Physical Landscapes in the UK: Coastal
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
1
New cards
Where are the UK’s uplands?
* Above the line drawn from the River Tees to the River Exe
* All highlands and mountains are generally separated by low areas
* All of Scotland and Wales are therefore considered uplands
* Also includes Northern Ireland
* All highlands and mountains are generally separated by low areas
* All of Scotland and Wales are therefore considered uplands
* Also includes Northern Ireland
2
New cards
Where are the UK’s lowlands?
* Below the line drawn from the River Tees to the River Exe
\
\
3
New cards
Describe constructive waves
* Found in sheltered bays - build sandy beaches
* More common in summer
* Swash stronger than backwash
* Build up beaches
* More common in summer
* Swash stronger than backwash
* Build up beaches
4
New cards
Describe destructive waves
* Found in exposed bays - build up pebbled beaches
* More common in winter
* Stronger than a constructive wave in general
* But backwash is stronger than its swash
* Force generated by a breaking destructive wave can erode a headland
* More common in winter
* Stronger than a constructive wave in general
* But backwash is stronger than its swash
* Force generated by a breaking destructive wave can erode a headland
5
New cards
Describe all the weathering processes
mechanical
chemical
(pg 124)
chemical
(pg 124)
6
New cards
Describe all the types of mass movement
sliding
slumping
rock falls
(pg 124)
slumping
rock falls
(pg 124)
7
New cards
What is erosion?
The removal of material by waves
8
New cards
What is weathering?
The breaking down of rock where it is
9
New cards
What is mass movement?
The downslope movement of rock, soil or mud under the influence of gravity
10
New cards
What is a landslide?
The downhill movement of a large amount of rock, soil or mud
11
New cards
Describe all the types of erosion
hydraulic power
abrasion
attrition
(pg 126)
abrasion
attrition
(pg 126)
12
New cards
How is sediment transported along a coast?
Longshore drift
The direction is determined by prevailing wind
\
The direction is determined by prevailing wind
\
13
New cards
What conditions cause deposition?
* Where constructive waves are dominant
* A large source of sediment updrift
* When tidal material is trapped behind a spit
* Where engineered structures like groynes trap sediment
* A large source of sediment updrift
* When tidal material is trapped behind a spit
* Where engineered structures like groynes trap sediment
14
New cards
How do hard and soft rocks affect landforms?
Hard rocks are less easily eroded than soft rocks
They therefore project into the sea as headlands and form high cliffs
Soft rocks are eroded faster, and become bays
this forms headlands and bays
They therefore project into the sea as headlands and form high cliffs
Soft rocks are eroded faster, and become bays
this forms headlands and bays
15
New cards
How does rock structure affect landforms?
* How rocks are aligned in relation to the coast (concordant or discordant)
* How rocks dup down to the sea as a result of folding
\
* How rocks dup down to the sea as a result of folding
\
16
New cards
What is a disconcordant coast?
Where there are alternating layers of hard and soft rock almost at right angles to the shore
17
New cards
What is a concordant coast?
Where the alternating layers of rock run parallel to the coast
18
New cards
What are the characteristics of a headland?
* Near vertical cliff face
* Hard rock jutting out to sea
* High energy area affected by destructive waves
* Caves forming in its sides
* Land rising steeply behind the cliff
* Hard rock jutting out to sea
* High energy area affected by destructive waves
* Caves forming in its sides
* Land rising steeply behind the cliff
19
New cards
What are the characteristics of a bay?
* Soft rock forming a crescent-shaped beach
* Low energy constructive waves
* Two headlands marking the edges of the bay
* Low energy constructive waves
* Two headlands marking the edges of the bay
20
New cards
How are headlands and bays formed?
* Discordant coastline has rocks of different hardness
* They have different rates of erosion
* Soft rocks are eroded at faster rate than hard rocks
* This results in hard rocks jutting out while soft rocks rescinding
* Once the pattern has emerged, the processes reverse
* Sheltered bays become low-energy environments where deposition occurs
* Exposed headlands become targets for erosion
* They have different rates of erosion
* Soft rocks are eroded at faster rate than hard rocks
* This results in hard rocks jutting out while soft rocks rescinding
* Once the pattern has emerged, the processes reverse
* Sheltered bays become low-energy environments where deposition occurs
* Exposed headlands become targets for erosion
21
New cards
What are the characteristics of cliffs?
