3. connective tissue
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
what are 6 examples of Connective Tissue?
Adipose Tissue
Tendon
Ligament
Cartilage
Bone
Blood
all connective tissues consist of
cells
extraceullar matrix
variation in connective tissues is due to
cell = type + function
matrix = qualities + volume relative to cells
extracelluar matrix
is a
gel-like watery substance that surrounds the outside of cells
Extraceullar Matrix
contains 2 things
Protein Fibers
Ground Substance
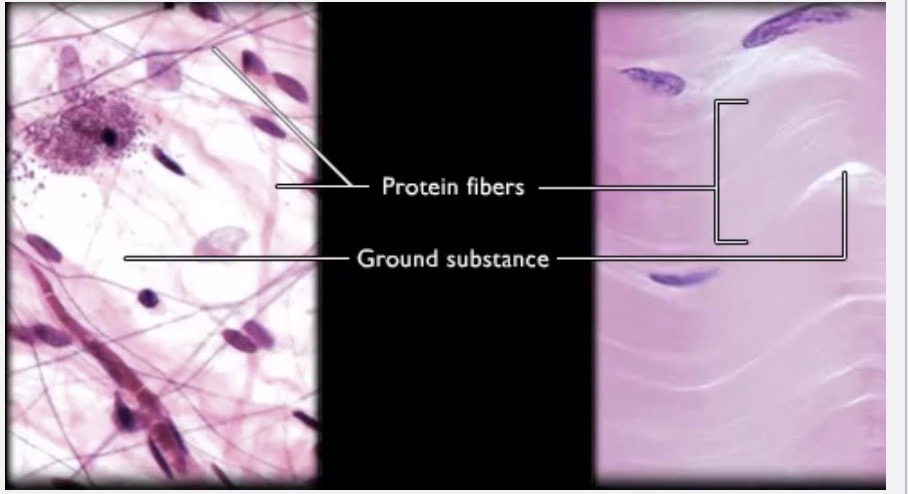
What are the 3 protein fibers?
Collagen
Elastin
Reticular
Ground Substance
is
the watery substance itself that holds a good amount of body’s water
Cytosol
is
gel-like watery substance inside the cell that holds the organeles
What are the 3 types of Connective Tissue ( CT )?
Fibrous CT
Supportive CT
Fluid CT
Fibrous Connective Tissue
includes what 2 types?
Loose Tissue
Dense Tissue
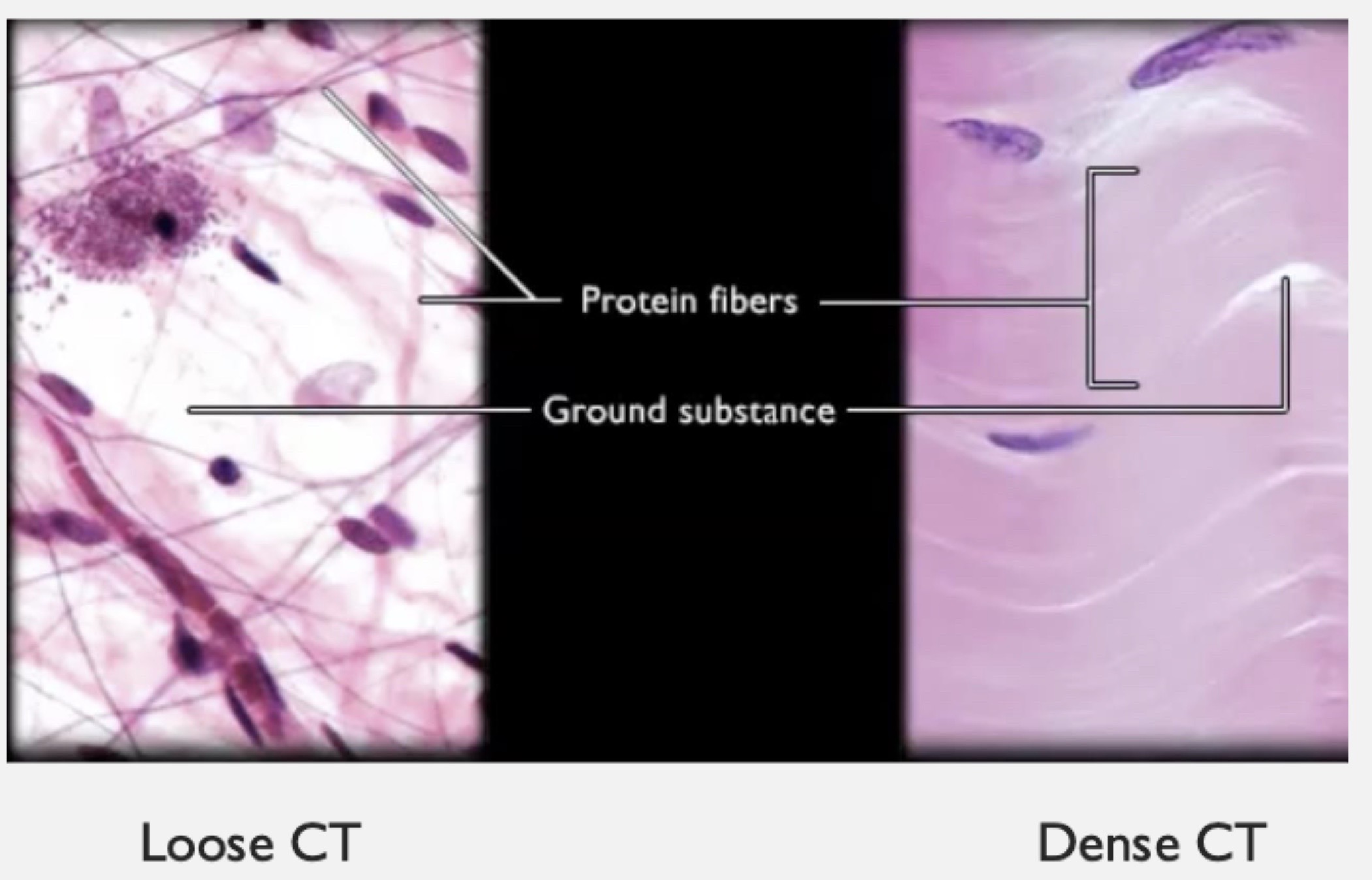
What’s the main protein fiber present in fibrous connective tissues?
collagen fiber
( tough + flexible + resists stretching )
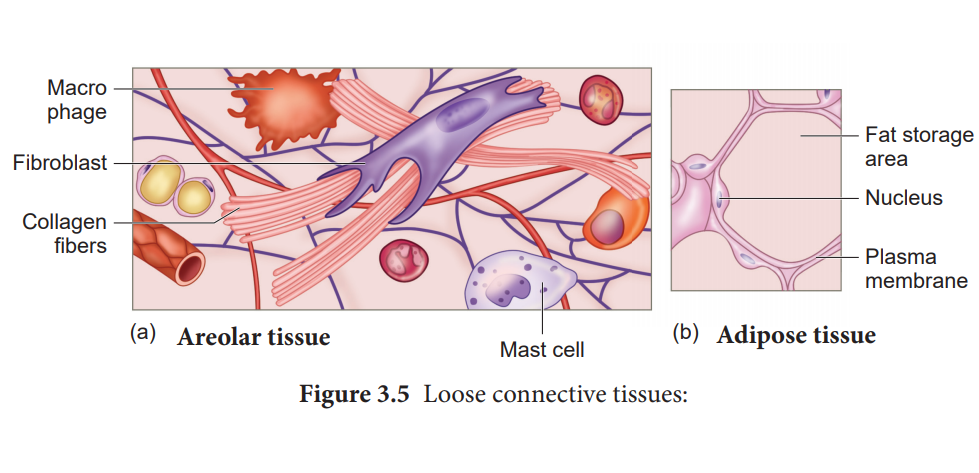
what other cells are present in fibrous connective tissue?
macrophages + leukocytes + plasma cells
adipocytes
fibroblasts
macrophages + leukocytes + plasma cells
will
help with immune response to protect the organ + tissue
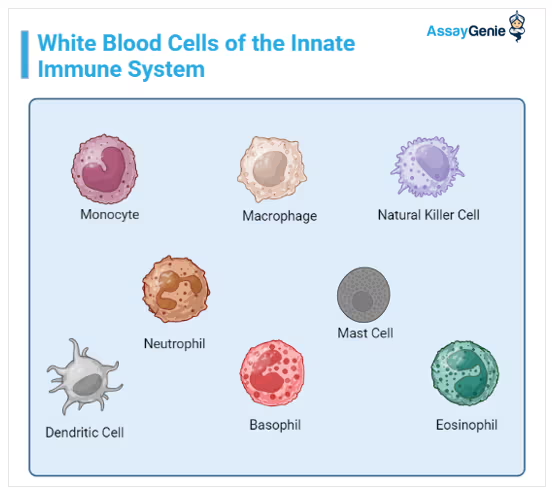
what tissue are they more abundant in?
