CMPP -- Colon Polyps and Colorectal Cancer
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
fecal occult blood test (FOBT)
guaiac-based testing indirectly detects the HEME portion of hemoglobin breakdown; common to blood from all sources; resistant to degradation in the intestine
red meat, horseradish, broccoli
what foods can give one a false positive in FOBT?
ASA, NSAIDs, Vitamin C
what medications can give one a false positive in FOBT?
three times on three different days
due to the intermittent bleeding pattern of tumors, FOBT should be performed...
Fecal Immunochemical Test
test for CRC that reacts with antibodies specific for GLOBIN portion of human hemoglobin molecule;
delayed return of sample
what can lead to false negatives in FIT?
heme/peroxidase activity, entire GI tract
FOBT tests for _____, and it detects bleeding from________.
globin, lower GI
FIT tests for _____, and it detects bleeding from________.
Stool DNA testing
relies on stool detection of abnormal neoplastic cells shed from tumor; may be able to detect high grade adenomatous polyps OR colonic malignancies; done via collection of stool sample x 1
clear liquids x 24 h
bowel prep with colonoscopy recommendations
patient prep for a CT colonography
thin rectal catheter is placed, colon is distended with air or CO2, scanned in supine and prone position
no IV/PO contrast needed
how CT colonography is performed
acute colonic inflammation, recent diverticulitis, recent colorectal surgery, recent colon biopsy, bowel perforation/obstruction
when is a CT colonography contraindicated?
Flexible Sigmoidoscopy
limited endoscopic evaluation that can visualize the colon for up to 60 cm; however, cancer/polyp detection is only good for this area (poor visualization of right sided cancers); can be performed without sedation
two sodium phosphate enemas given the morning of the procedure
how to bowel prep for a flexible sigmoidoscopy
Colonoscopy
the GOLD STANDARD for screening/diagnosis of CRC/polyps; biopsy and polyp removal are possible with this procedure
good bowel prep -- poor bowel prep limits visualization of right sided cancers
need for anesthesia/transportation
need for hold of anticoagulation
drawbacks to colonoscopy
family hx of colon cancer
personal hx of colon polyps OR colon cancer
IBD
who is considered "high risk" for colon cancer
COLONOSCOPY IS ONLY RECOMMENDED SCREENING TEST
what is the recommended screening test for those with a high risk for colon cancer?
first degree relative with CRC BEFORE age 60
two or more second decree relative
who meets the criteria for having a family history of colorectal cancer?
Age 40 OR 10 years before youngest CRC diagnosis (whichever is earlier)
when to start screening those who have a family history of colon cancer
every 5 years
frequency of screening for CRC in high risk patients
clear liquid diet -- NO RED/PURPLE LIQUIDS
--> no "stuff" in it
NPO after midnight
diet preparation for colonoscopy
Miralax with bisacodyl + Gatorade
Commercial preparations available by prescription
bowel preparation for a colonoscopy
Streptococcus gallolyticus
group D strep that is a common cause of endocarditis and bacteremia; considered a risk factor for CRC
Colonoscopy
Negative -- repeat in 4-6 months
If STILL negative -- screen as average risk adult
if one has Streptococcus gallolyticus endocarditis/ bacteremia, what should they do once it has resolved
Colon polyps
a protuberance of tissue into the lumen above the surrounding colonic mucosa; usually asymptomatic, but occasionally can ulcerate and bleed, cause tenesmus (if in rectum), cause obstruction (if large); may be neoplastic or non-neoplastic
Adenomatous polyps
Most carcinomas of the colon are believed to arise in these preexisting lesions
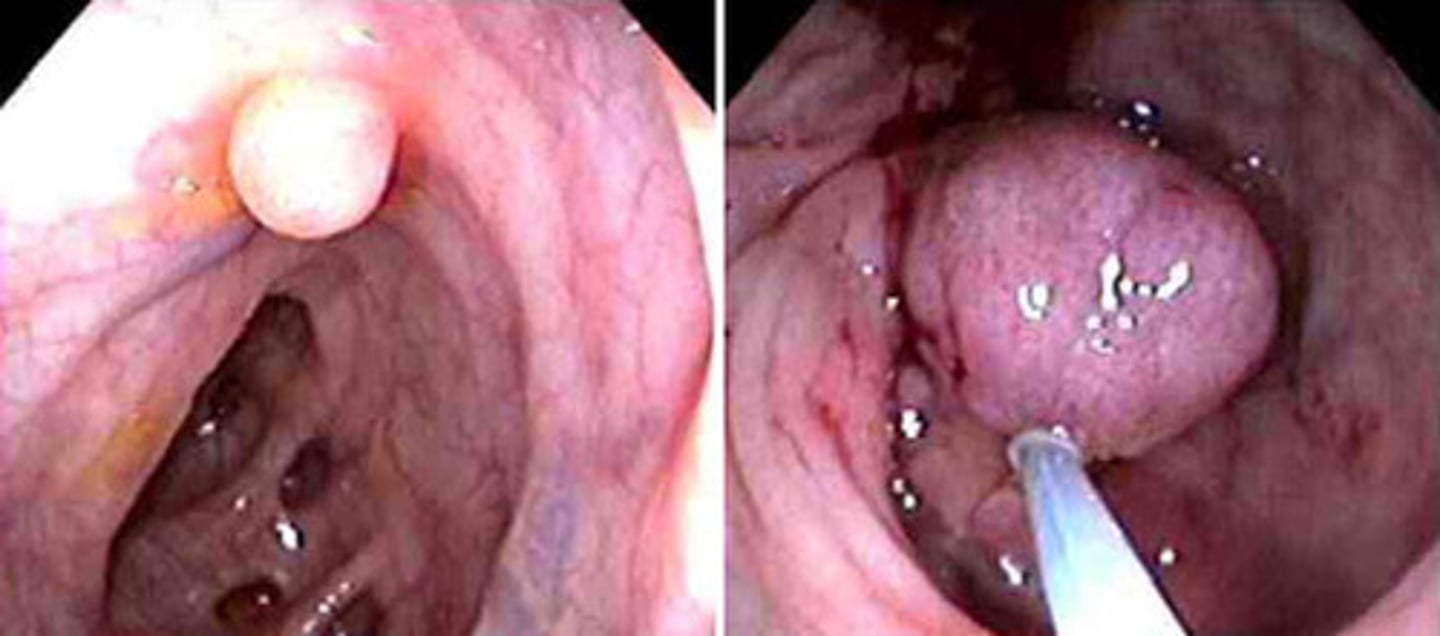
more common in men
large adenomas are more common in black populations (R sided) -- screening starts at 45
