Neuroscience Exam #2
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
The thoracic component only exists in the _______ region.
lumbar region
What is the function of the Phrenic nerve?
to help with respiration and to fix any damage in the trunk region
The Phrenic nerve is associated with the
cervical plexus
Arm damage occurs if the _______ plexus is affected
brachial plexus
The ___________ ends at the elbow
Musculocutaneous
The lumbar/sacral plexus carries information to the
lower extremities
Dermatomes are
one area of skin innervated by one spinal nerve
_________ is a gateway to Zoster
Chicken Pox
Shingles occurs when
one dermatome is impacted
A Myotome is
one muscle being innervated by one spinal nerve
The C4 myotome controls the
Trapezius - Shoulder shrug
The C7 myotome controls which part and which movement?
Triceps - Elbow extension
The L5 myotome controls which part and which movement?
Quadriceps Femoris - Knee Extension
The S2 myotome controls which part and which movement?
Gastrocsoleus - Planarflexion
The _________ nerve connects sensory to motor
Integration nerve
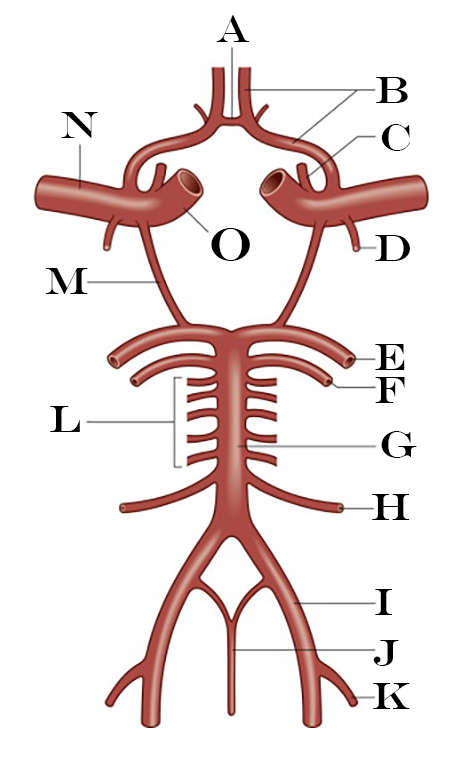
What is A?
Anterior Communicating Artery
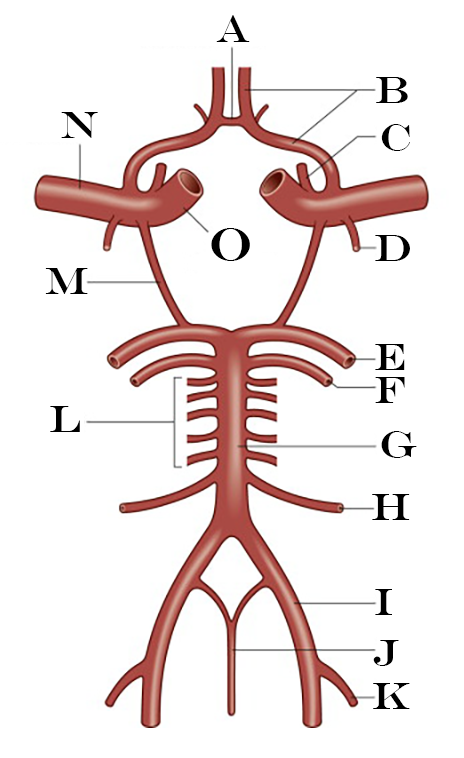
What is B?
Anterior Cerebral Artery
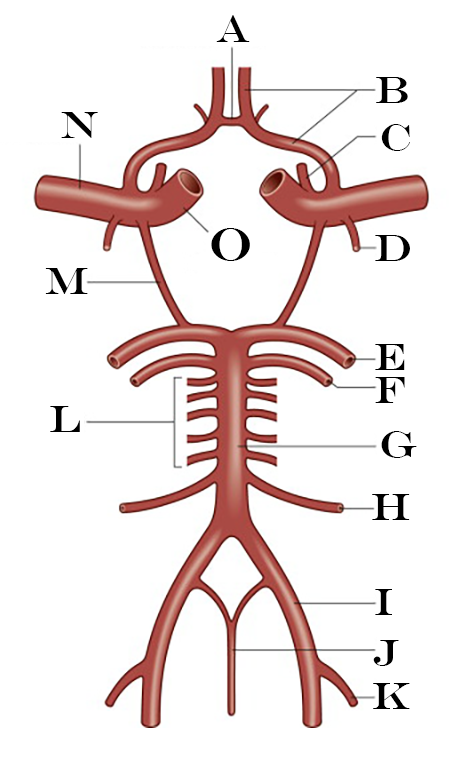
What is C?