* Hard rock
* Horizontal bedding
* Layers of harder rock jutting out
* Near-vertical bare rock cliff face
* Wave-cut notch at the base
* Horizontal bedding
* Layers of harder rock jutting out
* Near-vertical bare rock cliff face
* Wave-cut notch at the base
22
New cards
What are the characteristics of a wave-cut platform?
* Slopes down to the sea gently
* Bare rock, smoothed in places by attrition
* Deep cracks in some places
* Bare rock, smoothed in places by attrition
* Deep cracks in some places
23
New cards
How are cliffs and wave-cut platforms formed?
* Land slopes down to the sea
* Weathering weakens the rock
* Erosion is concentrated between the high and low watermark
* Hydraulic action and abrasion erode the base
* Continued erosion causes rock to break away and collect at the base of the cliff 0 destructive waves remove this material
* Therefore there is a notch at the base
* The notch is eventually enlarged to the point where the overhanging cliff breaks away and falls onto the beach due to gravity
* Cliff retreats, and the wave cut platform will be continuously smoothed by shingle grinding over it
* Weathering weakens the rock
* Erosion is concentrated between the high and low watermark
* Hydraulic action and abrasion erode the base
* Continued erosion causes rock to break away and collect at the base of the cliff 0 destructive waves remove this material
* Therefore there is a notch at the base
* The notch is eventually enlarged to the point where the overhanging cliff breaks away and falls onto the beach due to gravity
* Cliff retreats, and the wave cut platform will be continuously smoothed by shingle grinding over it
24
New cards
How are caves, arches and stacks formed?
* a large crack in enlarged due to hydraulic power
* the crack grows into a notch and then a cave as destructive waves continue to erode it
* the cave becomes larger over time
* the caves form back to back
* the sea breaks through the back of the caves, forming an arch
* weathering continues to weaken the top of the arch
* the top of the arch eventually collapses
* this leaves behind a pillar called a stack
* the stack will eventually topple, leaving only a base
* the crack grows into a notch and then a cave as destructive waves continue to erode it
* the cave becomes larger over time
* the caves form back to back
* the sea breaks through the back of the caves, forming an arch
* weathering continues to weaken the top of the arch
* the top of the arch eventually collapses
* this leaves behind a pillar called a stack
* the stack will eventually topple, leaving only a base
25
New cards
Characteristics of a sea arch?
* Unsupported top
* Wave-cut notches at the base
* Wave-cut notches at the base
26
New cards
How are Sandy beaches formed?
* low energy constructive waves transport material onto the shore
* Awash is stronger than backwash, so sediment is slowly but constantly moved up the beach
* Awash is stronger than backwash, so sediment is slowly but constantly moved up the beach
27
New cards
How are pebble beached formed
* plunging nature of destructive waves w/strong backwash means that pebbled are not moved far up the beach
* Beach profile is steep
* Storm beach may form when there is wild, storm weather
* Waves hurl large pebbles to back of beach
* Beach profile is steep
* Storm beach may form when there is wild, storm weather
* Waves hurl large pebbles to back of beach
28
New cards
Characteristics of sandy beach
Gradient: shallow
Dominant wave: constructive
Distance stretches inland: far
Back of beach p: sand dunes
Other: sand may have a rippled appearance
Dominant wave: constructive
Distance stretches inland: far
Back of beach p: sand dunes
Other: sand may have a rippled appearance
29
New cards
Characteristics of a pebble beach
Gradient: steep
Dominant wave: destructive
Distance stretches inland: not far
Back of beach: storm beach w/large pebbles
Other: pebbles increase in size towards back of beach
Dominant wave: destructive
Distance stretches inland: not far
Back of beach: storm beach w/large pebbles
Other: pebbles increase in size towards back of beach
30
New cards
What is a beach profile?
A beach profile shows the gradient from the back of the beach to the sea
31
New cards
What do sand dunes need to form?
