National 5 Physics - Electricity
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
What is electrical current?
The electric charge transferred per unit time
What is current measured in?
Amps, A
What is electrical charge measured in?
Coulombs, C
What is the relationship between electrical charge, current, and time?
Q = It
What is electricity?
The flow of charged particles, usually negatively charged electrons
What are the two types of current?
Alternating current and direct current
What is alternating current?
When the current/flow of electrons periodically changes direction
What is direct current?
When the current/flow of electrons is always in the same direction
What does the oscilloscope trace for alternating current look like?
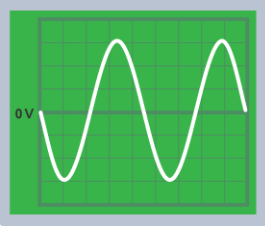
What does the oscilloscope trace for direct current look like?
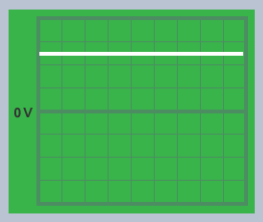
Is a battery a.c. or d.c.?
Batteries are always d.c.
The frequency of mains supply is 50 Hz; what does this tell us about the number of complete cycles it goes through in one second?
The current changes direction 100 times per second, making the frequency of the mains supply 50 Hz
What is voltage?
The “force” that pushes electrons around a circuit
When is an electric field created?
Whenever a charge exists
How do you determine the direction of electric field lines?
Imagine the path that a positive charge would take when placed in that field
If electric field lines are close together…
The electric field is strong
If electric field lines are far apart…
The electric field is weak
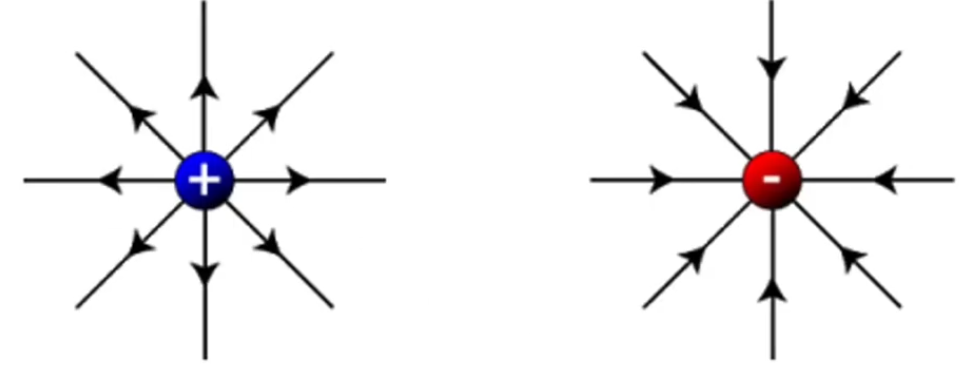
Draw two radial fields.
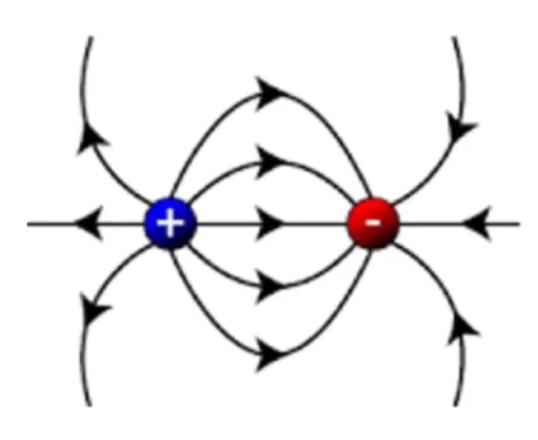
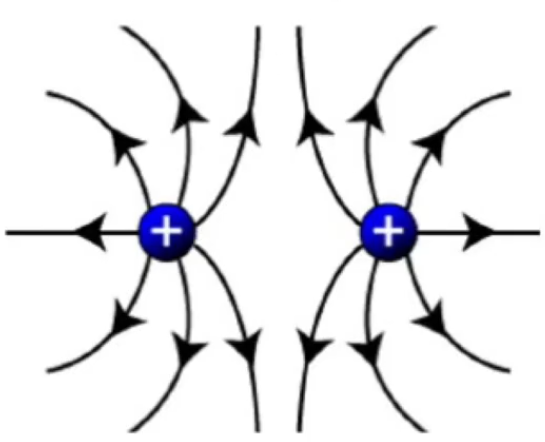
Draw the electric field lines for two adjacent oppositely charged particles.
Draw the electric field lines for two adjacent like charged particles.
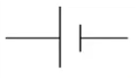
What is this and what is its function?
It is a cell and it powers a circuit
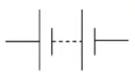
What is this and what is its function?
It is a battery, which is a collection of cells and powers a circuit
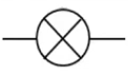
What is this and what is its function?
It is a bulb and it converts electrical energy into light energy
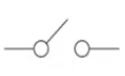
What is this and what is its function?
It is a switch and it can be used to make or break a circuit

