A&P Practical 1
1/107
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Georgia Southern Anatomy 1 Practical 1 Terms
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
108 Terms
anatomical position
erect, feet forward, arms at side with palms facing forward, head facing forward
-all positions are switched to be applied as the conduit would be
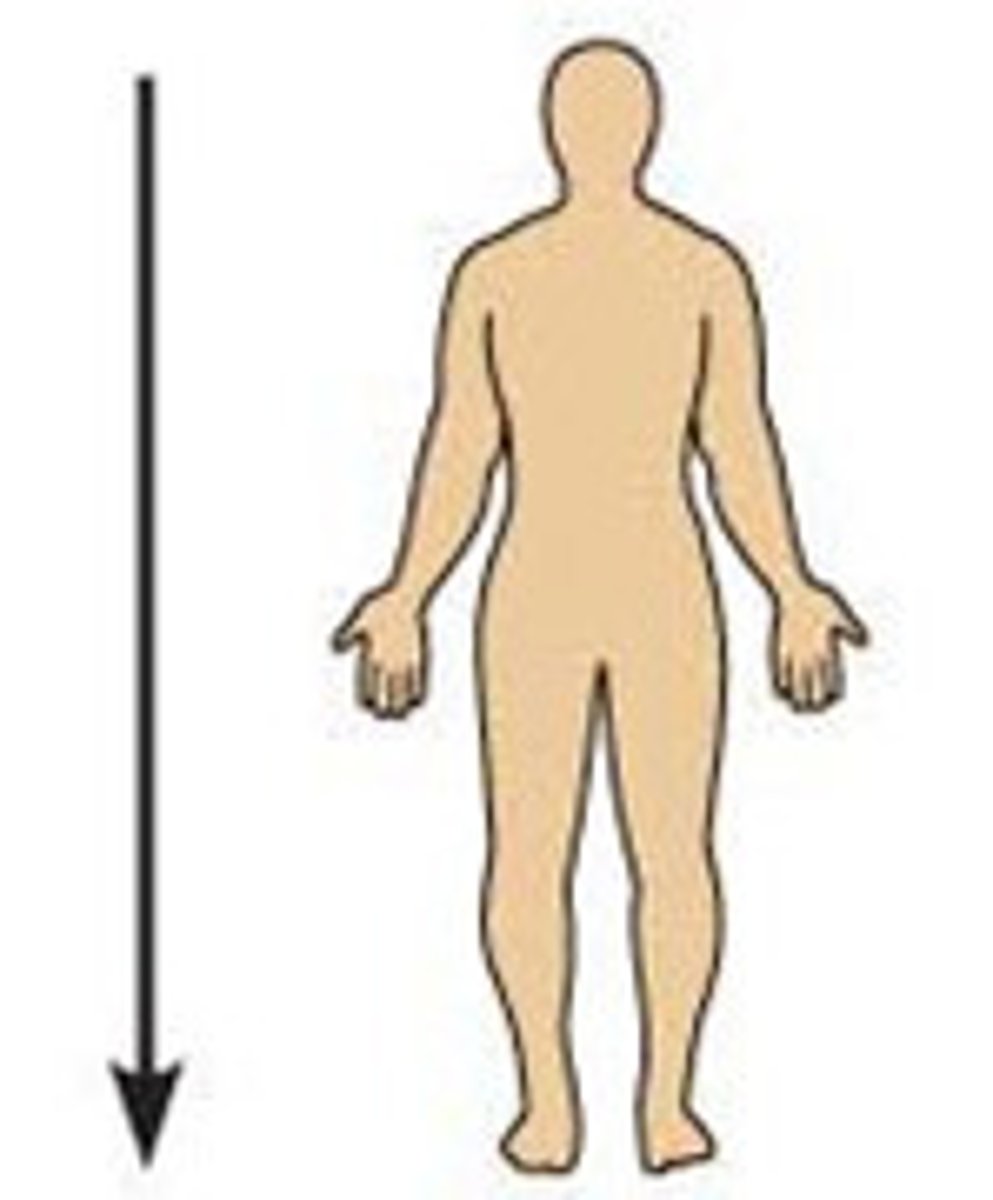
Superior (cranial)
above, higher than
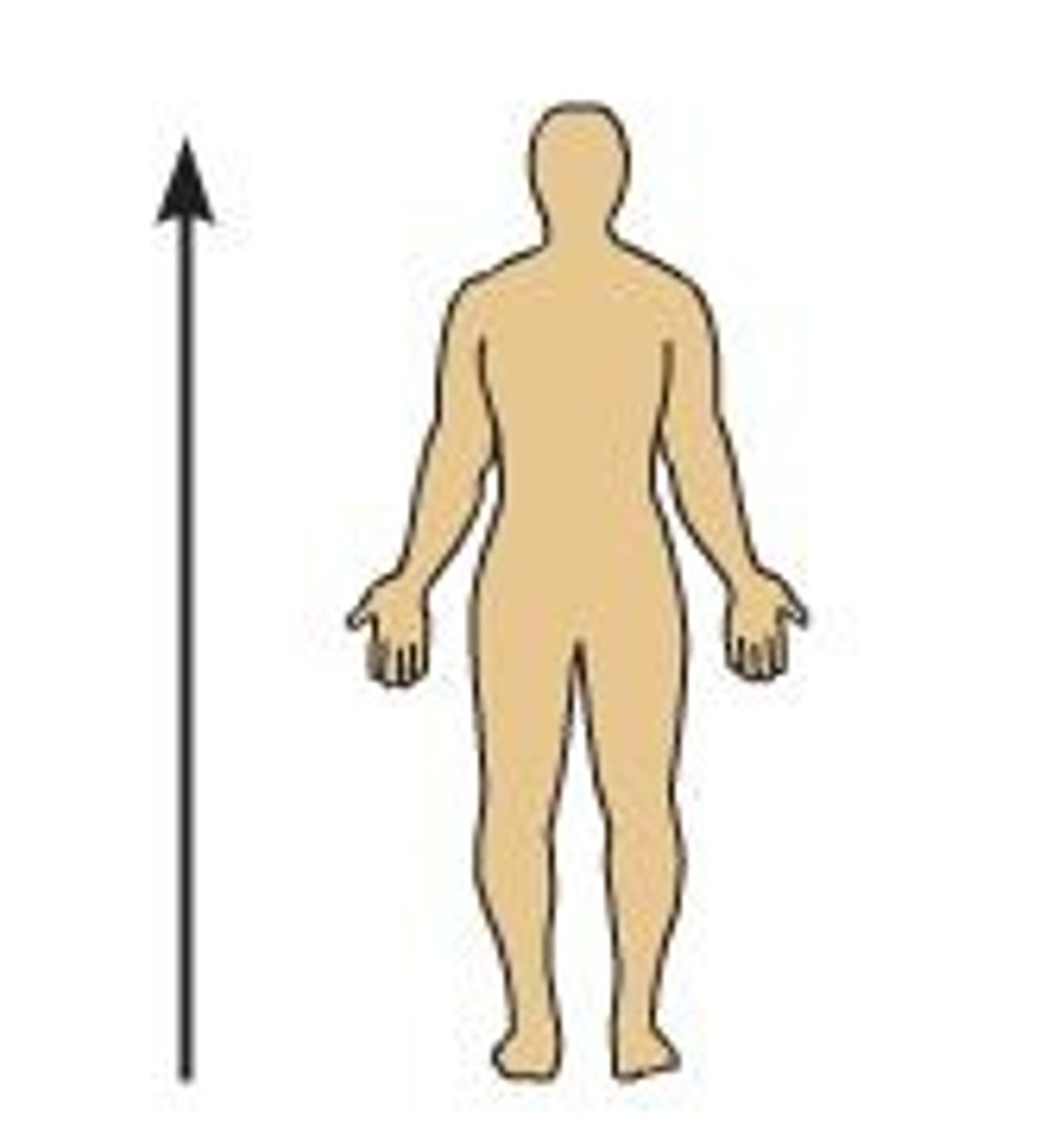
inferior (caudal)
below, lower than
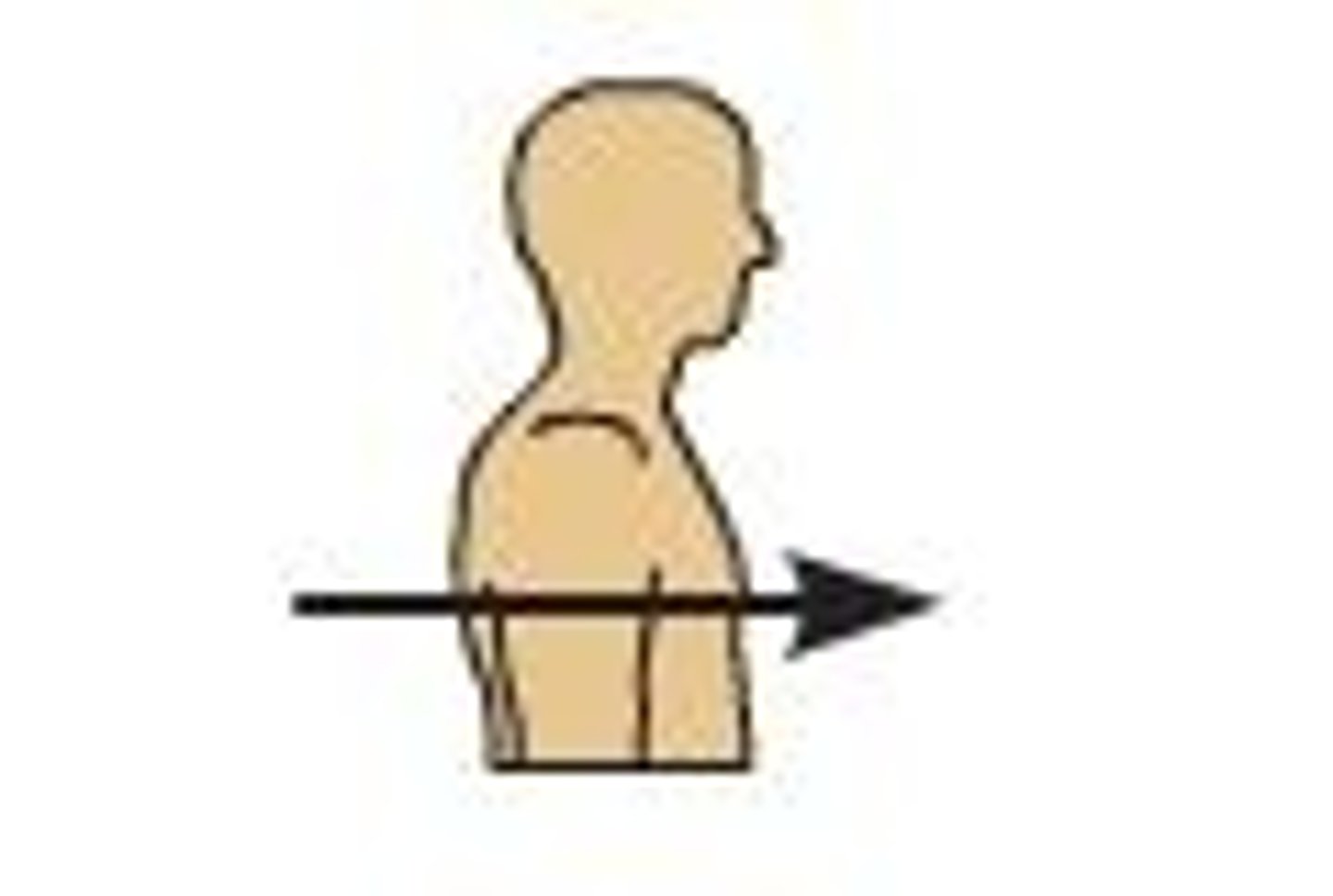
anterior (ventral)
front, forward
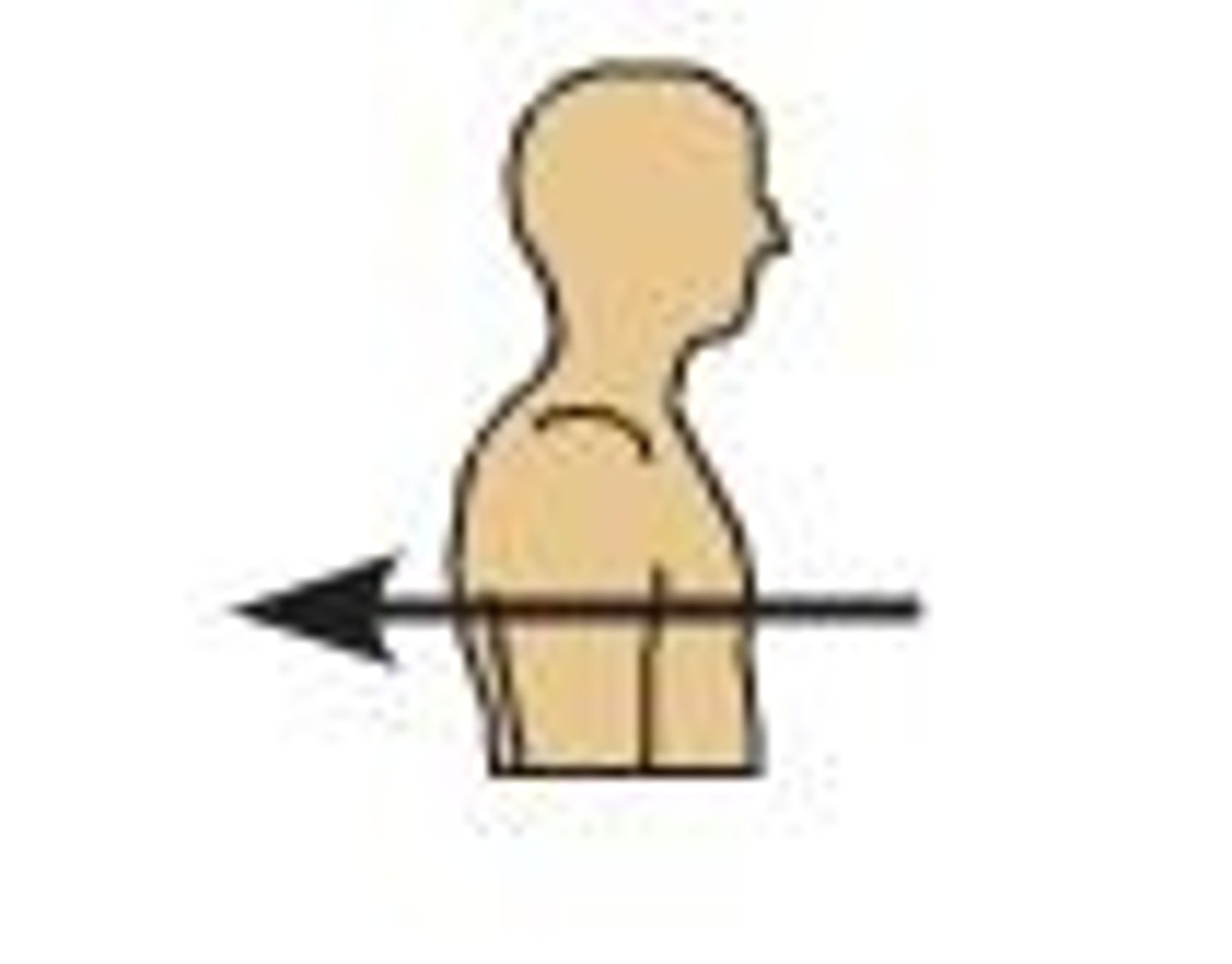
posterior (dorsal)
back, behind
remedial (medial)
near, close to body, in a limb
lateral
away from the middle, nearest to the outside
proximal
near, close to body, in a limb
distal
far away, farthest from body
superficial
on the surface, exterior
deep
inner layer, away from surface
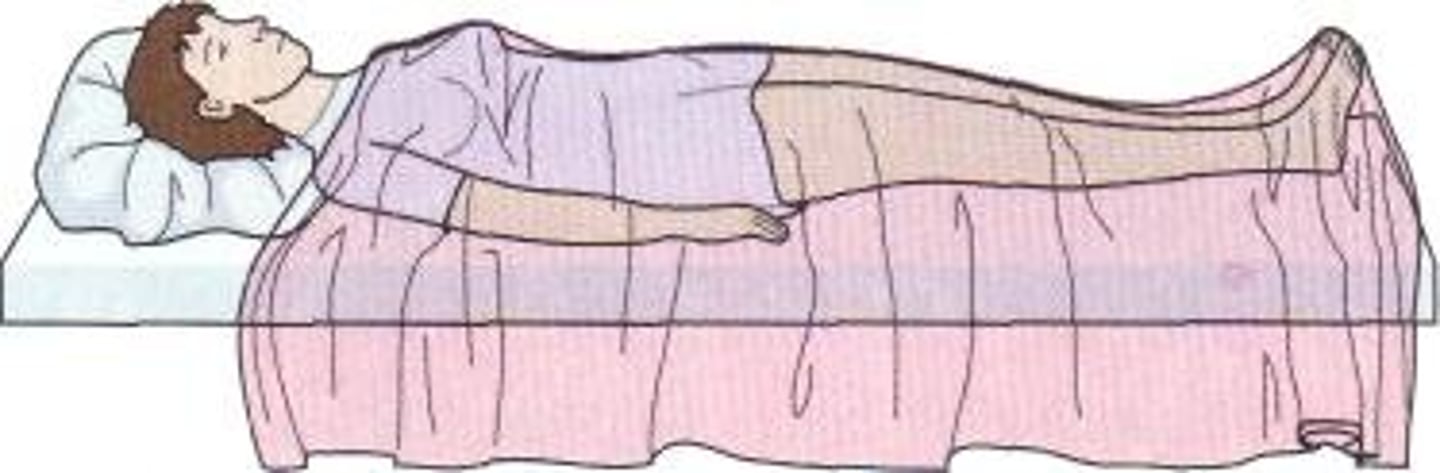
prone
lying down

supine
facing up
rostral
toward the forehead or nose
caudal
toward the tail
oral
pertaining to the mouth
buccal
pertaining to the cheek
orbital
pertaining to the eye socket
cervical
7 vertebrae closest to the head