loose connective tissue
Adipocytes
are also known as
fat cells
adipocytes ( fat cells ) group together to form
adipose tissue
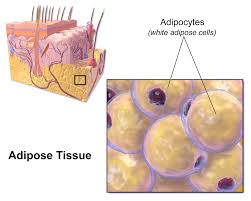
adipose tissue
will
provide insulation + energy storage
fibroblasts
will
produce
protein fibers ( collagen, elastin, reticular )
ground substance
of connective tissue’s extracellular matrix
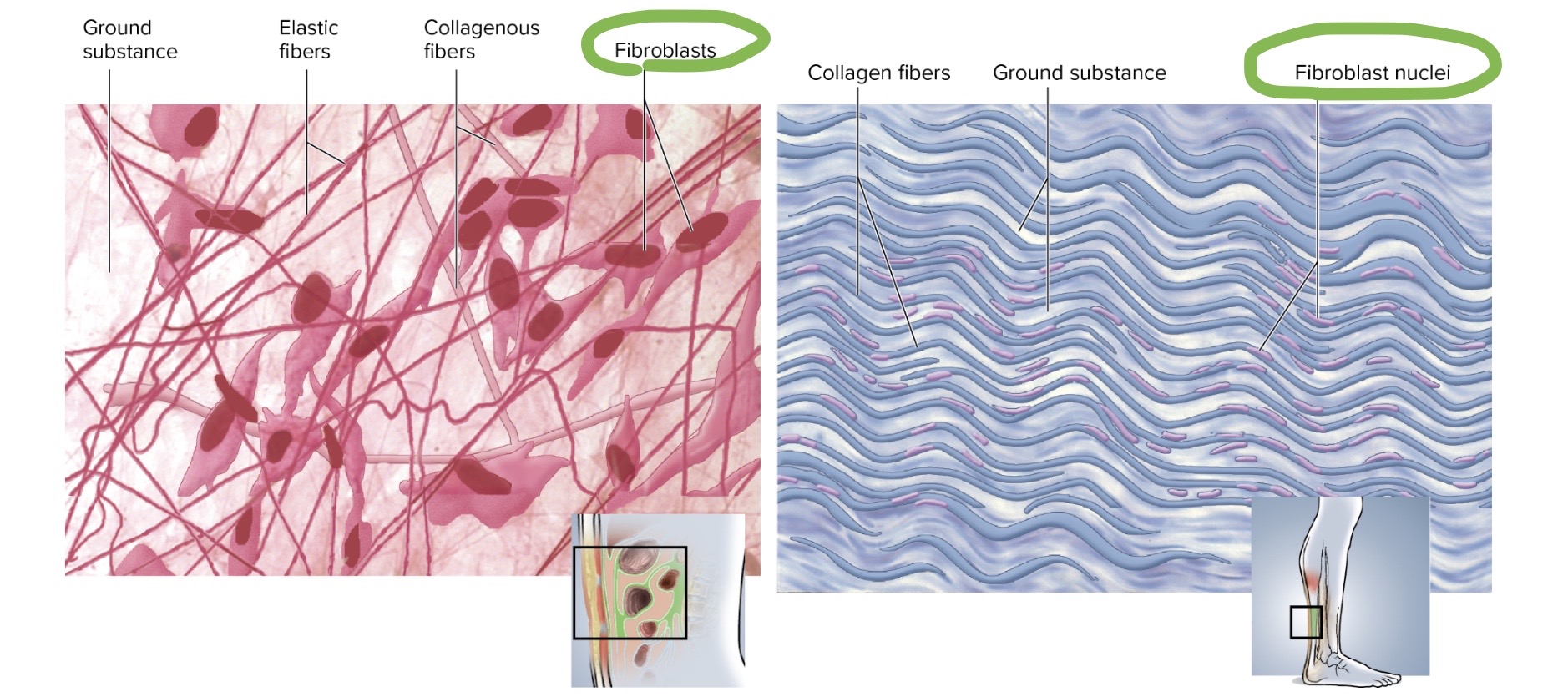
notice
it’s present in BOTH
loose connective tissue
dense connective tissue
Loose Connective Tissue
structure?
ground substance fills up more space than cells
+ loosely packed fibers
What are the 3 types of Loose Connective Tissue?
Areolar
Adipose
Reticular
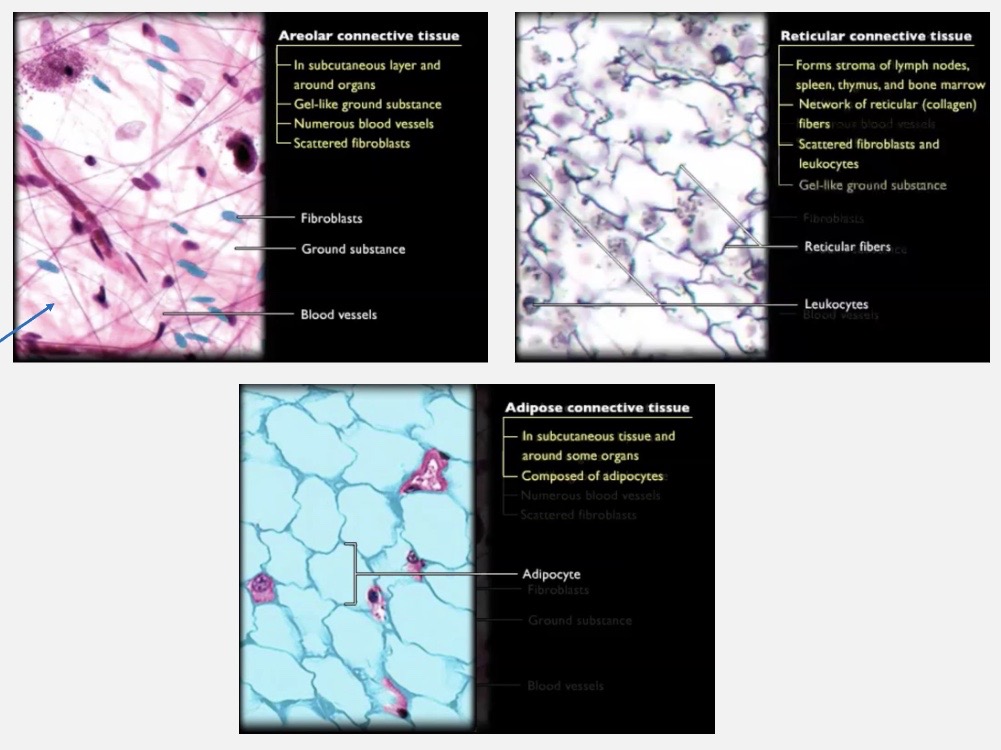