What is this and what is its function?
It is a resistor and it opposes the flow of current
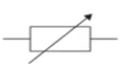
What is this and what is its function?
It is a variable resistor and its resistance can be varied to allow the current flowing through it to be varied as well
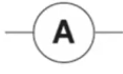
What is this and what is its function?
It is an ammeter and it measures the current flowing through a circuit
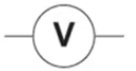
What is this and what is its function?
It is a voltmeter and it measures the voltage across a component
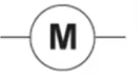
What is this and what is its function?
It is a motor and it converts electrical energy into kinetic energy
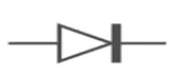
What is this and what is its function?
It is a diode and it allows current to flow in only one direction
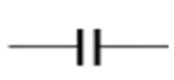
What is this and what is its function?
It is a capacitor and it stores charge
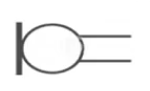
What is this and what is its function?
It is a microphone and it converts sound energy into electrical energy (which means it is an example of an input device)
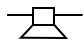
What is this and what is its function?
It is a microphone and it coverts electrical energy into sound energy
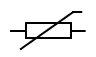
What is this and what is its function?
It is a thermistor and its resistance changes with temperature
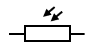
What is this and what is its function?
It is an LDR (Light Dependant Resistor) and its resistance varies with light intensity
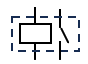
What is this and what is its function?
It is a relay and it allows a lower powered primary circuit to control a higher powered secondary circuit
How do you measure the current flowing through a component?
By connecting an ammeter in series with the component
How do you measure the voltage across a component?
By connecting a voltmeter in parallel with the component
An LED is always protected by a…
Resistor
Why does an LED always need to be protected by a resistor?
To prevent the LED from drawing excessive current, which would cause it to overheat
What does LED stand for?
Light Emitting Diode
What is a transistor?
A transistor is a semiconductor that acts a switch
What is the symbol for an npn transistor?
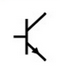
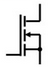
What is the symbol for a MOSFET transistor?
What is a semiconductor?
A material which only conducts under certain conditions
What are semiconductors usually made of?
Silicon
What is the function of an npn transistor?
To amplify current and act as a switch
What are the three terminals of an npn transistor?
The base, the collector, and the emitter
How does an npn transistor work?
When the base-emitter voltage reaches 0.7V, the transistor will saturate and allow current to flow
What does MOSFET stand for?
Metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor
What are the basics of band gap theory?
Whether a material conducts or not depends on the band gap energy; this is the energy gap between the valence band (outermost electrons) and the conduction band (the electrons which are free to move)
How does voltage behave in a series circuit?
The voltage splits across each of the components (in proportion to their resistances)
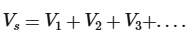
How does current behave in a series circuit?
The current is the same at every point in the circuit

How does voltage behave in a parallel circuit?
The voltage is the same at every point in the circuit
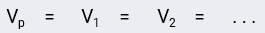
How does current behave in a parallel circuit?
The current splits up among each branch and then recombines before entering the source

In a series circuit, as you add more resistors, what happens to the overall resistance of the circuit?
It increases
In a parallel circuit, as you add more resistors, what happens to the overall resistance of the circuit?
It decreases
What is a voltage divider?
A circuit with two resistors in series that divides a larger input voltage into a smaller, more precise output voltage
What are control circuits?
They usually involve a voltage divider and a transistor (which will switch on or off depending on certain conditions) and an output
What three parts can we split a control circuit into?
Input, process, and output
Describe an advantage of using a variable resistor instead of a fixed resistor in a control circuit.
Allows the user to change the temperature/ight intensity etc. required to activate the circuit OR To allow the sensitivity of the circuit to be adjusted
What are the four factors which affect the resistance of a conductor?
Material, length, thickness, and temperature
What effect does increasing the length of a wire have on its resistance?
Longer wires have a greater resistance
What effect does increasing the thickness of a wire have on its resistance?
Wires with a smaller diameter have a greater resistance
What effect does increasing the temperature have on a wire’s resistance?
The wire’s resistance will increase
What is Ohm’s Law?
V = IR
A filament type electric light bulb has a resistance of 980Ω when operating at normal brightness. Before it was switched on, the light bulb had a resistance of only 64Ω, suggest a reason for this difference in resistance.
Resistance has increased as the filament became hotter
What effect does increasing the voltage of a power supply have on a circuit with a fixed resistance?
The circuit current increases