Ambulation and Shoes
1/106
Earn XP
Description and Tags
BIOL 313 Final Exam
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
How many young drivers believe it is illegal to drive barefoot
2/3
what are the two sources for facts
personal experience and the word of other (authority)
why do we believe that shoes are required by law or health codes?
thats what we’ve always been told
How do shoes harm your feet? (4 main ways)
Alter the skeleton of the feet
Alter the muscles of the feet
Alter the fascia of the feet
Alter the biomechanics of standing, walking, and running
Where in the body do shoes have acute and chronic affects?
the feet, ankles, knees, hips, and back
How many women a year are hospitalized for high heels
over 20,000
how many shod children suffered psuedomonas infections after nail puncture?
50%
What happens when a nail enters your foot through a shoe?
shoe particulate matter is embedded in the wound
how many barefoot children suffered pseudomonas infections after nail puncture?
0%
Shoes are…
incubators for growing bacteria and fungi and the leading cause of athlete’s foot
what is the most prevalent skin infection
athlete’s foot
how many people in the general population have athletes foot
15%
how many male marathon runners have athletes foot?
24%
How many female marathon runners have athlete’s foot
6%
Ratio of men to women with toenail fungus
2:1
why is athlete’s foot so prevalent?
foot sole has a high density of sweat glands but closed-toe shows don’t allow the sweat to evaporate
what is the cause of foot odor?
the breeding ground of microorganisms in your shoes
only field of medicine in which a healthy body part is considered insufficient to perform its function without support
podiatry
what do support structures do
weaken body parts
shoes _________ the foot
immobilize
shoes reduce _____ and ______ flow
blood and lymph
shoes cause ________ of the muscles
atrophy
shoes weaken what three things
ligaments, tendons, soft tissues
shoes change the biomechanics of what three things
standing, walking, running
what are the four unnatural ways shoes immobilize the foot?
toes compressed, toes elevated, arch lifted, heel elevated
what are the most damaging features of shoes?
elevated heel, thick hard outer sole, thick inner sole, toe spring, tapered toe box, arch support, curved last, large sole surface area, instep support panels, cinching features (laces)
what is hallux valgus
an abnormal deviation of the great toe (hallux) laterally toward the other toes
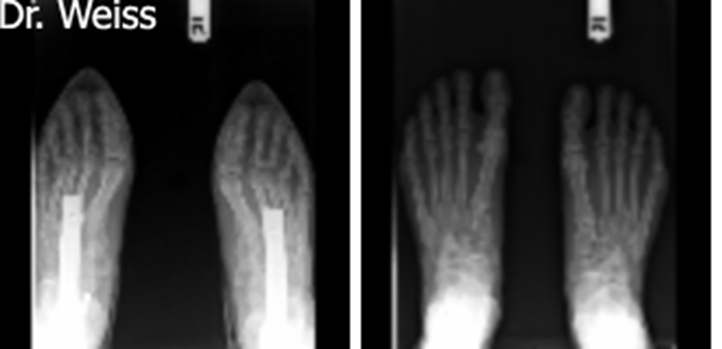
What is this called?
hallux valgus
bunion
an abnormal enlargement of the first MTP joint
hallux valgus is caused by
skeletal remodeling
what is hammer toe
the extensor tendons are too long and/or flexors are too short and pull too tightly
what causes hammer toe?