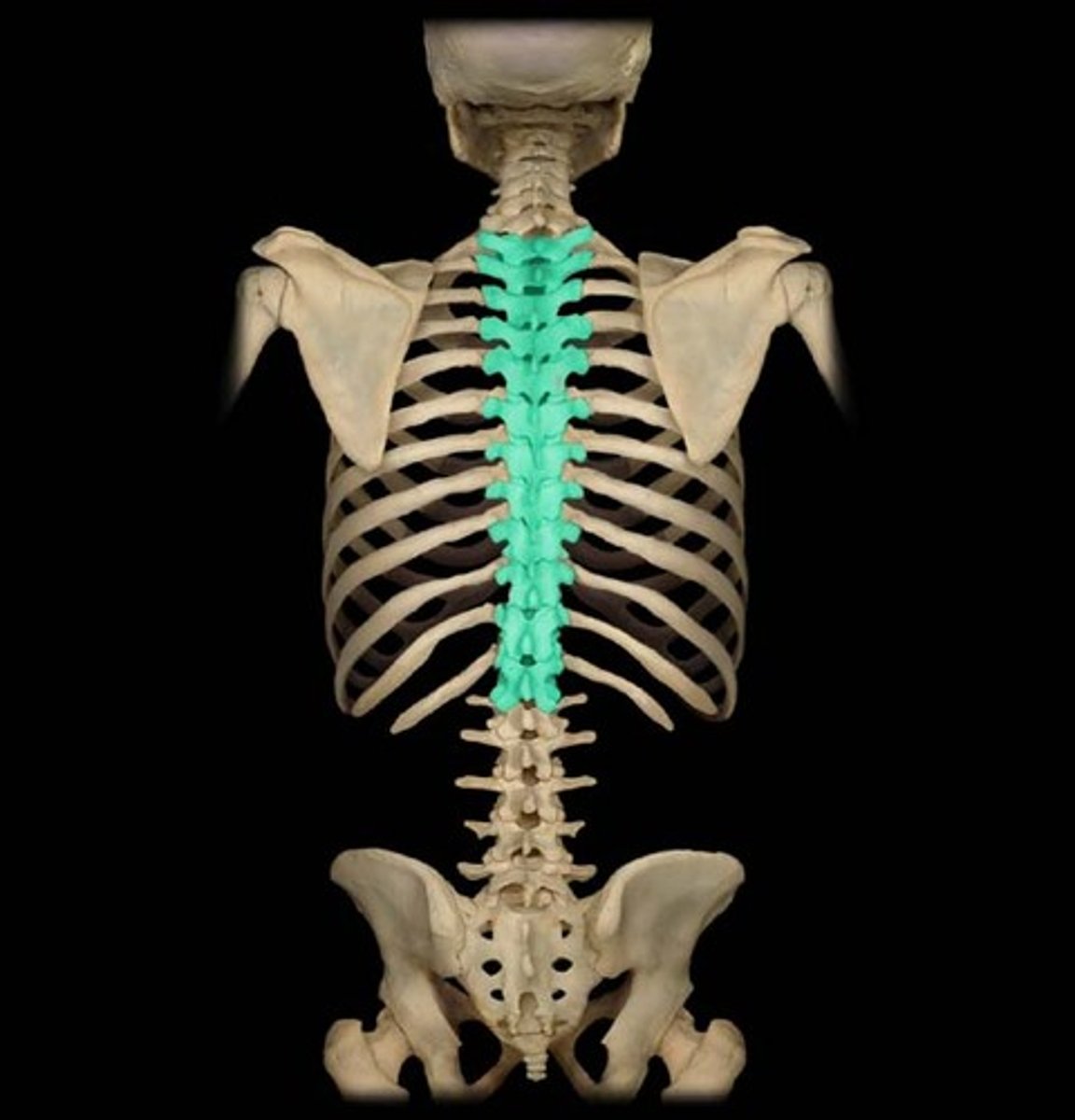
thoracic
12 vertebrae connected to the ribs
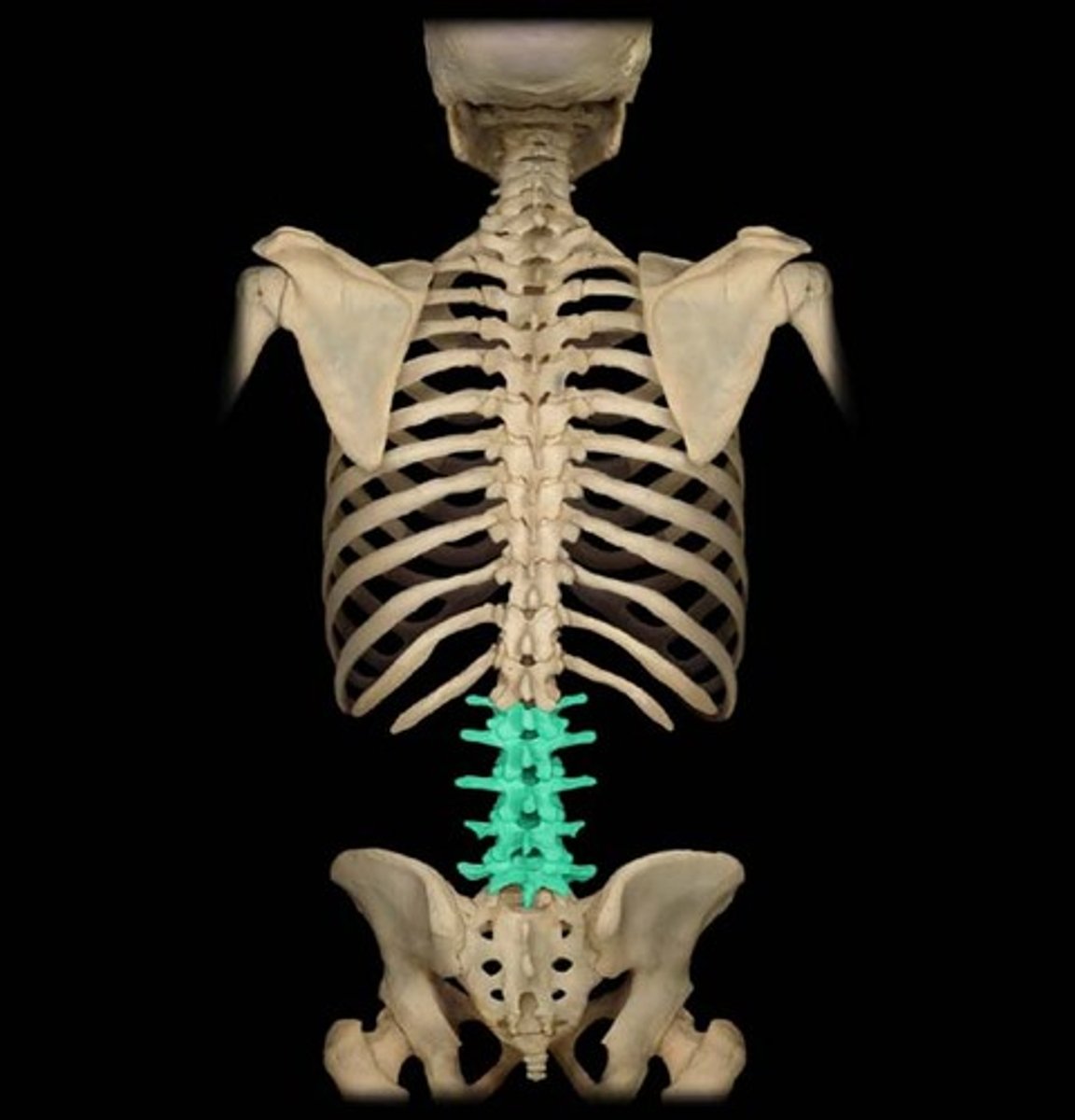
lumbar
5 vertebrae in the lower back
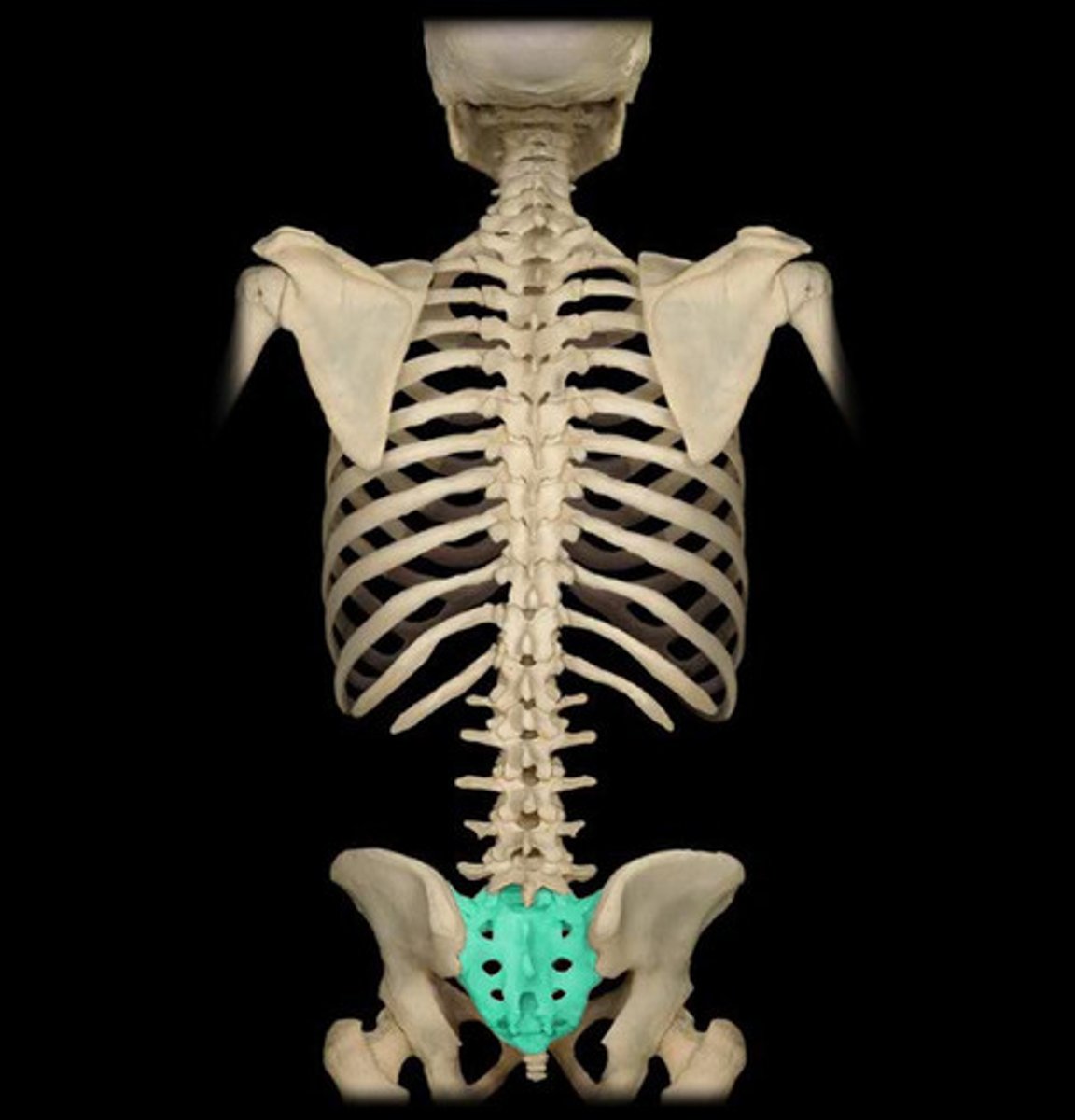
sacral
5 fused vertebrae connected to the pelvis
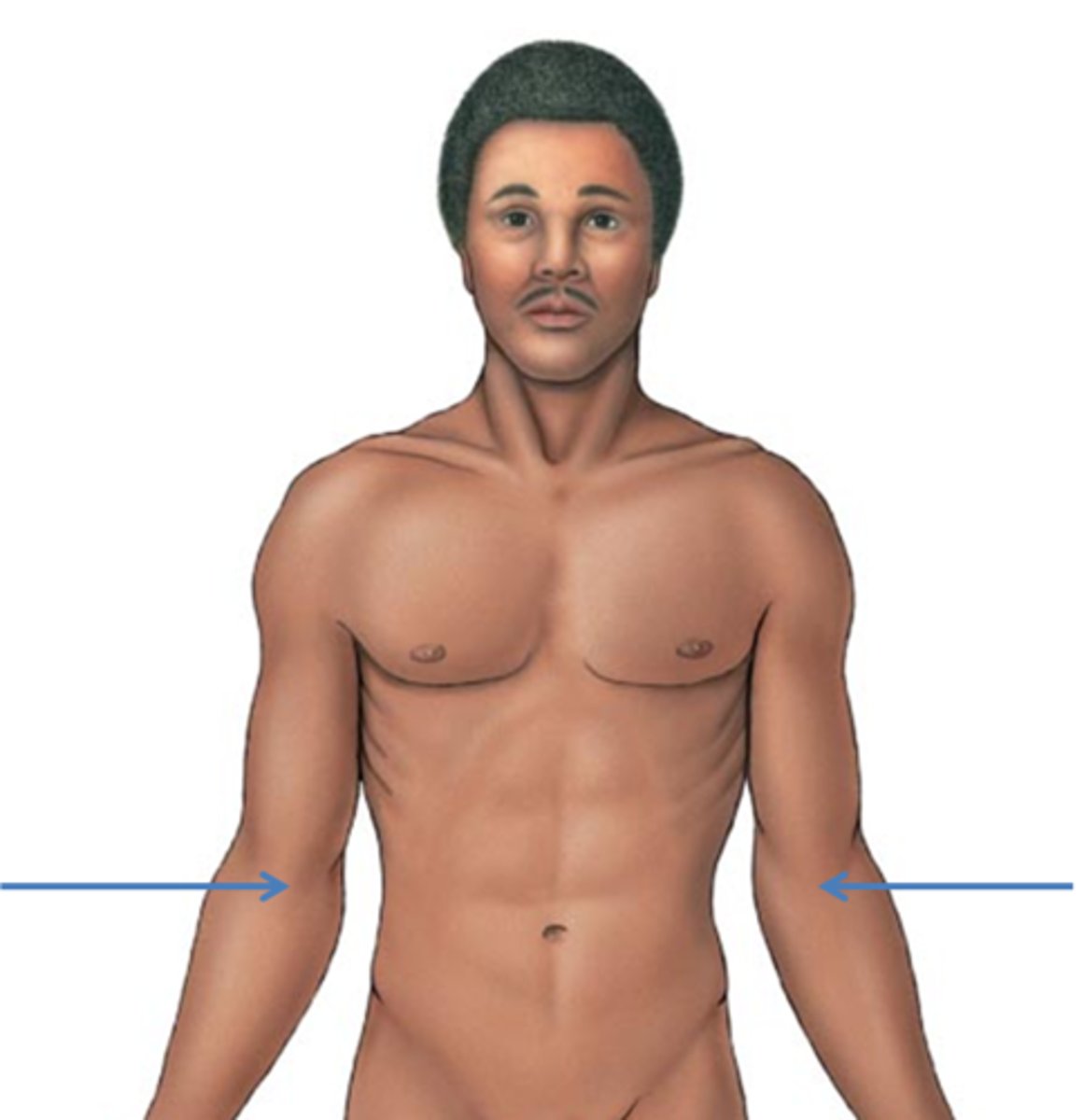
antecubital
anterior to the elbow
umbilical
pertaining to the belly button
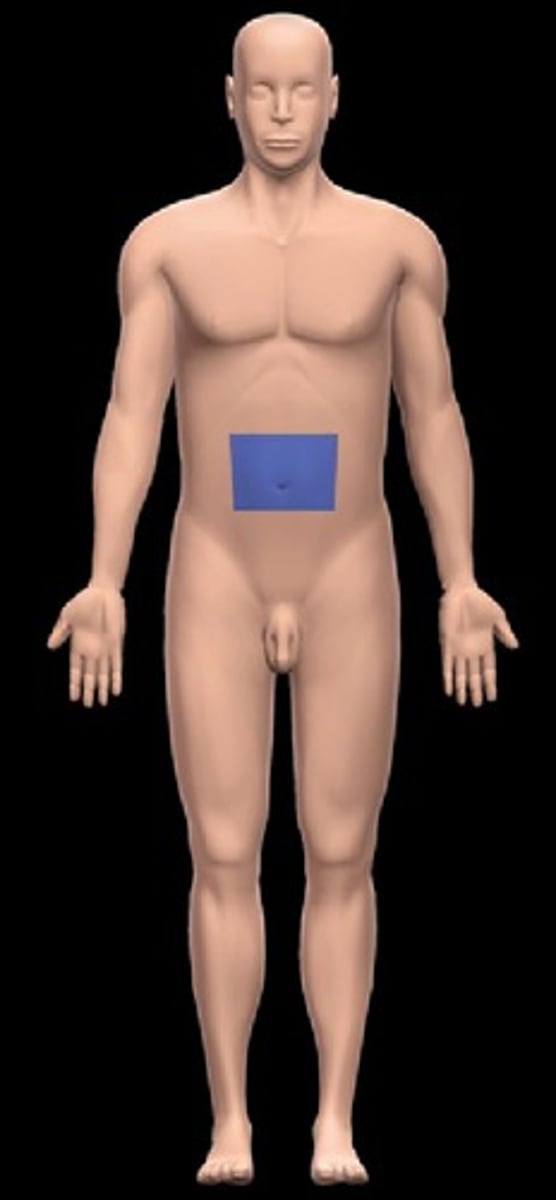
abdominal
