2.3. Levels of processing
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
2.3. Levels of processing
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Levels of processing was proposed by;
CRAIK & LOCKHART
Craik & Lockhart challenged
the assumption that simply holding items in the short-term store for long enough would guarantee learning.
Craik & Lockhart proposed
Principle of levels of processing
principle of levels of processing maintains that
Learning depends on the way in which material is processed
Craik & Lockhart focused on:
Memory processes
Craik & Lockhart suggests that information can be
processed at different levels
from a superficial to a depth
elaborated level
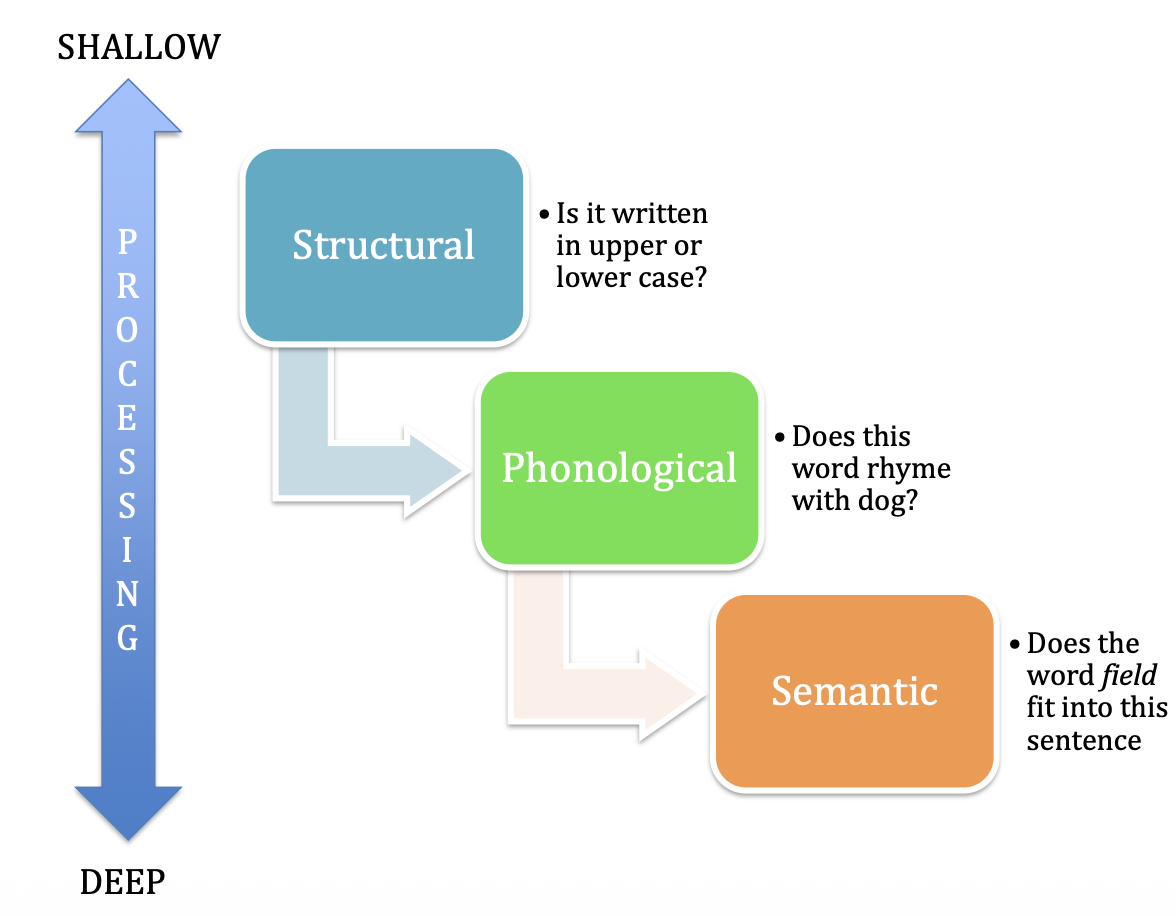
Superficial to a depth elaborated level according to Craik & Lockhart
Visual/structural processing (focusing on stimuli´s visual aspects).
Phonological processing (focusing on stimuli´s auditory or phonological aspects).
Semantic processing (focusing on stimuli´s meaning).
Craik & Lockhart suggests that the way information is processed
Affect the likelihood of it being stored & retrieved in the future.
the more deeply an item is processed, the better will be its retention.
According to CRAIK AND LOCKHART the greater "depth" implies a greater degree of
semantic or cognitive analysis.
