Ear Function and Structure
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
MI
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
cochlea
sound vibrations from the last bone of the middle ear are transmitted into this structure, which conducts the information to the brain through a nerve
malleus
this bone is attached to the tympanic membrane
pinna
cup-shaped, cartilaginous structure that gathers sound waves from the environment
tympanic membrane
this layer of skin/tissue separates the outer ear from the middle ear—it vibrates when struck by a sound wave
vestibular nerve
tied into the apparatus that helps with balance, this nerve can conduct information into the brain
stapes
this structure attached to the membrane-covered opening that connects the middle ear with the inner ear
eustachian tube
tube leading from the base of the middle ear to the back of your nose and upper part of your throat
internal auditory canal
sound travels down this canal to the tympanic membrane
incus
this structure is found within the middle of the chain of bones
oval window
structure on the cochlea that receives sound vibrations from the last bone of the middle ear
auditory nerve
tied into the hair cells lining the cochlea and this structure can convert the vibrations into electrical impulses to be transmitted to the brain
semicircular canals/vestibular apparatus
this structure detects motion by the movement of hair cells within it and can transmit this information to the brain to help us maintain our balance
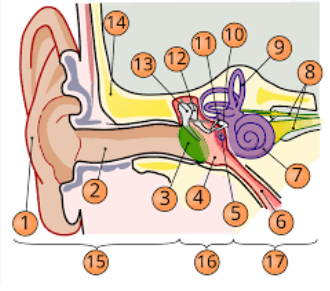
1
pinna
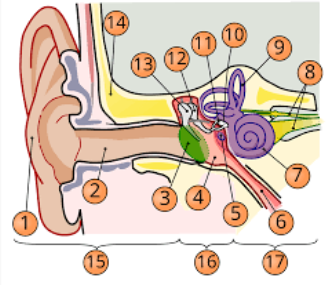
2
internal auditory cavity
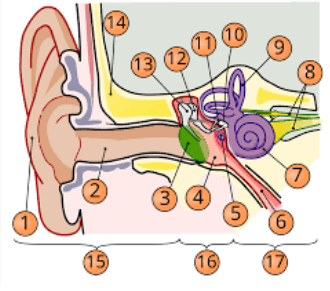
3
tympanic membrane
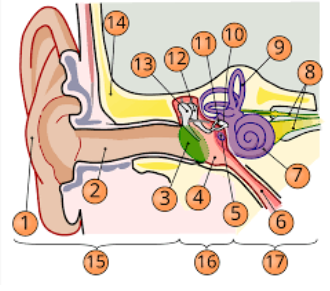
5
round window
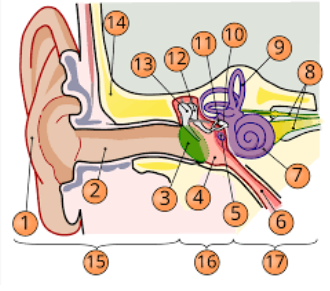
6
eustachian tube
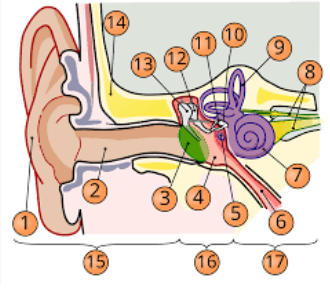
7
cochlea
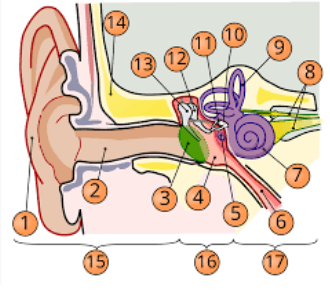
8
top arrow: vestibular nerve
bottom arrow: cochlear/auditory nerve
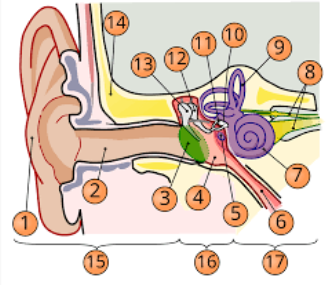
9
semicircular canal/vestibular apparatus
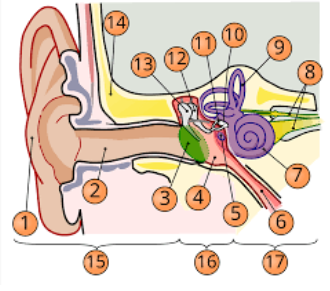
11
stapes
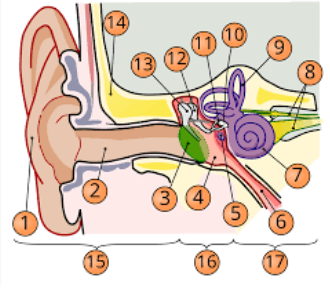
12
incus
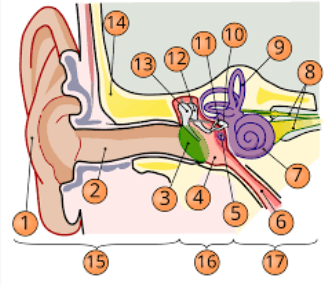
13
malleus