Occlusion, Jaw Movement and Occlusal Contacts
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Maximum intercuspation (MI)
mandible with the teeth are brought into full interdigitation wiht the maximum number of teeth contacting
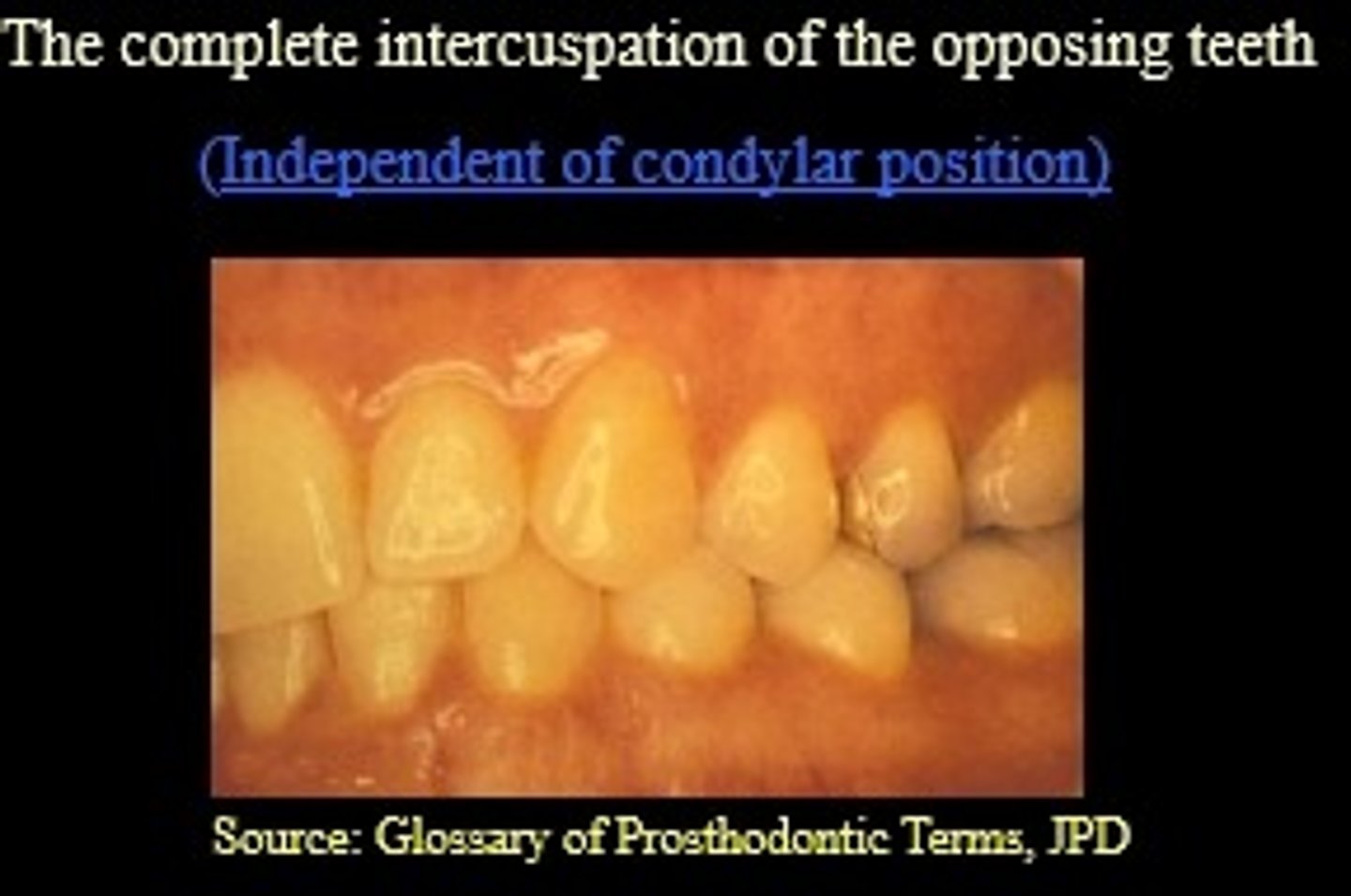
Where it is the most stable with interlocking the 2 arches considered to be?
maximum intercuspation
What is independent on condylar position (meaning only based on teeth)?
maximum intercuspation
Centric Occlusion (CO)
tooth guided position where it depends on the initial tooth contact when the mandible closes
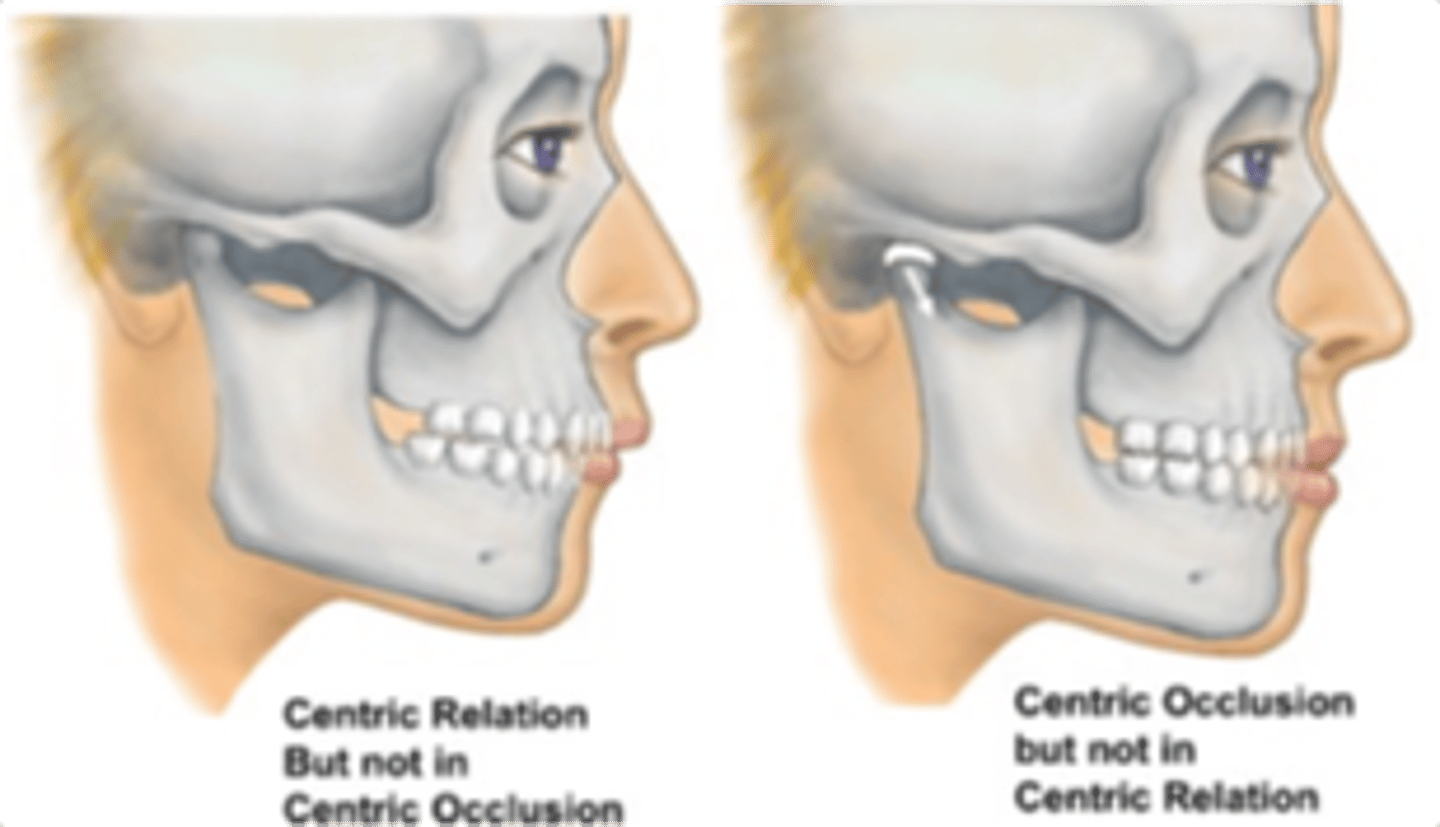
What dos the CO provide?
