Space physics
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
What lies at the center of the solar system
The sun is a star which makes 99% of the mass of the solar system
What is the difference between dwarf planets and normal planets
The gravitational field around planets is strong enough to have pulled in all nearby objects except natural satellites while dwarf plants gravitational field is not strong enough
What are moons
These are natural satellites that orbit around planets
What is an asteroid
This is a small rocky object that orbits the sun. The asteroid belt lies between Mars and Jupiter
What are comets
Comets are made of dust and ice and orbit the Sun in a different orbit to those of planets
The ice melts when the comet approaches the Sun and forms the comet’s tail
What is a nebula
A cloud of dust and gas in space
Describe the formation of the sun
The sun is formed from massive clouds of dust and gas in space
Gravity pulls the cloud together into a giant ball
As the nebula collapsed the center of this ball got very dense and hot and began to rotate
Eventually nuclear fusion was able to begin and a dense prostar was formed- our sun
Describe the forces in the sun
One of these forces is the force of gravity
This is an attractive force which pulls the outer layers inwards
The other force is the force of pressure
This is an outward force which is exerted from the expanding hot gases inside the star
Describe equilibrium in stars
When the inward pull of gravity and the outward pressure acting on the star are equal the star will be in equilibrium
How does increase in temperature affect equilibrium in a star
If the temperature of a star increases, the outward pressure will also increase
This will cause the star to expand
How does decrease in temperature affect equilibrium in stars
If the temperature drops (because, perhaps, the rate of fusion has slowed) the outward pressure will also decrease
This will cause the star to contract
Describe fusion in stars
