Energy levels and Spectra
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
conditions for electrons bound in gas atoms: (5)
1) an electron cannot have a quantity of energy between 2 levels
2) the energy levels are negative because external energy is required to remove an electron from the atom. The negative values also indicate that electrons are trapped within the atom
3) an electron with zero energy is free from the atom
4) the energy level with the most negative value is known as the ground level/state
what happens when the atom is said to be excited?
when an electron moves from a lower to a higher energy level within an atom in a gas
e.g photons of specific energy being absorbed by an atom
de-excitation
when an electron moves from a higher energy level to a lower one it looses energy. The energy is conserved and a photon is emitted from the atom, when the electron transitions between levels.
emission line spectra
each element produces a unique emission line spectrum because of its unique set of energy levels
continuous spectra:
all visible frequencies or wavelengths are present
absorption line spectra?
has a series of dark spectral lines against the backdrop of a continuous spectrum. The dark lines have exactly the same wavelengths as the bright emission spectral lines for the same gas atoms
each spectral line corresponds to photons with a specific wavelength
(each spectral line corresponds to an electron dropping/going up a specific set of energy level)
e.g 2 spectral lines cannot correspond to the same energy change between energy levels
Formation of an absorption line spectrum? (5)
1) formed when light from a source producing continuous spectrum passes through a cooler gas
2) as the photons pass through the gas some are absorbed by the gas atoms raising electrons up into higher energy levels and exciting the atoms
3) only photons with energy exactly equal to the difference between different energy levels are absorbed 4) this means only specific wavelengths are absorbed creating dark lines in the spectrum
5) eventually the electron will drop down to its origional energy level, and a photon will be remitted
Analysing star light (3)
Diffraction Grating:
1) the grating consists of a large number of lines ruled on a plastic or glass slide
2) diffraction grating forms sharper fringes compared to the double slit
Formation of Fringes:
1) For monochromatic light incident normally at a diffraction grating, light diffracts at each slit and interference pattern is formed in space beyond the grating. As a result maxima and minima are formed
(IMAGE IN BOOK)
black body
an idealised object that absorbs all the EM radiation that shines onto it and when in thermal equillibrium emits a characteristic distribution of wavelengths and a specific temperature
black body graph
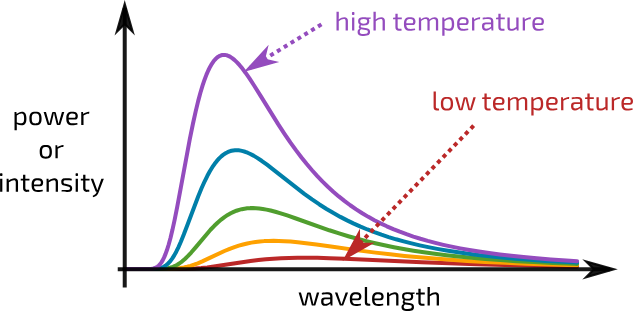
Wiens displacement law
relates the absolute temperature of a black body to the peak wavelength at which intensity is maximum
maximum wavelength and temperature relationship?
lamdamax is proportional to 1/ T
(as temp of object changes, so does the distribution of emitted wavelengths)
Stephans law:
Luminosity is directly proportional to Temperature4
equation using stephans law:

stephans constant value?
5.67×10-8 Wm-2K-4