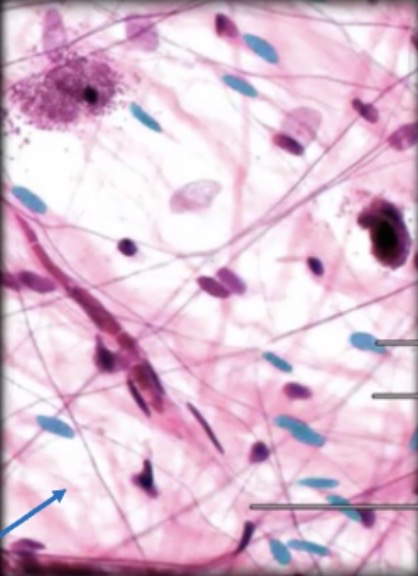
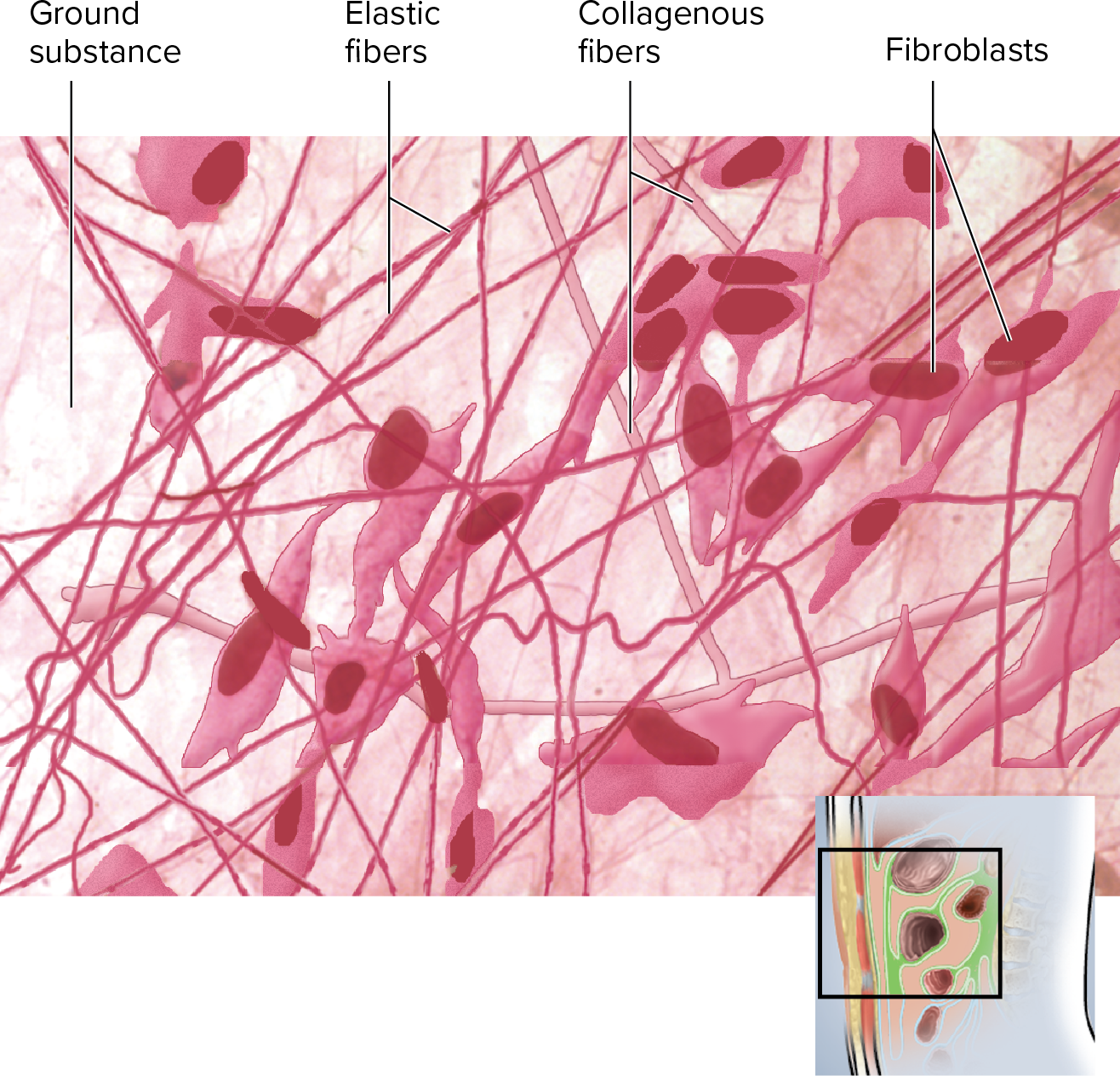
Areolar Connective Tissue
Areolar Tissue
will
connects + supports organs and tissues to provide flexibility
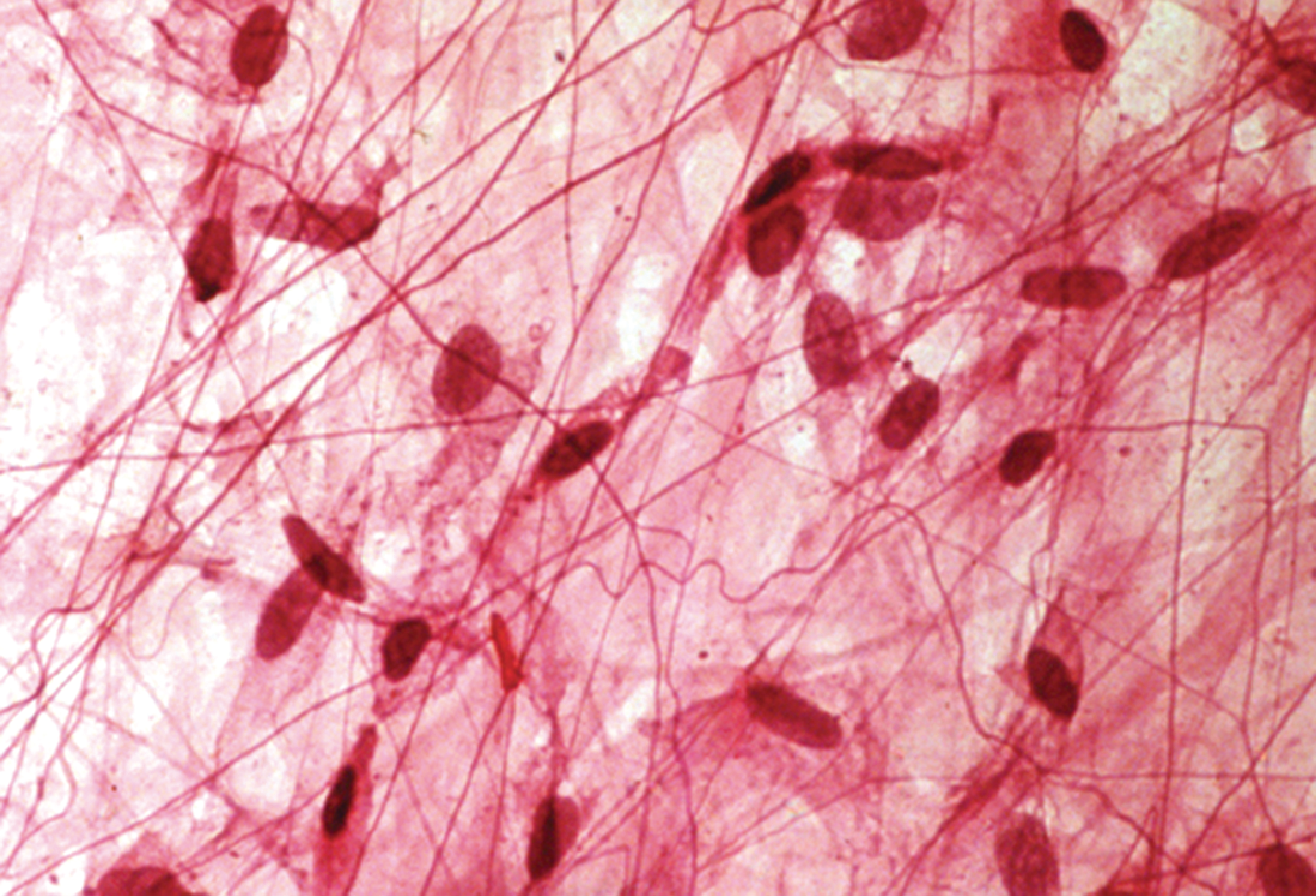
what’s an location example of areolar tissue?
it anchors epithelial tissue of skin to structures under it
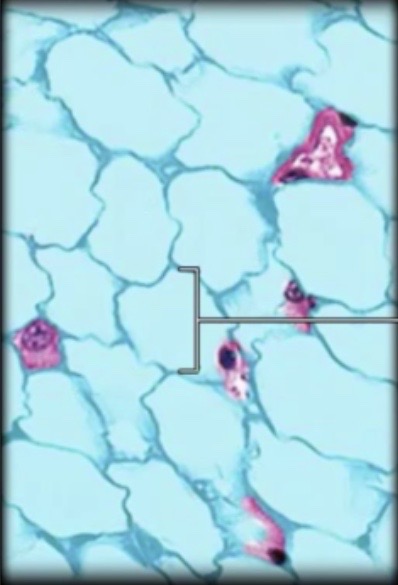
Adipose Connective Tissue
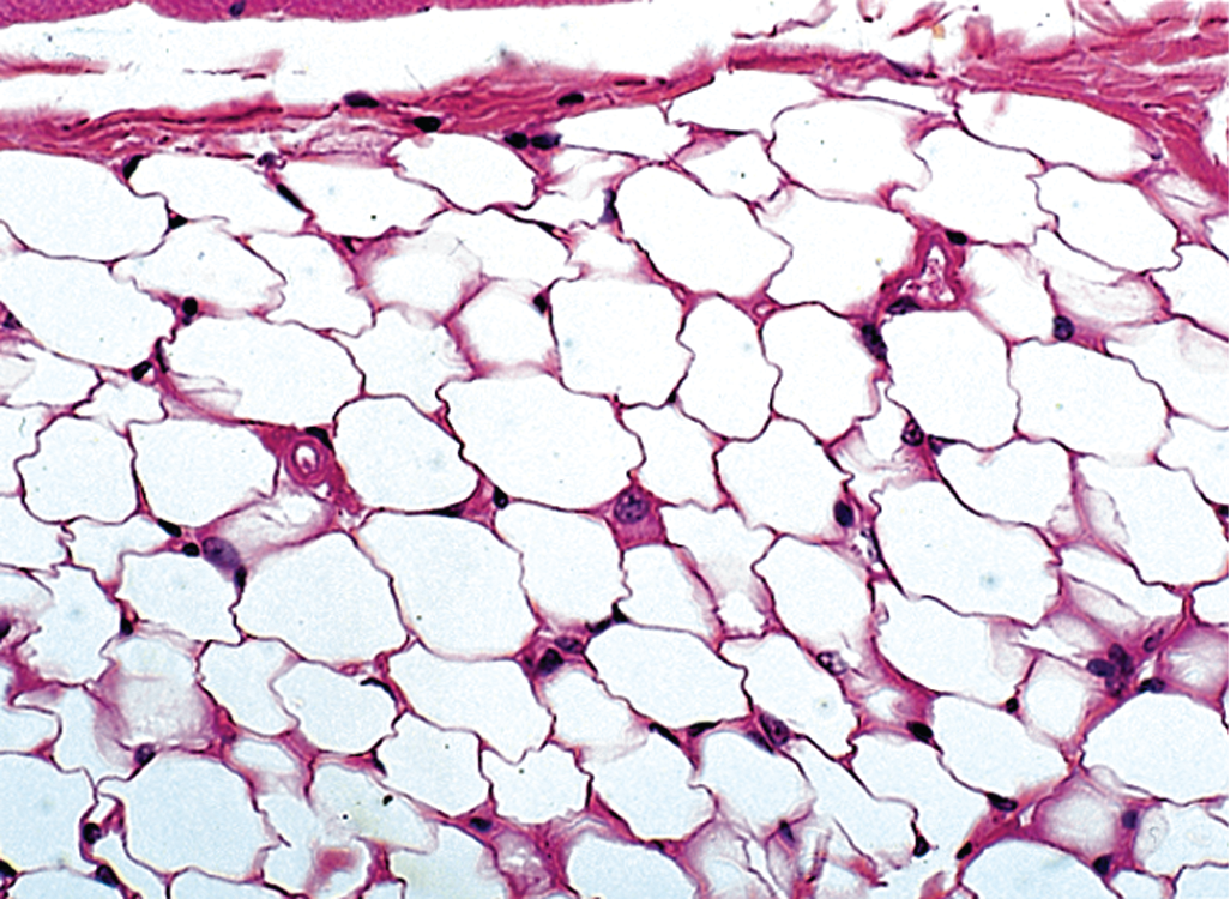
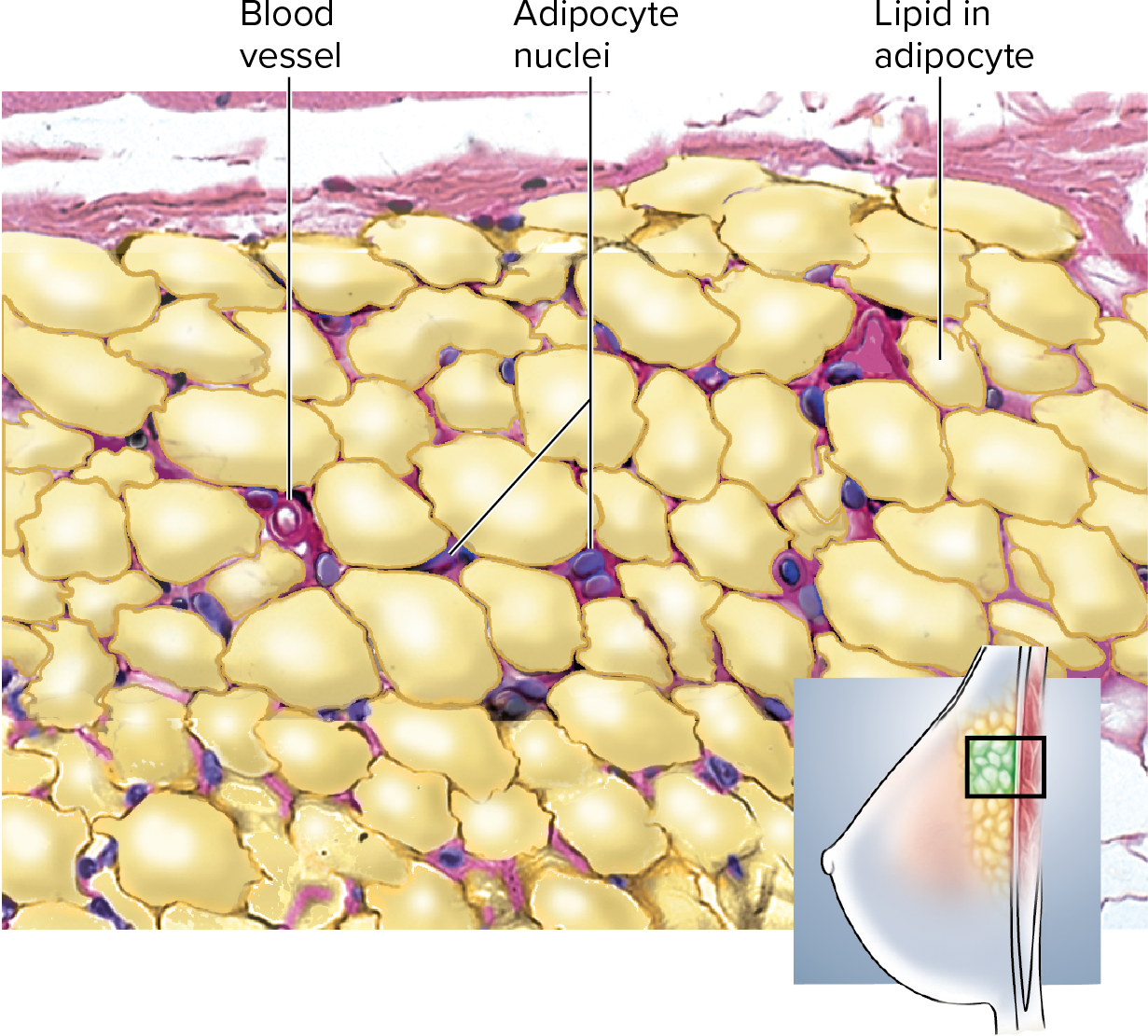
review
Adipose Tissue contains fat that will
provide insulation + energy storage
Reticular Connective Tissue
Reticular Tissue
will
provides structural framework for organs