shoes with short narrow toe boxes and/or shoes with toe springs
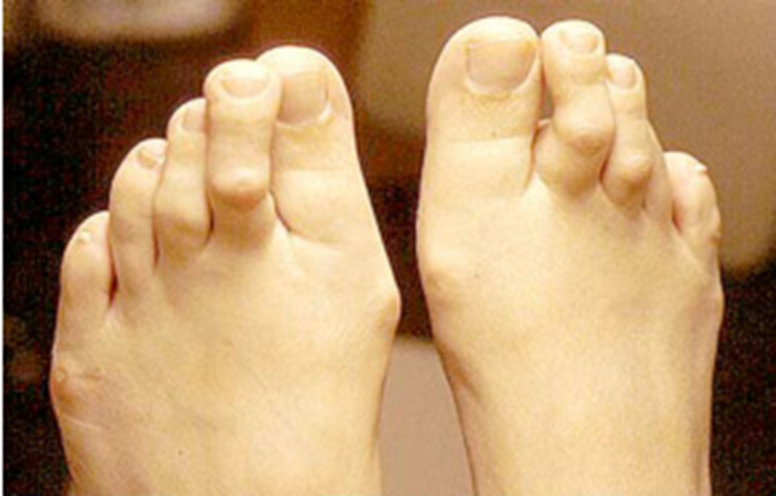
hammer toe
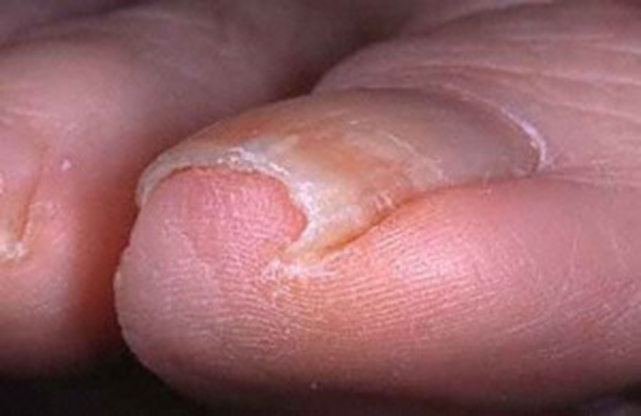
ingrown toenail
what often causes ingrown toenails?
excess pressure on the toes by shoes
flatfoot affects how much of the population?
25%
Shoes impede what by fixing the arch with an arch support?
the windlass mechanism
the windlass mechanism
a biomechanical process in the foot where the plantar fascia (a band of connective tissue) acts like a rope or cable to raise the medial longitudinal arch during the push-off phase of walking
shoes harbor _________ bacteria
pseudomonas
the narrow toe box of shoes
reduces the efficacy of the great toe during push off by shifting it laterally to the 2nd and 3rd toes
a narrow toe box eventually pushes
the hallux laterally
elevated heels shift body weight what direction?
anteriorly
90%
of the body’s weight is supported by the metatarsal heads in 3-inch heels