below the chest and above the pelvis
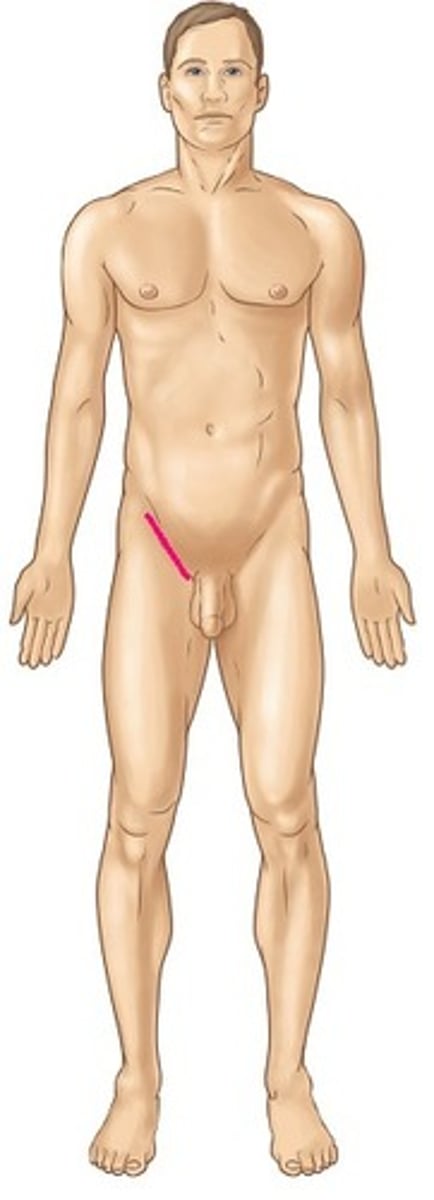
inguinal
pertaining to the groin
pubic
near pubic bone
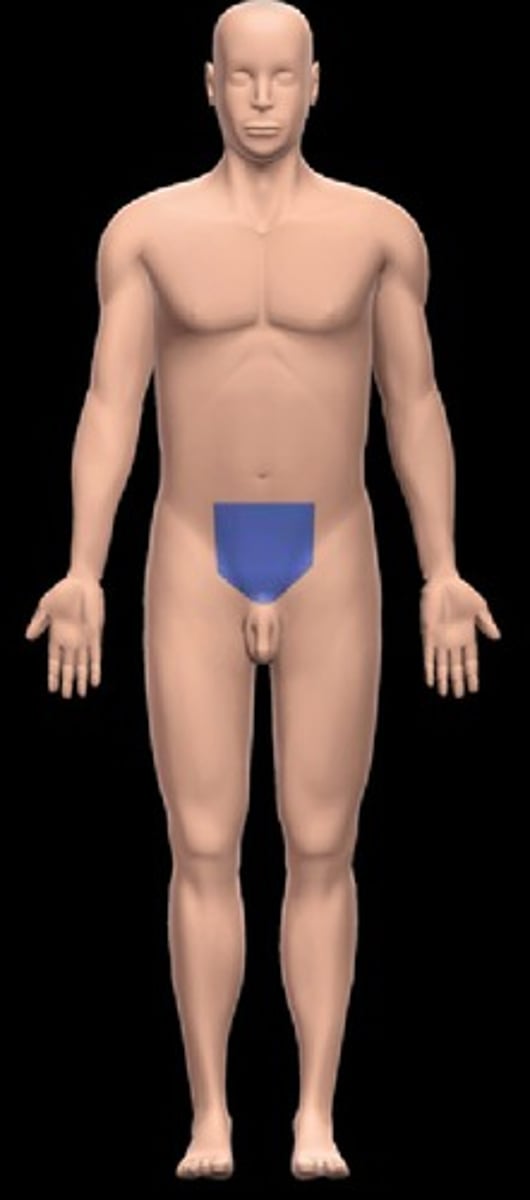
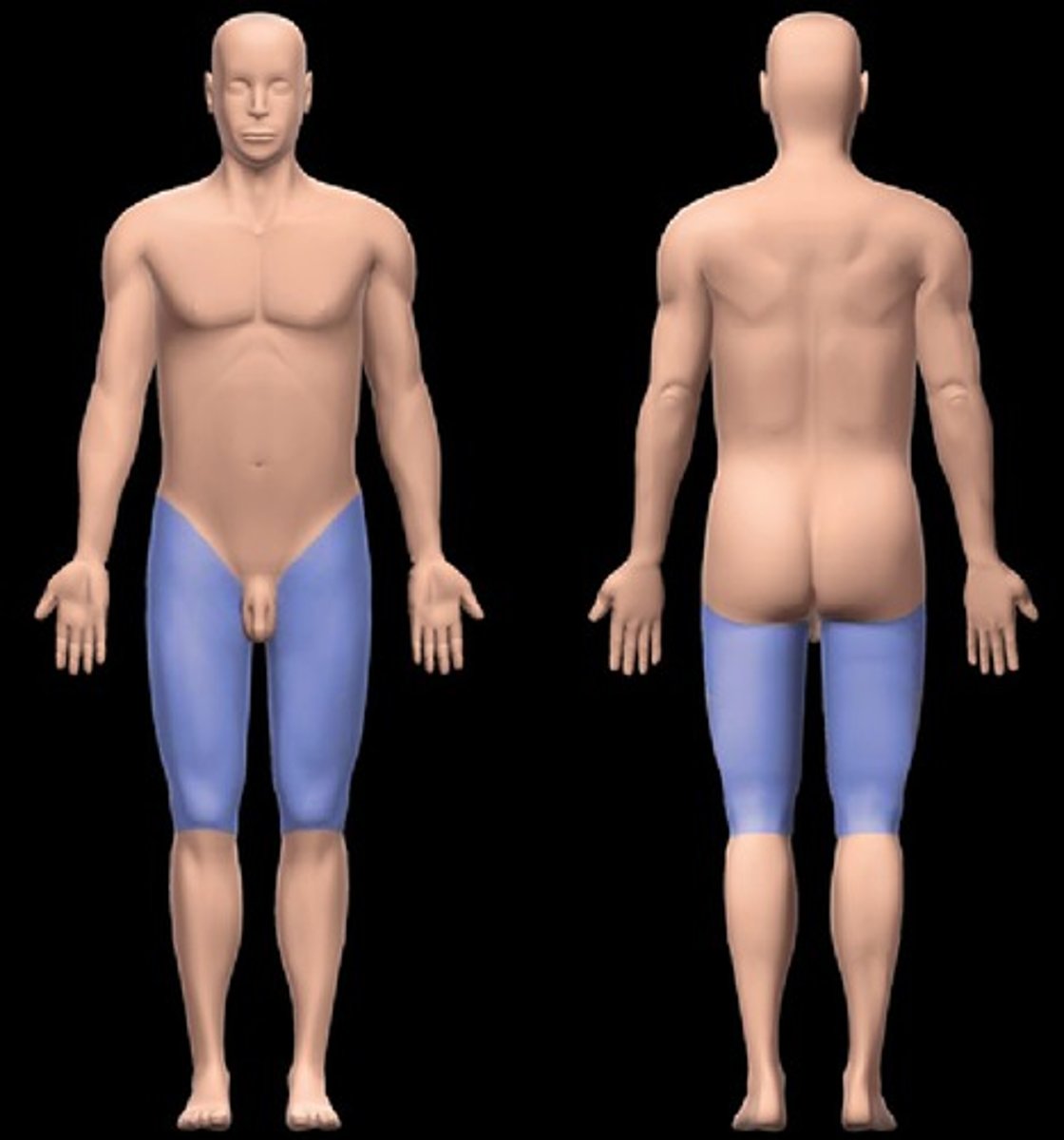
femoral
pertaining to the thigh
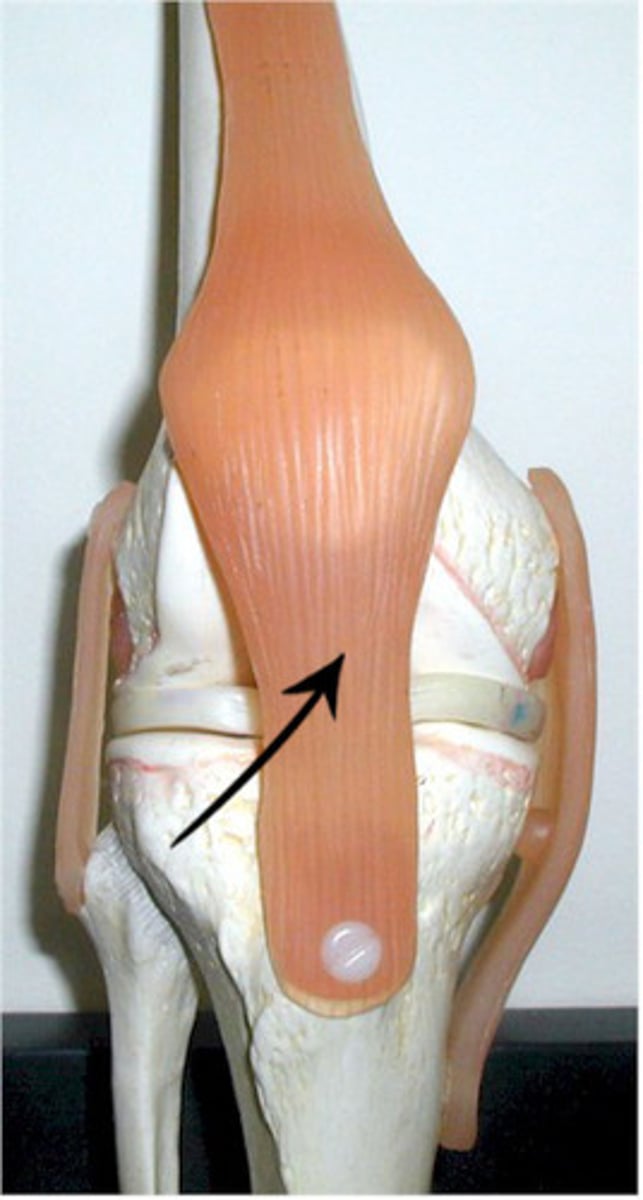
patellar
knee cap
digital
fingers and toes
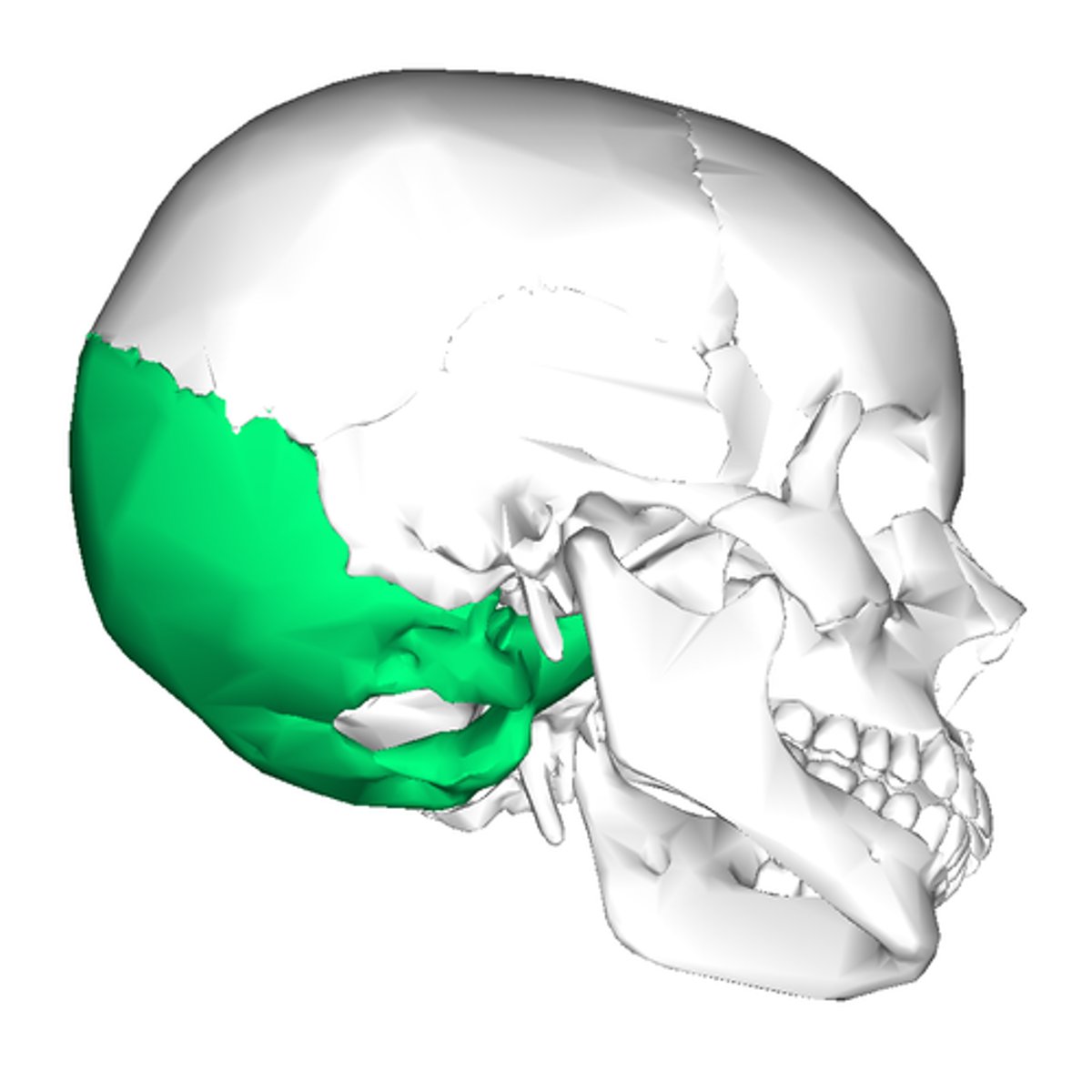
occiptial
back of the skull
deltoid
pertaining to the shoulder