especially in the immune system
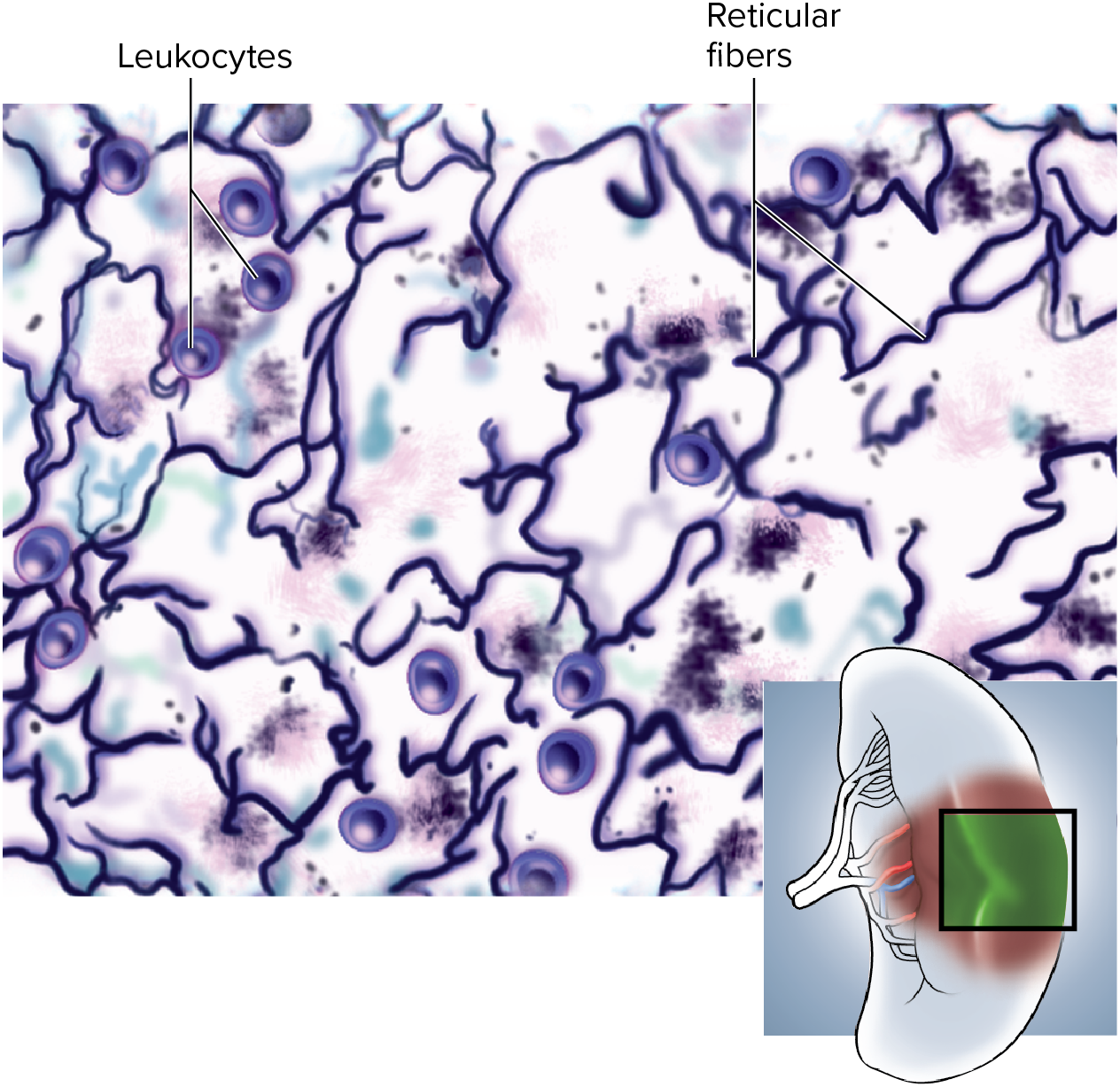
what’s an location example of reticular tissue?
it creates the stroma ( soft internal framework that holds things ) of lymph nodes
Dense Connective Tissue
structure?
tightly packed fibers fill up more space than ground substance + cell together
Dense Connective Tissue
makes up
tendons
ligaments
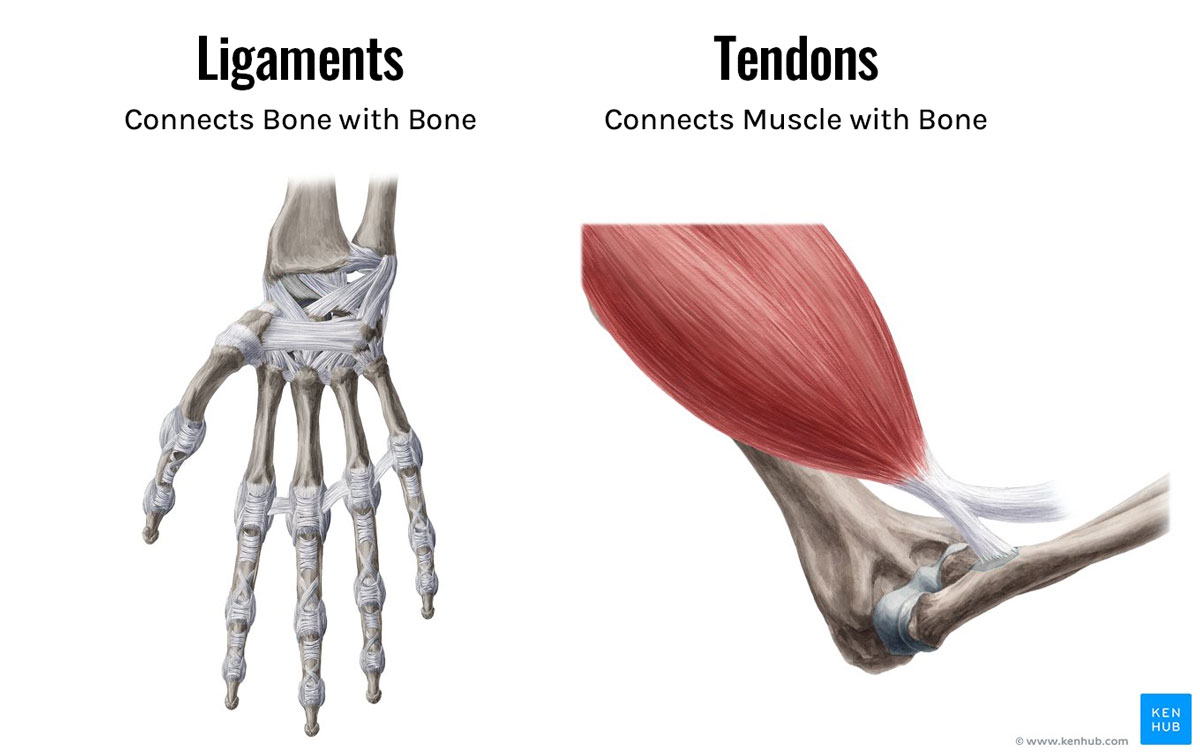
Dense Connective Tissue is more dense because it’s GOAL is to
have strength to transfer force between shorting muscle with bone.
so they don’t hold as many immune defender elements as loose tissue they focus on being tough instead
What are the 3 types of Dense Connective Tissue?