reference point in restorative procedures
Functional shift
small shift from CO to MI (grinding motion)
Functional occlusion
all contacts during chewing, swallowing, or normal actions
Normal contacts
made during chewing and swallowing
What is the most comfortable joint position?
centric relation
Centric Relation (CR)
maxillomandibular relationship where the functional heads of the condyles are in the most unrestrained, retruded anatomic position in the glenoid fossae of the temporomandibular joints
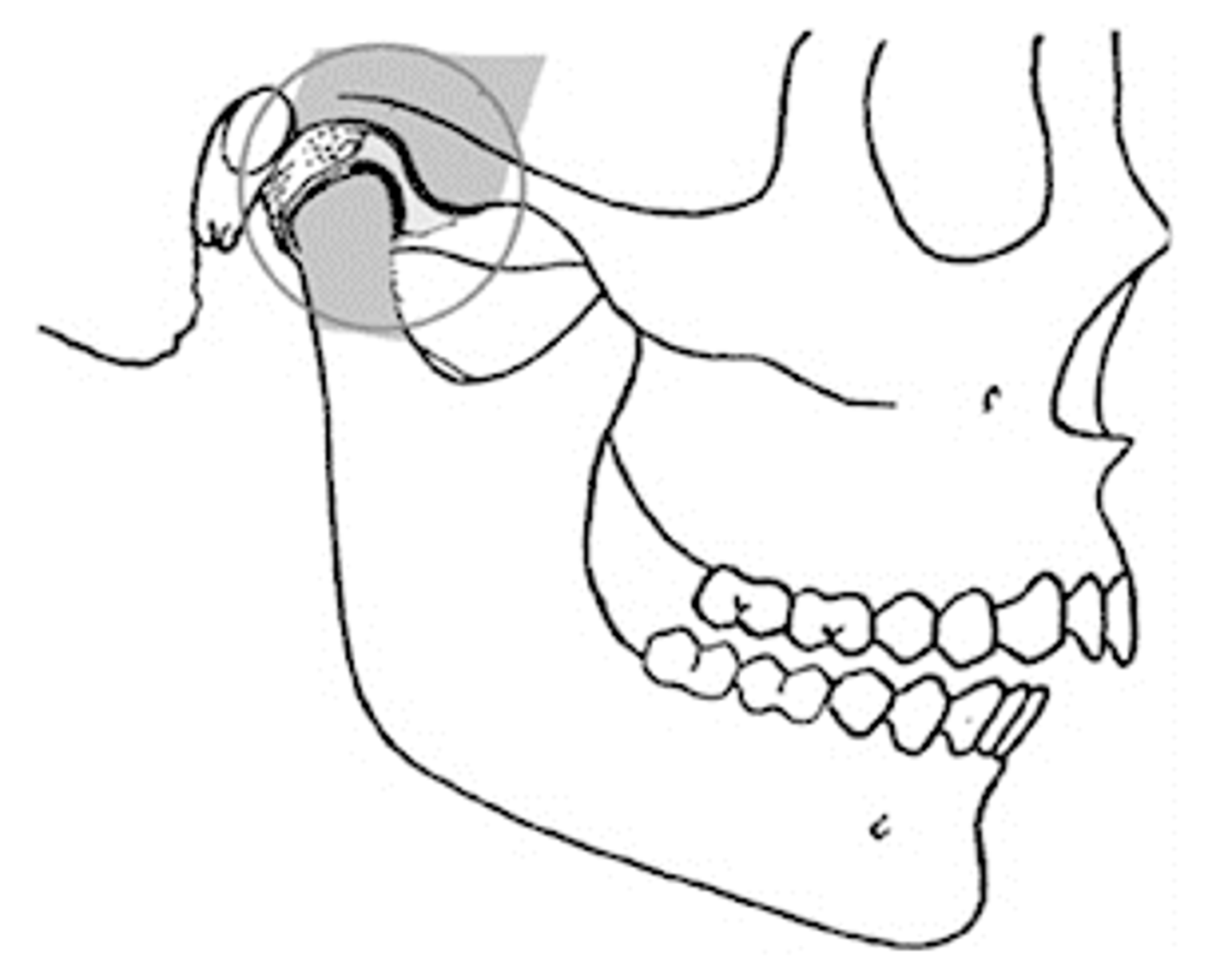
What is independent on tooth contacts (meaning only based on joint)?
centric relation
Guided ligament position and where the jaw should be
centric relation
Why can't the patients mandible be forced into CR from the rest position?
because a person's reflex neuromuscular defense would resist the applied force
When guiding to the centric relation, how should the mandible be?
relaxed and gently guided
Tonic stretch reflex of the mandibular elevators
usual reflex cited as the basis for the postural position of the mandible
All the muscles that open and close are said to be?
