Unit 1: Biochemistry - # 10 Passive and Active Transport (copy)
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Passive Transport
The movement of a substance across a membrane without the need to expend chemical energy (ATP)
Universe tends towards disorder (entropy)
If molecules are more concentrated on one side of a membrane, they will become equally distributed on both sides until equilibrium is reached
What are the three types of passive transport?
Simple Diffusion
Facilitated Diffusion
Osmosis
Simple Diffusion
The ability of a substance to move across a membrane unassisted
Movement of a substance from high to low concentration (no energy needed)
Rate of diffusion depends on the concentration gradient between two sides of a membrane
Dynamic equilibrium - even after the concentration of molecules is the same on both sides, they continue to move from one side to the other
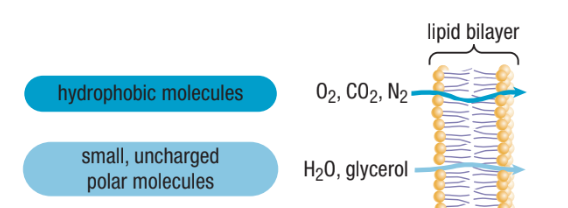
What can Diffuse Through The Phospholipid Bilayer?
Very small non-polar molecules can get through directly (eg. oxygen gas and carbon dioxide)
Small, uncharged polar molecules (eg. water and glycerol can also cross easily)
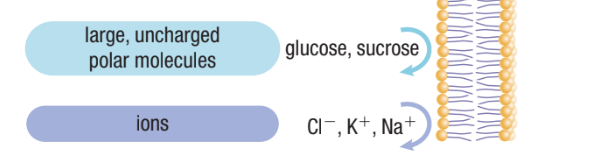
What Molecules Cannot Can’t Through Directly?
Ions (positively charged Cl, negatively charged K and positively charged Na)
Large uncharged polar molecules (polysaccharides and proteins)
Facilitated Diffusion
Diffusion through transport protein channels
Channels help move specific molecules across cell membrane
Still driven by concentration gradient (high to low concentration)
In what two ways does the membrane become semi-permeable?
Channel Proteins
Carrier Proteins
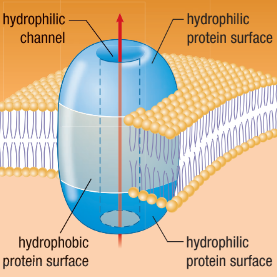
Channel Proteins
A hydrophilic pathway in a membrane that enables water and ions to pass through
Open tunnel
Specific channels allow specific material across cell membrane
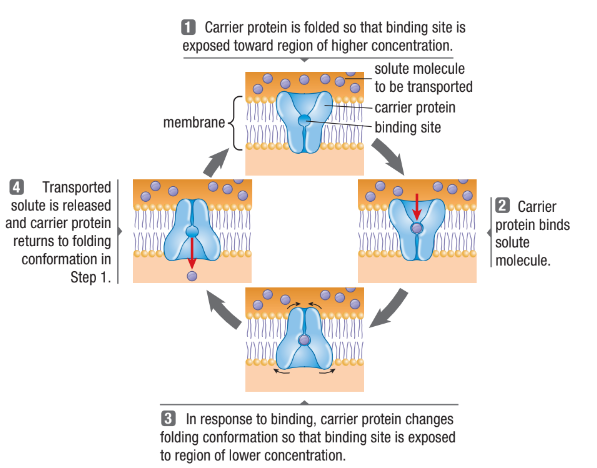
Carrier Proteins
Protein changes shape and allows the solute to enter/exit the cell
Form passageways through the lipid bilayer
Each binds to a specific solute and transports it across the bilayer
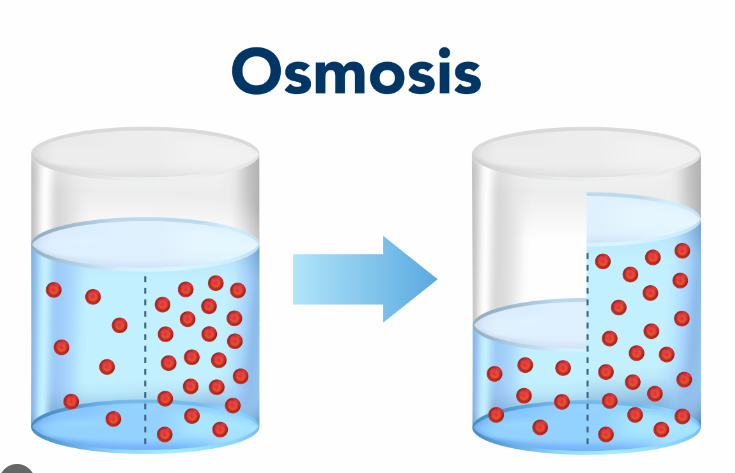
Osmosis
Diffusion of water from high concentration of water (low amount of solute) to low concentration of water (high amount of solute).
Water will move to the more concentrated side (more solute) to balance it out.