Regular
Irregular
Elastic
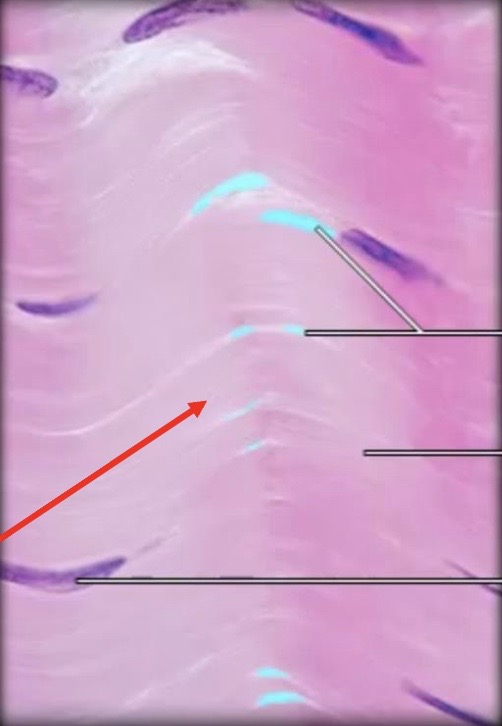
Regular Dense Connective Tissue
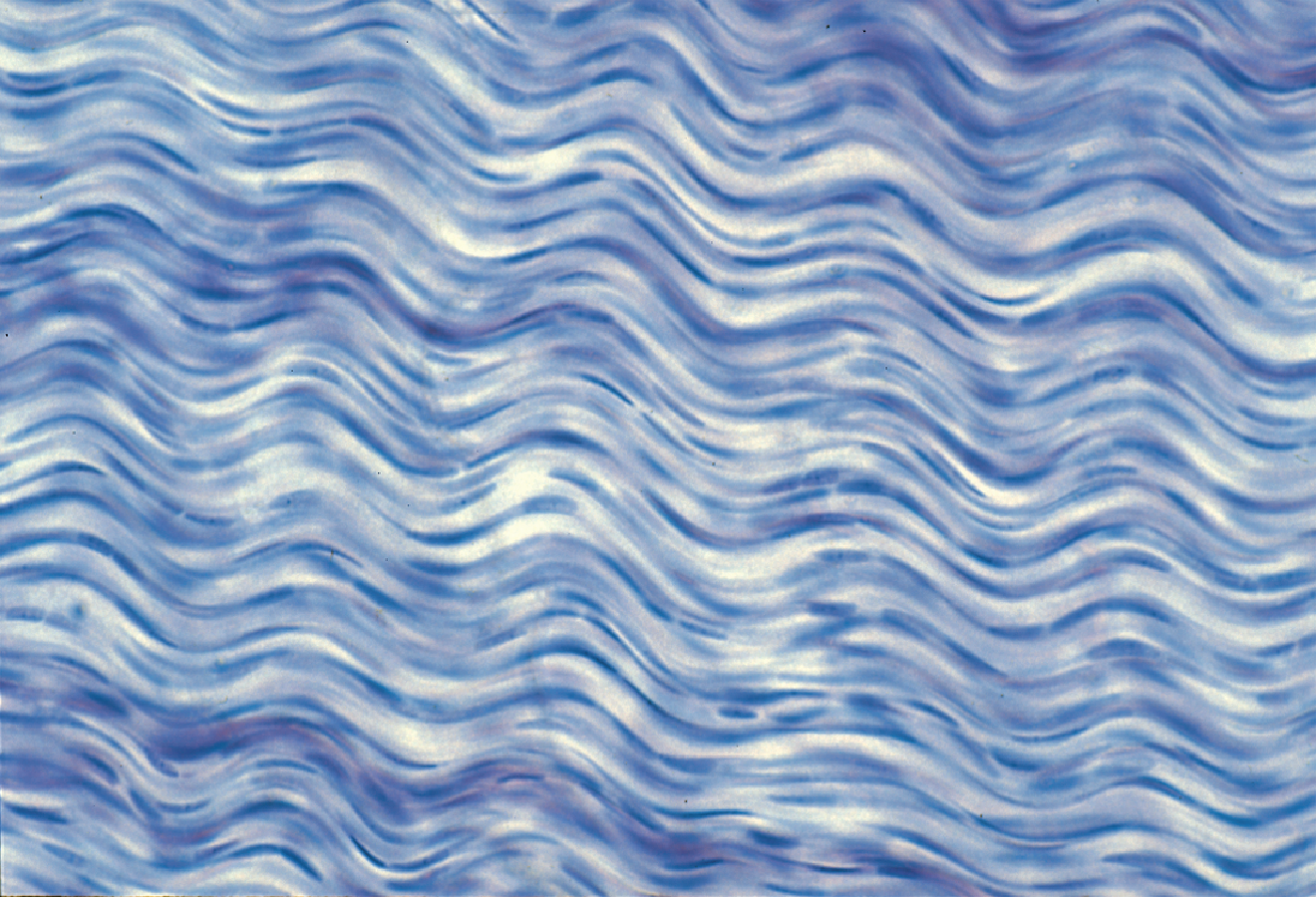
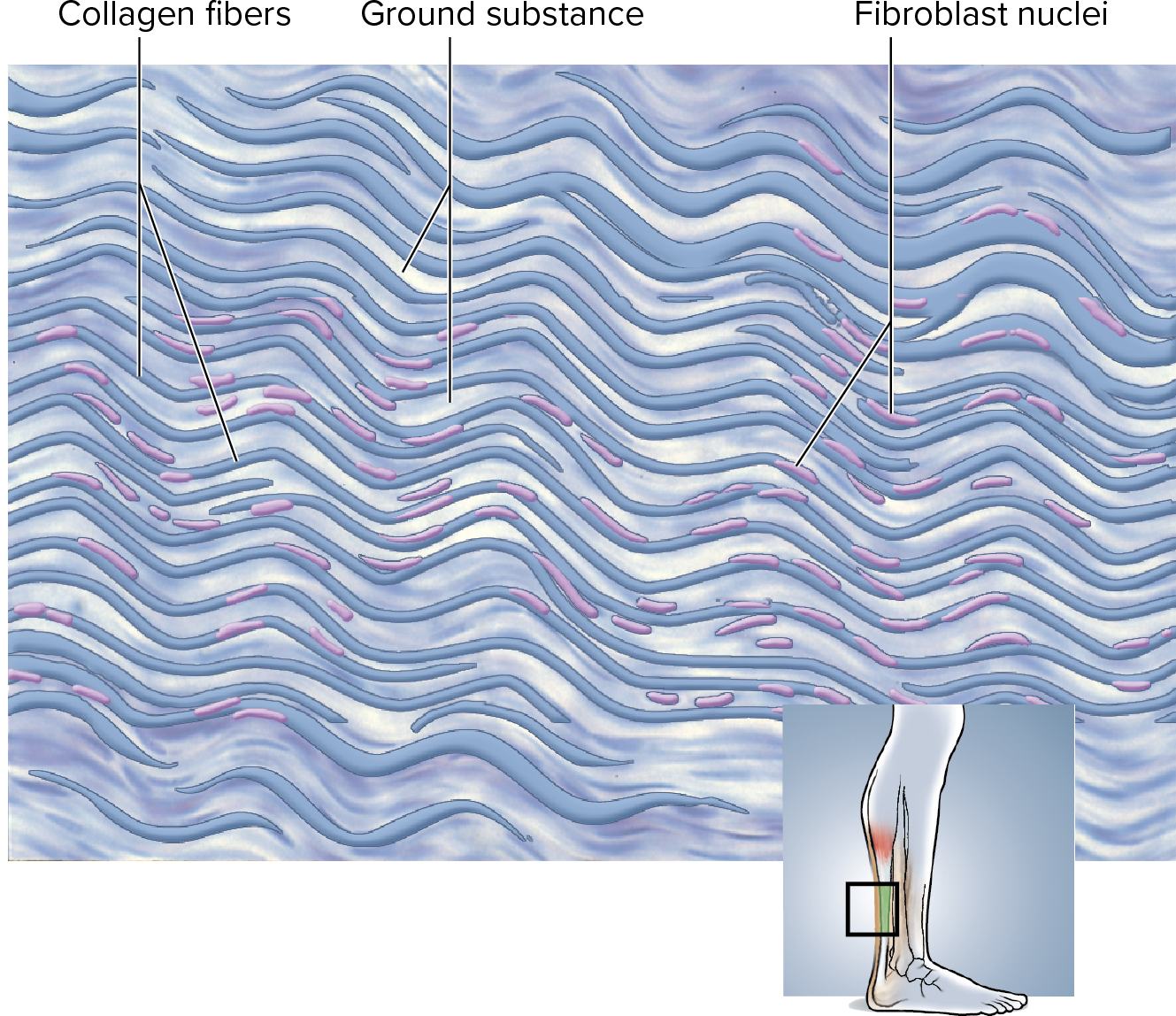
Regular Dense Connective Tissue
is structured with
abundant parallel collagen fibers
~ in a wavy line pattern going in one direction ~
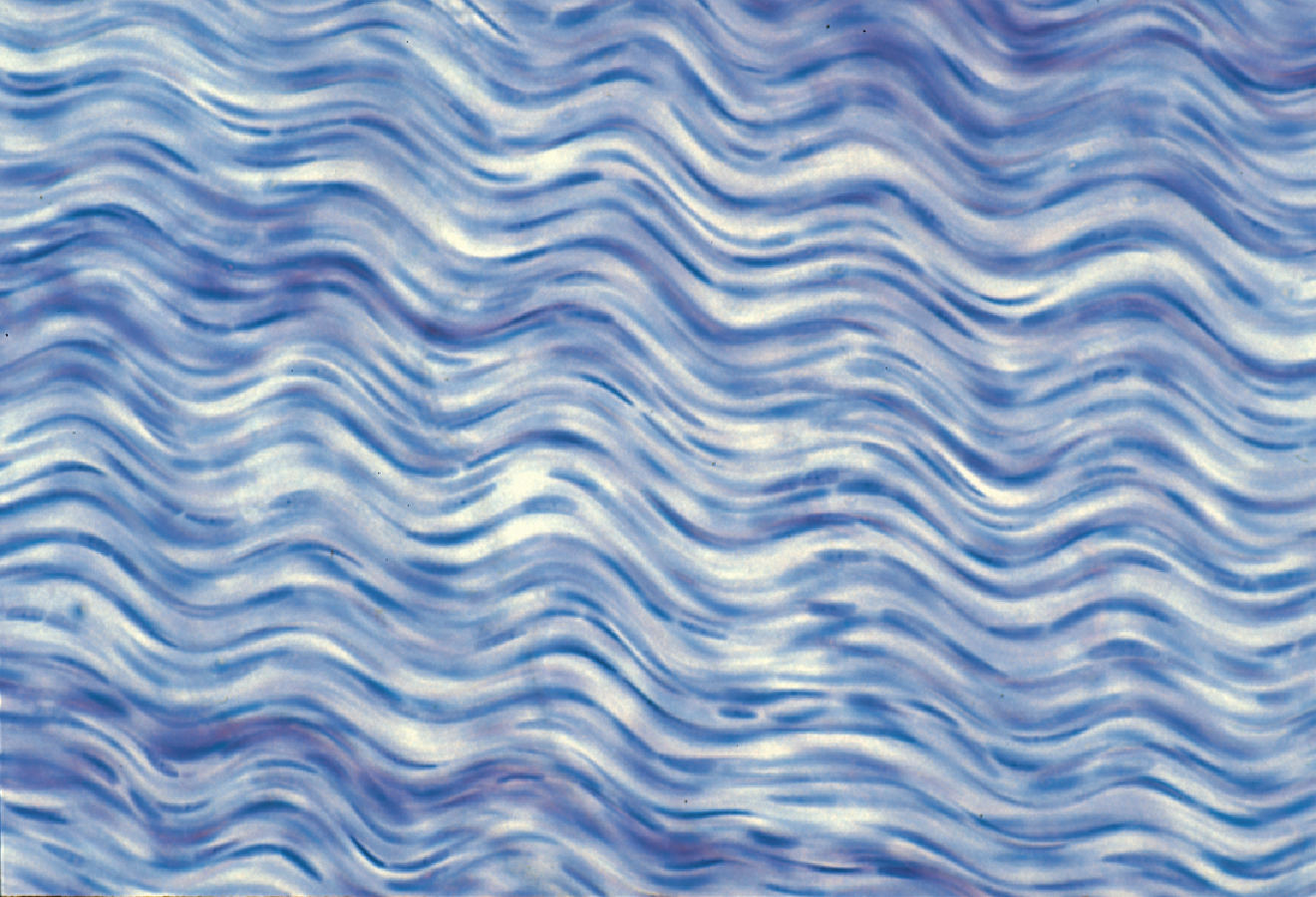
Regular Dense Connective Tissue
strength?
strong in the one direction it pulls in