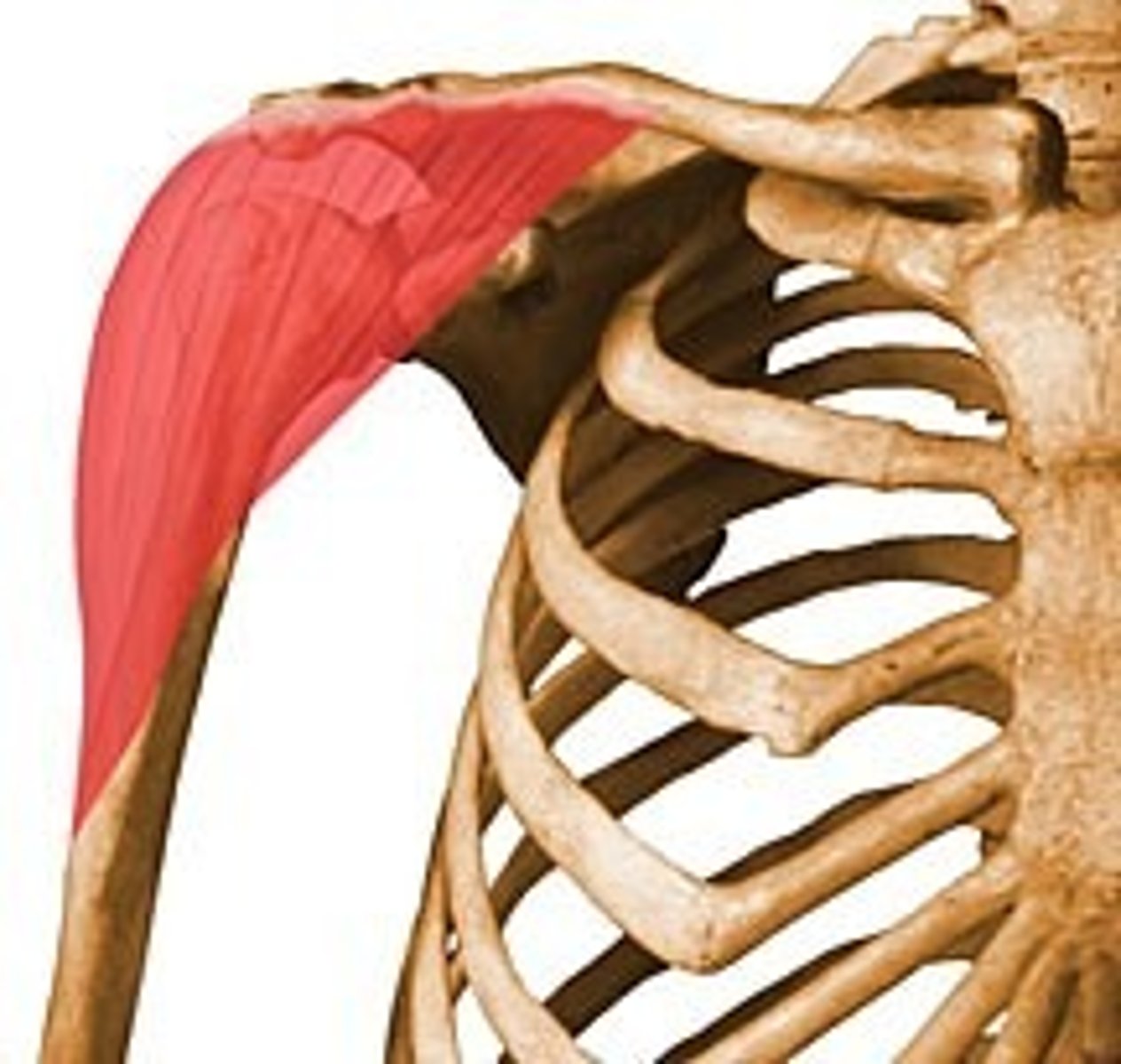
scapular
shoulder blade
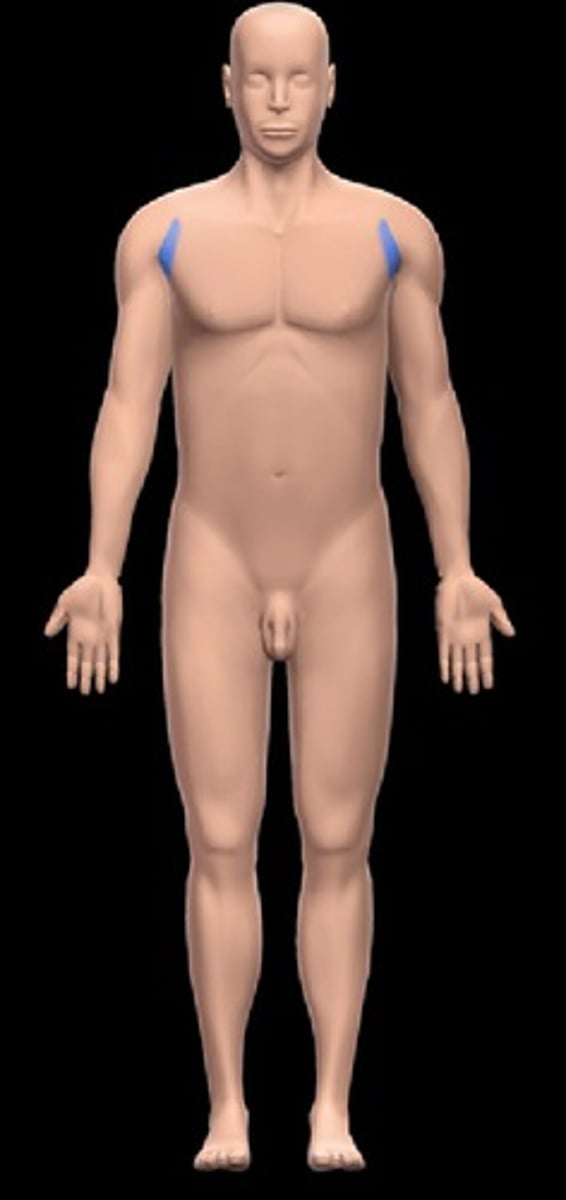
axillary
armpit
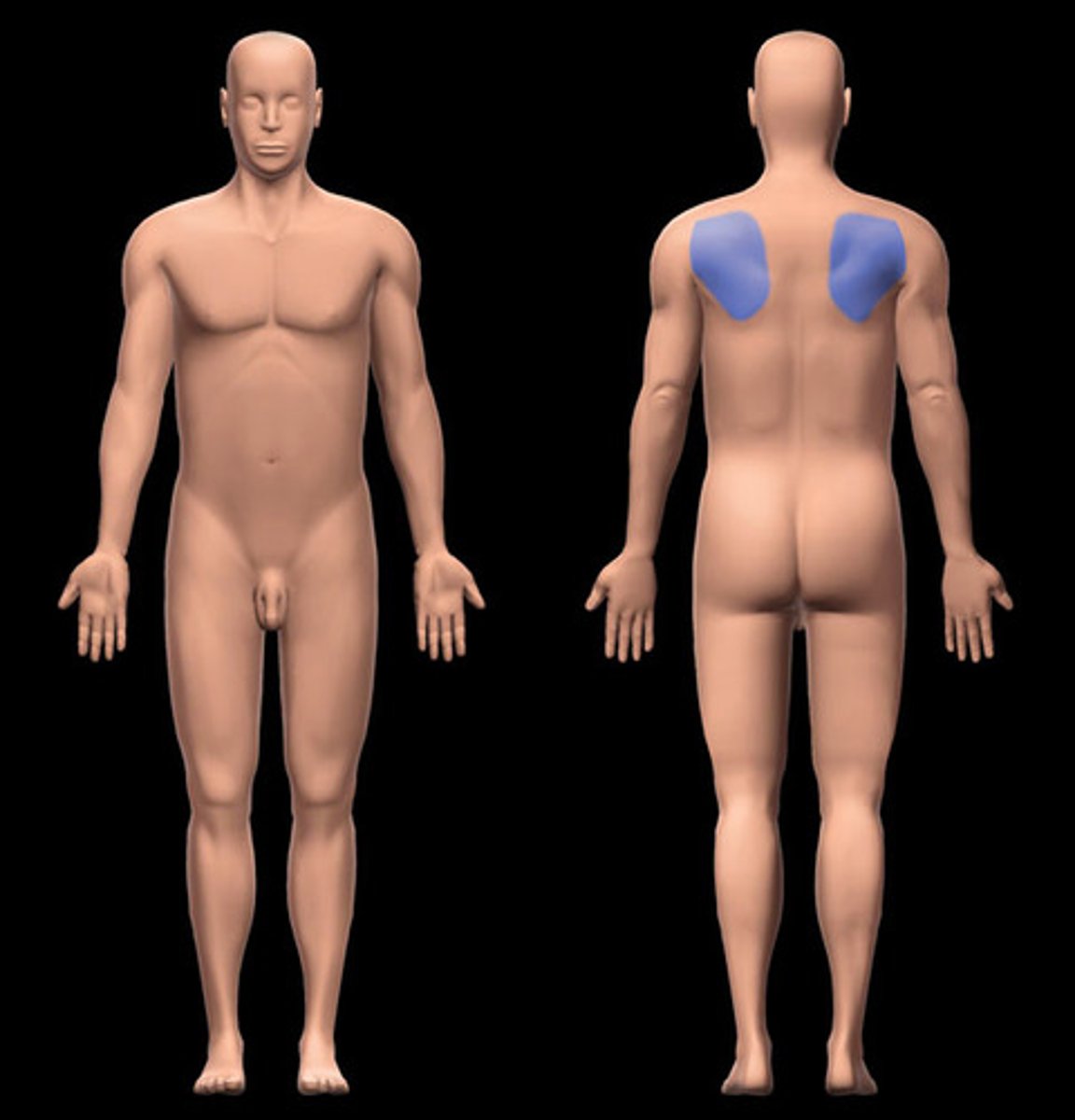
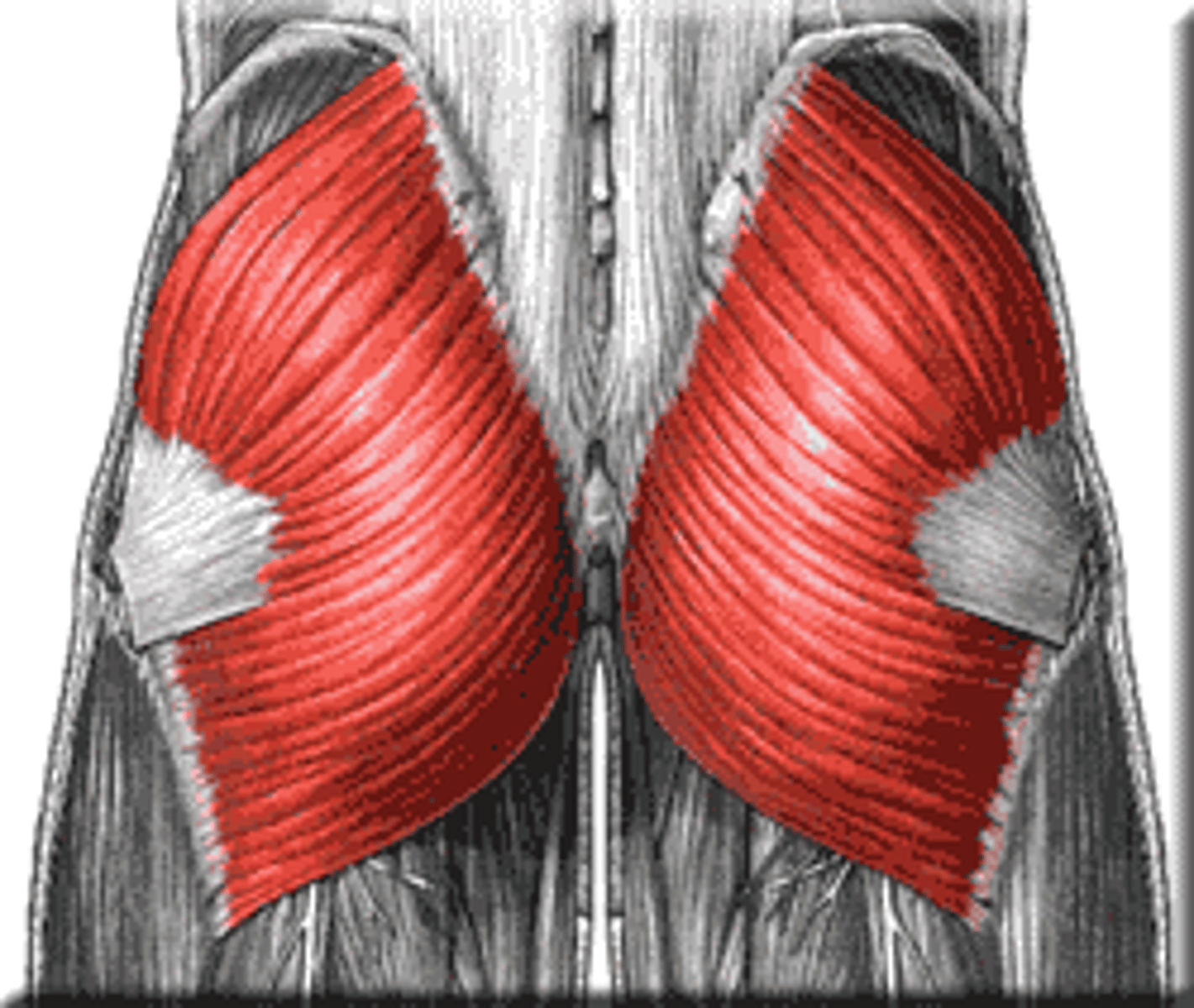
gluteal
the buttocks
popliteal
posterior knee
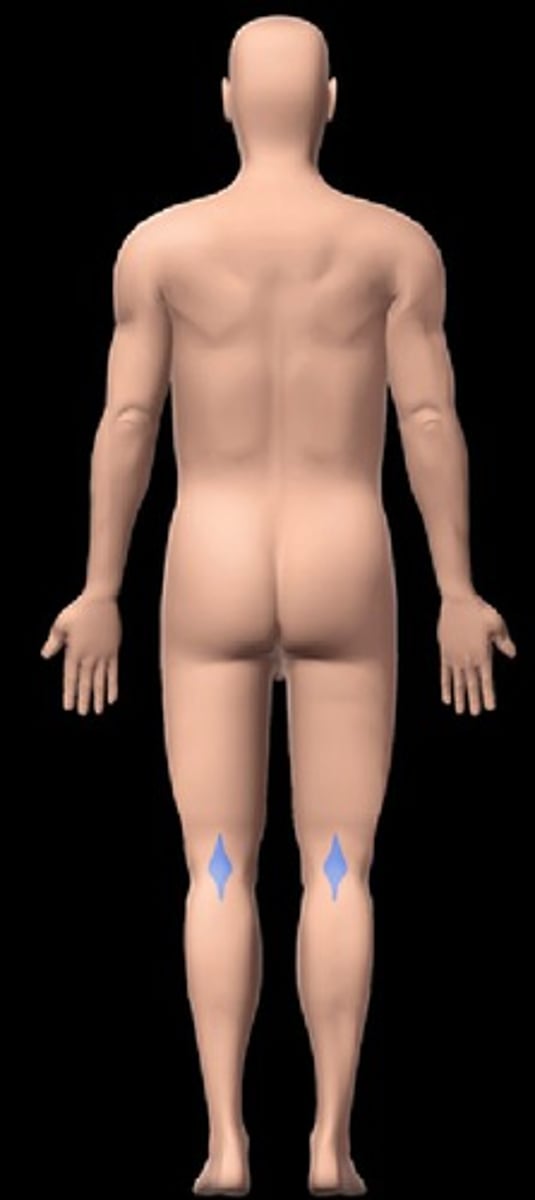
sural
calf
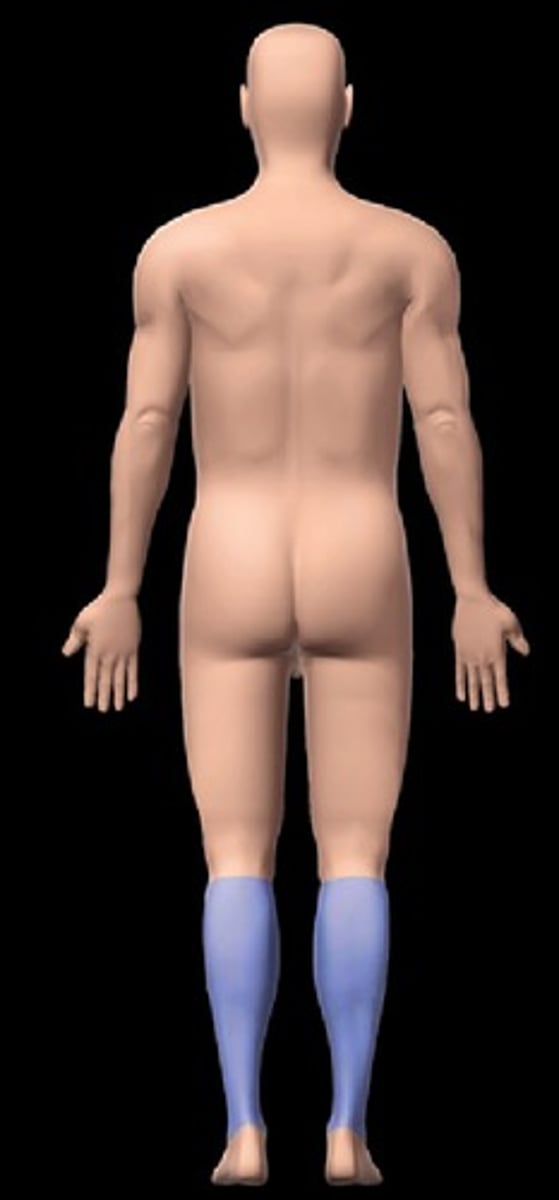
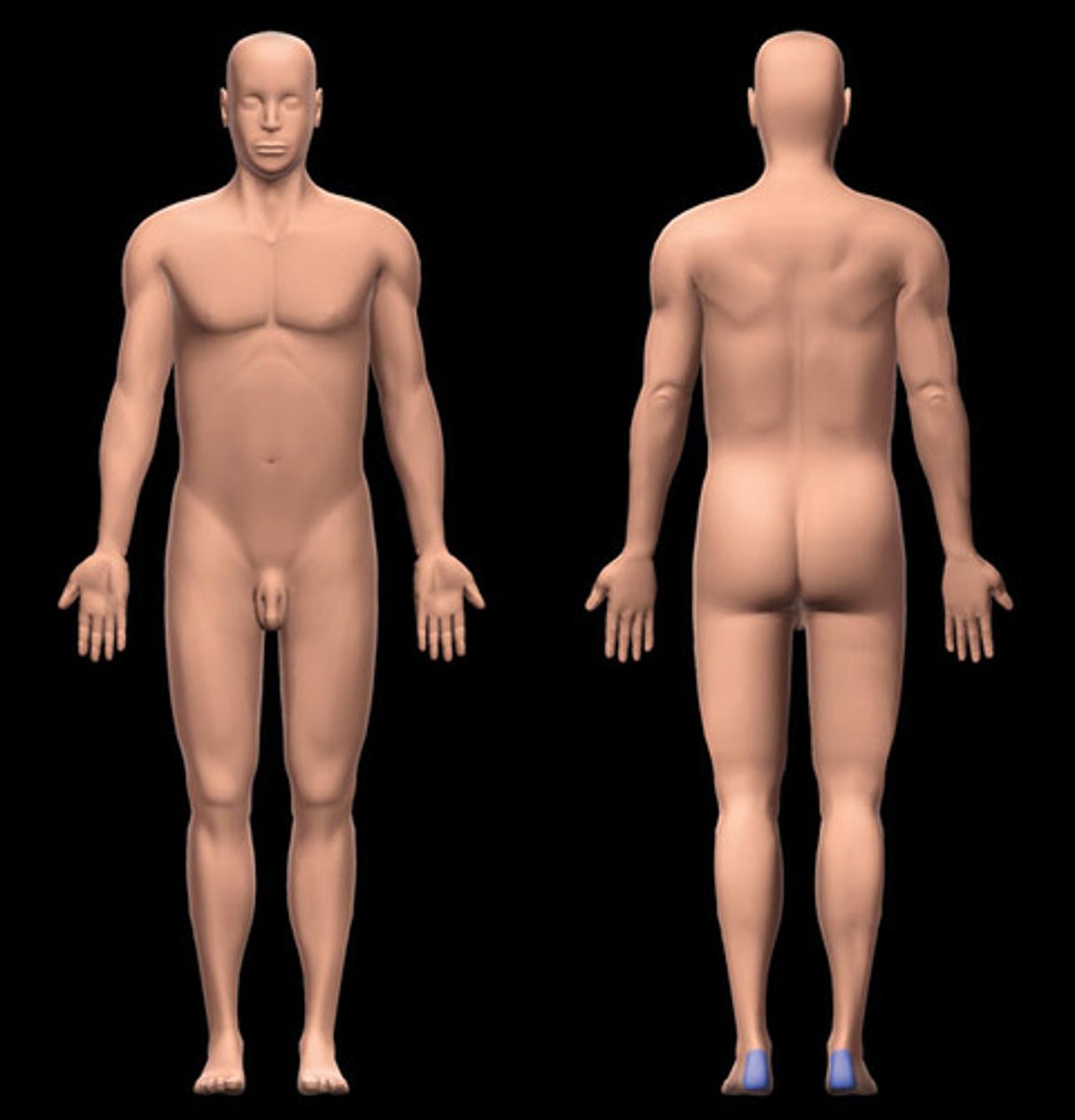
calcaneal
heel of foot
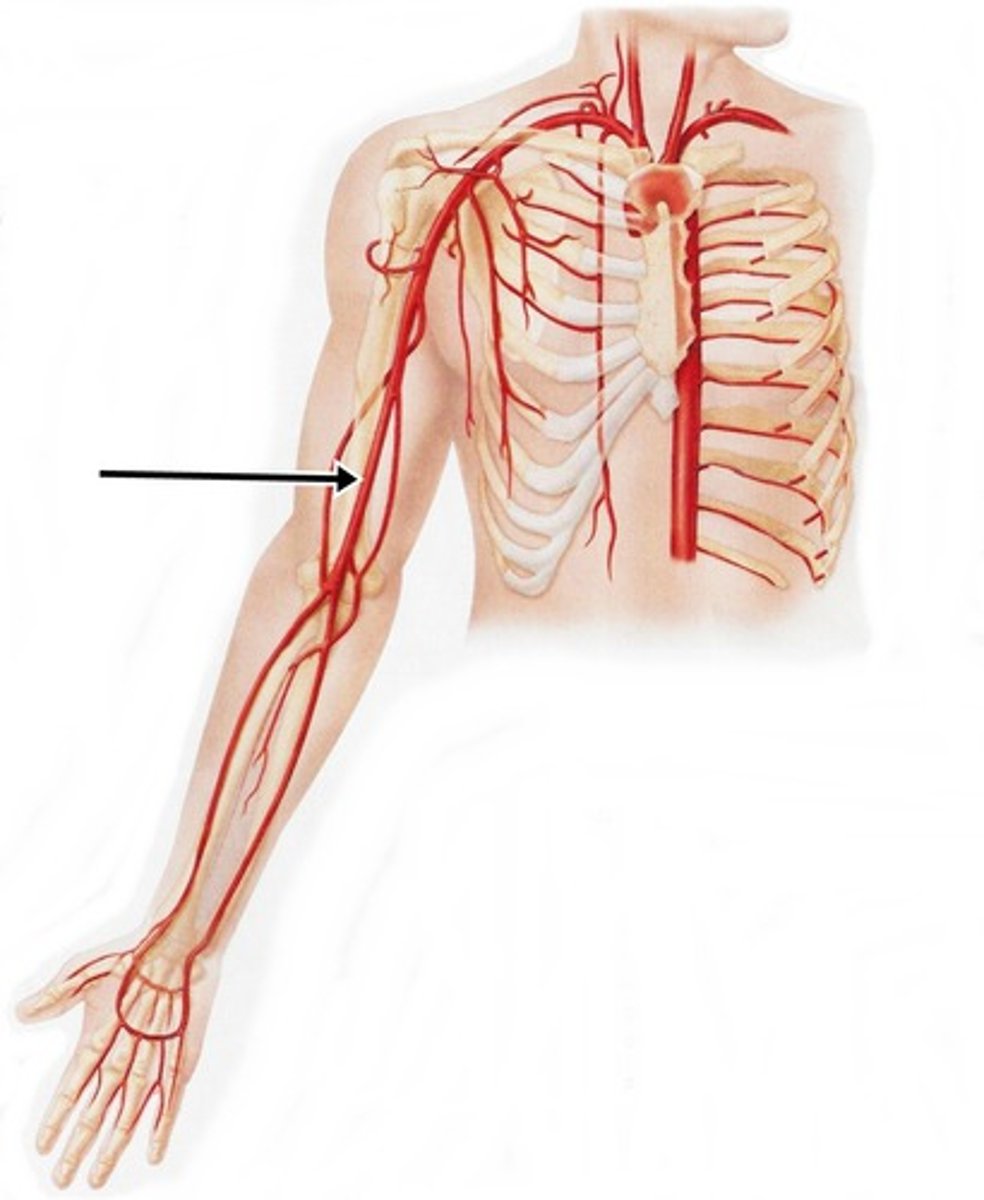