According to CRAIK & LOCKHART deeper levels of processing result in more
long lasting & more retrievable memories
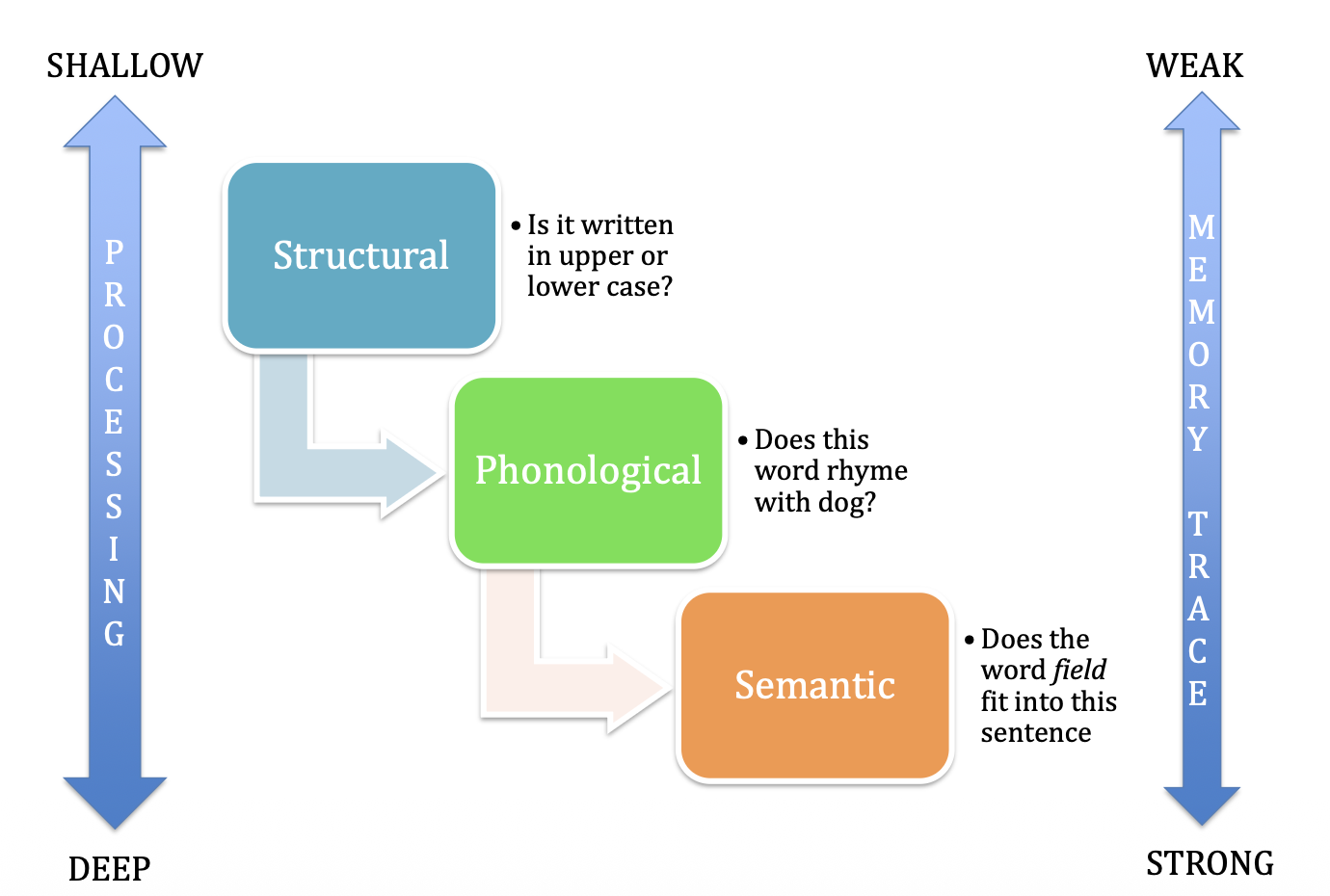
shallow levels of processing result in (CRAIK & LOCKHART)
memories that are less long-lasting & less likely to be retrieved
Craik & Tulving investigated the
effects of different types of processing on the recall of words
The method Craik & Tulving applied
Participants were shown 60 words, one at a time, & for each word they had to answer one of three questions
(tasks that provoked different types of processing)

Example: is the word in capital letters? is an example of
structurally processing
Example Does this word rhyme with Toy? is an example of
Phonological process → sound based processing
Example Does this word fit in the following sentence? is an example of
Semantic processing
meaning of the word & relating it to the rest of the sentence
Craik & Lockhart do assume the existence of
separate STM & LTM systems
they see the function of STM in terms of processes
IMPLICATIONS of Craik & Lockhart’s
Provided alternative to the structural approach to memory
Explains why elaborative rehearsal is more effective than maintenance or auditory
Emphasized how processes which occur during learning affect the extent to which material can be retrieved from LTM
Elaborative rehearsal involves
elaboration of the material to be recalled
Elaborative rehearsal can add
all kinds of extra images, associations & memories
to enrich the material which has to be learned, resulting in better recall
Key problems in the model of “levels of processing” → CRAIK & LOCKHART
The method applied to measure depth of processing → no independent way of assessing whether processing was deep or shallow.