( weak and would likely tear in other direction )

Regular Dense Connective Tissue
example?
tendons
ligaments
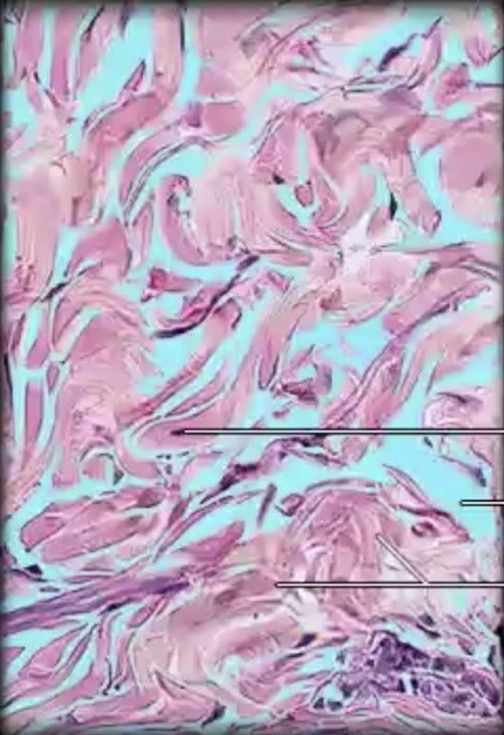

Irregular Dense Connective Tissue
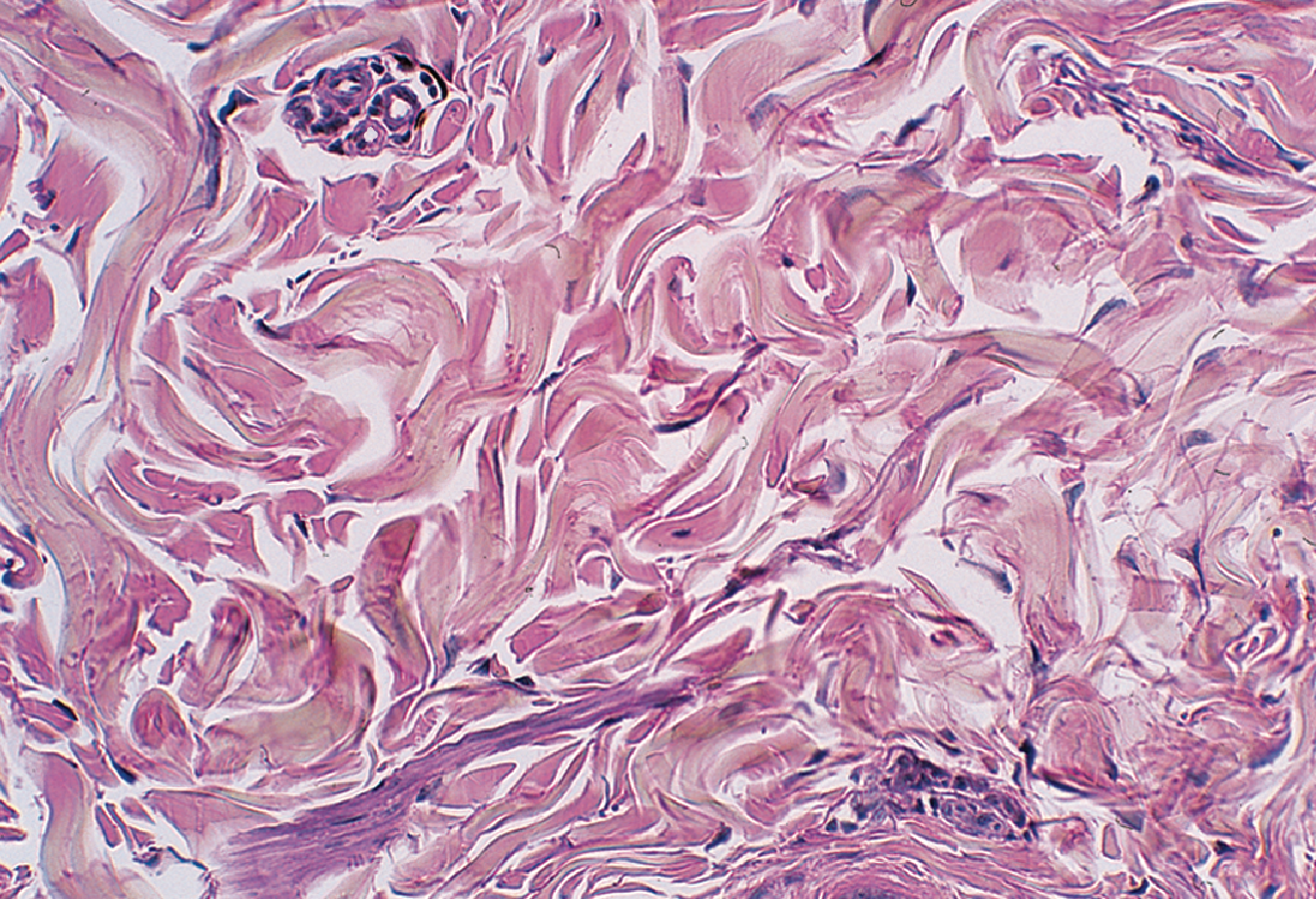
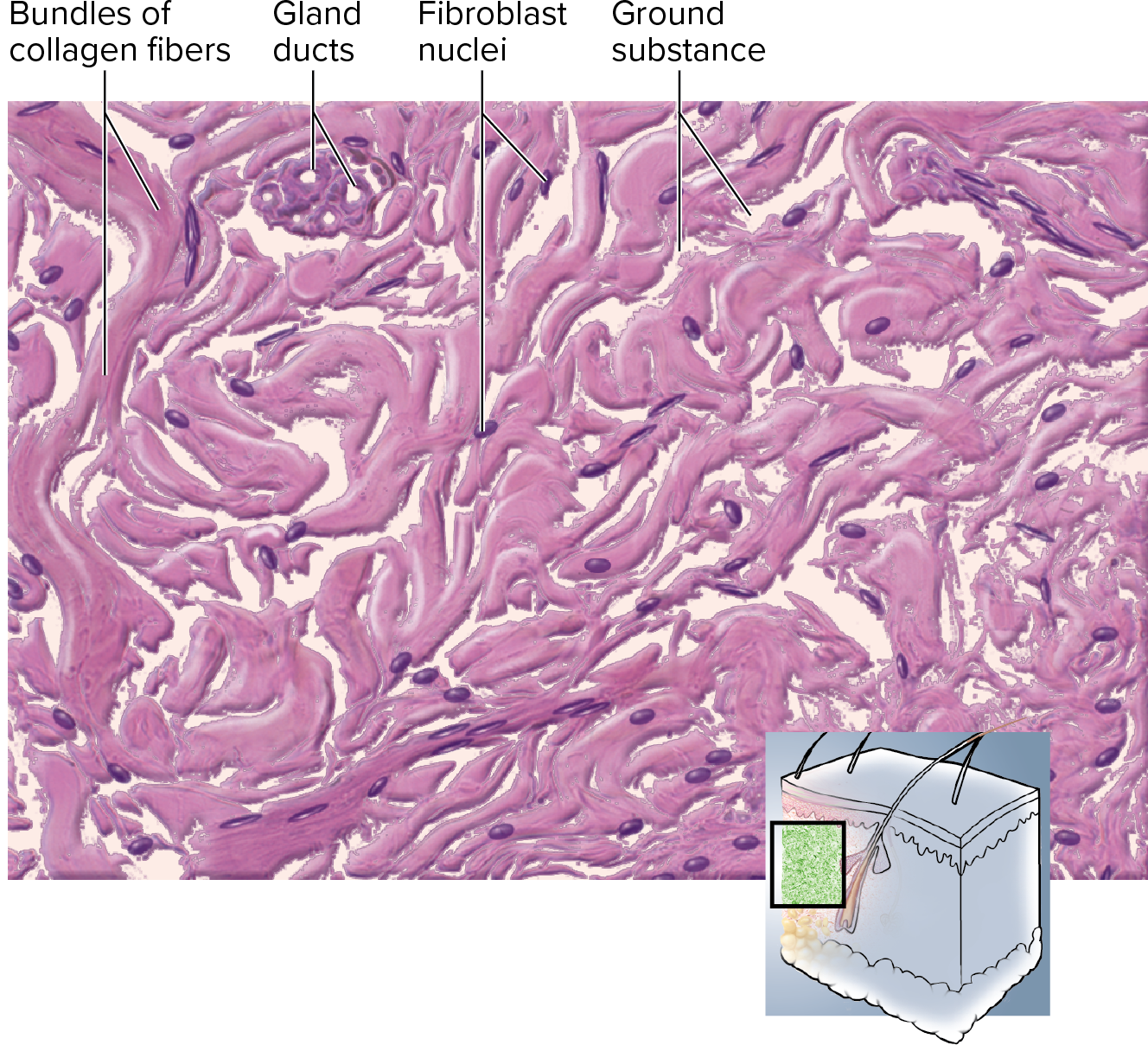
Irregular Dense Connective Tissue
is structured with
non-parallel collagen fibers
{ in irregular patterns }
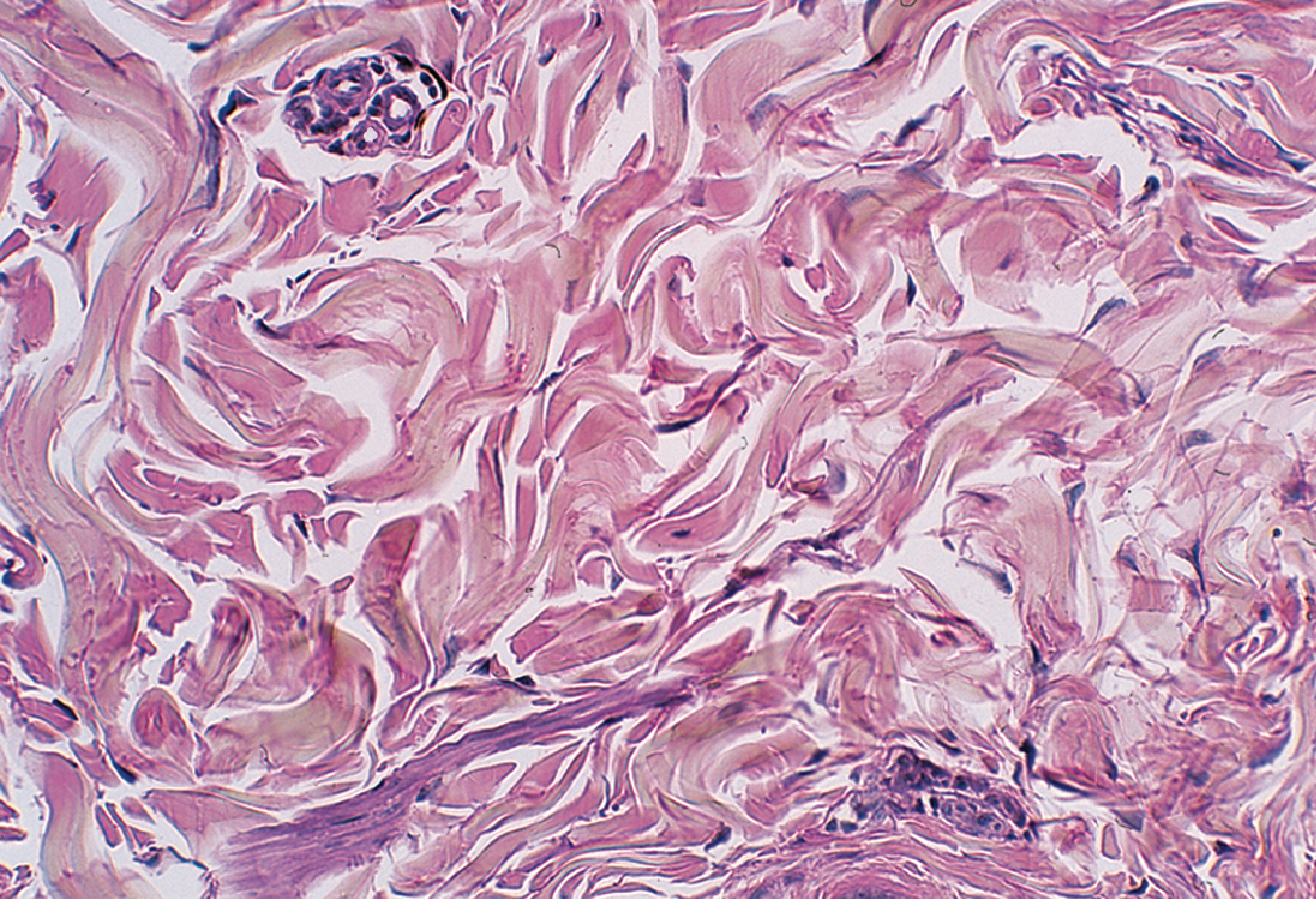
Irregular Dense Connective Tissue
strength?
