CFA Level 1 (Formulas/Main Concepts)
1/227
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
228 Terms
Future Value (FV) of a Single Cash Flow
FV = PV x (1+r)^n
where PV is the present value, r is the interest rate, and n is the number of periods.
Present Value (PV) of a Single Cash Flow
PV = FV / (1+r)^n
where FV is the future value, r is the interest rate, and n is the number of periods.
Present Value (PV) of Perpetuity
PV (perpetuity) = A / r
A= payment amount
Effective Annual Rate (EAR)
EAR = (1 + Periodic Rate)^m - 1
Periodic Rate = State Annual Rate / Number of Compounding Periods One Year
m = Number of Compounding Periods One Year
Arithmetic Mean
Sum of all observation values in sample/population, divided by # of observations
Geometric Mean
Gr = [(1+R1) x … x (1+Rn)(1/n) - 1
Harmonic Mean
Harmonic Mean = N / Σ(1/xi)
ex. N/(1/x1)x(1/x2)
Largest to Smallest of Quant Means
Arithmetic > Geometric > Harmonic
Skew and Mean/Median/Mode Relationship
Negative Skew: Mean < Median < Mode
Positive Skew: Mean > Median > Mode
In a negatively skewed distribution, the mean is less than the median, which is less than the mode, whereas in a positively skewed distribution, the mean is greater than the median, which is greater than the mode.
Weighted Average Mean
Xw = ∑ Wi x Xi
Mean Absolute Deviation
MAD = ∑ | Xi - X̄| / n
Percentile
Percentile = Ly = (n + 1) x (y/100)
Quartile = Distribution / 4
Quintile = Distribution / 5
Decile = Distribution / 10
Trimmed Mean
A trimmed mean is a statistical measure that adjusts the mean by removing a specified percentage of the lowest and highest values from a dataset, providing a more robust estimate of central tendency. This helps mitigate the influence of outliers.
Winsorized Mean
A Winsorized mean is a statistical measure that limits extreme values in the dataset to reduce the impact of outliers, typically by replacing the smallest and largest values with the nearest remaining values.
Population Variance
σ2 = ∑ (xi - μ)2 / N
Sample Variance
S2 = ∑ (xi - X̄ )2 / (n - 1)
Target Downside Deviation (Semi - Deviation)
STarget = √(∑ ( Xi - target)2 / n-1)
The sum of the numerator and denominator together is used to calculate the average of squared deviations from the specified target, providing a measure of downside risk.
Coefficient of Variation
CV = Standard Deviation of x / Average Value of x
CV = Sx / X̄
Coefficient of Variation: expresses how much dispersion exists relative to mean of a distribution; allows for direct comparison of dispersion across different data sets. CV is calculated by dividing standard deviation of a distribution by the mean or expected value of the distribution
Probability of A or B
P (A or B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(AB)
Joint Probability of Two Events
P(AB) = P(A|B) x P(B)
Conditional Probability of A given B
P(A|B) = P(AB) / P(B)
Expected Return (expected value of a random variable)
E(X) = ∑ P(X1)X1
E(X) = P(X1)X1 + P(X2)X2 +…+ P(Xn)Xn
Expected Variance (square root for std.dev.) / Probabilistic Variance
σ2(X) = ∑ P(Xi) [Xi - E(X)]2
σ2(X) = P(X1) [X1 - E(X)]2 + P(X2) [X2 - E(X)]2 …
Portfolio Expected Return
E(Rp) = wAE(RA) + wBE(RB)
Just R instead of E(R) if its actual returns
Portfolio Variance
Var(RP) = (wA2 x σ2(RA)) + (wB2 x σ2(RB)) + 2wAwBσ(RA)σ(RB)ρ(RA,RB)
Correlation
corr(Ri,Rj) = Cov(Ri,Rj) / (σ(Ri)σ(Rj))
Covariance
cov(Xi,Yj) = E[Xi - E(Xi) (Yj - E(Yj)]
Roy’s Safety - First Ratio
= r̄p - rtarget / σp
Portfolio with the highest ratio is preferred
Log Lin Model
ln(yi) = b0 + b1(xi) + ε (error term)
Relevant change in the dependent variable and an absolute change in the independent variable
Lin Log Model
yi = b0 + b1(ln(xi)) + ε (error term)
Absolute change in the dependent variable and a relative change in the independent variable
Log Log Model
ln(yi) = b0 + b1(ln(xi)) + ε (error term)
Relative change in boththe dependent and independent variables.