brachial
pertaining to the arm
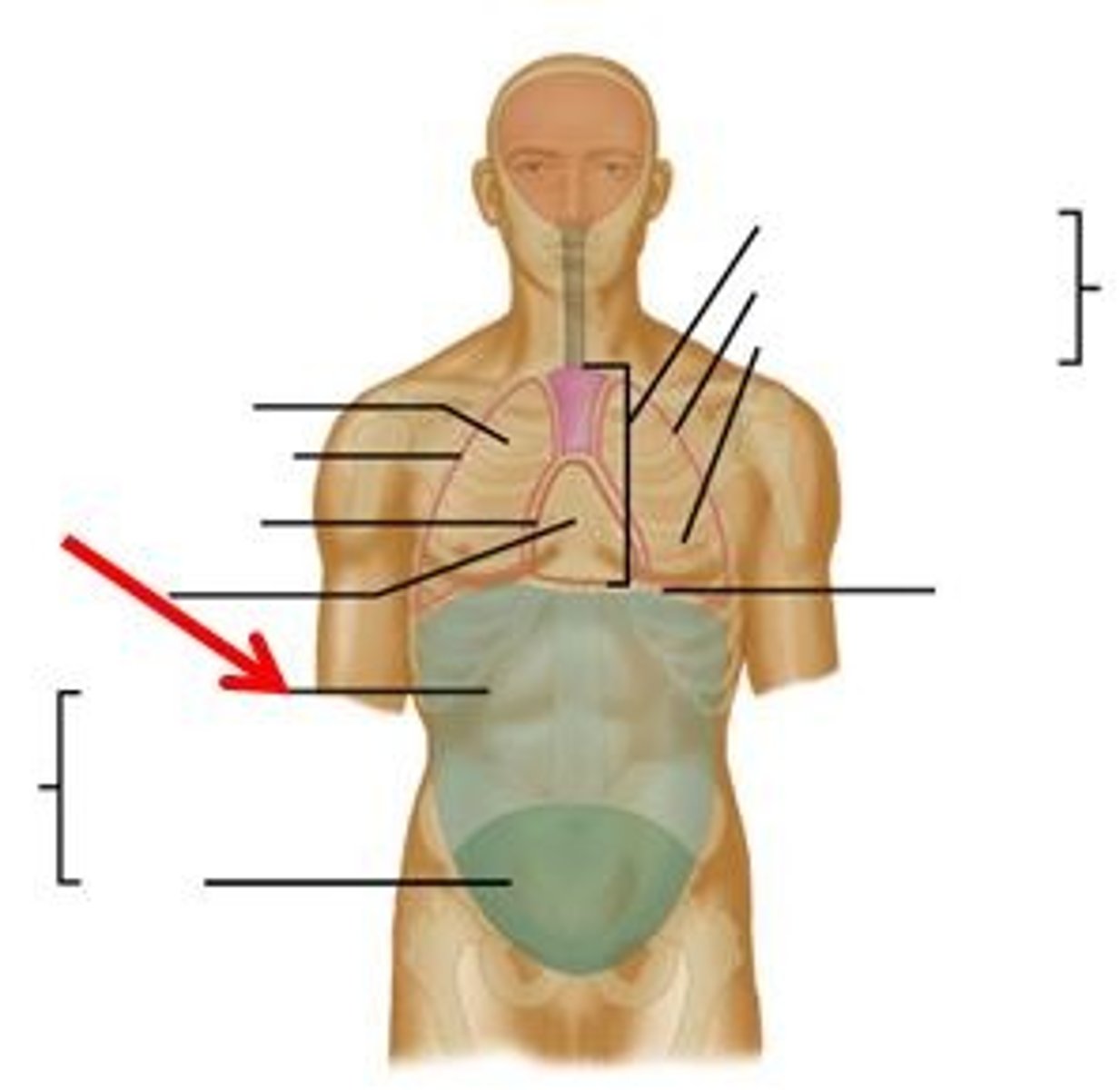
Regions of the stomach
right hypochondriac, epigastric, left hypochondriac, right lumbar, umbilical, left lumbar, right iliac, hypogastric, left iliac
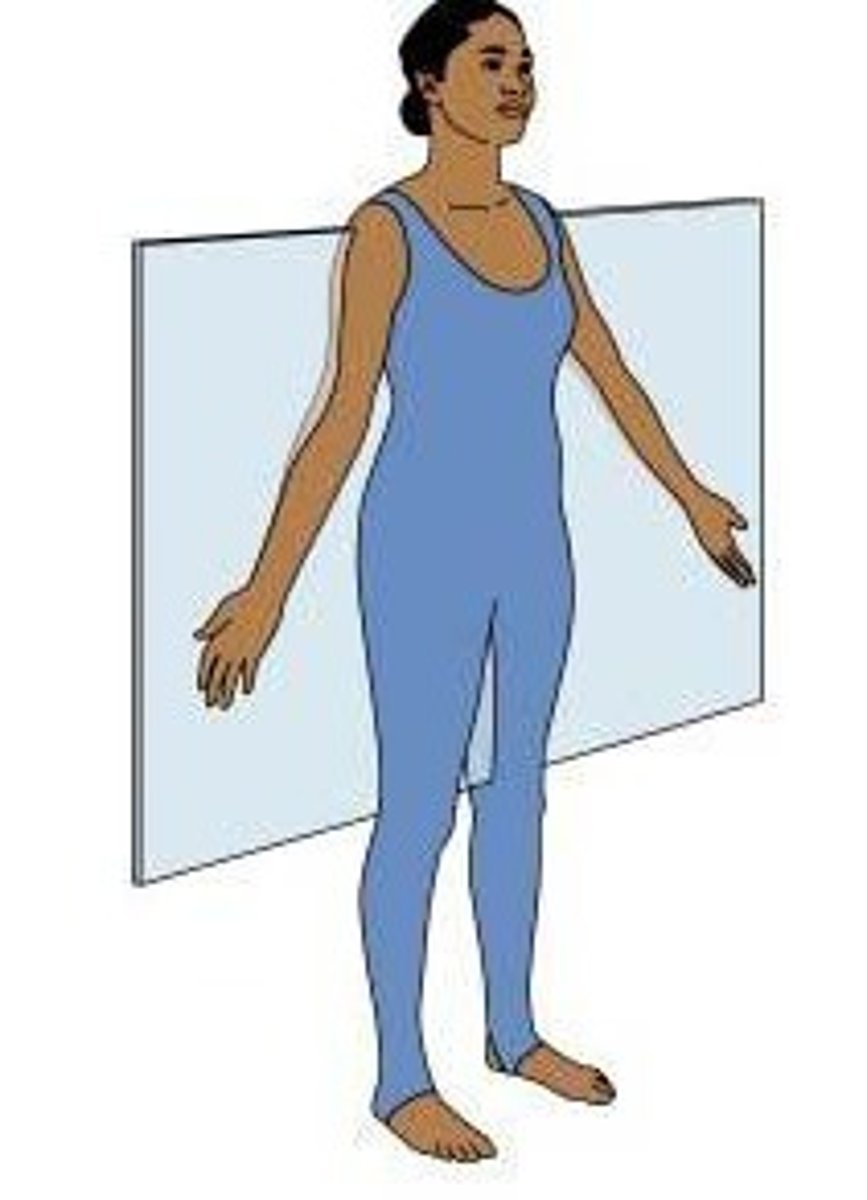
sagittal plane
splits body into left and right
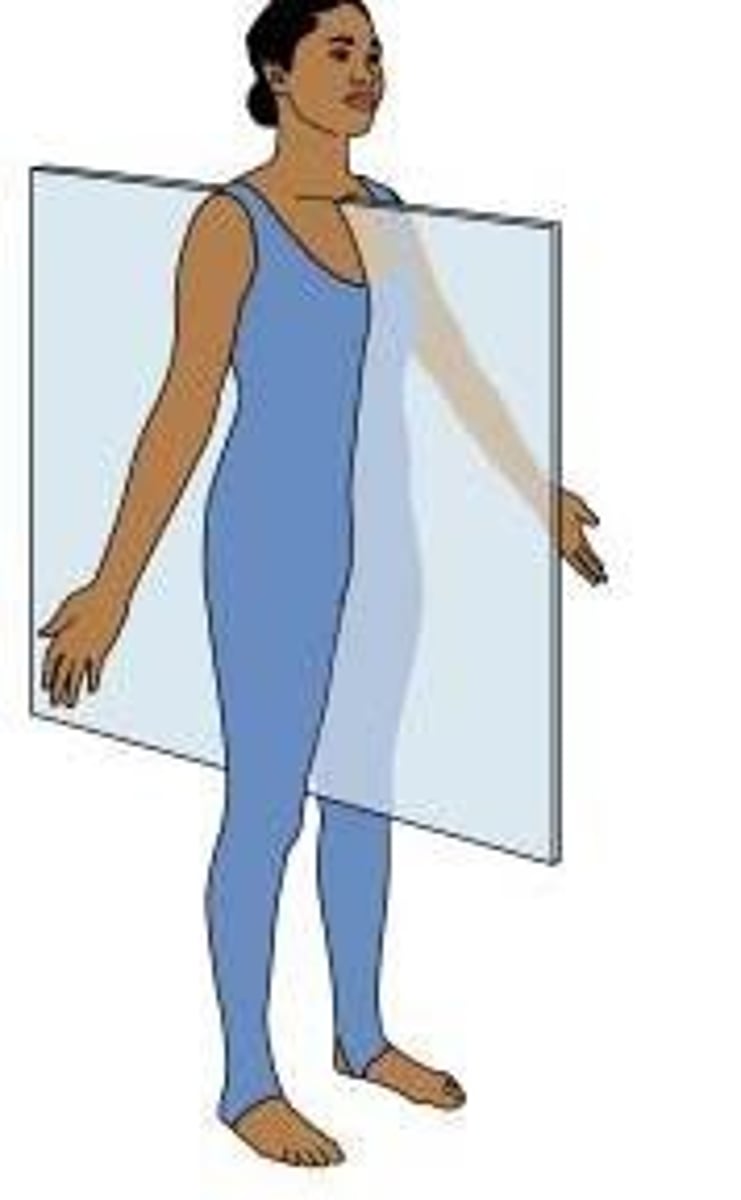
Transverse plane
horizontal division of the body into upper and lower portions