All the naturally occurring elements, apart from hydrogen, have been formed by nuclear fusion in stars
Nuclear fusion occurs when two light nuclei collide at high speed and join to create a larger, heavier nucleus
When the Universe was first formed, 13.8 billion years ago, the only element present was hydrogen
If two hydrogen nuclei collide with enough energy they will fuse into a helium nucleus
For example, the nuclei of two different isotopes of hydrogen (protium and tritium) can join to form a helium nucleus by the process of nuclear fusion
The process of nuclear fusion releases energy
The energy is released in the form of heat and light
Describe the formation of new elements lighter than iron in a star
During the majority of a star’s lifetime, hydrogen nuclei fuse together to form helium nuclei
As the star runs out of hydrogen, other fusion reactions take place forming the nuclei of other elements
For example, two helium nuclei (produced by the fusion of 2 hydrogen nuclei) could fuse together to form a beryllium nucleus

Two helium nuclei fusing together to form a beryllium nucleus
The beryllium nucleus could then fuse with a helium nucleus to form a carbon nucleus

A beryllium nucleus fusing with a helium nucleus to form a carbon nucleus
Elements lighter than iron are formed in fusion reactions like the ones above
Describe the formation of elements heavier than iron in a star
Elements heavier than iron are produced in supernovaexplosions
A supernova occurs at the end of a massive stars life
When the star explodes it releases very large amounts of energy and neutrons
All of the elements which have been produced by the fusion reactions get thrown out and combine with the neutrons to form heavier elements
What is life cycles after of a star same size as the sun
Stella nebula→ protostar→ main sequence star → stars about the same size as the sun→ red giant star → planetary nebula → white dwarf → black dwarf
Describe the nebula stage of a star
1. Nebula