Beta
Betai = covi,mkt / varmkt
Joint Probability of any number of independent events
P(ABCDE) = P(A) x P(B) x P(C) x P(D) x P(E)
Bayes Formula
P(Event | Information) = [ P(Information | Event) / P(Information) ] x P(Event)
Normal Distributions
Normal Distribution is completely described by its mean and Variance
68% of observations fall with ± 1σ
90% of observations fall with ± 1.65σ
95% of observations fall with ± 1.96σ
99% of observations fall with ± 2.58σ
Computing Z - Scores
x - μ / σ
Degrees of Freedom of a Students’ T-distribution
df = number of sample observations -1 = n-1
Central Limit Theorem
When selecting simple random samples of size n from population with mean µ and finite variance σ2 , the sampling distribution of sample mean approaches normal probability distribution with mean µ and variance equal to σ2 /n as the sample size becomes large.
Standard Error the Sample Mean
Standard error of the sample mean is the standard deviation of distribution of the sample means.
known population variance: σx = σ / √n
unknown population variance: Sx = S / √n
Resampling Techniques (Jackknife and bootstrap)
Jackknife: Calculate multiple sample means, each with one observation removed, the calculate standard deviation of the sample means
Bootstrap: Draw repeated samples of size n from the full dataset, replacing the sampled observations each time, then calculate the standard deviation of the sample means
Null and Alternative Hypothesis
Null Hypothesis (Ho) : hypothesis that contains the equal sign (=, <=, >=)
Alternative Hypothesis (HA) : concluded if there is sufficient evidence to reject the null hypotheses
Type I and Type II Errors
Type I Error = rejecting the null hypothesis when it is true
Type II Error = failing to reject the null hypothesis when it is false.
Hypothesis Tests
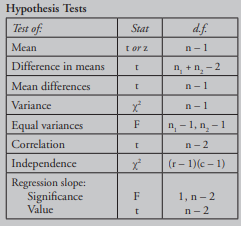
Power of a Test
1 - P(Type II Error)
Significance Level
Given a significance level of 5% (Confidence interval 95%), a test will reject a true null hypothesis 5% of the time
Regression Coefficient
Y = b0 +b1X1 + εi
Where:
Y= Dependent Variable
X= Independent Variable
b0 = Intercept Term
b1 = Slope Term
ε = Error Term (Residual)
Estimated Intercept and Slope Terms
b0 = ȳ - bix̄
b1 = COVXY / σ2X
Analysis of Variance (ANOVA)
Total sum of squares (SST) = sum of squared differences between actual Y-values and the mean of Y
Sum of squares regression (SSR) = sum of squared distances between predicted Y-values and the mean of Y
Sum of squared errors (SSE) = sum of squared distances between actual and predicted Y-values
Coefficient of Determination
Coefficient of Determination R2 = SSR/SST = percentage of variation in the dependent variable explained by variation in the independent variable
Explained Variance / Total Variance
Assumptions of Simple Linear Regression (Linearity, Homoscedasticity, Independence, Normality)
Linearity: A linear relation exists between the dependent variable and the independent variable
Homoscedasticity: Variance of the error term is the same for all observations
Independence: The error term is uncorrelated across observations
Normality: the error term is normally distributed
TSS (total sum of squares)
TSS = SSE + RSS
SSE: sum of the squared errors (unexplained variance)
RSS: regression sum of squares (explained variance)
Breakeven and Shutdown Points
Breakeven Point: Total Revenue = Total Cost
Shutdown Point (short run): Total Revenue < Total Variable Cost
Shutdown Point (long run): Total Revenue < Total Cost
Market/Firm Structures
Perfect competition: Many firms with no pricing power; very low or no barriers to entry; homogeneous product.
Monopolistic competition: Many firms; some pricing power; low barriers to entry; differentiated products; large advertising expense.
Oligopoly: Few firms that may have significant pricing power; high barriers to entry; products may be homogeneous or differentiated.
Monopoly: Single firm with significant pricing power; high barriers to entry; advertising used to compete with substitute products. In all market structures, profit is maximized at the output quantity for which marginal revenue = marginal cost
Profit Maximization Point (All Firms)
Marginal Revenue = Marginal Cost
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
GDP Expenditure Approach) = Consumption + Investments + Government Spending + New Exports
GDP (Income Approach) = Household Income + Business Income + Government Income
GDP ( Value-Added Approach): Sum incremental value-added at each stage of production
Nominal and Real GDP
Nominal GDP = (Deflator x Real GDP) / 100
Real GDP = Nominal / Deflator
GDP Deflator = (Value of current year output at current prices / Value of current year output at base year prices) x 100
Savings, Investments, Fiscal Balance, and Trade Balance
Fiscal budget deficit (G - T) = excess of saving over domestic investments (S - I) - trade balance (X - M)
S= Private Savings
I= Gross private domestic investment. It consists of business investments in capital goods as well as inventory changes.