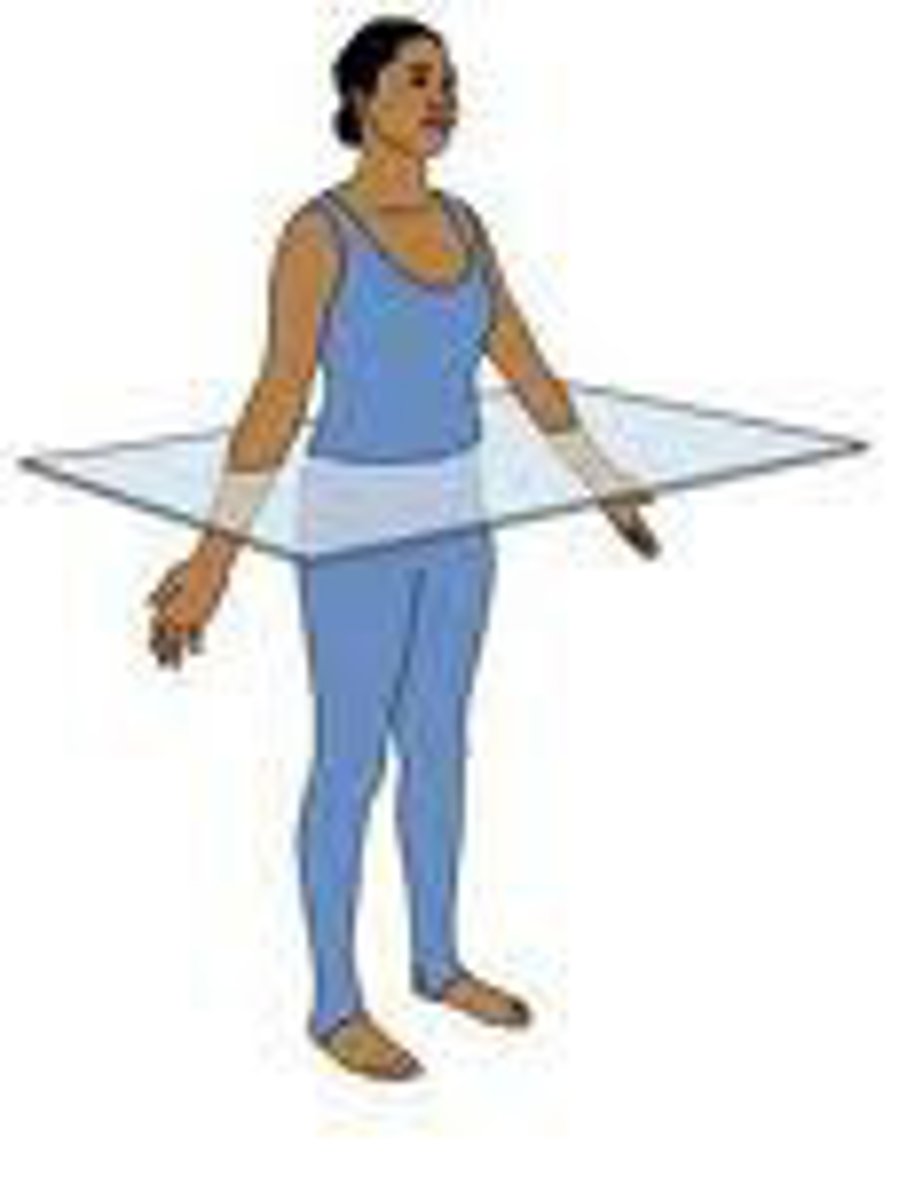
frontal plane
Divides the body into front and back portions.
extension
increases the angle of a joint
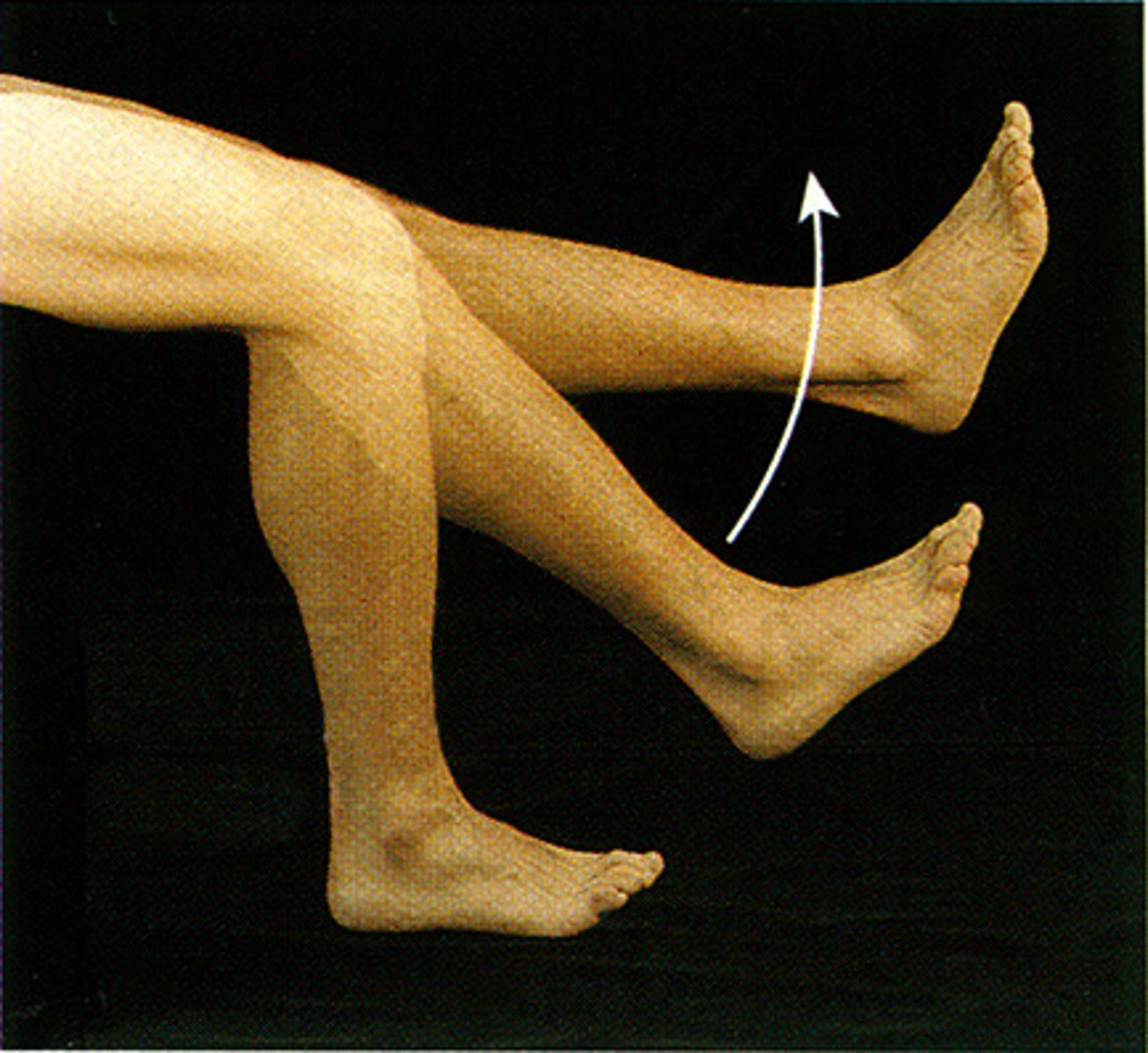
Flexion
Decreases the angle of a joint
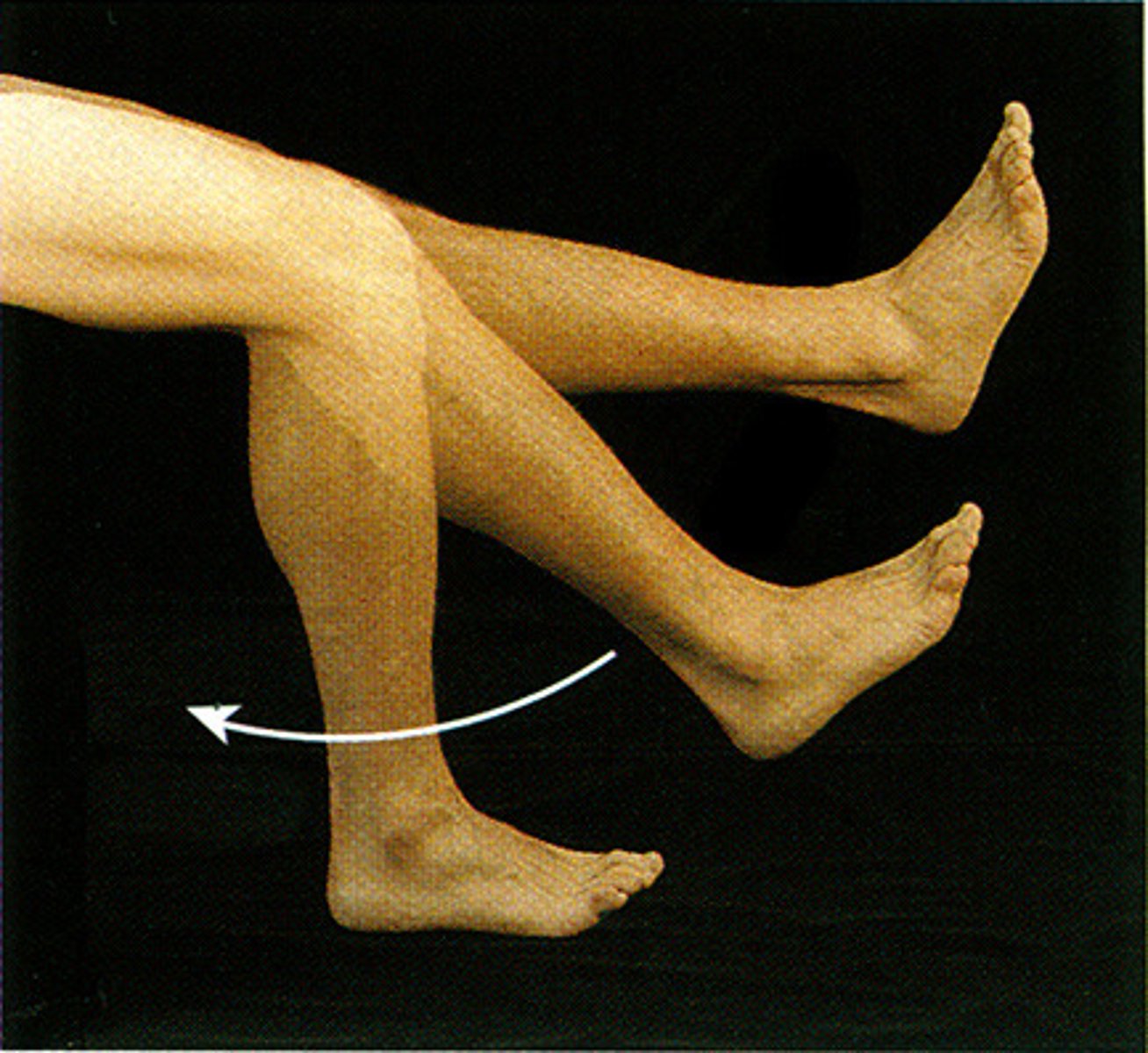
abduction
movement away from the midline
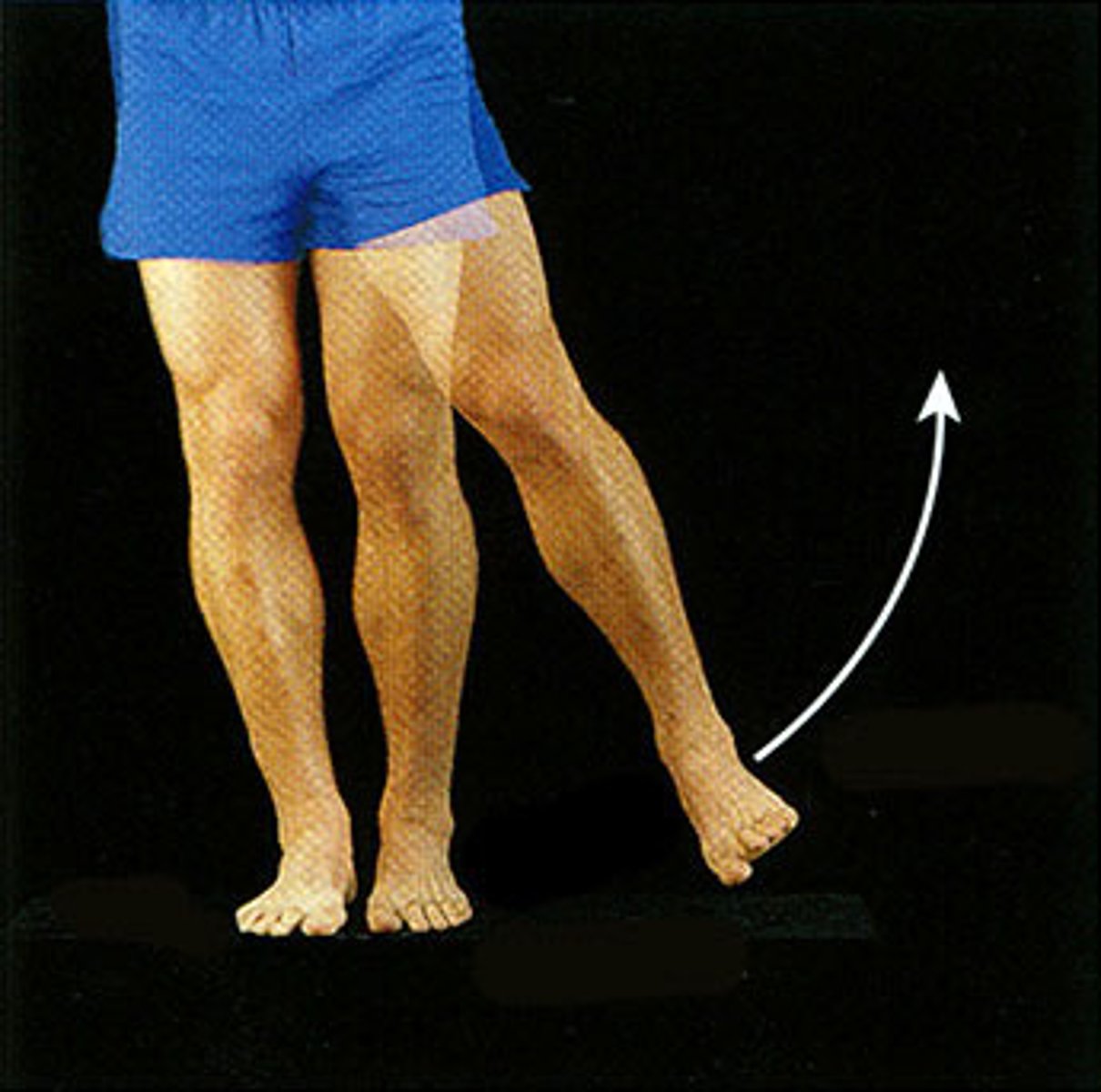
Adduction
Movement toward the midline of the body
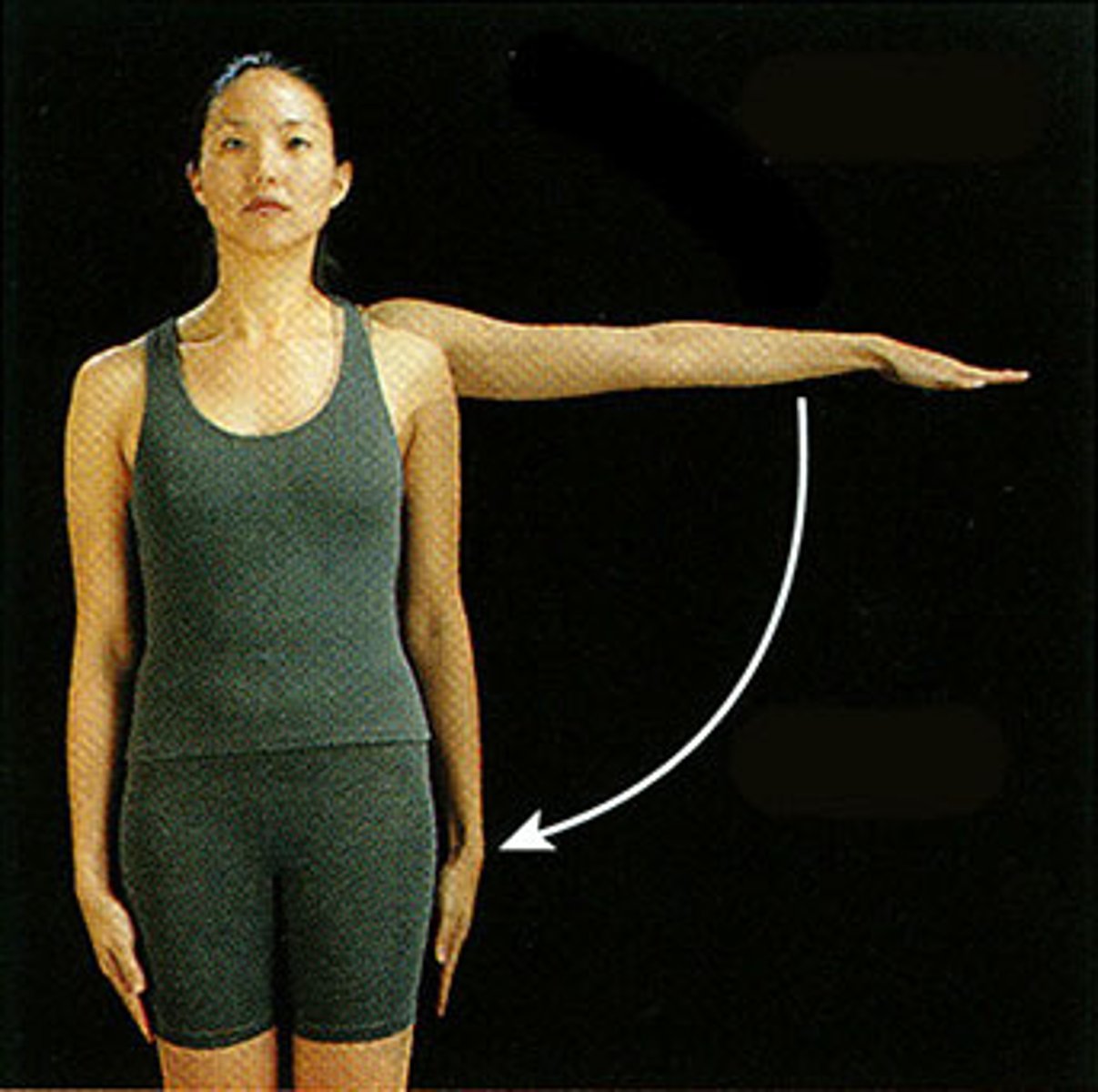