Ophthalmic Artery
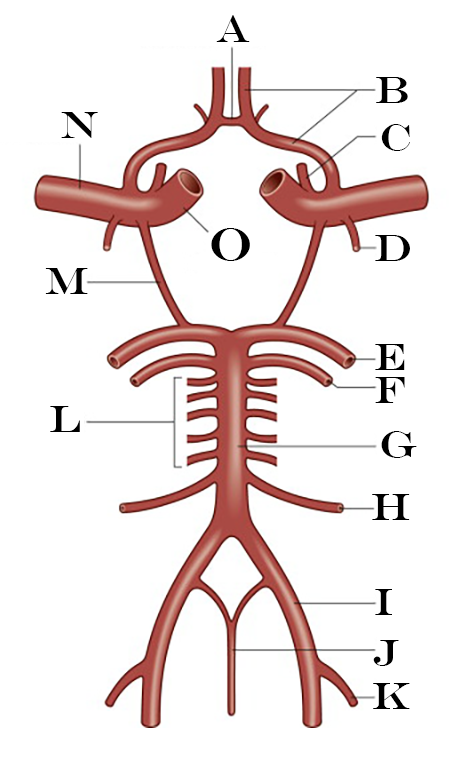
What is D?
Anterior Choroidal Artery
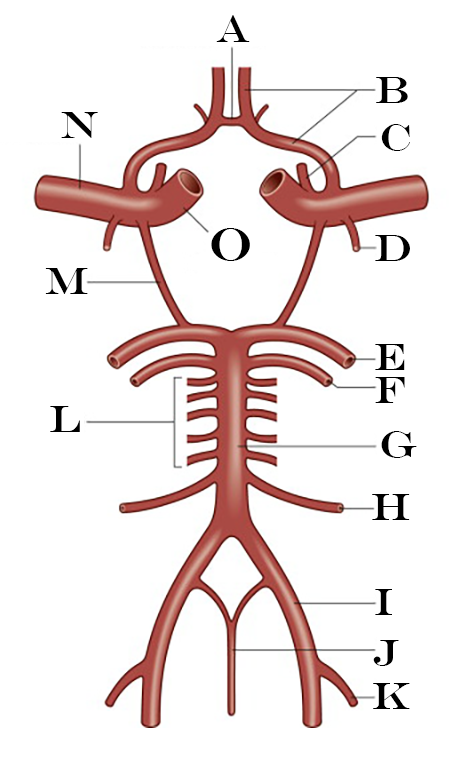
What is E?
Posterior Cerebral Artery
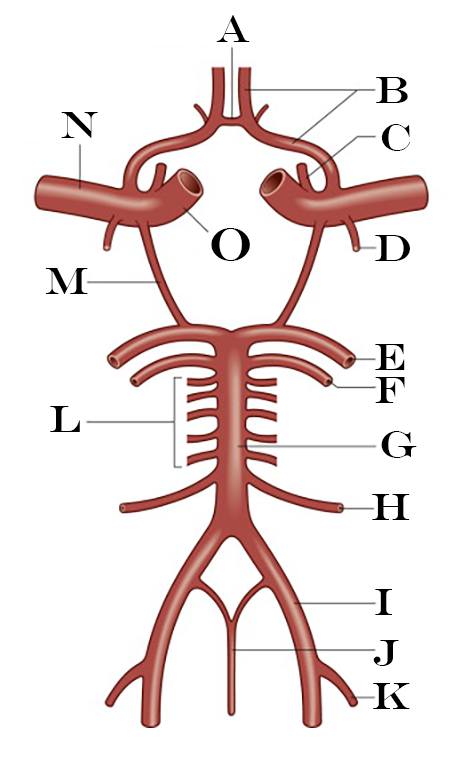
What is F?