* large flat beach
* Large supply of sand
* Large tidal range - time for sand to dry
* Onshore wind to move sand to back of the beach
* An obstacle for the dune to form against
* Large supply of sand
* Large tidal range - time for sand to dry
* Onshore wind to move sand to back of the beach
* An obstacle for the dune to form against
32
New cards
How does wind move the sand for a sand dune?
\
Saltation - 95%
Creep - 4%
Suspension - 1%
Saltation - 95%
Creep - 4%
Suspension - 1%
33
New cards
How does a sand dune form?
* heaviest grains of sand will settle against the obstacle to form a small ridge
* The area facing the wend eventually begin dos to reach a crest - this is because the pile of sand becomes so steep it becomes unstable and begins to collapse under its own weight
* Lighter grains of sand fall down the other side on the LEE cave
* Sand stops slipping at an angle of 30-34 degrees
* Repeated cycles causes the sand dune to migrate inland over time
* Sand dune might itself become an obstacle, so more dunes may form in front of it
* The area facing the wend eventually begin dos to reach a crest - this is because the pile of sand becomes so steep it becomes unstable and begins to collapse under its own weight
* Lighter grains of sand fall down the other side on the LEE cave
* Sand stops slipping at an angle of 30-34 degrees
* Repeated cycles causes the sand dune to migrate inland over time
* Sand dune might itself become an obstacle, so more dunes may form in front of it
34
New cards
Characteristics of a sand dune?
* Unstable, steep slip slope on leeward side
* Crests
* Gentle slope on windward side
* Crests
* Gentle slope on windward side
35
New cards
How so dunes change inland?
* grow taller
* Size increases
* Vegetation bind the sand together, preventing further migration
* Dunes closest to beach are yellow, dunes further back are grey
* Inland, dunes have more vegetation
* Each line of dunes is separated by a trough called a slack
* Pg 139
* Size increases
* Vegetation bind the sand together, preventing further migration
* Dunes closest to beach are yellow, dunes further back are grey
* Inland, dunes have more vegetation
* Each line of dunes is separated by a trough called a slack
* Pg 139
36
New cards
What is a spit?
A spit is a sand or shingle beach that is joined to the land but projects downland into the sea
They form where the coastline suddenly changes or at a river estuary
They form where the coastline suddenly changes or at a river estuary
37
New cards
How is a spit formed?
* when a coastline changes shape the waves begin to lost energy
* There is deposition and the spit grows out to sea
* The prevailing win makes the awash at a right angle to shore
* The pebbles become more rounded towards the end due to attrition
* They become smaller as the longshore drift becomes weaker
* There is deposition and the spit grows out to sea
* The prevailing win makes the awash at a right angle to shore
* The pebbles become more rounded towards the end due to attrition
* They become smaller as the longshore drift becomes weaker
38
New cards
characteristics of a spit?
* hooked distal end
* Mudflats and salt marshes
* Lagoons
* Large hook
* Pebbles become smaller towards end
* Mudflats and salt marshes
* Lagoons
* Large hook
* Pebbles become smaller towards end
39
New cards
What is a bar?
When the spit stretches from one side of a bay to the other, forming a lagoon behind it
40
New cards
How are bars formed?
* due to longshore drift transporting sediment from one side of a bay to the other
41
New cards
What are the characteristics of a bar?