All stars form from a giant cloud of hydrogen gas and dust called a nebula
Describe protostar stage
2. Protostar
The force of gravity within a nebula pulls the particles closer together until it forms a hot ball of gas, known as a protostar
As the particles are pulled closer together the densityof the protostar will increase
This will result in more frequent collisions between the particles which causes the temperature to increase
Describe main sequence star stage
Once the protostar becomes hot enough, nuclear fusion reactions occur within its core
The hydrogen nuclei will fuse to form helium nuclei
Every fusion reaction releases heat (and light) energy which keeps the core hot
during the main sequence the star is in equilibrium
Describe red giant stage
After several billion years the hydrogen causing the fusion reactions in the star will begin to run out
Once this happens, the fusion reactions in the core will start to die down
This causes the core to shrink and heat up
The core will shrink because the inward force due to gravity will become greater than the outward force due to the pressure of the expanding gases as the fusion dies down
A new series of reactions will then occur around the core, for example, helium nuclei will undergo fusion to form beryllium
These reactions will cause the outer part of the star to expand
It will become a red giant
It is red because the outer surface starts to cool
Describe planetary nebula stage
Once this second stage of fusion reactions have finished, the star will become unstable and eject the outer layer of dust and gas
The layer of dust and gas which is ejected is called a planetary nebula
Describe white dwarf stage
The core which is left behind will collapse completely, due to the pull of gravity, and the star will become a white dwarf
The white dwarf will be cooling down and as a result, the amount of energy it emits will decrease
Describe black dwarf stage
Once the star has lost a significant amount of energy it becomes a black dwarf
It will continue to cool until it eventually disappearsfrom sight