Superior Cerebellar Artery
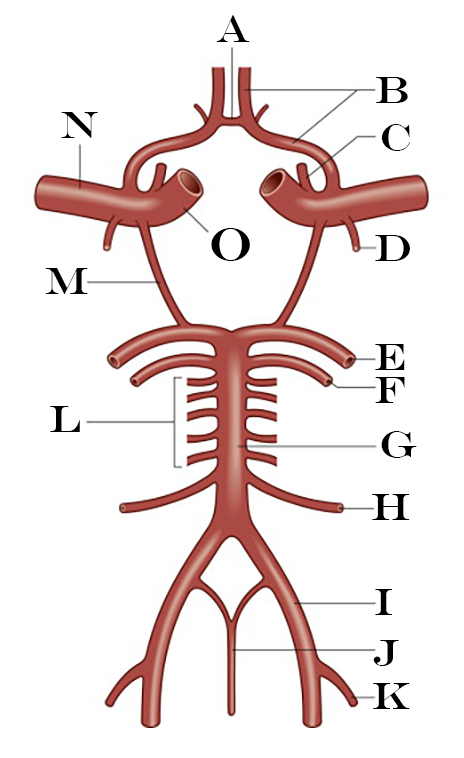
What is G?
Basilar Artery
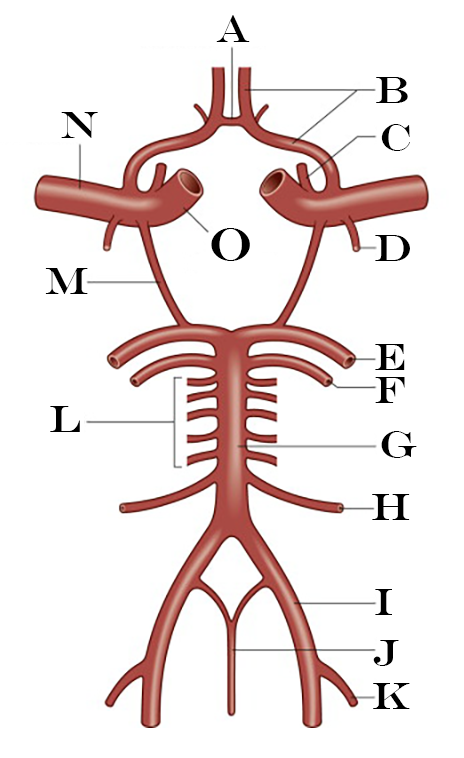
What is H?
Anterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery
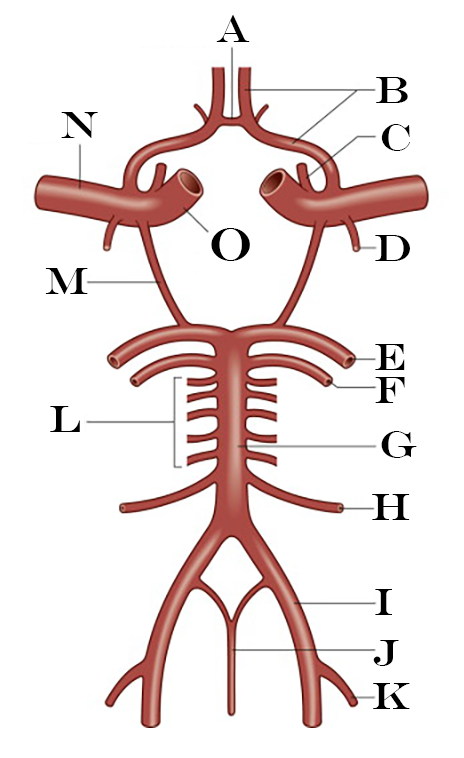
What is I?
Vertebral Artery
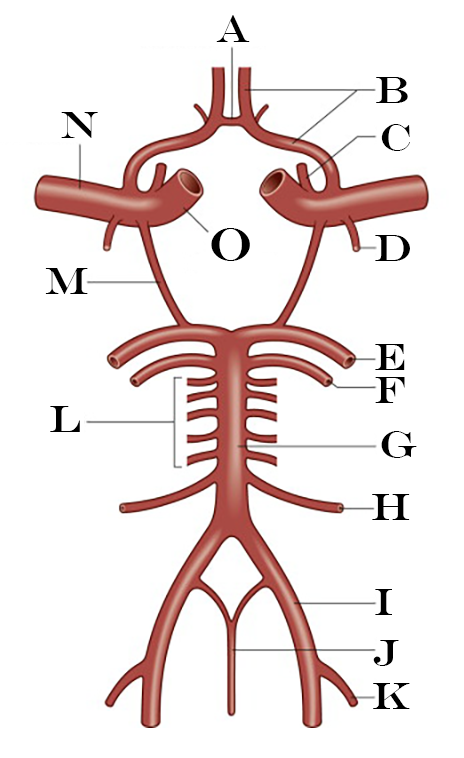
What is J?