withstands forces from many different directions

Irregular Dense Connective Tissue
example?
dermis of skin
→ can get pulled in many directions
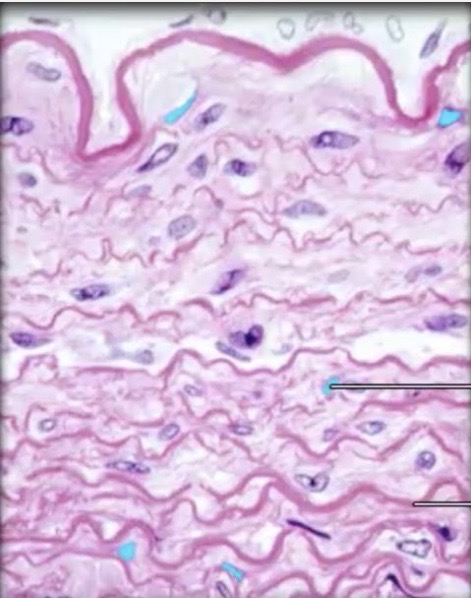
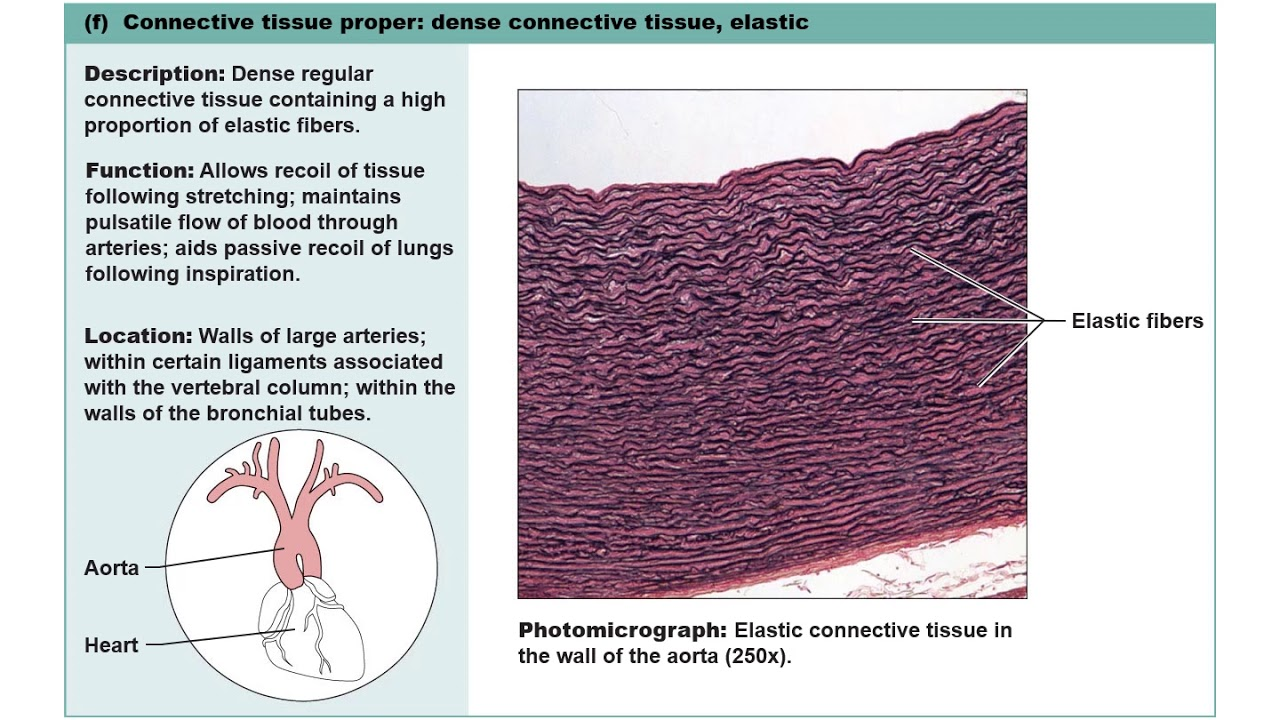
Elastic Dense Connective Tissue
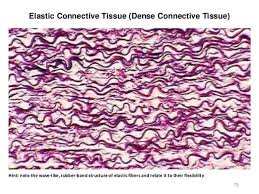
Elastic Dense Connective Tissue
is structured with
abundant elastic fibers
( more than collagen fibers )
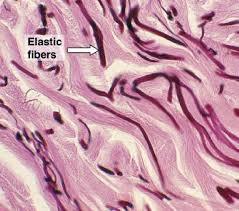
Elastic Dense Connective Tissue
strength?