Inversion
turning inward
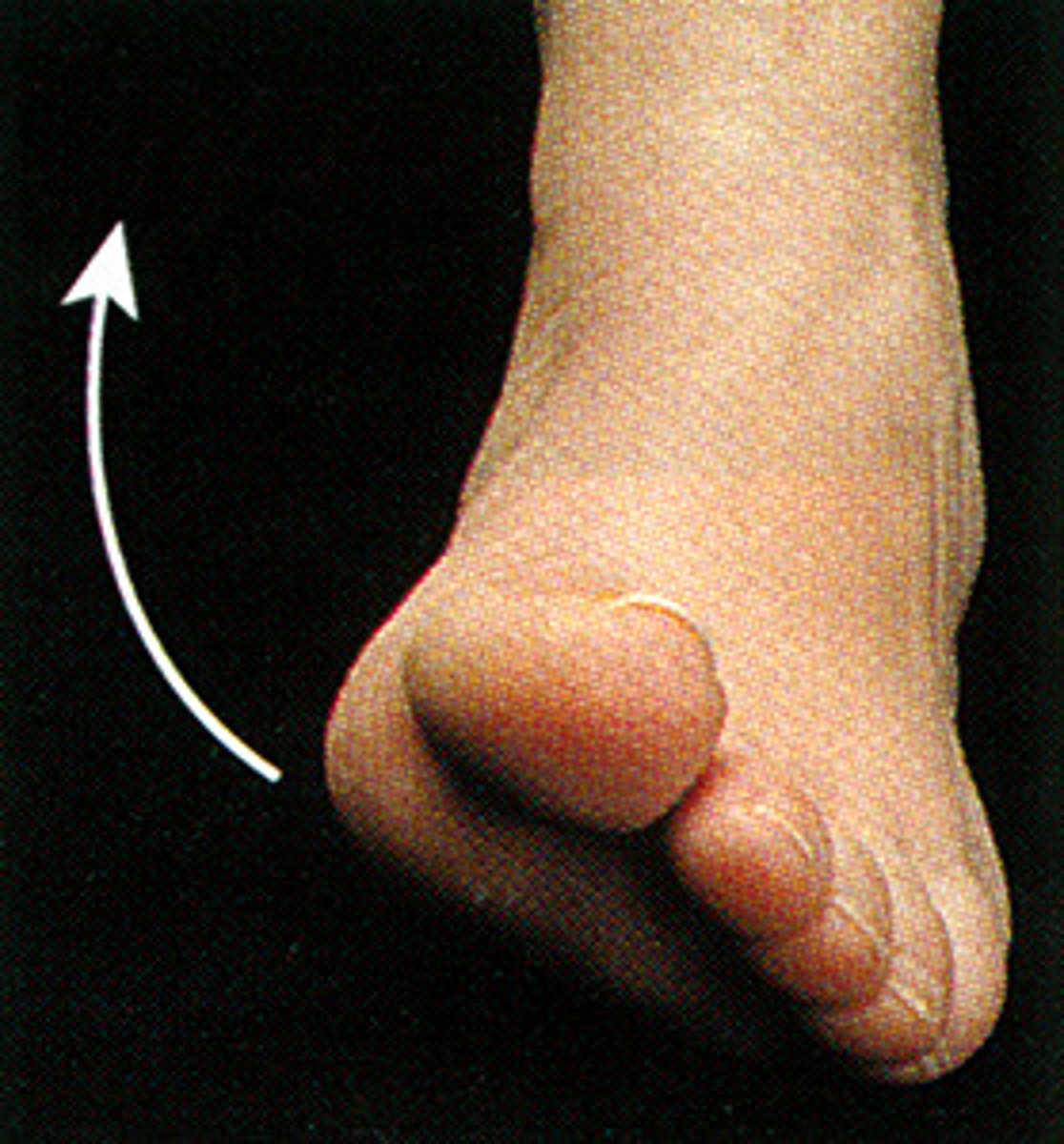
Eversion
turning outward
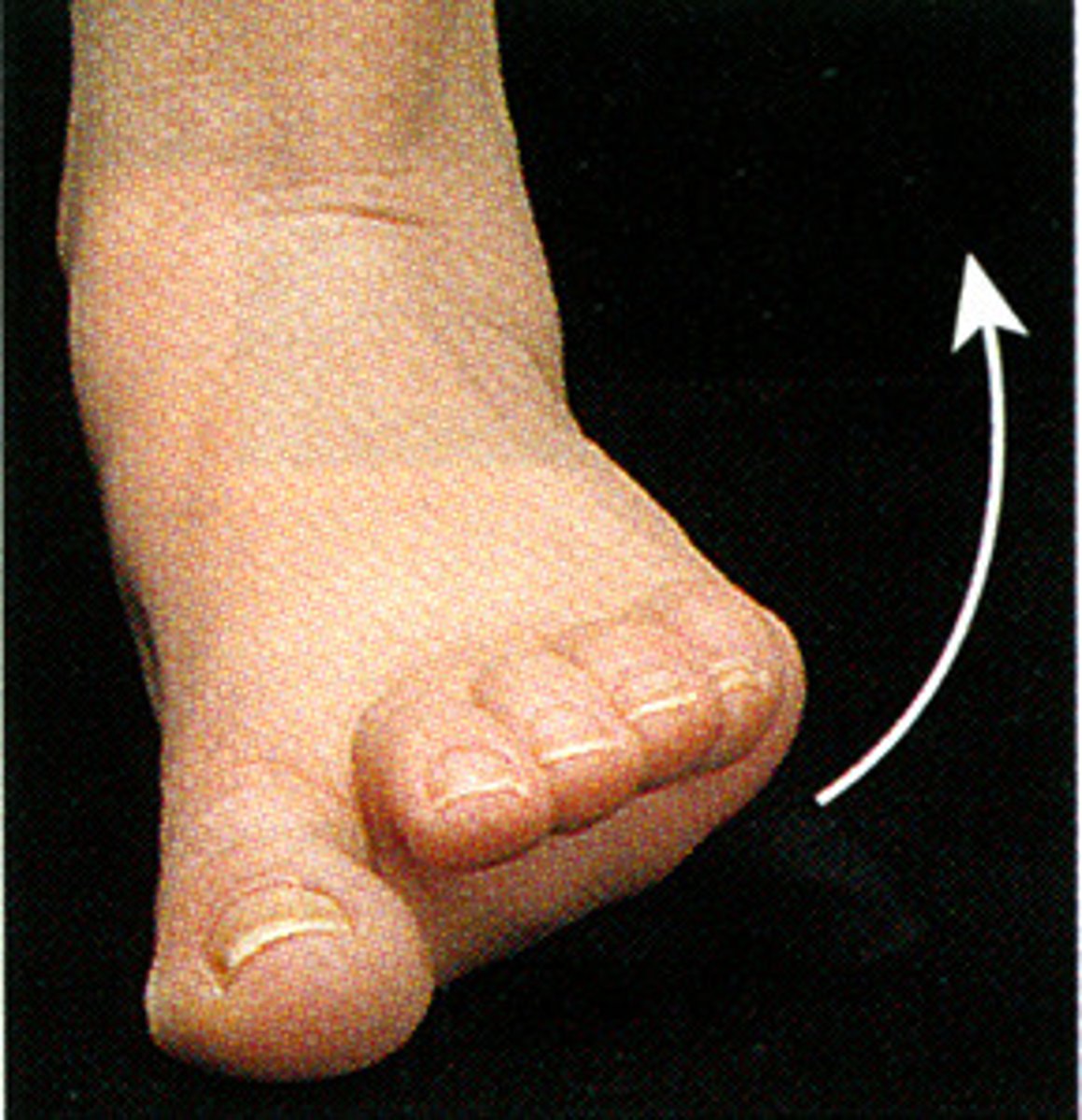
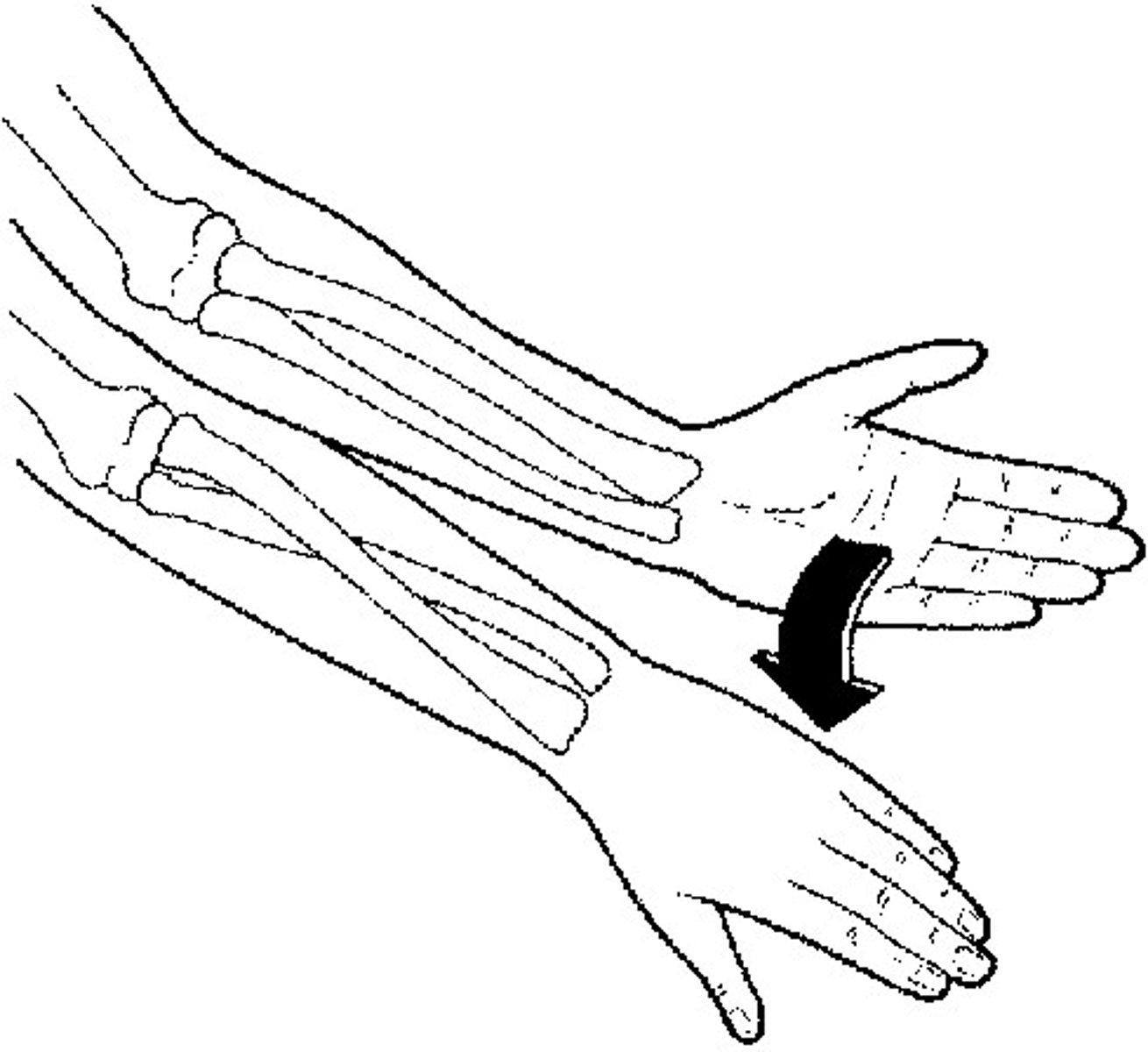
Supination
movement that turns the palm up
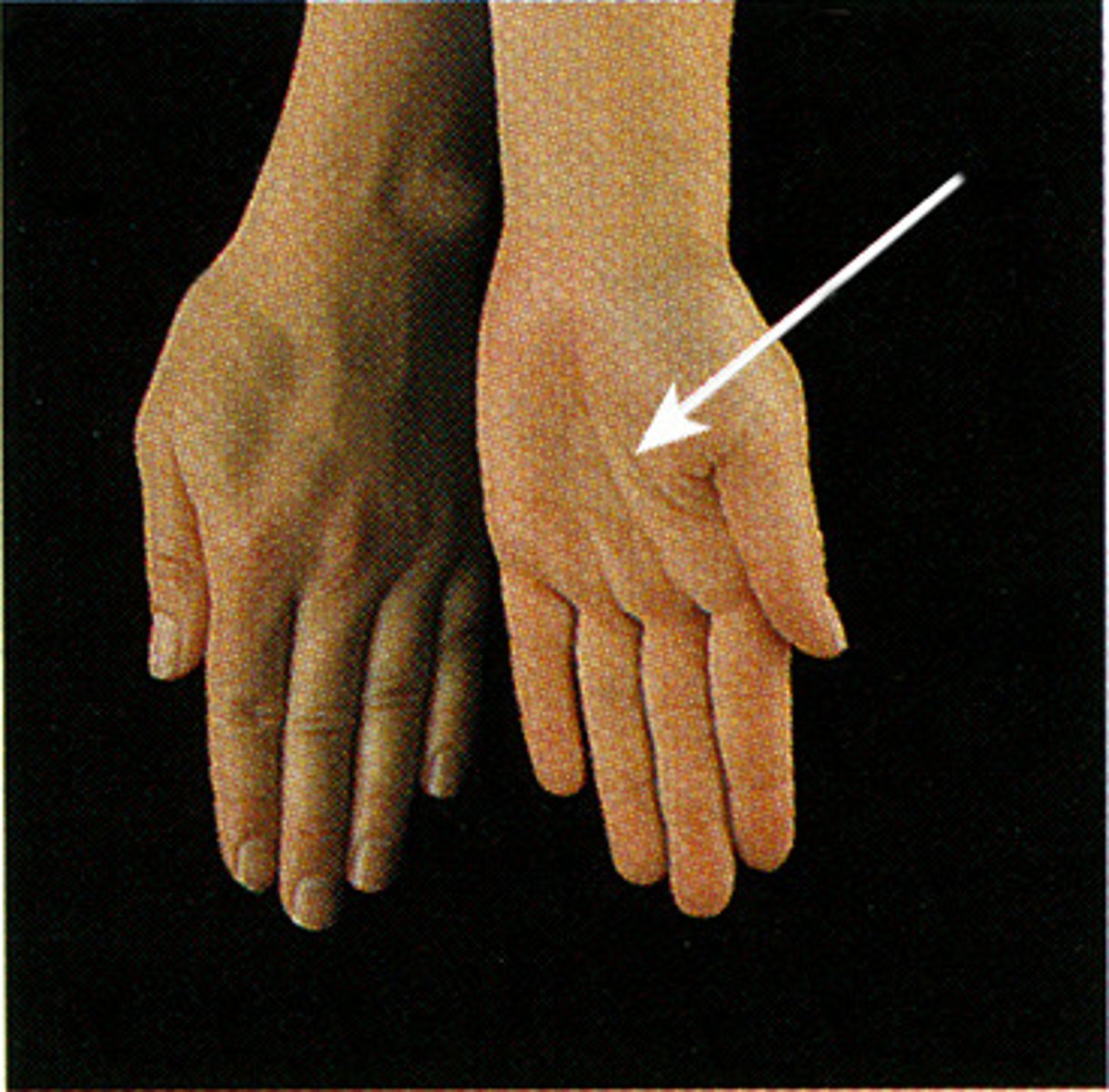
Pronation
turning the palm downward
neutral
Not favoring either side
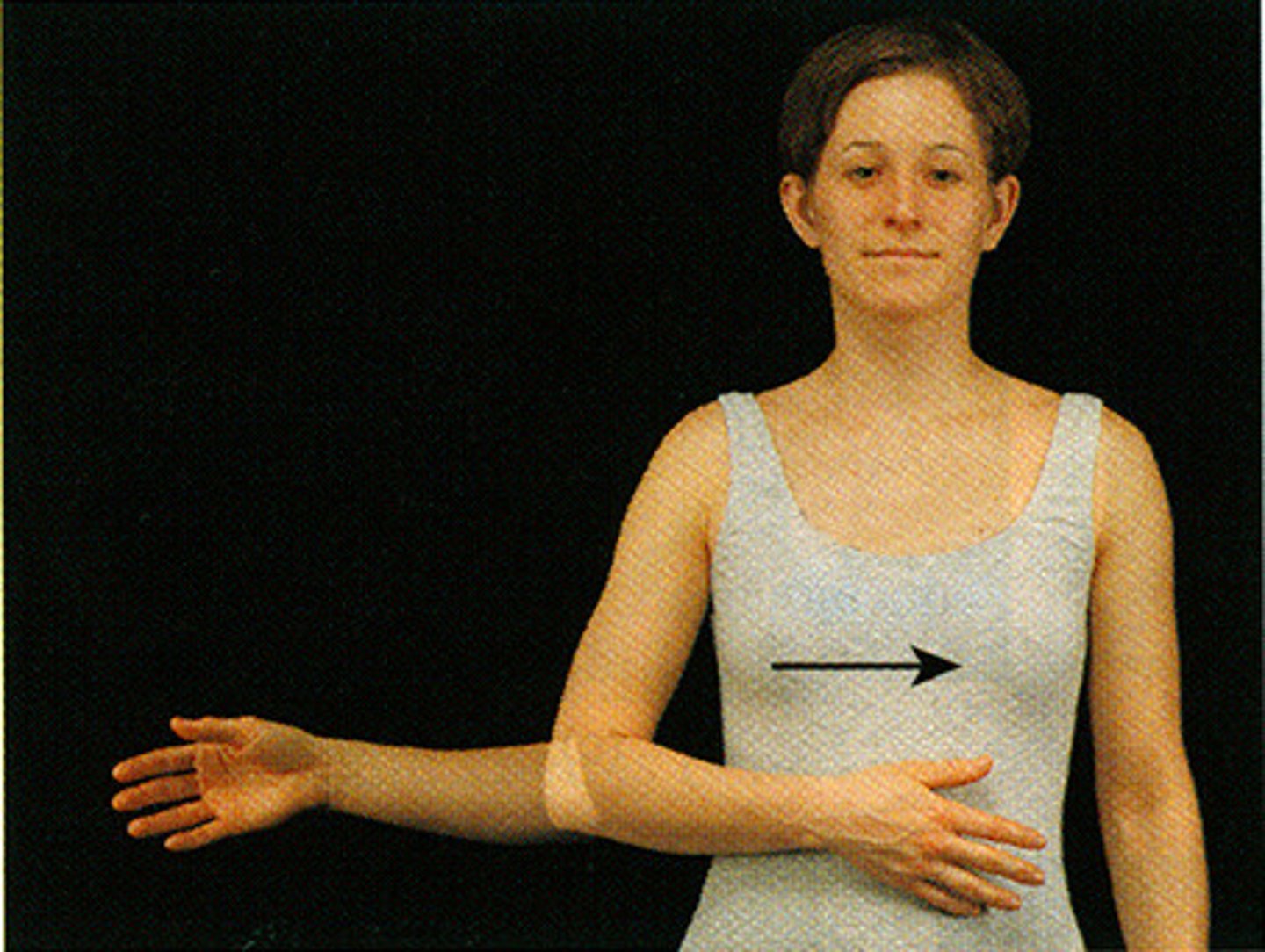
medial rotation
inward (medial) movement of a body segment in the transverse plane
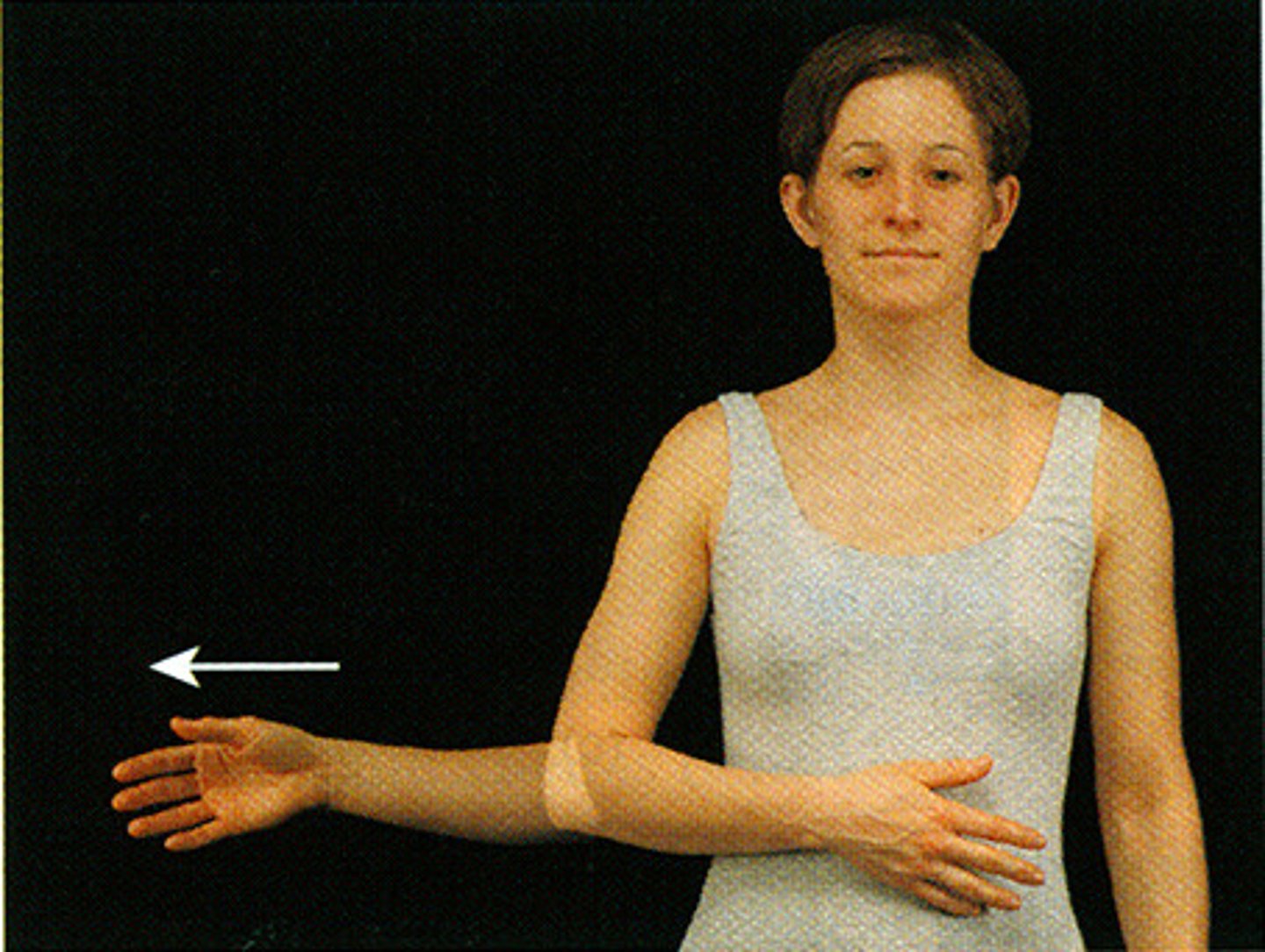
lateral rotation
outward (lateral) movement of a body segment in the transverse plane
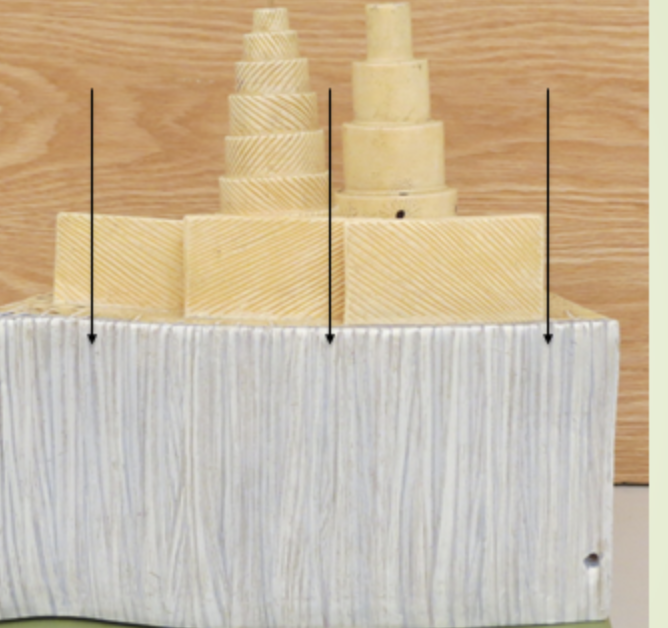
Endosteum
membranous lining of the hollow cavity of the bone
endosteum
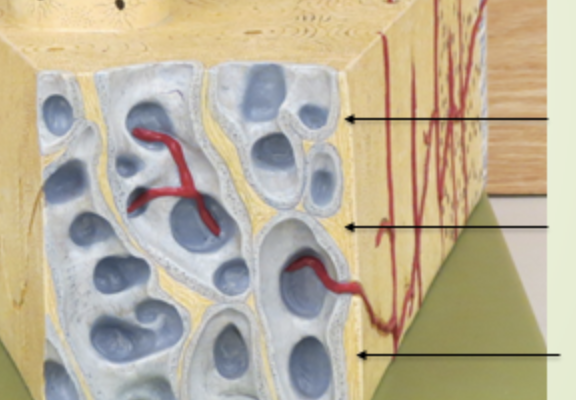
periosteum
surrounding area, outside area
sharpeys fibers
spikes on the side
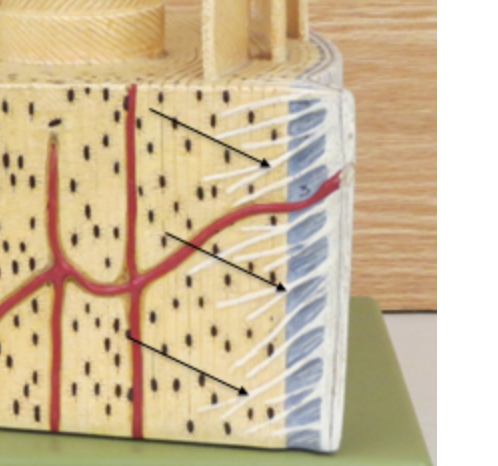
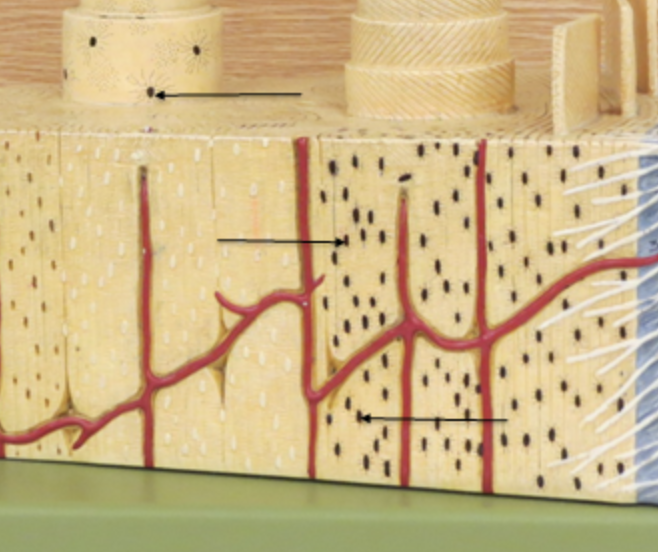
Volkmanns canal
horizontal canal
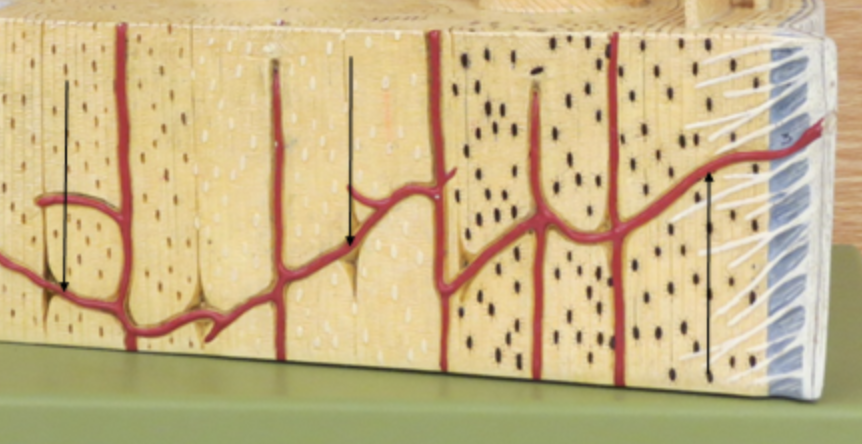
Haversian Canal
vertical canal
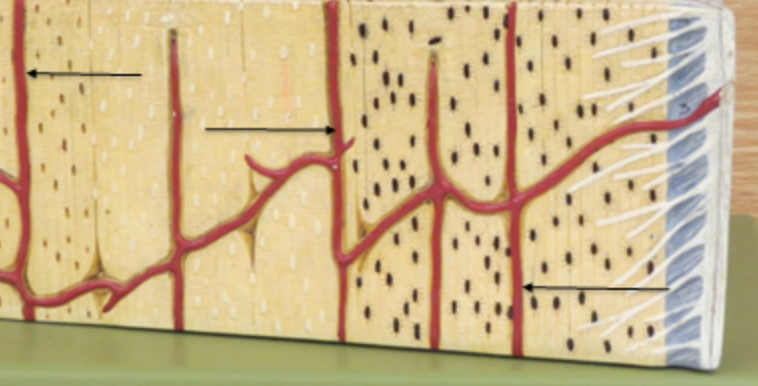
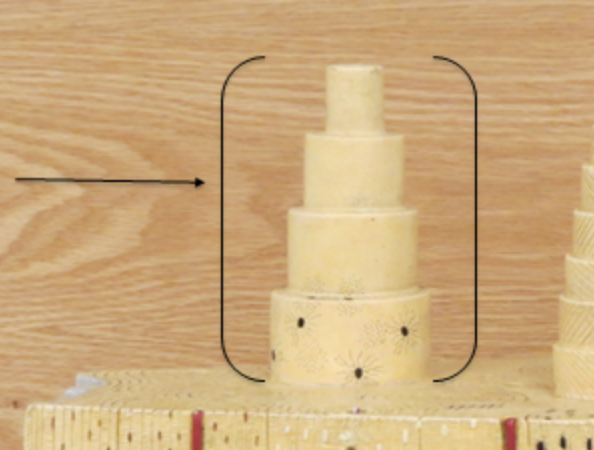
osteon
pillars
central canal
canal of blood vessels, what hole the blood moves through