Anterior Spinal Artery
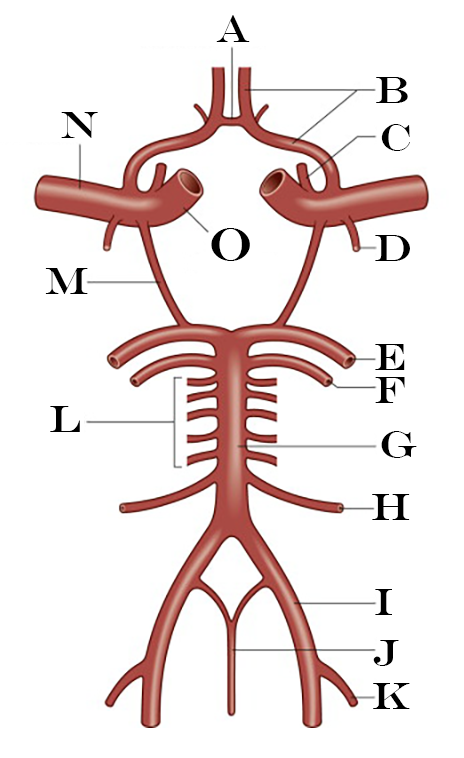
What is K?
Posterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery
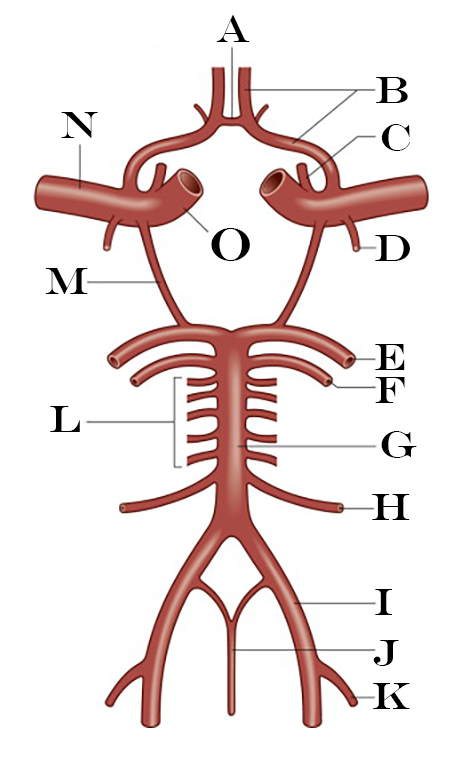
What is L?
Pontine Arteries
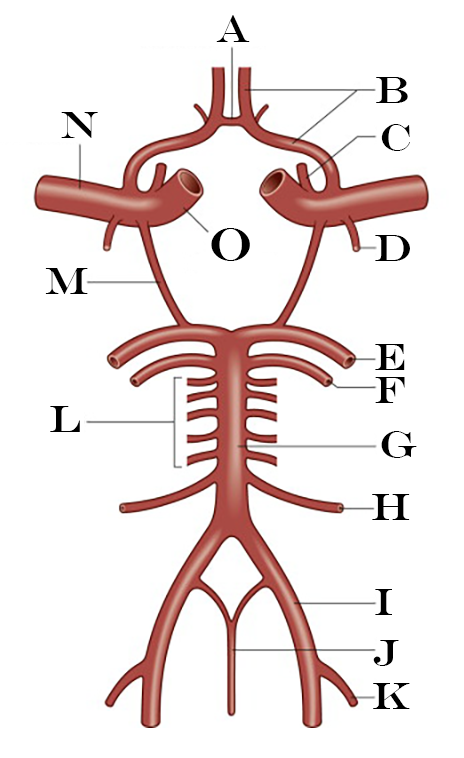
What is M?