* at high tide the bar is submerged and can only be identified by the waves that break on it
* At low tide a sandy beach running parallel to the shore is seen -this is a bar
* At low tide a sandy beach running parallel to the shore is seen -this is a bar
42
New cards
Name and describe all hard coastal management schemes
* sea walls
* rock armour
* gabions
* groynes
* (Pg142)
* rock armour
* gabions
* groynes
* (Pg142)
43
New cards
Name the benefits and costs for each hard coastal management scheme

44
New cards
Name and describe all the examples of soft engineering
* beach nourishment
* reprofiling
* dune regeneration
* (Pg 146)
* reprofiling
* dune regeneration
* (Pg 146)
45
New cards
What are the benefits and costs of each soft engineering scheme
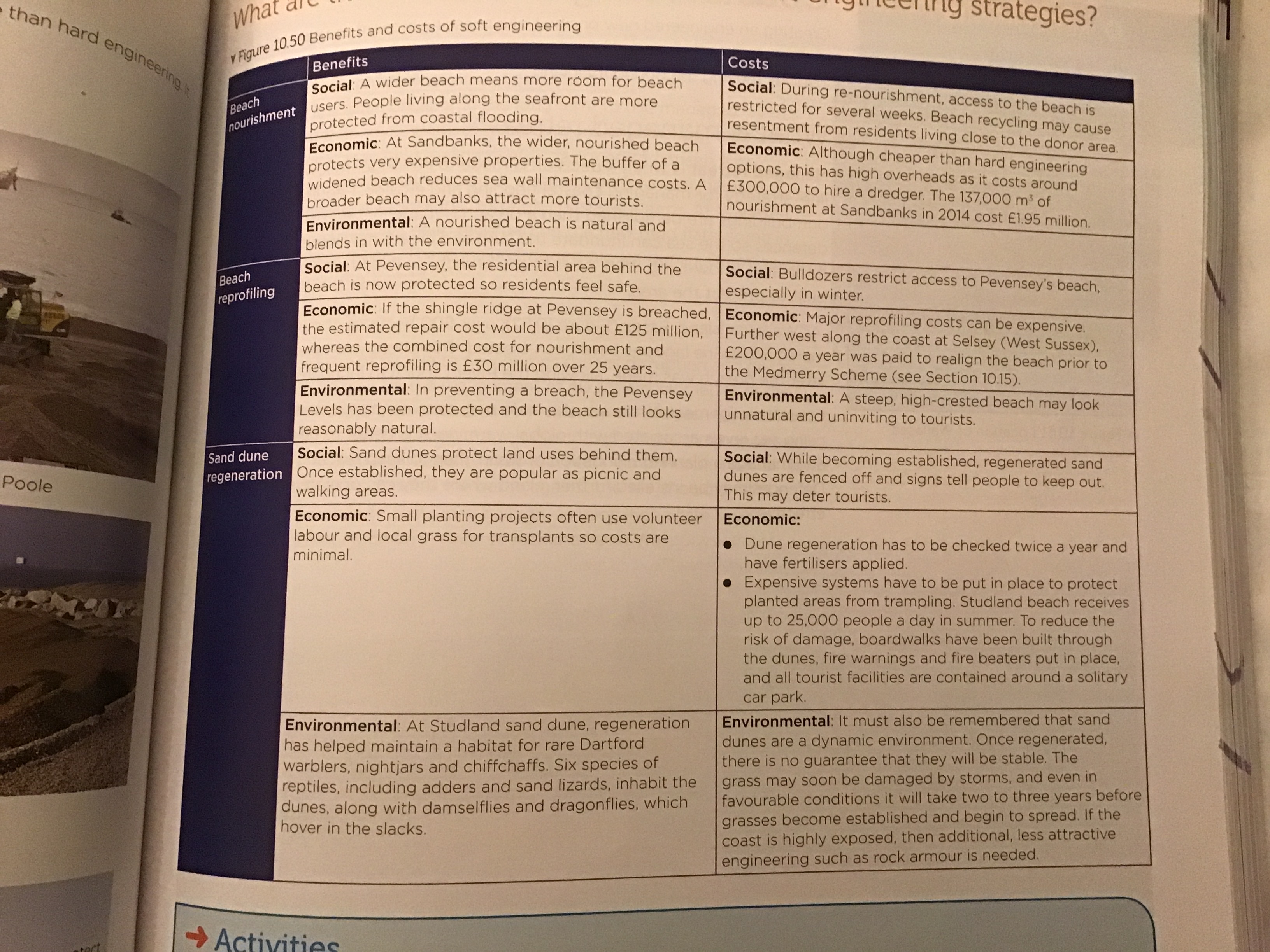
46
New cards
What is managed retreat?
When a decision is made to no longer follow a ‘hold the line’ strategy for managing coastal flooding and erosion. People are moved out, buildings are demolished, etc.
47
New cards
What are the benefits and costs of managed retreat?