in a state of minimal contraction only to main posture
The mandible is how man y mm away from MI
2-4
Freeway space/interocclusal rest space/interocclusasl distance
distance that the mandible is from the MI
Canine or Cuspid protected occlusion
occlusal relationship in which the vertical overlap of the maxillary and mandibular canines produces a disclusion of all the posterior teeth when the mandible moves to either side
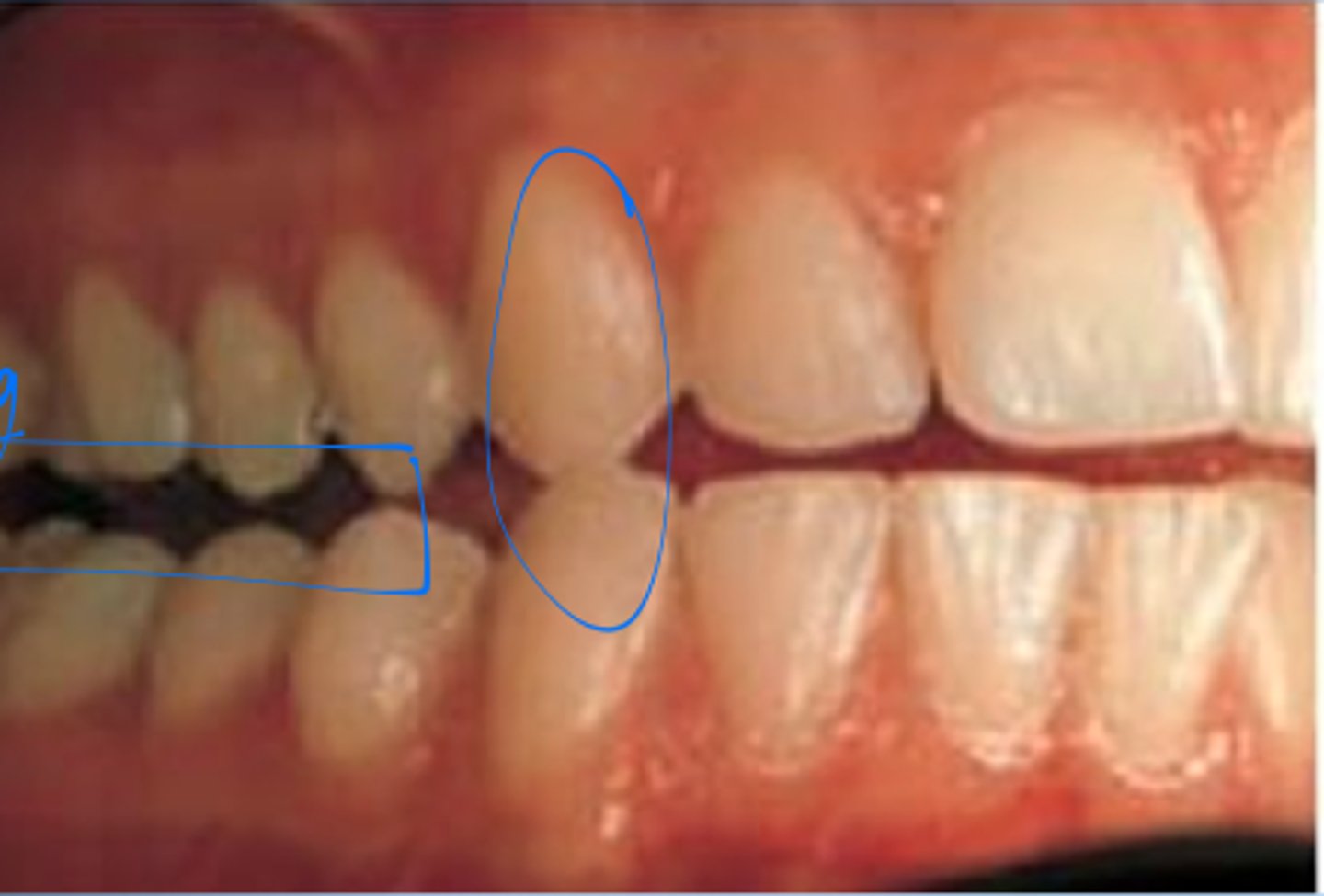
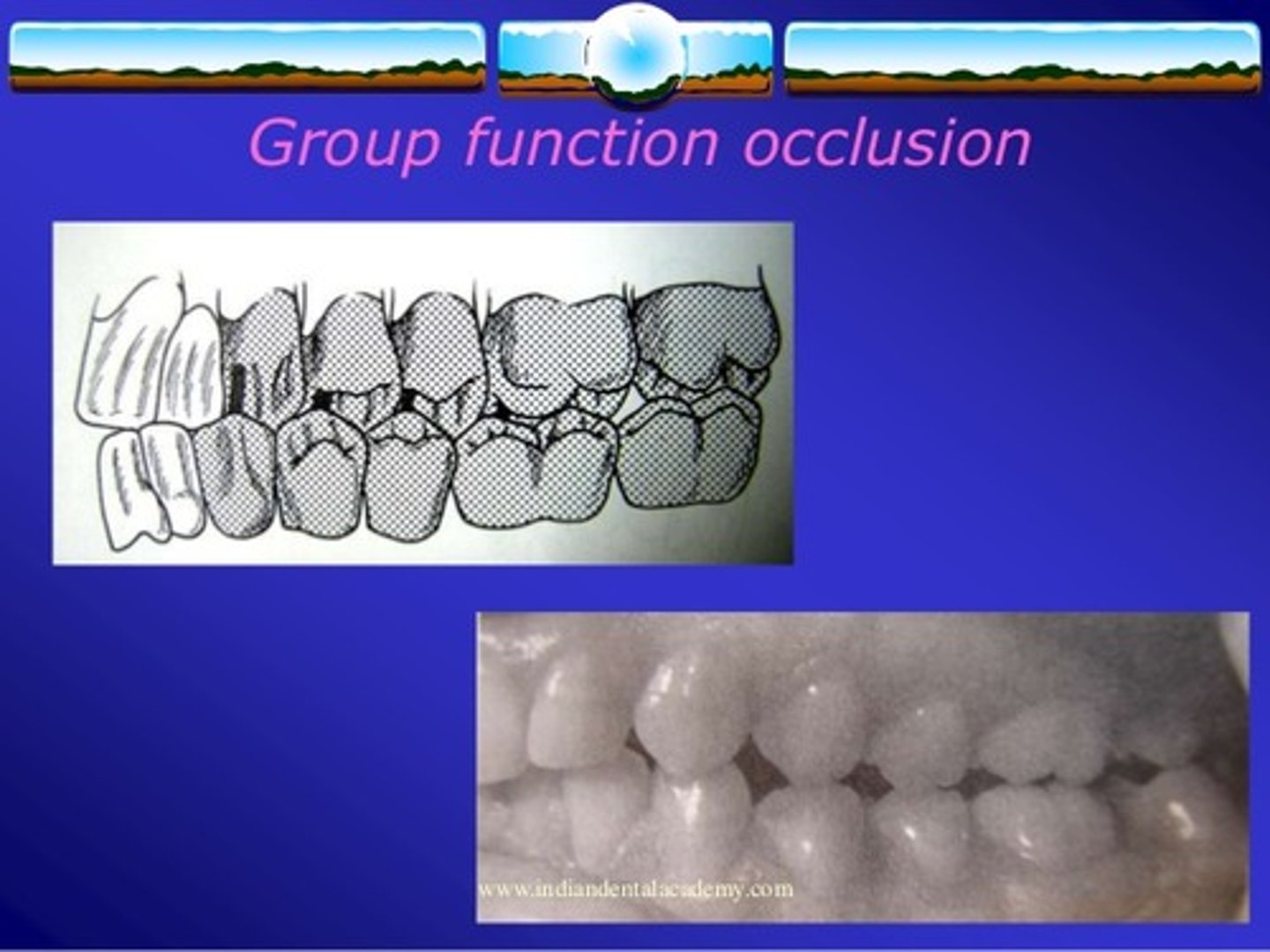
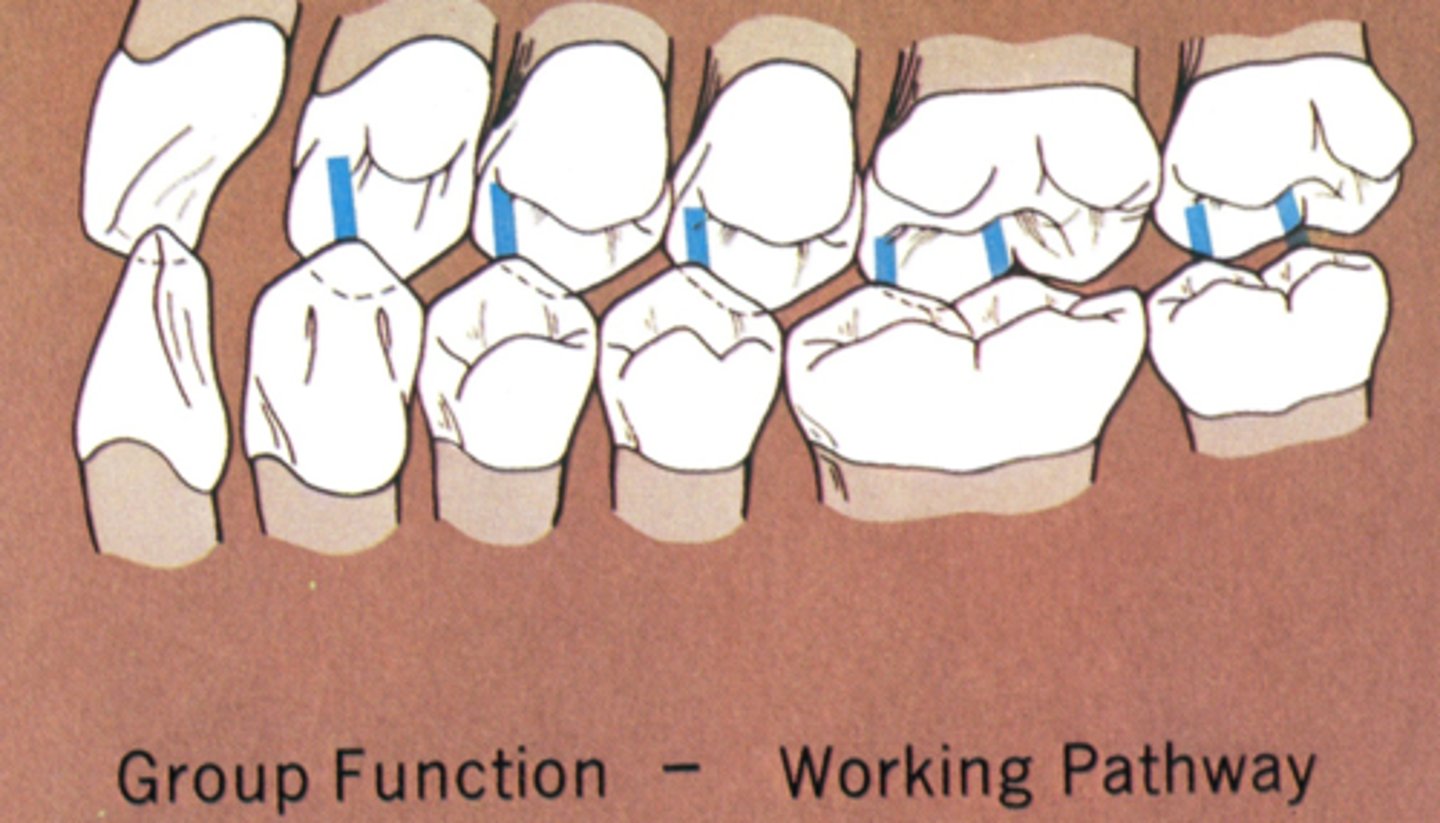
Group function
multiple tooth contacts between the maxilla and mandible in lateral jaw movements
Working side
side to which mandible has been moved during lateral occlusion. the condyle will stay in its fossa, rotates, and moves laterally (working condyle)
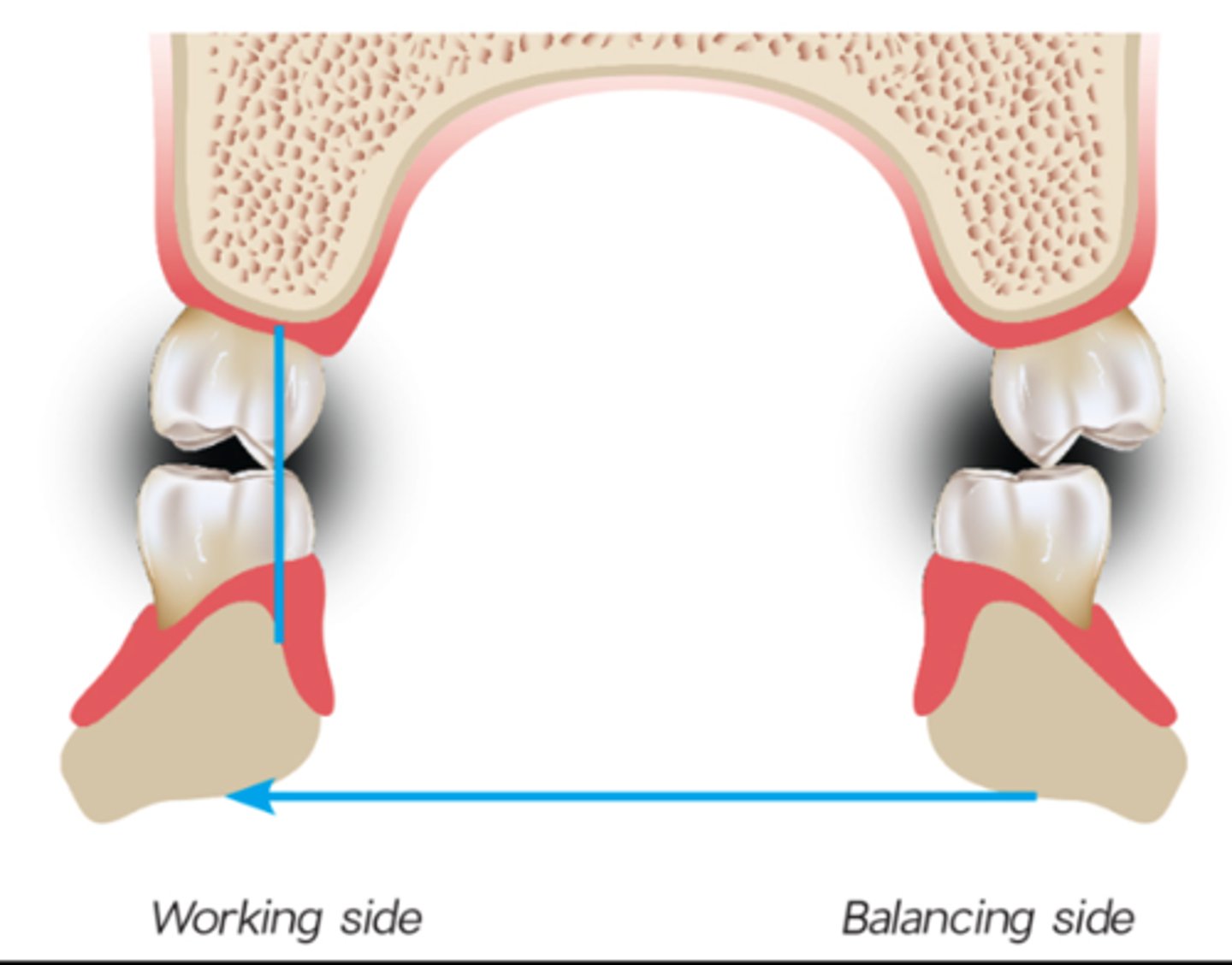
