Intergrative Functions of the Main Organ Systems
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
What is the adaptive immune system?
The adaptive immune system is the part of the immune response that targets specific pathogens with long-term immunity.
What is the innate immune system?
The innate immune system is the body’s first line of defense against pathogens.
How does the adaptive immune protect the body? (Adapt and remember)
It "learns" to recognize and remember invaders through specialized cells.
How does innate immune system protect the body? (Innate = Instant)
It provides immediate, non-specific protection using physical barriers, immune cells, and chemical signals.
What are granulocytes?
Granulocytes are a type of white blood cell that contain enzyme-filled granules used to fight infection, inflammation, and allergens. They’re part of the innate immune system and respond quickly to threats.
What are key granulocytes in the immune system?
“Never Eat Bananas” 🍌 Neutrophils, Eosinophils, Basophils—your rapid-reaction crew!
How does inflammation function within the innate immune system?
Inflammation is a rapid, non-specific response triggered by infection, injury, or irritation. It’s one of the first lines of defense in the innate immune system.
What is an erythrocyte?
An erythrocyte is a red blood cell (RBC).
Erythrocyte structure
Erythrocytes are disc-shaped, lack a nucleus, and are packed with hemoglobin, the protein that binds oxygen.
What is an eosinophil?
An eosinophil is a type of white blood cell (a granulocyte) involved in fighting parasites and responding to allergic reactions.
Eosinophil structure
It has bilobed nuclei and red-orange granules that stain with eosin dye.
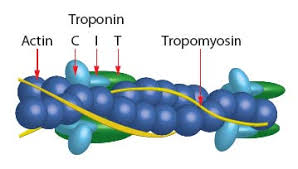
What is the troponin complex? ("Troponin is the C.I.T.Y. of muscle control")
C = Calcium binder (Troponin C)
I = Inhibitor (Troponin I)
T = Tropomyosin binder (Troponin T)
The troponin complex is made of these three proteins.
Where is the troponin complex found?
In skeletal and cardiac muscle
How are O₂ and CO₂ exchanged in the lungs?
They move across the alveolar-capillary membrane by diffusion.
O₂ diffuses into the blood from the alveoli.
CO₂ diffuses out of the blood into the alveoli.
What are alveoli?
Alveoli are tiny, balloon-like air sacs in the lungs where gas exchange takes place.
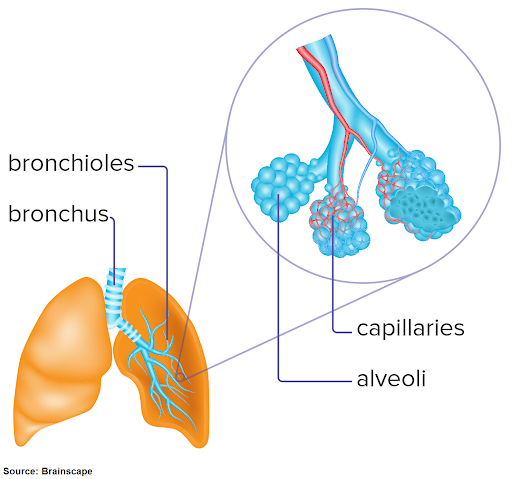
How do alveoli demonstrate the importance of surface area in biology?
The lungs contain millions of tiny alveolar sacs, creating a large total surface area (about the size of a tennis court!).
This large surface area allows for faster and more efficient gas exchange between air and blood.
What happens when the sensory receptors in the epidermis and dermis are injured?
Injury to epidermal and dermal sensory receptors leads to impaired touch sensation.
What is one major function of the skin related to body temperature?
The skin plays a key role in thermoregulation — maintaining stable internal body temperature.
What physiological mechanisms help increase body temperature?
The body raises temperature through:
Vasoconstriction of skin arterioles
→ Reduces blood flow to the skin, minimizing heat lossShivering
→ Involuntary muscle contractions generate heatPiloerection (goosebumps)
→ Hair stands up to trap an insulating layer of air (mainly in animals)
What are skin arterioles and what is their function?
Skin arterioles are small arteries located in the dermis of the skin. They play a major role in thermoregulation by controlling blood flow to the skin surface.
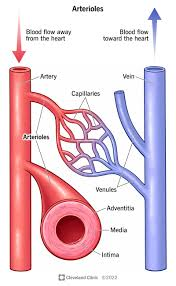
What mechanisms help the body cool down?
The body lowers temperature through:
Vasodilation of skin arterioles
→ Increases blood flow to the skin, allowing more heat to escapeSweating
→ Evaporation of sweat from the skin surface removes heat
What is the subcutaneous layer (hypodermis) composed of?
Adipose tissue (fat cells) — for insulation and energy storage
What do epidermal melanocytes do?
“Melanocytes = Melanin = UV shield for DNA of cells”
How do keratinized derivatives of the skin help protect the body?
Keratinized derivatives of the skin (such as hair, nails, and the outer layer of the epidermis) are composed of keratin, a tough, fibrous protein.
What are the three main layers of the skin?
“E-D-H: Every Dermatologist Helps!”
(Epidermis, Dermis, Hypodermis)
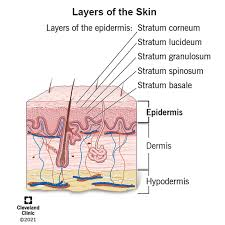
Epidermis function?
The epidermis acts as a physical barrier that protects the organism from the external environment
What structures are found in the dermis?
“Big Iguanas Sense Sweaty Hairy Skin”
(Blood vessels, Immune cells, Sensory receptors, Sweat glands, Hair follicles, Sebaceous glands)
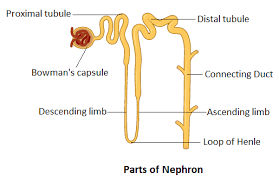
loop of henle
The Loop of Henle is a key structure in the nephron (the functional unit of the kidney) responsible for concentrating urine and conserving water. It creates a medullary osmotic gradient that allows the kidney to produce urine of varying concentrations.
parts of loop of henle:
"Descending loses water, Ascending loses salt."
D = Down = Water leaves
A = Up = Active salt transport (No water!)
When is it unethical to use a placebo in clinical research?
Unethical when:
Proven effective treatment exists.
Withholding treatment would cause harm or suffering.
parts of the nephron:
"Good People Love Doing Clean work"
G – Glomerulus: filters proteins
P – Proximal tubule: Reabsorbs ~65–70% of filtrate (Na⁺, Cl⁻, water, glucose, amino acids). Secretes H⁺ and organic acids/bases.
L – Loop of Henle: ion/water reabsorption
D – Distal tubule: Fine-tunes salt/water balance.
C – Collecting duct: Receives filtrate from several nephrons.
intestinal epithelium:
the single-cell layer lining the lumen of the intestines. main site of food absorption in the body.
How do increased levels of fatty acids in the intestine cause diarrhea?
Fatty acids act as osmotic agents, retaining water in the lumen.
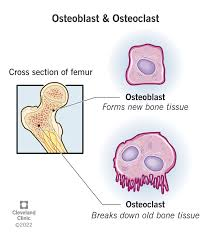
Osteoblasts vs Osteoclasts:
Osteoblasts ("Bone Builders")
Function: Form new bone (bone deposition).
Osteoclasts ("Bone Crushers")
Function: Break down bone (bone resorption).
What is the correct order in which filtrate passes through the tubular regions of a nephron?
Bowman’s capsule → proximal tubule → loop of Henle → distal tubule → collecting duct