in heels…
the toes are kept hyperextended and the windlass mechanism is disengaged
elevated heels engage what muscles to keep the body from falling forward
triceps surae and gluteus maximus
when wearing heels the pelvis
is tilted 15 degrees
how does wearing heels affect the knee?
body weight is shifted forward in the knee
knee osteoarthritis in women and men
4x higher in women
toe springs are required because
of the stiff nature of the shoe sole
shoes encourage
overpronation
orthotics
arch support
processes dramatically reduced by immobilization and arch support
windlass mechanism, shock absorption, and spring action
what is the most common foot complaint in the US?
plantar fasciitis (PF)
what characterizes plantar fasciitis
sharp heel pain, especially in the morning
treatments for plantar fasciitis
steroid injections, physical therapy, orthotics
-itis
inflammation
-iosis
dead tissue
plantar fasciitis
inflammation of the plantar fascia
tissue death of the plantar fascia
plantar fasciosis
cause of plantar fasciosis
permanently hyperextended toes reduced blood perfusion of plantar fascia leading to necrosis
running shoes
dramatically reduce tactile feedback from foot sole
shoe running
over-striding, over-extended knee, dorsiflexion, and heel striking
barefoot running
flexed hip, knee, and ankle; flatfoot landing
GRF
ground reaction force
running in shoes creates a sharp
GRF that is absent when barefoot
when running barefoot
impact forces on the knee and hip are zero
foot arches take _______ years to fully develop
8-10
little muscle activity is required to
stand at ease
when standing what is true of our hips and knees
they are in the most stable positions and fully extended
the body’s center of gravity is
slightly anterior to the rotational pivot point of the ankle
muscles counter the forward sway of our body