Non-working side
Side that the mandible moves away from during a lateral excursion, non-working condyle
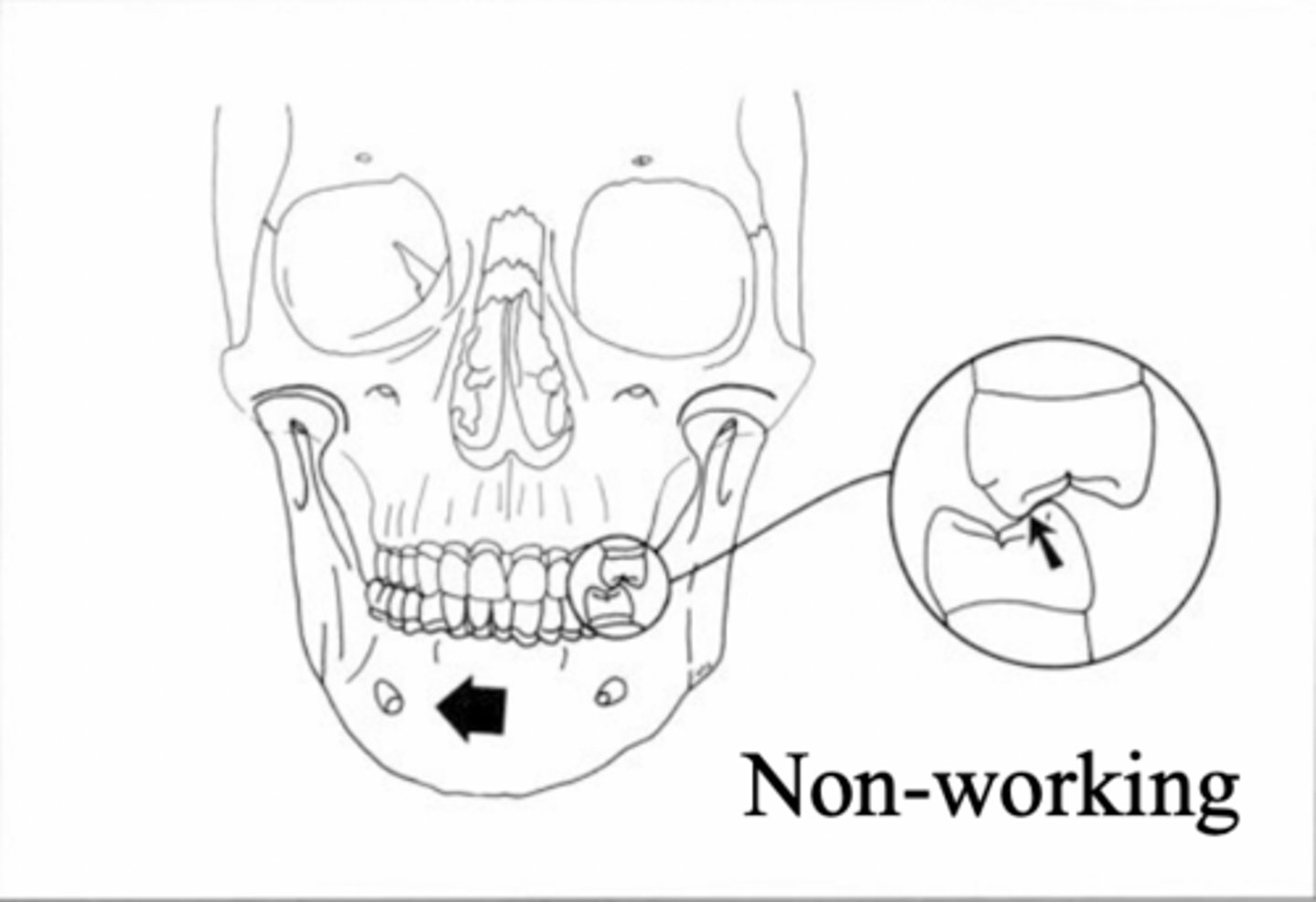
Interfering contact (non-working side)
pathway of the maxillary cusps on the mandibular posterior teeth is towards the DISTOBUCCAL
What arch is considered mobile?
mandibular
The contact of lateral movements takes place on which said the maxillary and mandibular inclines?