Across a semipermeable membrane
Water will always chase the hypertonic side (high amount of solute)
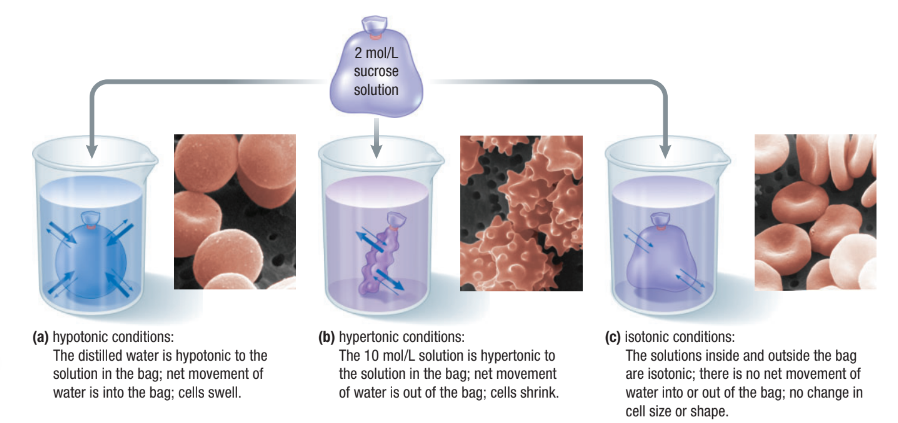
Concentration of Water
Direction of osmosis is determined by comparing total solute concentrations
Hypertonic: More solute, less water
Hypotonic: Less solute, more water
Isotonic: Equal solute, equal water
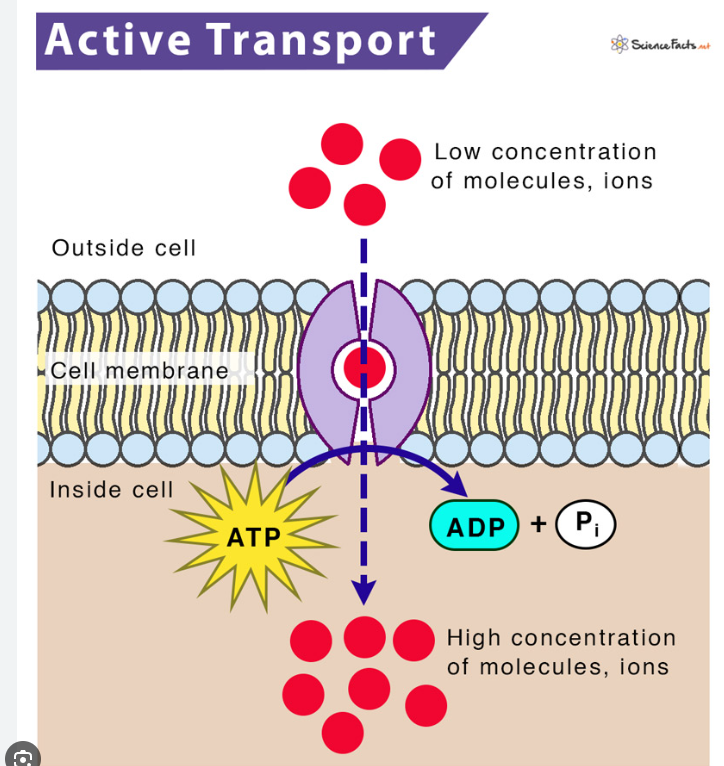
Active Transport
Cells may need to move molecules against concentration gradient
From low concentration to high concentration
Use of protein “pumps”
The term “active” refers to the fact that the cell has to expend energy = ATP
What are the two types of active transport?
Primary Active Transport
Secondary Active Transport Pumps
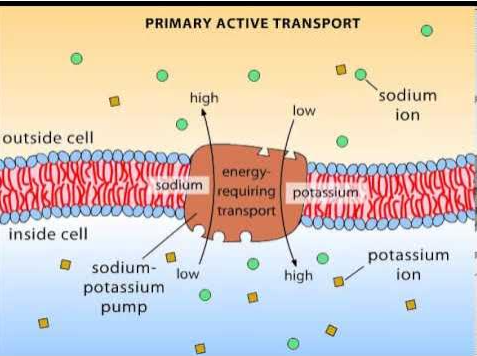
Primary Active Transport
Pumps (carrier proteins) that move positively charged ions across the membrane
Electrochemical Gradient:
Voltage across a membrane is a difference in electrical charge on either side of a membrane
Forms as a result of many positive cations on one side of a membrane compared to the other
Both the voltage difference and difference in ion concentration creates an electrochemical gradient
It is a form of stored potential energy which is used in nerve impulse transmission or to make ATP
Example of Primary Active Transport
Sodium-potassium pump (Na+/K+ pump)
Transports sodium ions (Na+) out of the cell and potassium ions (K+) into the cell, both against their concentration gradients.
This process is essential for maintaining cell membrane potential and regulating cell volume and ion balance.
Secondary Active Transport Pumps
Uses the concentration gradient of an ion set up by a primary active transport pump as its energy source
As the ion flows back along its concentration gradient, it brings a second molecule/ion along with it
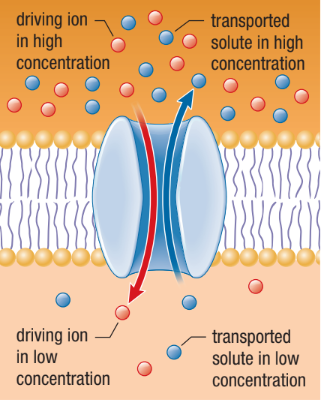
Symport
A solute that moves through the membrane channel in the same direction as the driving ion
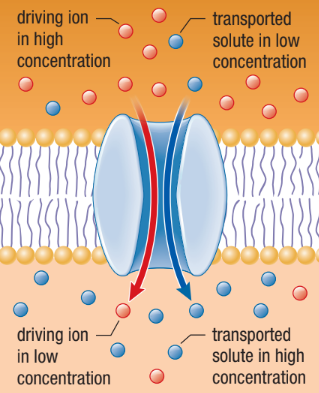
Antiport
The driving ion moves through the membrane in one direction providing energy for the transport of another molecule in the opposite direction