G= Government expenditure on finished goods and services
X= Export
M= Imports
Aggregate Demand and Supply
AD: shifts due to changes in household wealth, consumer and business expectations, capacity utilization, monetary policy, fiscal policy, exchange rates and foreign GDP
AS:
Short-Run Shifts: changes in changes in potential GDP, nominal wages, input prices, future price expectations, business taxes and subsidies and exchange rate
Long-Run Shifts: changes in labor supply, supply of physical and human capital and productivity and technology
Growth Accounting Equation
Growth in Potential GDP = growth in technology + growth in labor + growth in capital
Business Cycles
Trough (lowest point); expansion; peak (highest point); contraction
Expansion: Rising GDP, decreasing unemployment,
Credit Cycles
Tend to amplify business cycles, and do not coincide (tend to last longer)
Characteristics of the 4 Stages of the Business Cycle
Trough:
The GDP growth rate changes from negative to positive.
There is a high unemployment rate, and an increasing use of overtime and temporary workers.
Spending on consumer durable goods and housing may increase.
There is a moderate or decreasing inflation rate.
Expansion:
The GDP growth rate increases.
The unemployment rate decreases as hiring accelerates.
There are investment increases in producers' equipment and home construction.
The inflation rate may increase.
Imports increase as domestic income growth accelerates.
Peak:
The GDP growth rate decreases.
The unemployment rate decreases, but hiring slows.
Consumer spending and business investments grow at slower rates.
The inflation rate increases.
Contraction/recession:
The GDP growth rate is negative.
Hours worked decrease; unemployment rate increases.
Consumer spending, home construction, and business investments decrease.
The inflation rate decreases with a lag.
Imports decrease as domestic income growth slows.
Economic Indicators
Leading: Turning points occur ahead of peaks and troughs (S&P 500, manufacturing new orders, building permits)
Coincident: Turns coincide with peaks and troughs (employee payrolls, manufacturing sales, personal income)
Lagging: Turns after peaks and troughs (average prime rate, inventory-sales ratio, duration of unemployment)
Types of Unemployment
Frictional: Unemployment from time lag to find new job
Cyclical: Unemployment due to business cycle fluctuations
Structural: Unemployment due to lack of skills for job openings or distance factors
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
CPI =( Cost of basket at current prices / cost of basket at base period prices) x 100
Monetary Policy (expansion vs contraction)
Central bank activities that influence the supply of money and credit;
expansionary when policy rate < neutral interest rate
contractionary when policy rate > neutral interest rate
Central Bank Objectives
Full employment and Price Stability
Money Multiplier
= 1 / reserve requirement
Fiscal Policy
Fiscal Policy: government decisions about taxation and spending
expansionary when a budget deficit is increasing or surplus is decreasing
contractionary when a budget deficit is decreasing or a surplus is increasing
Fiscal Multiplier
= 1/ 1 - MPC(1-t)
Balance of Payments
Current account: measures flow of goods and services (merchandise and services; income receipts; unilateral transfers)
Capital account: measures transfers of capital (capital transfers; sales/purchases of nonfinancial assets)
Financial account: records investment flows (government-owned assets abroad; foreign-owned assets in the country)
Regional Trade Agreements
Free trade area: Removes barriers to goods and services trade among members.
Customs union: Members also adopt common trade policies with non-members.
Common market: Members also remove barriers to labor and capital movements among members.
Economic union: Members also establish common institutions and economic policy.
Monetary union: Members also adopt a common currency
Exchange Rate
Price Currency / Base Currency
(base is 1)
Real Exchange Rate
Nominal FX rate x [(base currency CPI) / (price currency CPI)]
No-Arbitrage Forward Exchange Rate
= Spot Rate x [(1 + price currency interest rate) / (1 + base currency interest rate)]
Exchange Rate Regimes
Formal dollarization: country adopts foreign currency.
Monetary union: members adopt common currency.
Fixed peg: ±1% margin versus foreign currency or basket of currencies.
Target zone: Wider margin than fixed peg.
Crawling peg: Pegged exchange rate adjusted periodically.
Crawling bands: Width of margin increases over time.
Managed floating: Monetary authority acts to influence exchange rate but does not set a target.
Independently floating: Exchange rate is market determined
Financial Statement Analysis Framework
1. State the objective and context
2. Gather data
3. Process the data
4. Analyze and interpret the data
5. Report conclusions or recommendations
6. Update the analysis
Auditors Opinion
Unqualified (unmodified, clean): Reasonable assurance that financial statements are free from material omissions and errors.
Qualified: Exceptions to accounting principles.
Adverse: Statements are not presented fairly or do not conform with accounting standards.
Disclaimer of opinion: Auditor is unable to express an opinion.