What are the stages of the lifecycle of a star larger than the sun
stellar nebula→ protostar→ main sequence star→ stars much bigger than sun → red super giant star → supernova→ neutron star or black hole
Why do stars larger than the sun have shorter lifespans
Stars that are larger than the Sun have much shorter lifespans - in the region of hundreds of millions of years (instead of billions)
This is because they burn through the fuel in nuclear fusion much quicker than smaller stars
The life cycle of a star bigger than the Sun starts in the same way as a solar mass star
Describe red super giant stage of a star larger than sun
Eventually, the main sequence star will reach a stage when it starts to run out of hydrogen gas in its core
Once this happens, the fusion reactions in the core will start to die down
This causes the core to shrink and heat up
The core will shrink because the inward force due to gravity is greater than the outward force due to the pressure of the expanding gases
A new series of fusion reactions will then occur around the core, for example helium nuclei will undergo fusion to form beryllium
These fusion reactions will cause the outer part of the star to expand and it will become a super red giant
A super red giant is much larger than a red giant
Describe the supernova stage of a star larger than the sun
Once the fusion reactions inside the red supergiant finally finish, the core of the star will collapse suddenlycausing a gigantic explosion
This is called a supernova
At the centre of this explosion a dense body, called a neutron star will form
The outer remnants of the star will be ejected into space during the supernova explosion, forming a planetary nebula
Describe the neutron star or black hole stage of stars larger than the sun
In the case of the biggest stars, the neutron star that forms at the centre will continue to collapse under the force of gravity until it forms a black hole