- maxillary inclines = distal
- mandibular inclines = mesial
In normal alignment, the ML cusp of the maxillary first molar will meet what?
the central fossa of the mandibular first molar
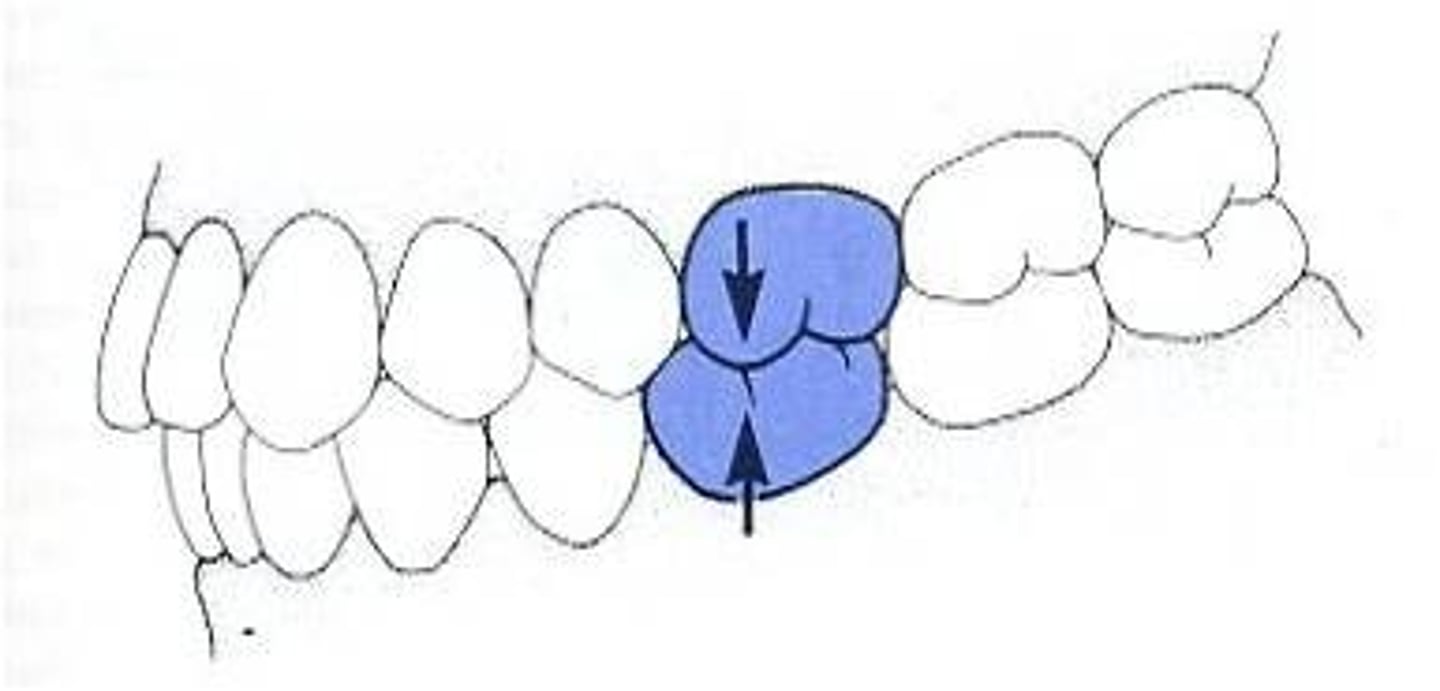
In normal alignment, the DB cusp of the mandibular first molar will meet what?
central fossa of the maxillary first molar
Centric stops
areas of occlusal contact that are supporting cusp makes with the opposing teeth in centric occlusion
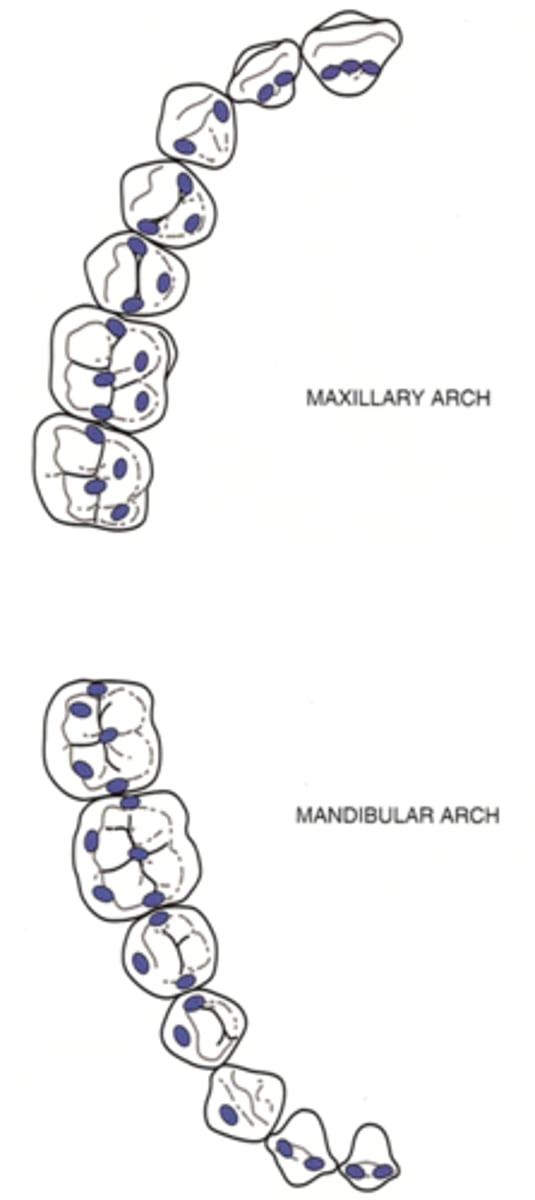
Centric contact relatioships depend on what to things?
1. supporting cusps to marginal ridges
2. supporting cusps to fossa
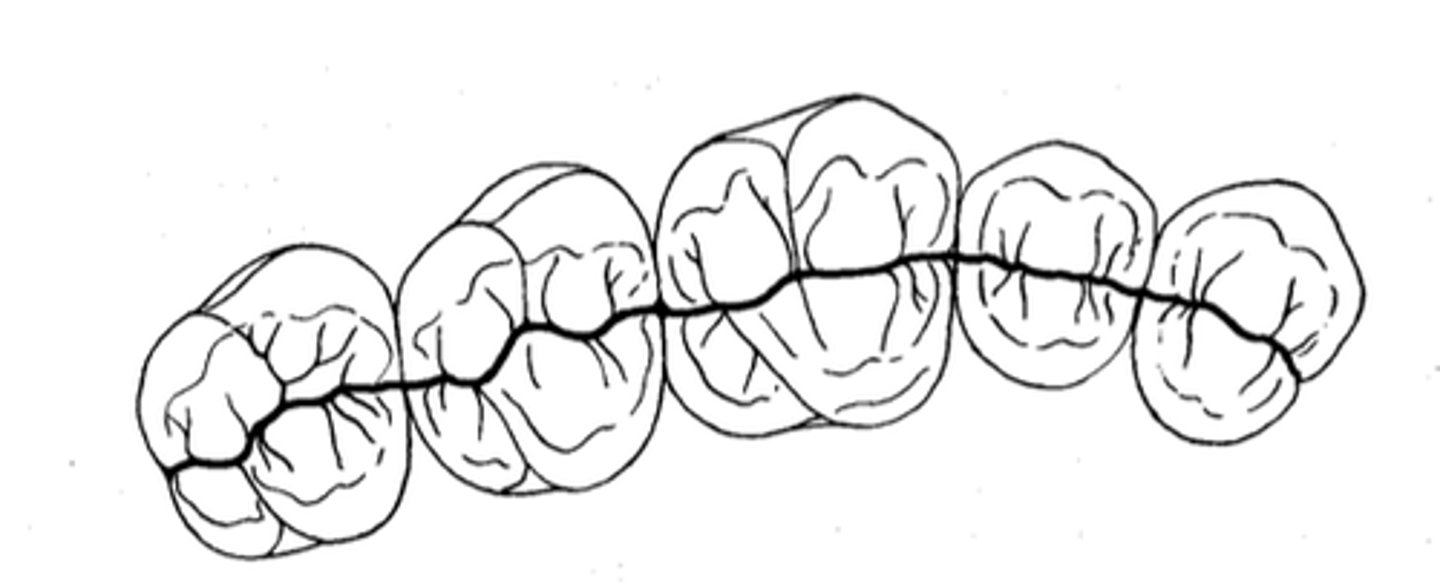
What of the posterior teeth are normally aligned continuously with each other in each quadrant?