gastrocnemius and soleus
two phases of the gait cycle
stance phase and swing phase
stance phase
60%
swing phase
40%
one gait cycle
heel strike of one foot to the next heel strike of the same foot
one step
heel strike of one foot to heel strike of other foot
both feet on the ground
double support
one foot on the ground
single support
20% of the stance phase
must be double support
ambulation
one of the most complex biomechanical achievements of the body
standard terminology for stance phase
heel strike
foot flat
midstance
heel off
toe off
standard terminology for swing phase
acceleration
midswing
deceleration
Rancho terminology for stance phase
initial contact
loading response
midstance
terminal stance
preswing
Rancho terminology for swing phase
initial swing
midswing
terminal swing
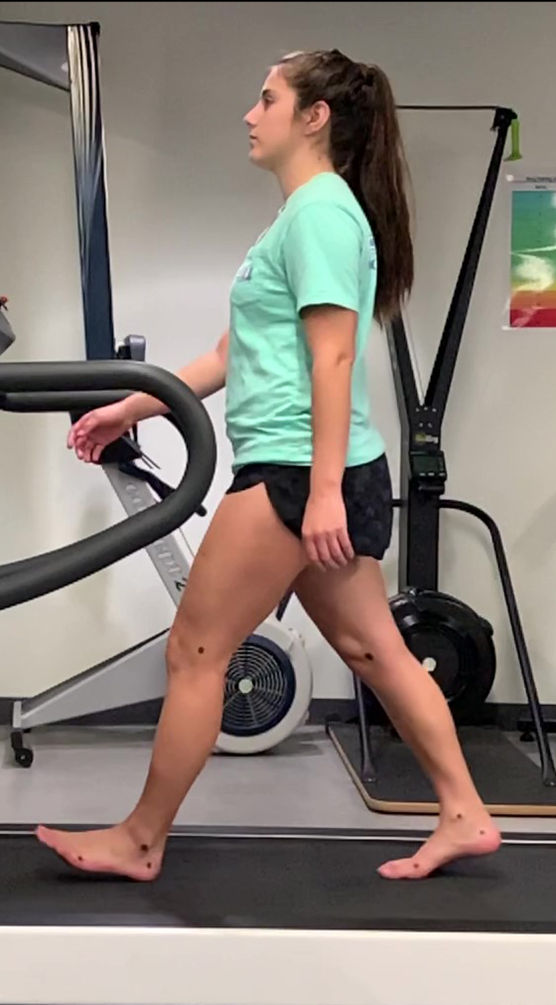

heel strike/initial contact
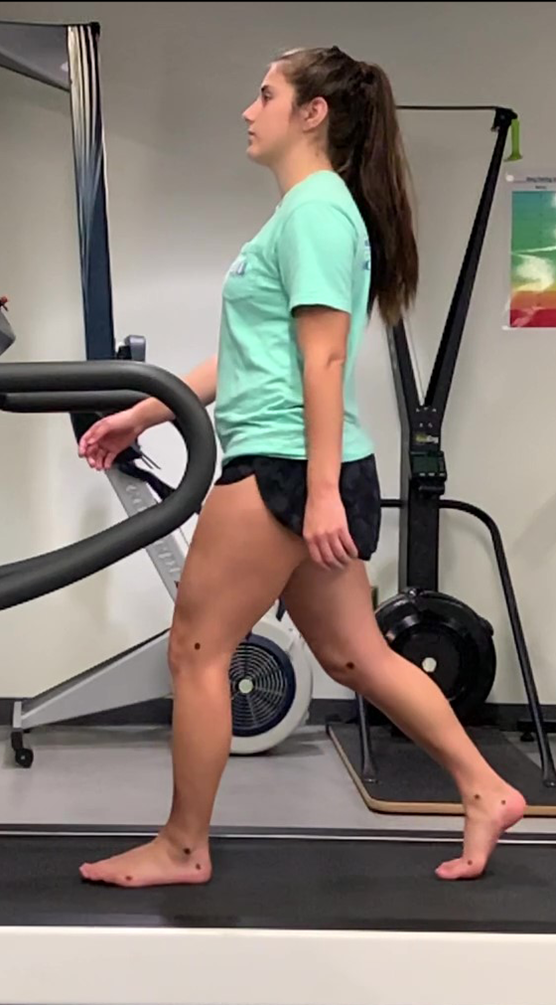

foot flat/loading response