Posterior Communicating Artery
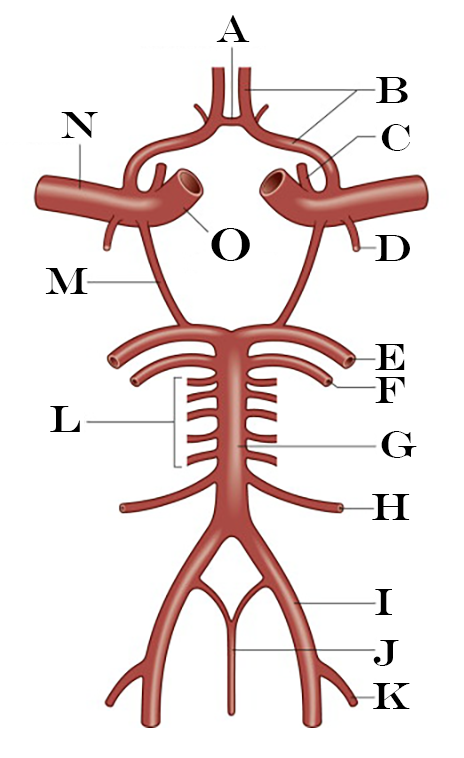
What is N?
Middle Cerebral Artery
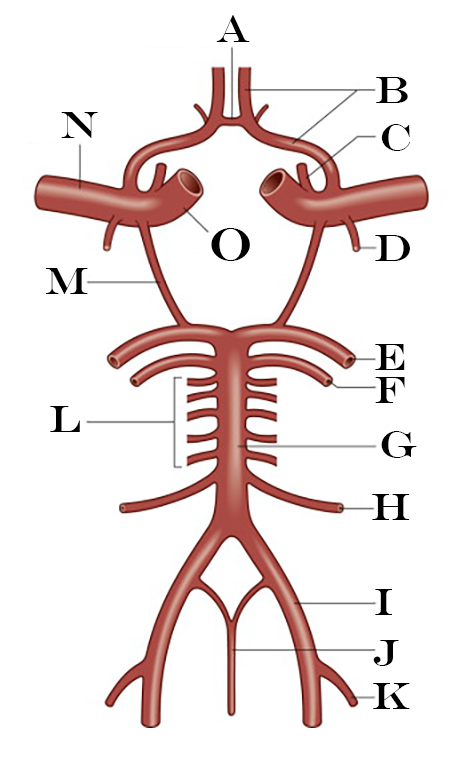
What is O?
Internal Carotid Artery
What does a Agonist Neurotransmitter do?
binds to another chemical that has a similar effect as the neurotransmitter
What does an Antagonist Neurotransmitter do?
blocks the action of the neurotransmitter
What are the two neurotransmitters that are in the Peripheral Nervous System?
Acetylcholine and Norepinephrine
What is the function of Acetylcholine?
To control muscle action
When Acetylcholine is in the PNS it is ___________.
Excitatory
When Acetylcholine is in the CNS it is ___________.
Inhibitory
Is the neurotransmitter Gamma-Aminobutyric excitatory and inhibitory?
inhibitory
Is the neurotransmitter Dopamine excitatory and inhibitory?
It is excitatory and inhibitory
Is the neurotransmitter Serotonin excitatory and inhibitory?
Inhibitory
Is the neurotransmitter Norepinephrine excitatory and inhibitory?
Excitatory
Is the neurotransmitter Glutamate excitatory and inhibitory?
Excitatory
Down-Regulation refers to
A decrease in the number of receptors on the surface of target cells
Synaptic Fatigue refers to
temporary loss or reduction of synaptic activity due to intense stimulation
Synaptic Delay refers to
the time it takes for the pre-synaptic neuron current to be transmitted to the post-synaptic neuron
Post-Tetonic Potentiation refers to
an increase in neurotransmitter release after a high-frequency train of action potentials
Excitotoxicity refers to
the process where nerve cells are damaged and killed by glutamate and other substances
Addiction is dangerous because
substances kill receptors at the post synaptic terminal which causes a desire to always need more
The Anterior Cerebral Artery feeds the
medial surface of the frontal and parietal lobes
The Middle Cerebral Artery feeds the
entire lateral surface of the cerebral hemisphere
The Posterior Cerebral Artery feeds the
medial and inferior aspects of the temporal lobe and the whole occipital lobe
What kind of dysfunction can happen in the Anterior Cerebral Artery?