A black hole is an extremely dense point in space that not even light can escape from
What is a supernova
supernova is a bright and powerful explosion that happens at the end of a massive star's life
It occurs when the star is bigger than the Sun
What happens during a supernova
The explosion releases a large amount of energy
During a supernova, all of the elements which were produced by the fusion reactions are exploded outalong with neutrons
The neutrons combine with the elements to form even heavier elements
These elements are ejected into the universe by the supernova explosion and form new planets and stars
Since Earth contains many heavy elements up to Iron, this is proof that it must have once been made from the remains of a Supernova
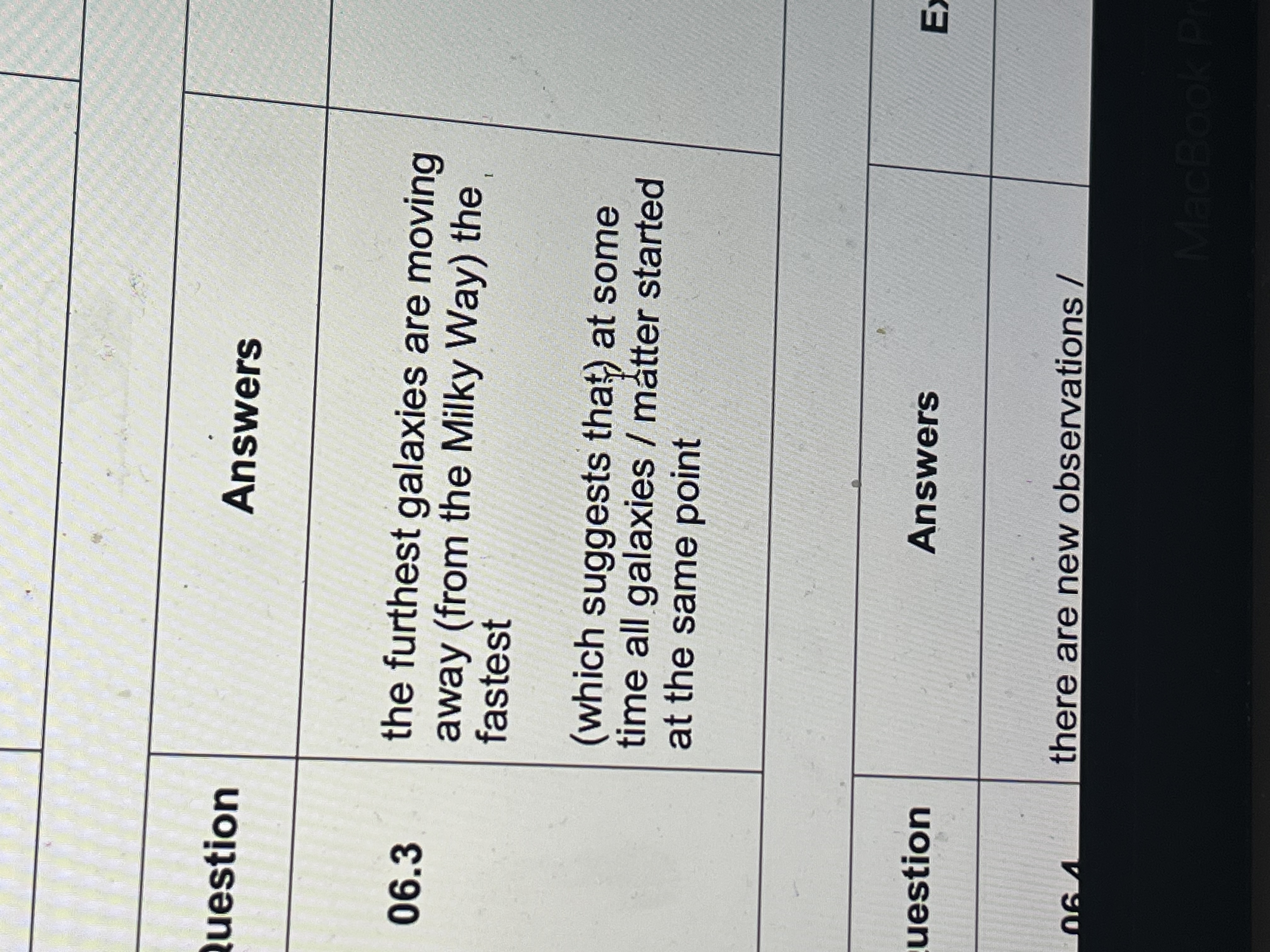
What are the orbits of different objects in solar systems
Describe the circular orbit of bodies in space
smaller body or object will orbit a larger body
In order to orbit a body such as a star or a planet, there has to be a force pulling things towards that body
Gravity provides this force
The gravitational force exerted by the larger body on the orbiting object is always attractive
Therefore, the gravitational force always acts towards the centre of the larger body
The gravitational force is the centripetal force as it will cause the body to move and maintain in a circular path
Describe the circular motion of an object in orbit
Planets travel around the Sun in orbits that are (approximately) circular
Objects in circular orbit are travelling at a constant speed
The orbit is a circular path, therefore the direction in which the object is travelling will be constantly changing direction
A change in direction causes a change in velocity
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity, therefore if the object is constantly changing direction then its velocity is constantly changing and so the object in orbit is accelerating
A resultant force is needed to cause an acceleration