highly flexible
can stretch + recoil
Elastic Dense Connective Tissue
example?
Lungs / Heart’s Blood Vessels
→ can stretch and collapse back
Supportive Connective Tissue
includes
cartilage
bone
Cartilage
what’s the qualities of it’s matrix?
flexible + rubbery matrix
what are the 3 types of cartilage?
Hyaline
Elastic
Fibrocartilage
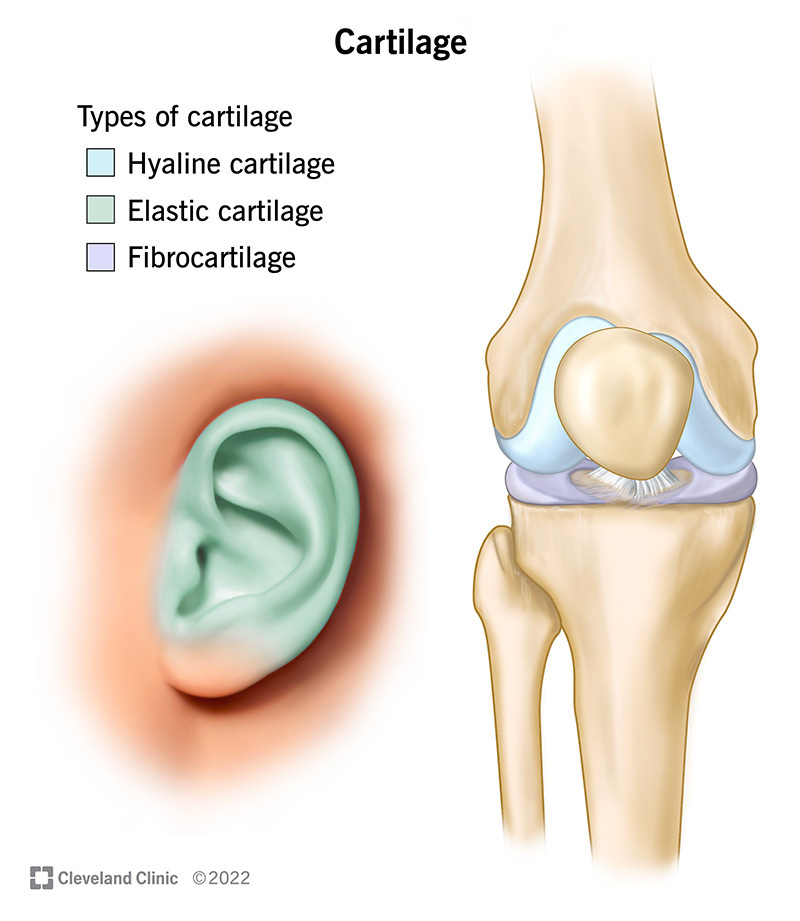
Hyaline Cartilage
is made of
fine collagen fibers
→ makes it very smooth!
review
Hyaline Cartilage
role is to
cover surfaces of articulating bones to prevent friction
review
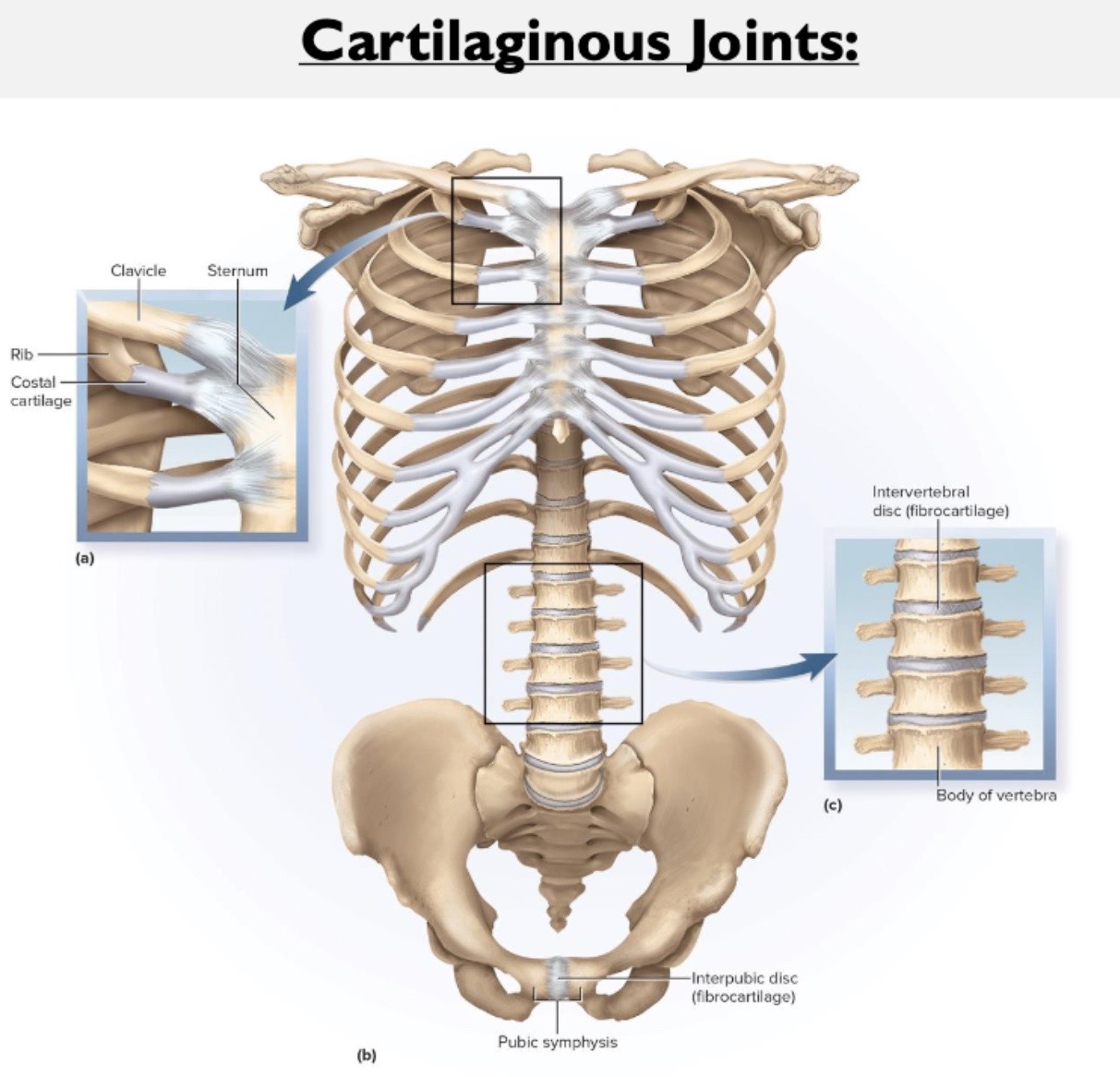
What are 2 location examples for Fibrocartilage?
intervertebral discs
pubic symphysis
Fluid Connective Tissue
includes
Blood
why blood?
its ground substance is plasma! carries the formed elements
transports certain dissolved matter and cells around
Blood is considered a connective tissue because it meets the defining characteristics of connective tissues, despite being quite different from the typical examples like bone or cartilage. Here’s why:
Origin: Blood, like other connective tissues, originates from mesodermal cells during embryonic development. It’s produced in the bone marrow, which is a connective tissue structure.
Cells and Extracellular Matrix:
Cells: Blood contains various types of cells like red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), and platelets (thrombocytes), all suspended in plasma.
Extracellular Matrix (ECM): Instead of the solid ECM found in other connective tissues like bone or cartilage, blood’s ECM is liquid, and it’s called plasma. Plasma consists of water, proteins, electrolytes, nutrients, and waste products.
Function: One of the key roles of connective tissues is to transport and support, and blood does just that. It transports nutrients, gases (like oxygen and carbon dioxide), hormones, and waste products. It also plays a role in immune response and clotting, which are essential functions that connect it to other tissues in the body.
In summary, despite its fluid nature, blood fulfills the structural and functional roles typical of connective tissue, including providing support and linking various parts of the body.