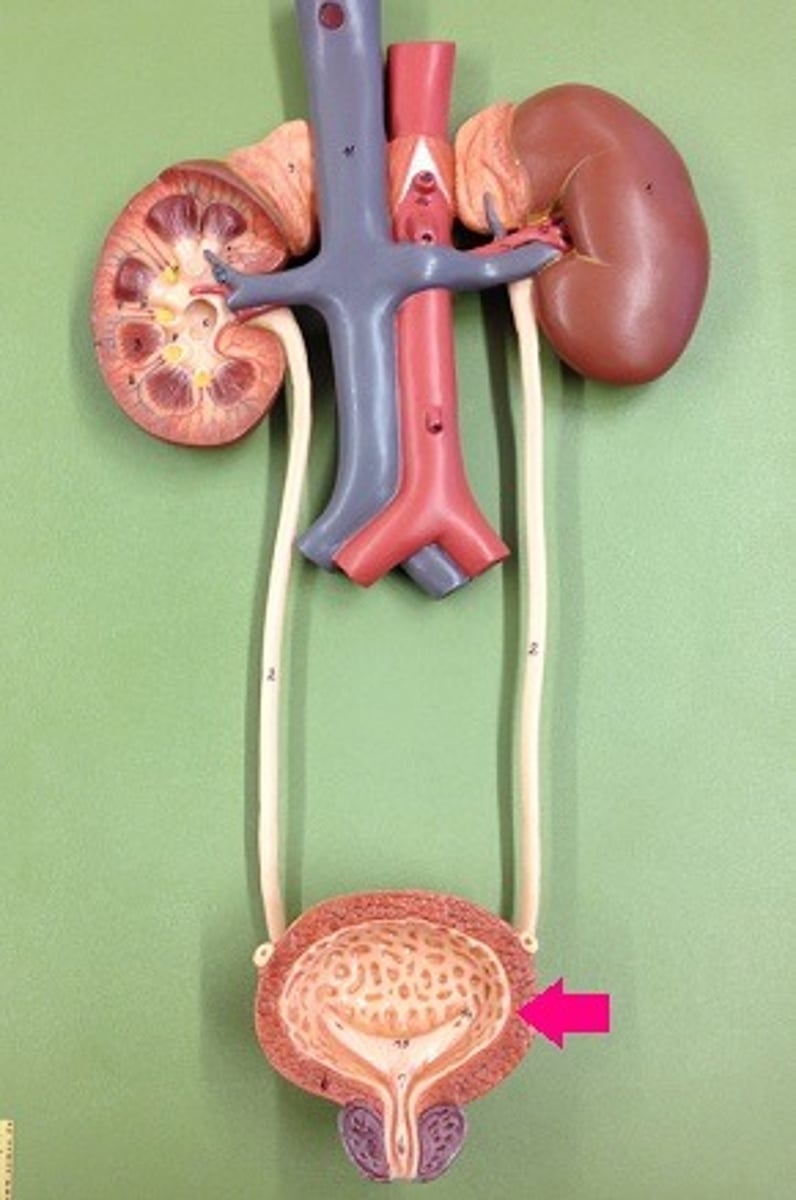
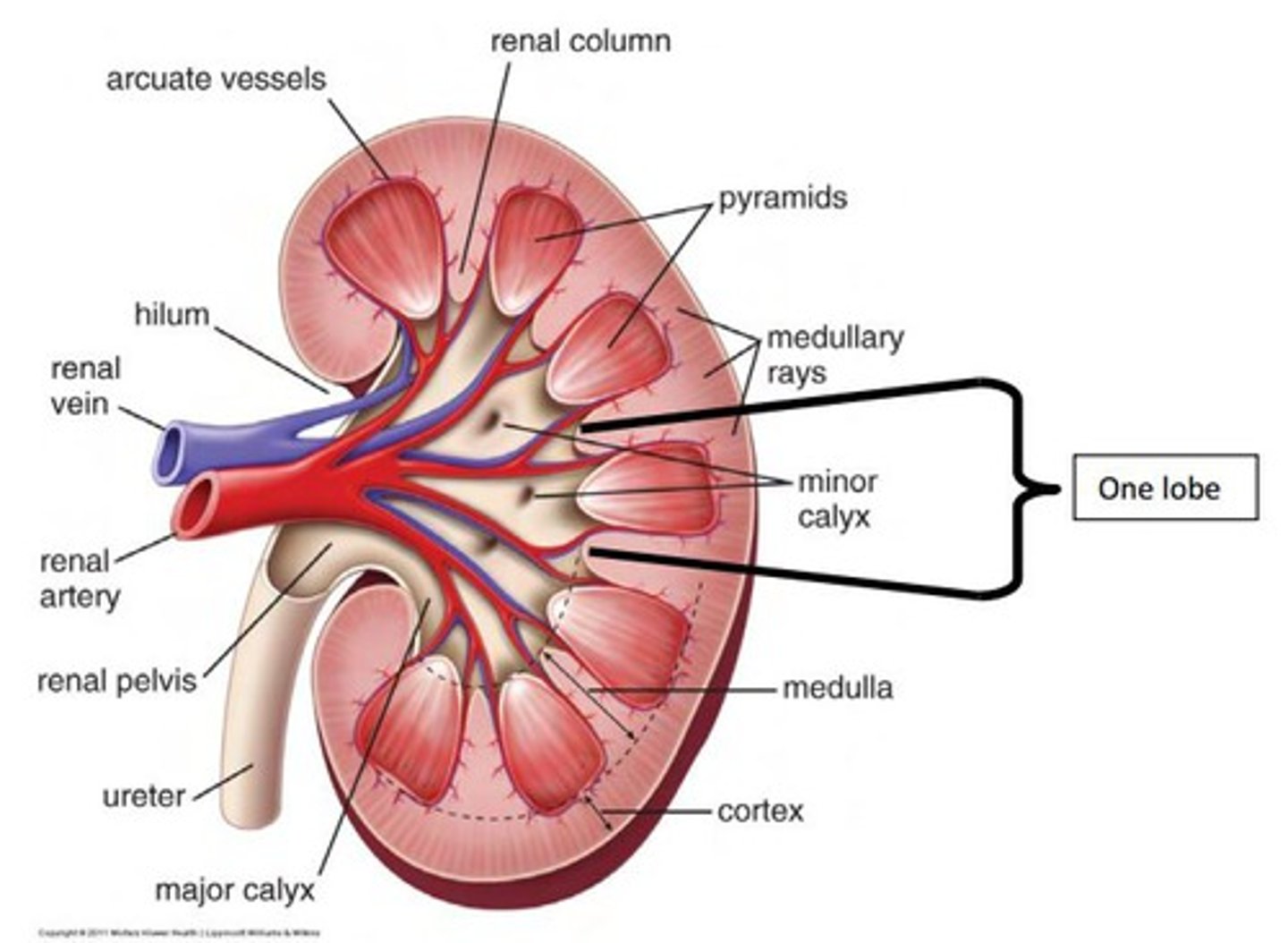
kidney
Filters waste from the blood like urea, water, salt and proteins.
urinary bladder
saclike organ in which urine is stored before being excreted