osteocytes
bone cells

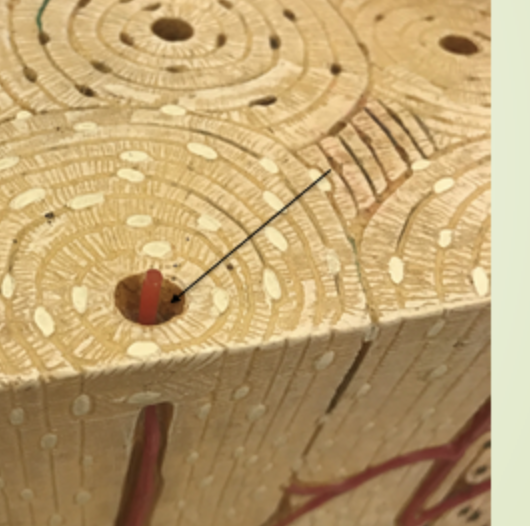
lacuna
where the osteocytes (bone cells) are located
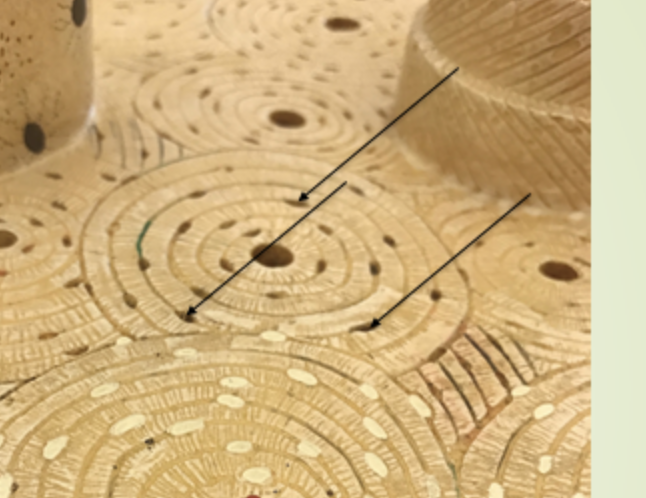

canaliculi
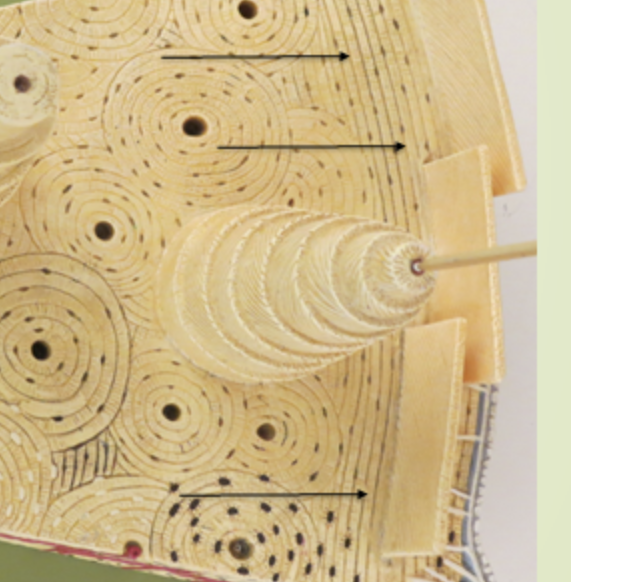
parts of the rings around the canals , communicates with the osteocytes
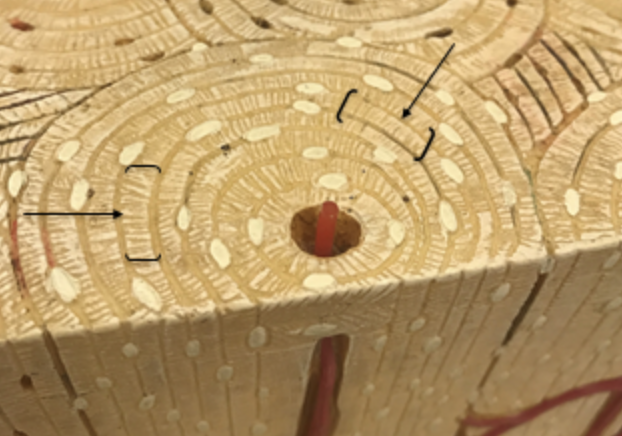

interstitial lamellae
irregularly shaped and fill in the spaces between osteons
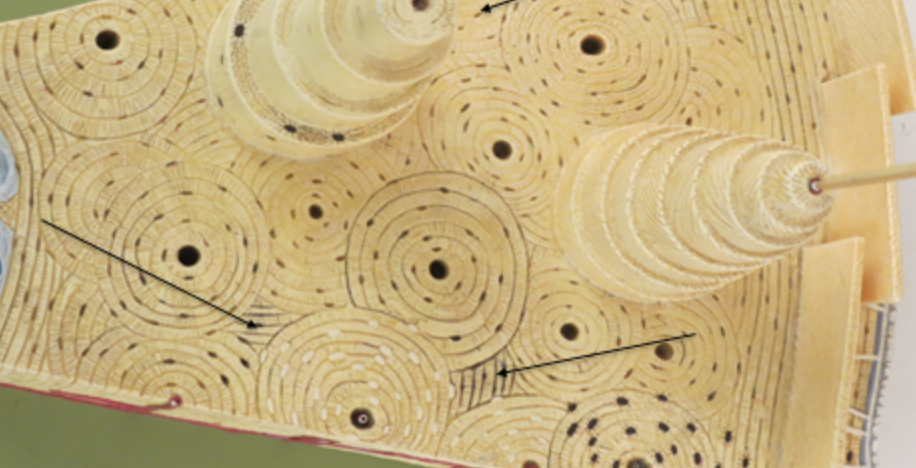

concentric lamellae
cylindrical rings of lamellae which are rich in collagen.
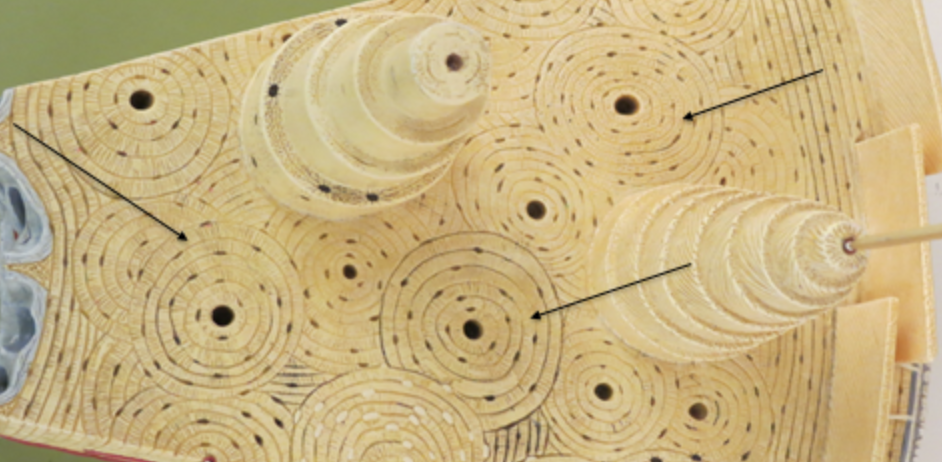

circumferential lamellae
one of the layers of bone that underlie the periosteum

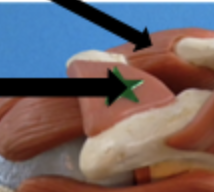
acromioclavicular ligament
on top of shoulder joint
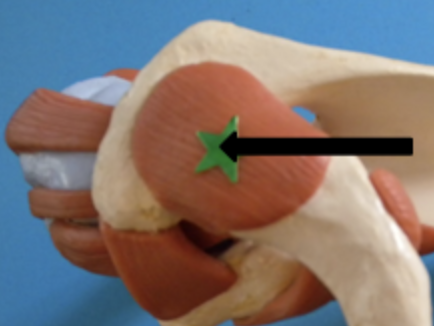
Coracoacromial ligament
middle of shoulder joint
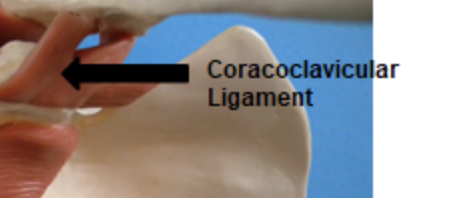
Coracoclavicular ligament
under shoulder joint
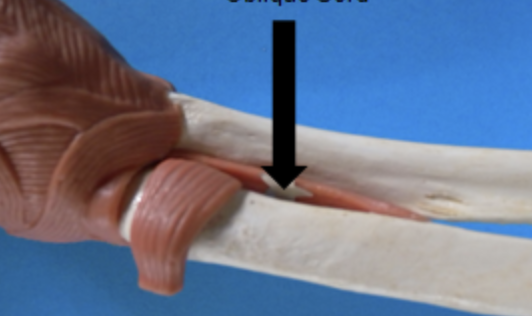
oblique cord
middle of elbow joint
ulnar collateral ligament
above funny bone in elbow joint
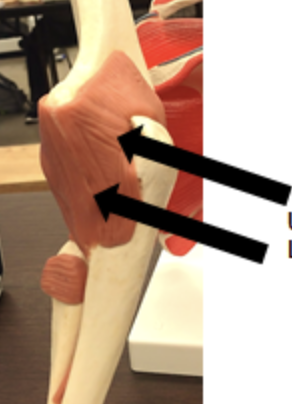
radial collateral joint
very inside (medial) elbow joint
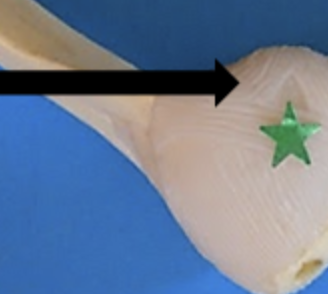
annular ligament
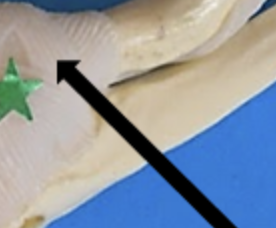
posterior cruciate ligament

anterior cruciate ligament

tibial collateral ligament
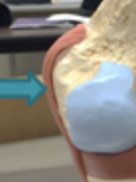
fibular collateral ligament
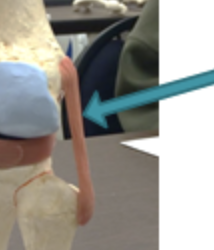
patellar tendon

patellar ligament
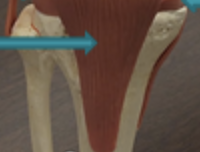
lateral Meniscus

medial meniscus
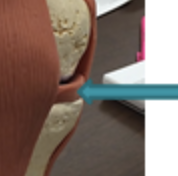
frontal bone
forehead

left parietal bone

right parietal bone

occipital bone

nuchal line

crista Galli

cribriform plate

lesser wing of sphenoid

foramen lacerum

foramen magnum
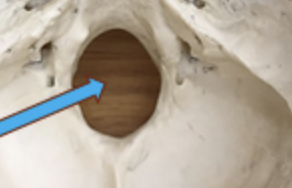
sella turcica
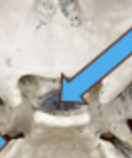
foramen ovale

foramen spinosum

ethmoid bone

greater wing of sphenoid

optic canal
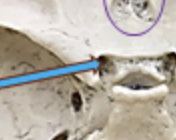
foramen rotundum