Revenue Recognition Principles
Requirements: 1) risk and reward of ownership is transferred, 2) collectability is probable
Five-step revenue recognition model:
1. Identify contracts
2. Identify performance obligations
3. Determine transaction price
4. Allocate price to obligations
5. Recognize when (as) obligations are satisfied
Expense Recognition Principles (matching)
Matching Principle: Match expenses with the revenues they help generate
Basic Earnings Per Share (EPS)
Basic EPS = (net income - preferred Dividends) / Weighted average # of common shares outstanding
Diluted EPS
Diluted EPS = (adj. income avail. for common shares) / ( wtd. avg. common shares plus potential common shares outstanding)
Diluted EPS = [(net income - pfd div) + convertible preferred dividends − (convertible debt interest) x (1-t)] / ([wtd. avg shares)+ shares from conversion of conv. pfd. share) + (shares from conversion conv debt) + (shares issuable from stock options)]
Marketable Security Classifications
Held-for-trading: fair value on balance sheet; dividends, interest, realized and unrealized G/L recognized on income statement.
Available-for-sale: fair value on balance sheet; dividends, interest, realized G/L recognized on income statement; unrealized G/L is other comprehensive income.
Held-to-maturity: amortized cost on balance sheet; interest, realized G/L recognized on income statement.
Comprehensive Income
= Net Income + Other Comprehensive Income
IFRS vs U.S. GAAP
IFRS
Interest Received: Operating or Investing
Interest Paid: Operating or Financing
Dividends Received: Operating or Investing
Dividends Paid: Operating or Financing
U.S. GAAP
Interest Received: Operating
Interest Paid: Operating
Dividends Received: Operating
Dividends Paid: Financing
Cash Flows from Operations (CFO)
Direct method: start with cash collections (cash equivalent of sales); cash inputs (cash equivalent of cost of goods sold); cash operating expenses; cash interest expense; cash taxes.
Indirect method: start with net income, subtracting back gains and adding back losses resulting from financing or investment cash flows, adding back all noncash charges, and adding and subtracting asset and liability accounts that result from operations
Increase in a Current Asset: -
Decrease in a Current Asset +
Increase in a Current Liability: -
Decrease in a Current Liability: +
Free Cash Flow (FCF)
Free Cash Flow (FCF) measures cash available for discretionary purposes and is equal to operating cash flow less net capital expenditures
Free Cash Flow to the Firm (FCFF)
FCFF = NI + NCC + Int(1 - tax rate) - FCInv - WCInv
FCFF = CFO + Int(1 - Tax rate) - FCInv
NCC = Net Noncash Charges
FCInv = Fixed Capital Investments
WCInv = Working Capital Investments
Free Cash Flow to Equity (FCFE)
FCFE = CFO - FCInv + Net Borrowing
FCFE = NI + NCC - CapEx - ∆Working Captital + Net Borrowing
NCC = Net Noncash Charges
FCInv = Fixed Capital Investments
Common-Size Financial Statement Analysis (Balance Sheet, Income Statement, Cash Flow Statement)
Common size balance sheet expresses all balance sheet accounts as a percentage of total assets
Common size income statement expresses all income statement items as a percentage of sales
Common size Cash Flow Statement expresses each line item as a percentage of net revenue
Horizontal common-size financial statements analysis expresses each line item relative to its value in a common base period
Liquidity Ratios: Current Ratio, Quick Ratio, Cash Ratio
Current Ratio = current assets / current liabilities
Quick ratio = cash + marketable securities + receivables / current liabilities
Cash Ratio = Cash + marketable securities / current liabilities
Defense Interval
Defense Interval = cash + mkt. sec. + receivables / daily cash expenditures
Cash Conversion Cycle
CCC = DOH + DSO - DPO
where DOH is Days of Inventory Held, DSO is Days Sales Outstanding, and DPO is Days Payable Outstanding.
Receivables Turnover
Days Sales Outstanding (DSO)
Receivables Turnover = Annual sales / average receivables
DSO = 365 / Receivables turnover
Inventory Turnover
Days Inventory on Hand
Inventory Turnover = COGS / average inventory
Days Inventory on Hand = 365 / Inventory Turnover
Payables Turnover Ratio
Number of Days Payables
Payables Turnover Ratio = Cogs / Average Payables
DPO = 365 / Payables turnover ratio
Total Asset Turnover
Fixed Asset Turnover
Working Capital Turnover
Total asset turnover = Revenue / average total assets
Fixed asset turnover = Revenue / average fixed assets
Working capital turnover = Revenue / average working capital
Gross Profit Margin
Operating Profit Margin
Net Profit Margin
ROA
ROE
Gross profit margin = gross profit / revenue
operating profit margin = operating profit / revenue = EBIT / net sales
net profit margin = net income / revenue
ROA = net income / average total assets
ROE = net income / average total equity
Return on Total Capital (ROTC)
return on assets (total capital) = EBIT / average total capital
Debt to assets (total debt) ratio
Debt to equity ratio
Financial leverage
Debt - Assets = Total Debt / Total Assets
Debt - Equity = Total Debt / Total Equity
Financial Leverage = Total Assets / Total Debt