This resultant force is gravity and it must act at right angles to the instantaneous velocity of the object to create a circular orbit
This is always towards the centre of the orbit
The instantaneous velocity of the object is the velocity at a given time
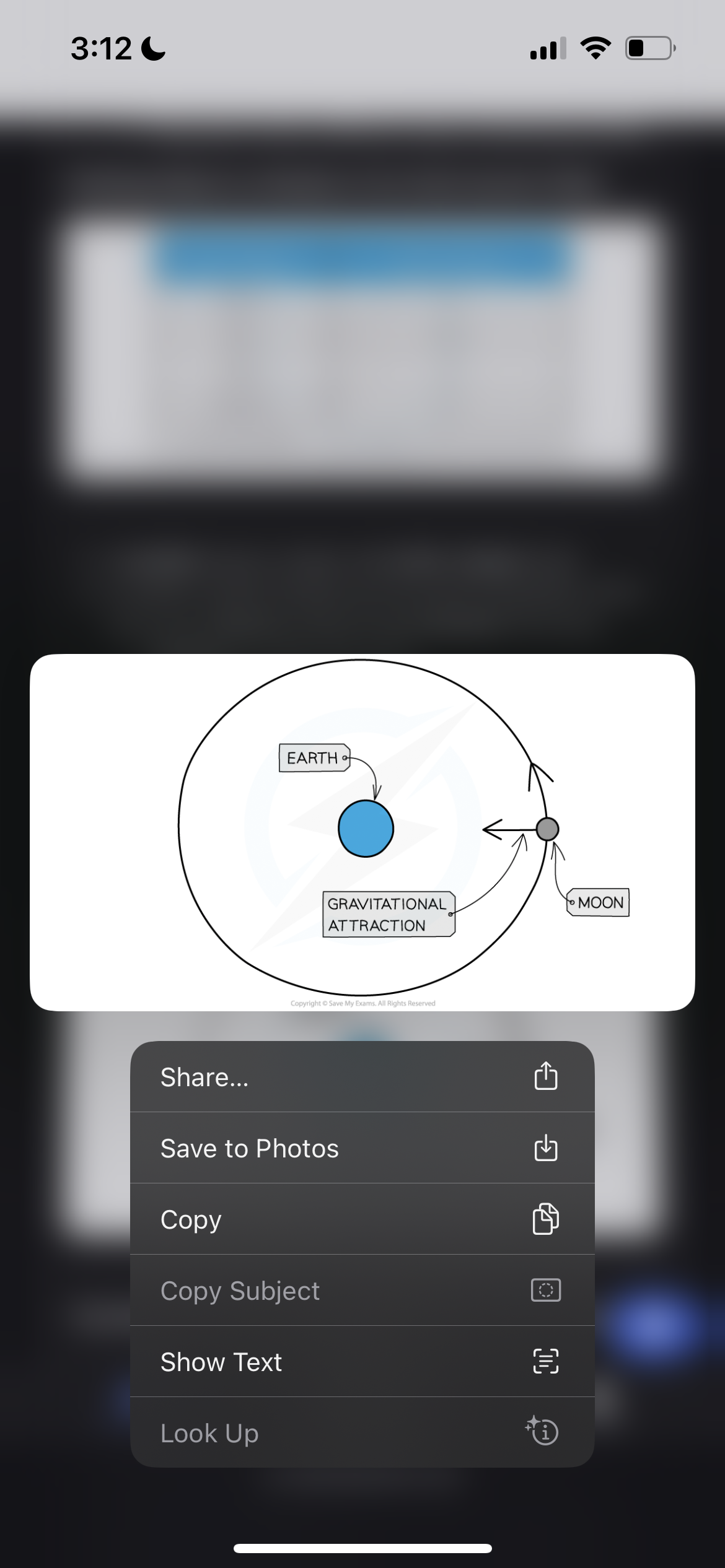
What are the similarities in the way different planets orbit the sun
Their orbits are all slightly elliptical (stretched circles) with the Sun at one focus (approximately the centre of the orbit)
They all orbit in the same plane
They all travel the same direction around the Sun
What are the differences in the way different planets orbit the suj
They orbit at different distances from the Sun
They orbit at different speeds
They all take different amounts of time to orbit the Sun
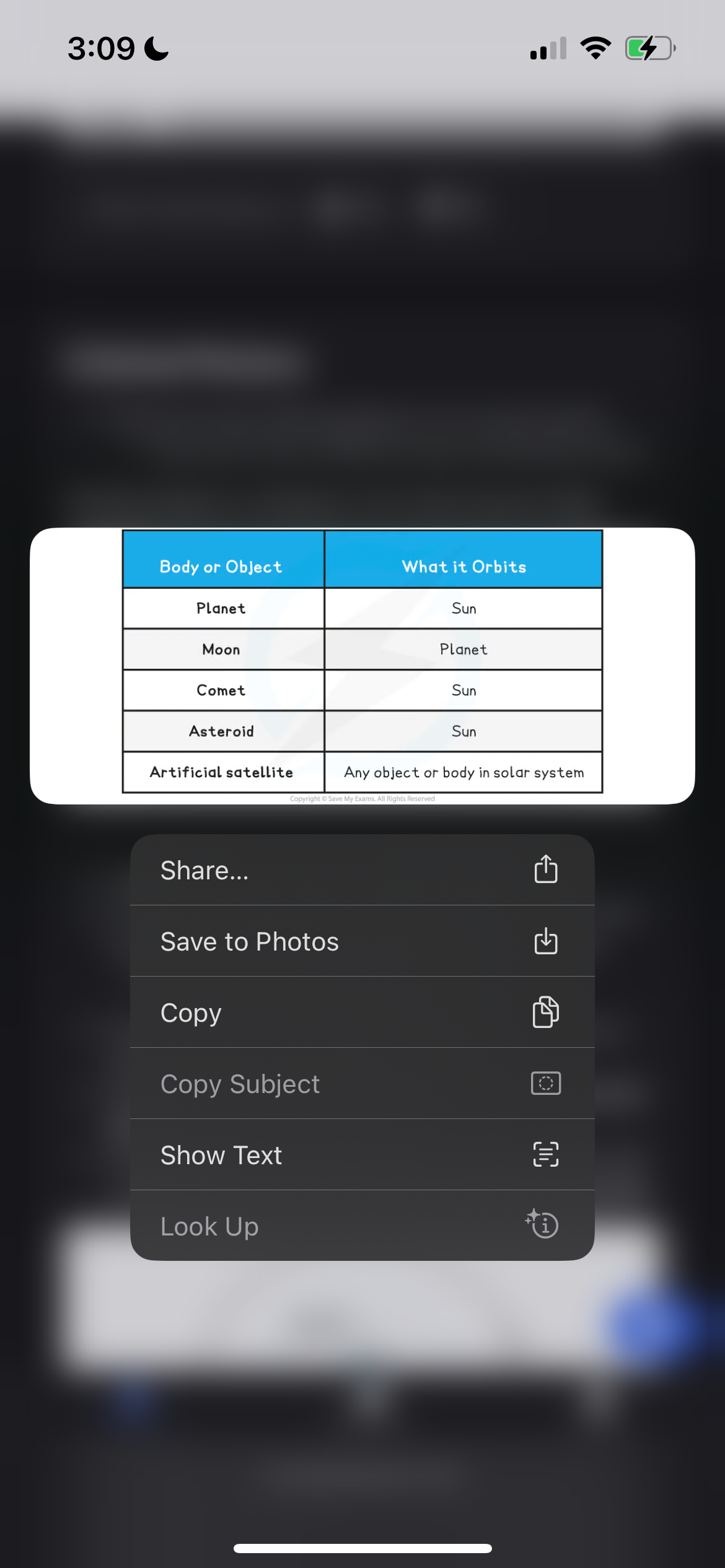
Define orbit of moons
Moons will orbit planets in a circular path
Some planets will have more than one moon
The closer the moon is to the planet:
The shorter the time it will take to orbit
The greater the speed in the orbit
Describe the orbit of artificial satellites
A satellite needs to travel at a specific speed to maintain a circular orbit at a particular distance from the object
Describe what happens when the speed of an artificial satellite is too big
If the speed of the satellite is too big:
The radius of the orbit will increase and the satellite will spiral into space
This is because the gravitational attraction cannot provide enough force to keep it in orbit
What happens if the speed of a satellite is too small
If the speed of the satellite is too small:
The radius of the orbit will decrease and the satellite will move towards the object it should be orbiting
This is because the gravitational attraction is too strong to maintain a constant orbital radius
How do satellites obtain a stable orbit
If an artificial satellite is to change the radius at which it is orbiting then the speed at which it is travelling must change
To maintain a stable orbit:
If the speed increases the radius must decrease
If the speed decreases the radius must increase