risk factors for adenomatous polyps
pendunculated (stalked)
flat
depresssed
sessile (flat based)
types of adenomatous polyps
sessile villous adenomatous polyps
most cases of CRC develop from what kind of polyps?
high fat low fiber diet
smoking
obesity
diet high in red meat
older age
male sex
risks for developing adenomatous polyps
must visualize entire colon
repeat colonoscopy every 3-5 years
if one visualizes an adenomatous polyp on sigmoidoscopy, what is the next step?
adenomatous polyps are thought to require >5 yers of growth before becoming clinically significant
what is the significance of the timeframe for screening of polyps?
Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP)
autosomal dominant trait that results from a genetic mutation resulting in defective colonic mucosa; results in abnormal proliferation pattern and impaired DNA repair; causes innumerable colonic polyps that appear during childhood

start at age 10 or 12
when to start screening patients with FAP for CRC
yearly flex sigmoidoscopy -- once polyps identified, screening transitions to yearly colonoscopies
test to order to screen those with FAP for CRC
total colectomy
patients with FAP will eventually require a...
NSAIDS and celecoxib (Celebrex)
what medications are shown to decrease the number and size of polyps in FAP?
Lynch Syndrome (HNPCC)
autosomal dominant syndrome that is characterized by the lack of polyps; they will often develop cancer without preceding polyps (and it usually IS NOT in the colon, but they are still high risk)
Endometrial carcinoma
other sites include ovary, stomach, small bowel, breast, and prostate
what is the most common Lynch syndrome associated cancer
48 y/o, right sided lesions
when and where do patients with Lynch syndrome typically get CRC?
Amsterdam II criteria
3 or more individuals with Lynch-related cancers (CRC, endometrial, small bowel, transition cell, ureter/renal pelvis);
2 successive generations of Lynch-syndrome related cancers;
1 Lynch-related cancer dx <50yo
3 or more individuals with Lynch-related cancers;
2 successive generations;
1 Lynch-related cancer dx <50yo
3-2-1 rule
asymptomatic at early stages, varies based on anatomic location of tumor
clinical presentation of CRC
may become large without any changes in bowel habits (can be v liquid)
commonly ulcerate
chronic insidious blood loss without a noticeable change in the stool color, fatigue, palpitations, iron-deficiency anemia
clinical presentation of right sided CRC
stool becomes more formed as it passes through the transverse colon and into the left colon -- tumors in this area are more likely to cause obstruction, abdominal cramping
APPLE-CORE LESION
presentation of a left-sided CRC

hematochezia
tenesmus
narrow stool, ribbon stool
anemia may be less common
how does a rectosigmoid colonic malignancy present?
COLONOSCOPY -- localize/biopsy
flexible sigmoidoscopy is NOT a recommended test -- misses right sided tumors
how to work up CRC
get biopsy and await pathology results
staging (CT abdomen/pelvis +/- PET scanning)
tumor markers
steps after colonoscopy in CRC
TNM system
T- tumor spread
N- node involvement
M- presence of distant metastasis
spreading through lymph nodes and portal venous system
how does metastasis of CRC usually occur?
LIVER -- usually goes here first!
what is the most common site of mets from CRC
spreads via paravertebral venous plexus and therefore bypasses the portal system to reach lungs
distal rectal cancer does NOT usually metastasize to the liver first -- where does it go and why?
CEA (carcinoembryonic antigen)
tumor marker for CRC, but has low diagnostic ability to detect primary CRC; can be elevated in non-cancer related conditions; role is in FOLLOW UP of people already diagnosed with CRC.
used to see prognosis/how patient is responding to care
role of CEA in CRC