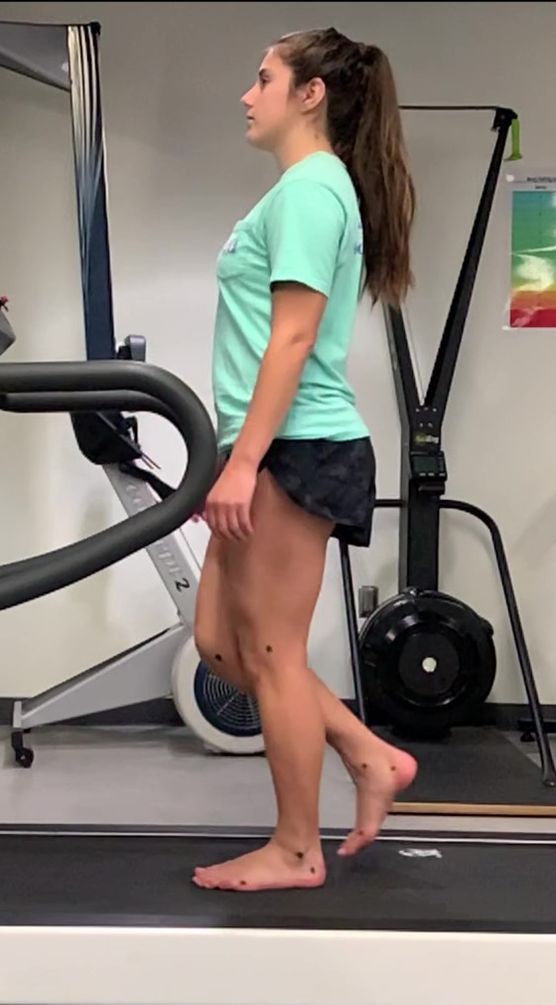
midstance
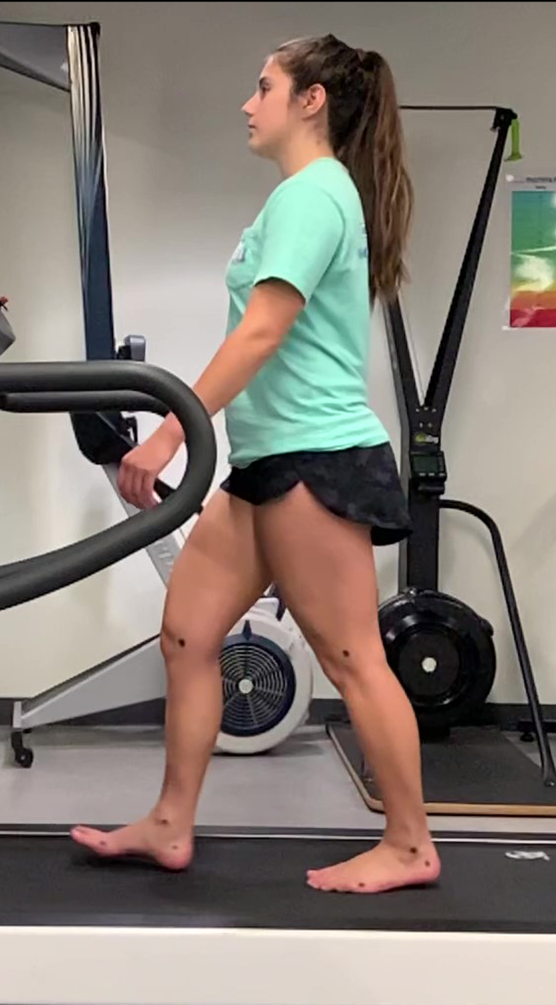

heel off/terminal stance
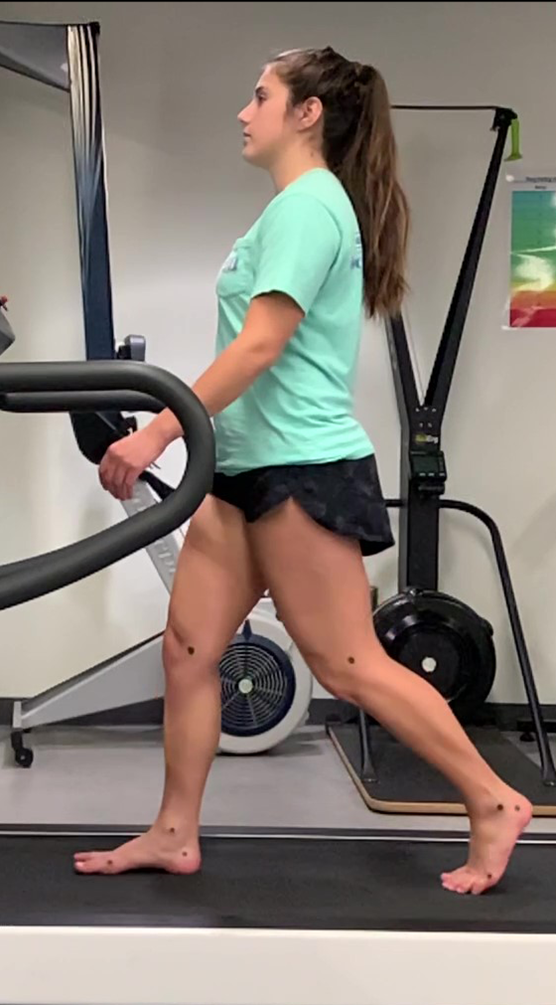

push off
what is push off
most forceful part of gait, just before toe off (a Howell introduction)
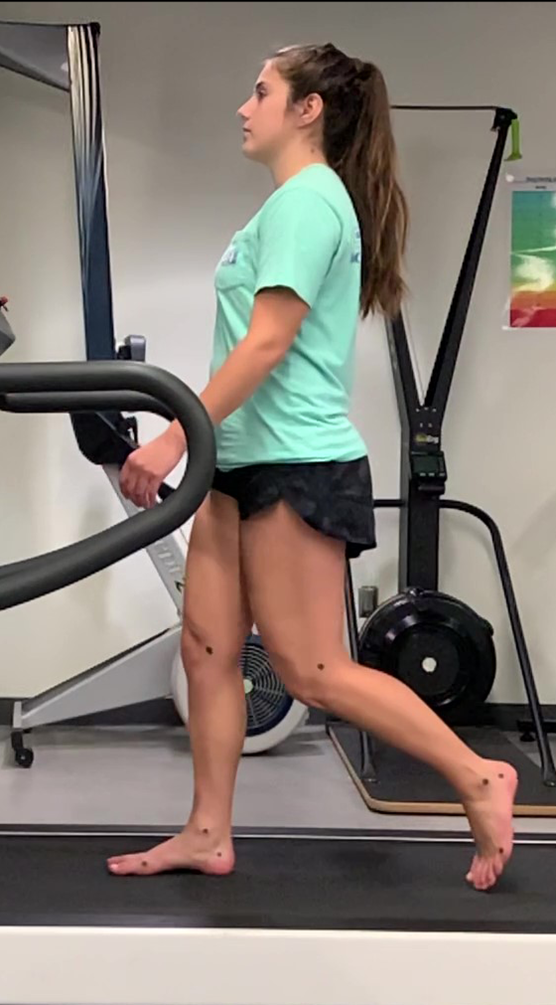
toe off/preswing
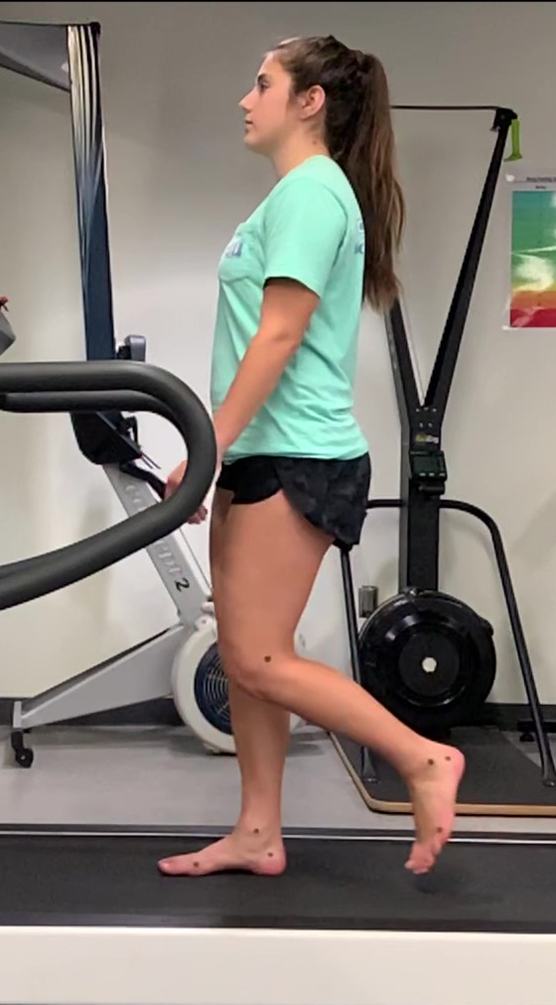
initial swing/acceleration
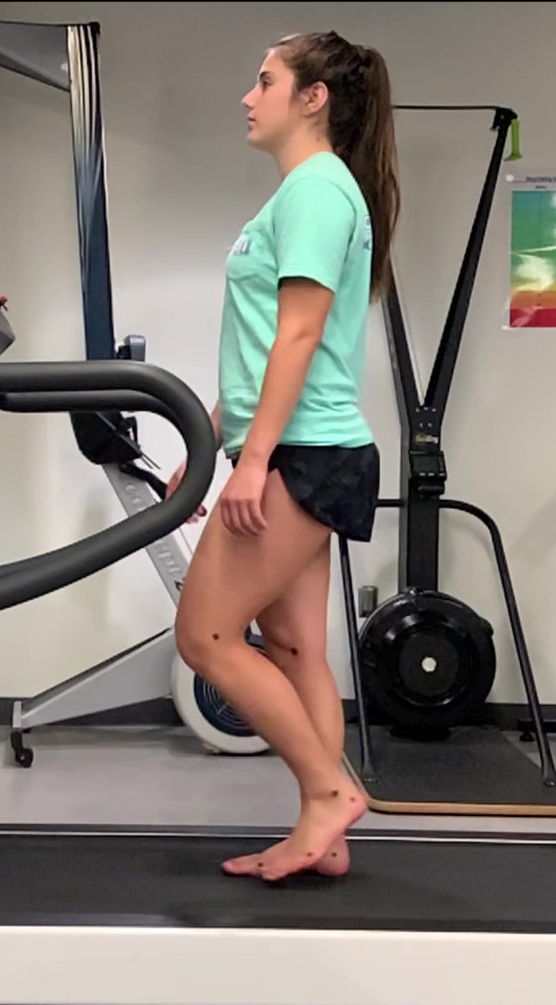
midswing
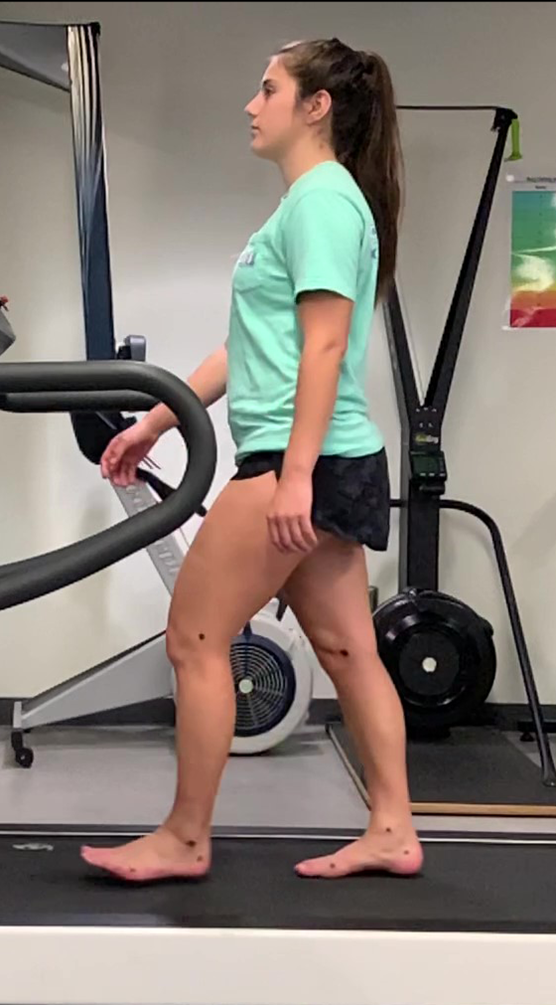

terminal swing/deceleration
What terminology was focused on single vs double support?
Richard terminology
the four phases of Richard terminology
first double support, single support, second double support, swing
the single support and swing phases of Richard terminology have what three phases?
early, middle, late
vertical CoM is about
5cm at 1.8m/s
tallest part of gait cycle
midstance
mediolateral displacement when walking
2 cm left and right