Can cause difficulties in cognitive and affective function
What kind of dysfunction can happen in the Middle Cerebral Artery?
can cause negative affects to perceptual deficits and apraxia
What kind of dysfunction can happen in the Posterior Cerebral Artery?
can cause memory loss and thalamic syndrome (unexplained pain)
What are the functions of the Blood Brain Barrier?
to protect the CNS and not allow blood to enter the nervous system
the exchange of nutrients between the CNS and Vascular system
The Blood Brain Barrier is formed by
tight junctions between endothelial cells and gliall cells
What are “Leaky Areas” in the Blood Brain Barrier?
areas in the blood brain barrier that help get medicine through
Where are the “Leaky Areas” located in the brain?
in the hypothalamus and pituitary/pineal glands
The blood-brain barrier blocks ___% of therapeutic drugs from accessing the brain.
98%
What can L-Dopa do in the brain?
it can cross the blood-brain barrier and convert into dopamine which helps with Parkinsons disease
What diseases are affected by the blood-brain barrier?
Meningtis
Rabies
Tumors
Alzheimers
MS
What is CVA? (Strokes)
a group of clinical syndromes that form following ischemic and hemorrhagic lesions
What is a Transient ischemic Attack (TIA)?
a smaller stroke that does not have very significant symptoms
What is a Cerebral Hemorrhage?
when a blood vessel has broken open in the body and produces significant effects
What is a Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformation?
A malfunction that can go unnoticed, but has significant effects and can cause a stroke
What are the symptoms of a stroke that occur in the Left Hemisphere?
Brocas area is affected and causes trouble speaking
Movement is affected on right side of body
Visual processing in right field is affected
Processing of verbal information is affected
What are the symptoms of a stroke that occur in the Right Hemisphere?
Movement on the left side of body is affected
Nonverbal memory is affected
Visual processing on the left field is affected
Affects processing of nonverbal auditory information
What is a Traumatic Brain Injury? (TBI)
Damage that results from penetration of the skull and blunt external forces to the brain
What are the symptoms of a TBI?
Loss of Consciousness
Coma
Rigidity
Change in vitals
Fixed pupils
What are some types of TBI?
Penetrating brain injuries
Skull fractures
Closed Head Injuries
What is a Spinal Cord injury?
When the vertebrae is fractured or dislocated
What does a Traumatic Spinal Cord injury consist of?
Compression
Shearing Force
Contusion
What does a Non-Traumatic Spinal Cord injury consist of?
Tumor pressing on the cord
Progressive neurodegenerative disease
Stroke in the spinal cord
What is Paraplegia?
type of paralysis that affects all portions of the victims torso
What is Quadripledia?
type of paralysis that affects all parts of the body
What are the symptoms of a Spinal Cord Injury?
Automatic Dysreflexia
Decreased Respiratory function
Loss of Temperature controls
Sexual dysfunction
Loss of bowel/bladder control
Changes in muscle tone
What are the different types of Cerebral Palsey?
Spastic
Dyskinetic
Ataxic
Spastic CP has a lesion at the ______ cortex
motor cortex
What are the symptoms of Spastic CP?
Increased muscle tone
Increased intensity of reflex responses
Dyskinetic CP has a lesion at the
basal ganglia
Dyskinetic CP involves fluctuations in
muscle tone
Ataxic CP has a lesion at the
cerebellum
What are the symptoms of Ataxic CP?
Hypotonia
Ataxic movement patterns
The function of the neuron is to
send, receive, and store electrical/chemical information
The most common type of neuron is the
Multipolar Neuron
What can help to increase action potential speed?
More myelin and bigger diameter of axon
Depolarization is a change that
causes the cell to become less negative and more excitable
Repolarization is a moment
after depolarization and before hyper-polarization
Hyper-polarization is a change that
causes the cell to become more negative and more inhibitory
In order to achieve an action potential, the cell must reach ____ mV
- 55 MV
____ is resting membrane potential
- 70 MV
Spatial summation is when
multiple presynaptic neurons create enough energy to make an action potential
Temporal summation is when
one presynaptic neuron releases a neurotransmitter many times that eventually creates enough energy to make an action potential
What are the 5 important spinal cord tracts?
Lateral Corticospinal
Dorsal Columns
Lateral Spinothalamic
Spinocerebellar Tracts
Vestibulospinal
A reflex arc is triggered by
a stimulus in the enviornment
The Lateral Corticospinal tract is (ascending/descending)
descending
The Dorsal Columns tract is (ascending/descending)
ascending
The Lateral Spinothalamic tract is (ascending/descending)
ascending
The Spinocerebellar Tracts is (ascending/descending)
ascending
The Vestibulospinal tract is (ascending/descending)
descending
What are the five steps in the reflex arc?
Receptor
Sensory Neuron
Integration
Motor Neuron
Effector