central developmental grooves
Protrusive movement
accomplished when the mandible is moved straight forward until the maxillary and mandibular incisors contact edge-to-edge
In what direction do the condyles of the mandible move in protrusive movement?
downward and forward - moves MI to maximum protruded position
What affects the surface morphology of posterior teeth?
Anterior guidance (vertical and horizontal overlap of anterior teeth)
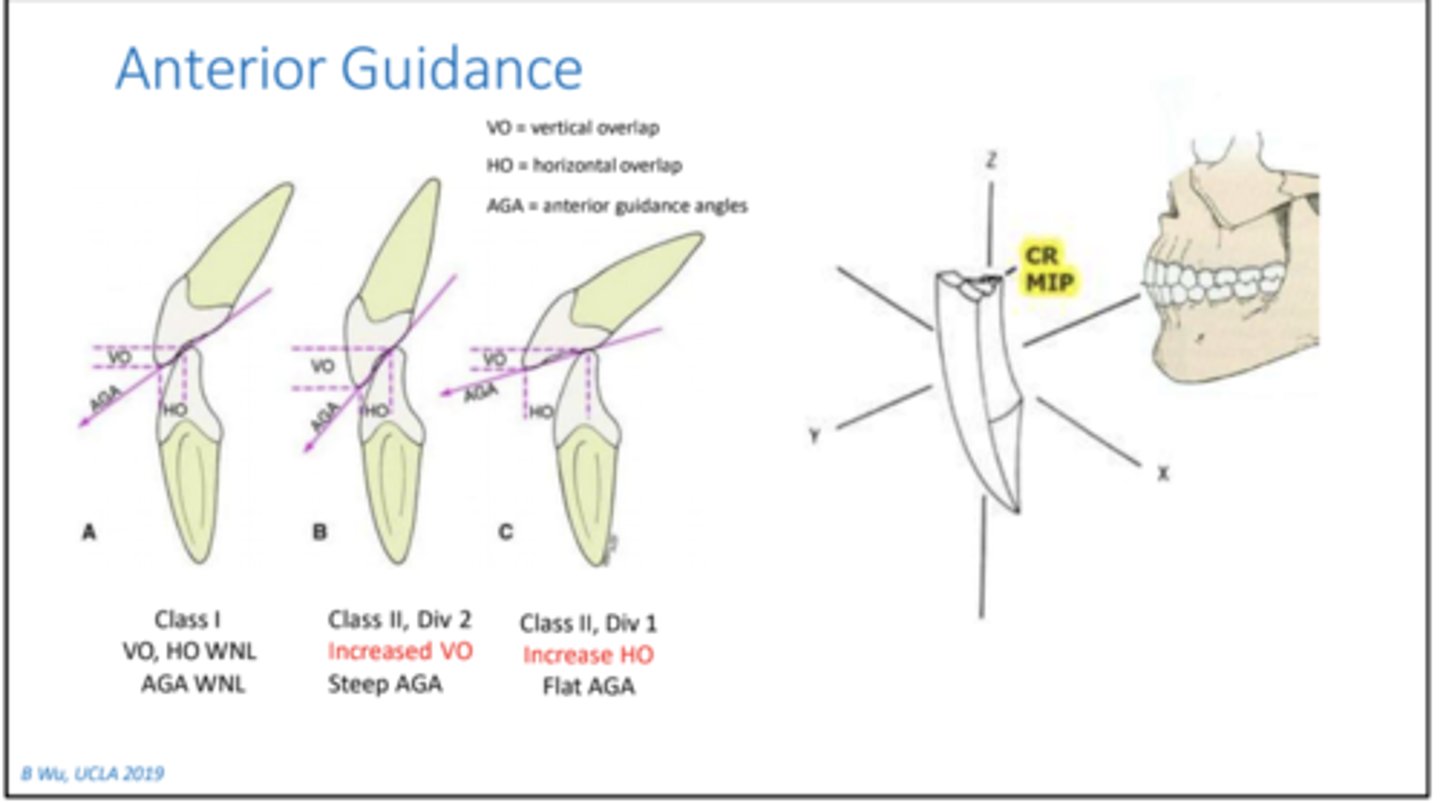
in ideal occlusion, the axes of crowns and roots of both arches are kept __________.
parallel
occlusion is dictated by what?
underlying basal bone
which arch tends to be larger?
maxilla arch
since the maxillary arch is larger than the mandibular arch is, what happens?
the teeth will overlap buccal slightly
Angle’s classification of malocclusion only considers what?
the sagital aspect of occlusion
what is a “normal” sagittal relationship of the dental arches called?
class 1
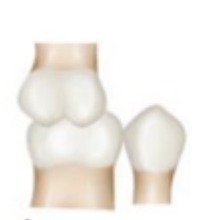
if the position of the mandibular arch is too posterior in relation to the maxillary arch, what occurs?
distocclusion which is also known as Class II malocclusion
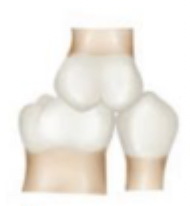
what class of occlusion is this?
class II
if the position of the mandibular arch is too far anterior in relation to the maxillary arch, what happens?
mesiocclusion, also known as class III malocclusion
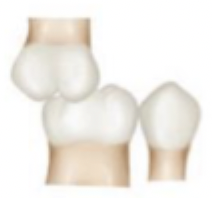
what class is this picture?
class III
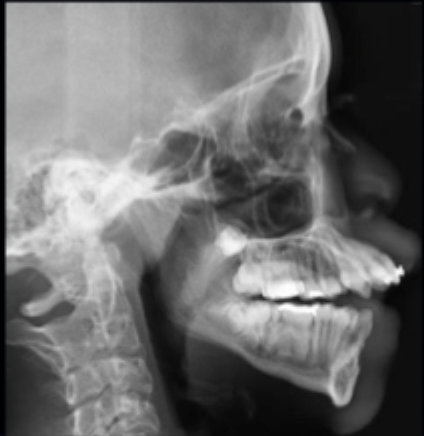
what class of occlusion is shown in this x-ray?
