Hemoglobin Shifts and Carbon Dioxide
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
What does a right shift in the O2-hemoglobin dissociation curve mean?
Hemoglobin releases O2 more easily
What factors cause a right shift in the O2-hemoglobin dissociation curve?
⬆Increased temperature
⬇Decreased pH
⬆Increased 2,3-DPG
Why do temperature, pH, and 2,3-DPG changes matter during excercise?
They help hemoglobin release O2 to active tissues
Bohr Effect
High CO2 and low pH weaken Hb’s hold on O2, helping release O2 into tissues
Which gas is more soluble in blood - CO2 or O2?
CO2
What are the 3 ways CO2 is transported in blood?
Dissolved in plasma (10%)
Bound to globin part of Hb (30%)
As bicarbonate ions (60%)
How is CO2 turned into bicarbonate ions (HCO3-)?
CO2 enters RBC’s → carbonic anhydrase converts it to carbonic acid → breaks into H+ and HCO3-
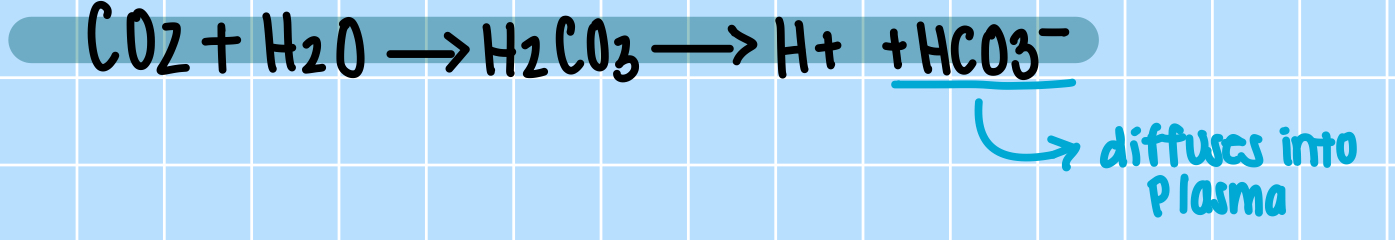
What enzyme converts CO2 to bicarbonate in RBC’s?
carbonic anhydrase
Which CO2 transport method is most common?
Bicarbonate transportation
When CO2 binds to hemoglobin, does it attach to iron?
No, it binds to amino acids in the globin chains
Chloride shift
Cl- enters RBC’s to balance the charge when HCO3- leaves