class II (x-ray)
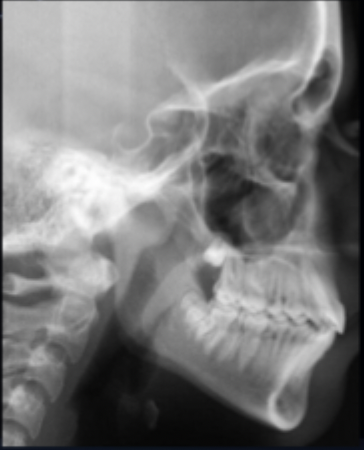
what class of occlusion is shown in this x-ray?
class I (x-ray)
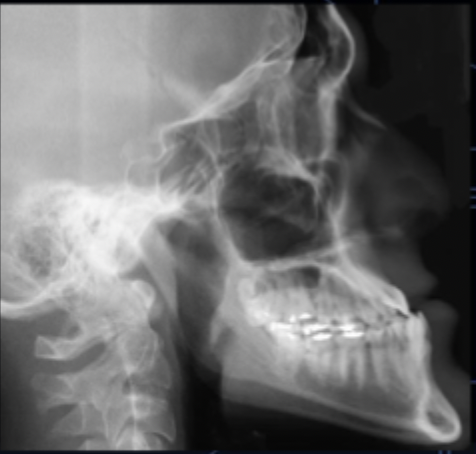
what class of occlusion is shown in this x-ray?
class III (x-ray)
in class II, division 1 malocclusion, what occurs?
maxillary incisors are inclined normally or too far labially
in class II, division 2 malocclusion, what occurs?
two or more maxillary incisors are palatally inclined
in severe class II, division 1 malocclusions, the lower lip is what?
positioned between the mandibular and maxillary incisors
in class II, division 2 malocclusions, the lips are what?
closed
what is the curve of spee?
the curvature which begins at the tip of the canines and follows the buccal cusps of the posterior teeth, when viewed from the facial; continues up the arch through the condyle
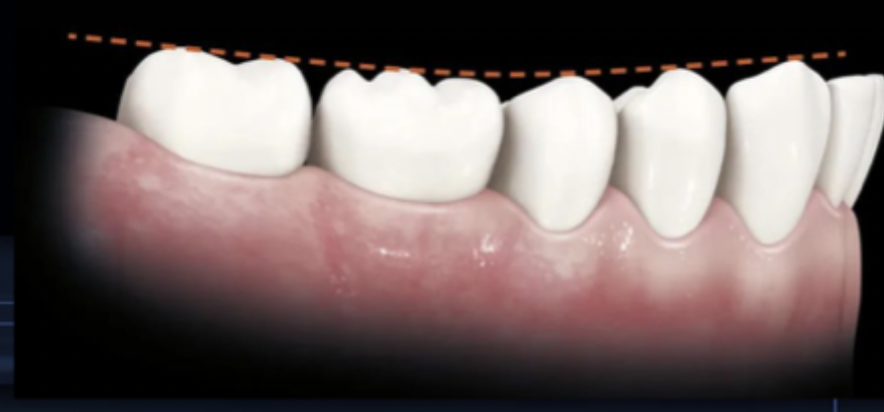
what is the curve of wilson?
mediolateral curvature of the occlusal plane of posterior teeth
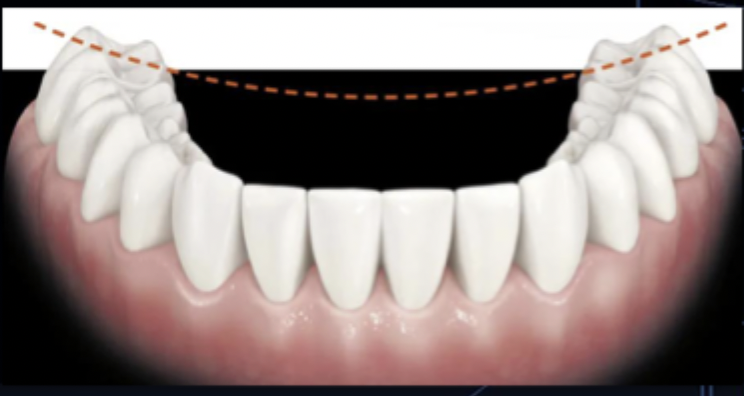
what is the purpose of the curve of wilson?
complement the paths of the condyles during movements of the mandible
what is the curve of monson (also known as sphere of Monson)?
three-dimensional curvature of the occlusal plane, which is a combination of the curve of spee and curve of wilson
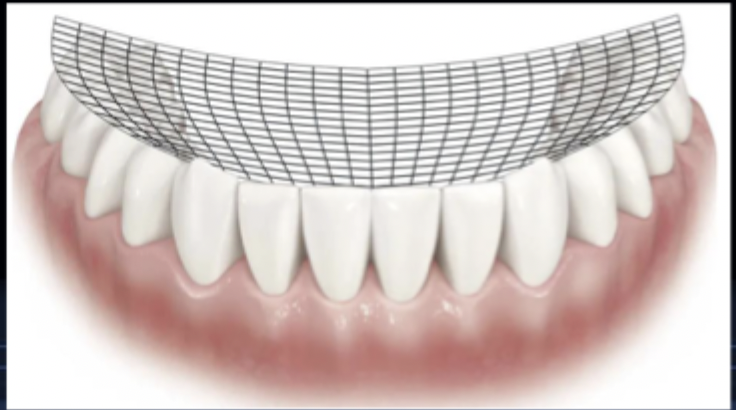
jaw movement dictates what?
cuspal height and depth of fossae
in ideal occlusion, what cusps of maxillary teeth are the functional cusps?
lingual cusps
in ideal occlusion, what cusps of maxillary teeth are the non-functional cusps?
buccal cusps
in ideal occlusion, what cusps of mandibular teeth are the non-functional cusps?
lingual cusps
in ideal occlusion, what cusps of mandibular teeth are the functional cusps?
buccal cusps
the non-functional cusps of maxillary molars and premolars help what?
keep the cheek out of the occlusal table, avoiding soft tissue trauma
mandibular lingual cusps (nonfunctioning cusps) help do what?
shear food as it passes to the functional cusps for chewing
keep the tongue away from the occlusal table to avoid trauma
when looking from mesial or distal, the crowns of teeth have uniform curvatures where?
buccal: cervical thirds
lingual: middle third
the buccal and lingual contours can deflect what?
food away from the gingival margins during mastication
what are the four embrasures per contact area?
labial or buccal
lingual
incisal or occlusal
gingival or cervical