Describe orbit of a comet
The orbits are highly elliptical (very stretched circles) or hyperbolic
This causes the speed of the comets to change significantly as its distance from the Sun changes
Not all comets orbit in the same plane as the planets and some don’t even orbit in the same direction
As the comet approaches the Sun, it loses gravitational potential energy and gains kinetic energy
This causes the comet to speed up
This increase in speed causes a slingshot effect, and the body will be flung back out into space again, having passed around the Sun
As it moves away from the Sun the body will slow down, eventually finishing its orbit and falling back into towards the Sun once more
In this way, a stable orbit is formed
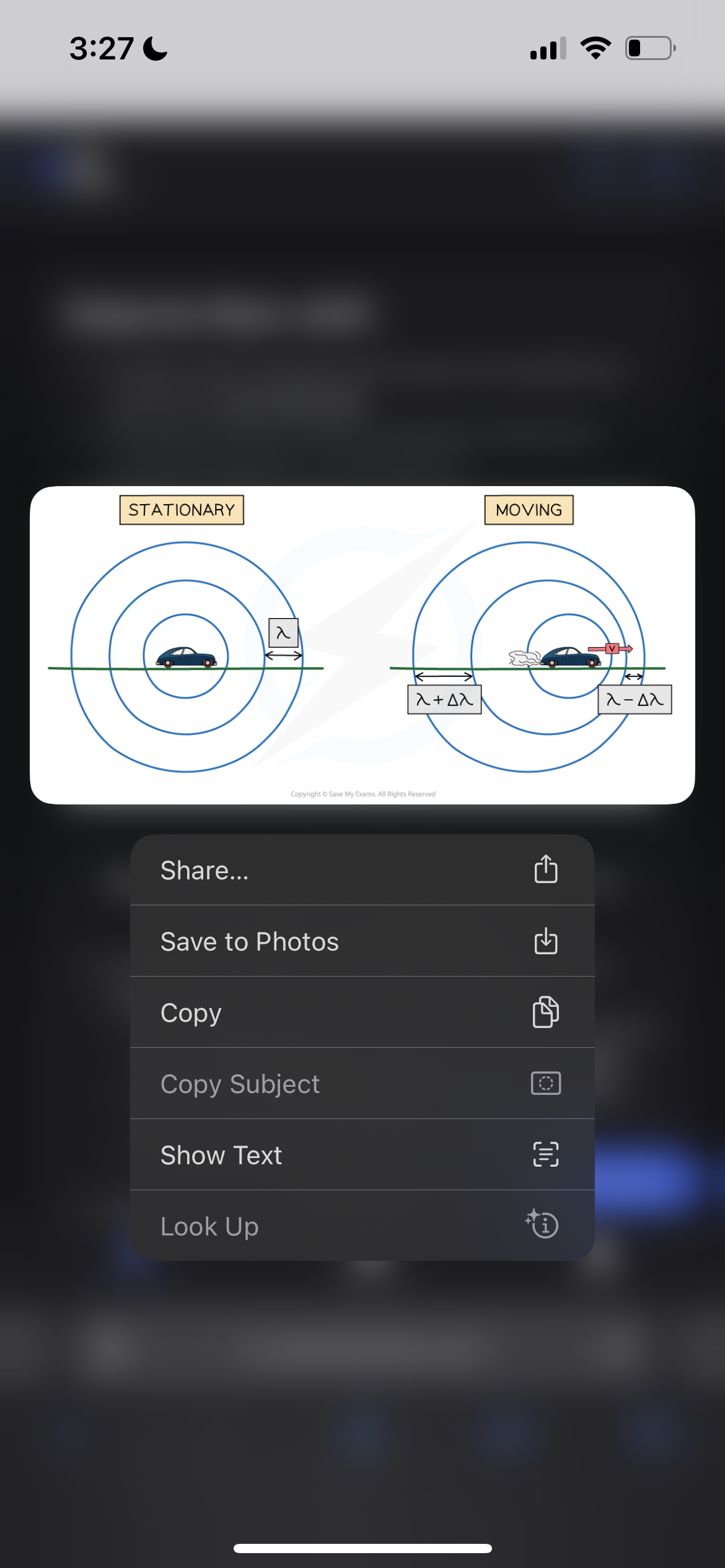
Describe the wavelength of a moving object
A moving object will cause the wavelength, λ, (and frequency) of the waves to change:
The wavelength of the waves in front of the source decreases (λ – Δλ) and the frequency increases
The wavelength behind the source increases (λ + Δλ) and the frequency decreases
This effect is known as the Doppler effect
What is the Doppler effect
The change in frequency or wavelength due to the relative motion between a source and an observer
Describe how the Doppler effect affects light
The Doppler effect also affects light
If an object moves towards an observer, the wavelength of light decreases
This is known as blueshift as the light moves towards the blue end of the spectrum
If an object moves away from an observer, the wavelength of light increases
This is known as redshift as the light moves towards the red end of the spectrum
What is red shift
The observed increase in the wavelength of light due to the source moving away from the observer
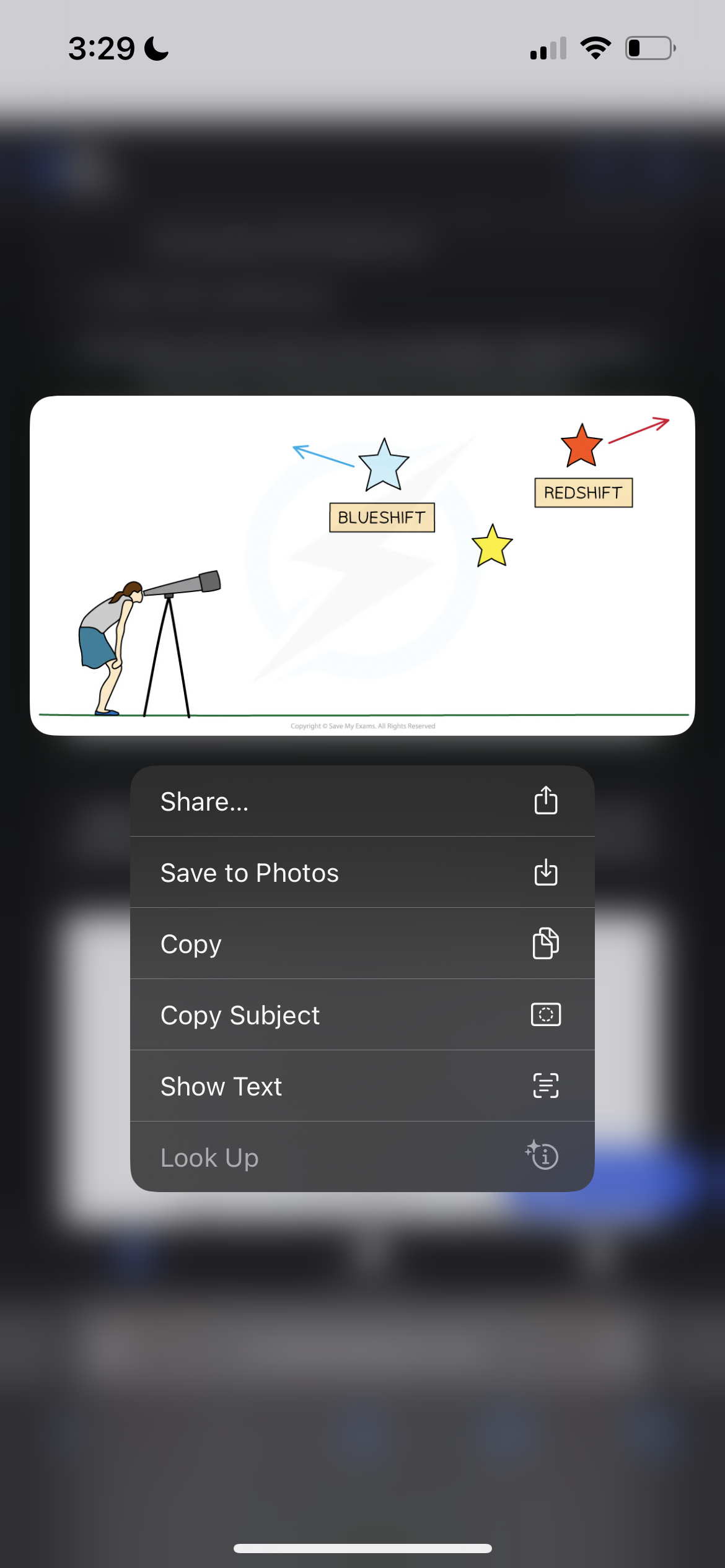
Describe the motion of light from a star
Light from a star that is moving towards an observer will be blueshifted and light from a star moving away from an observer will be redshifted
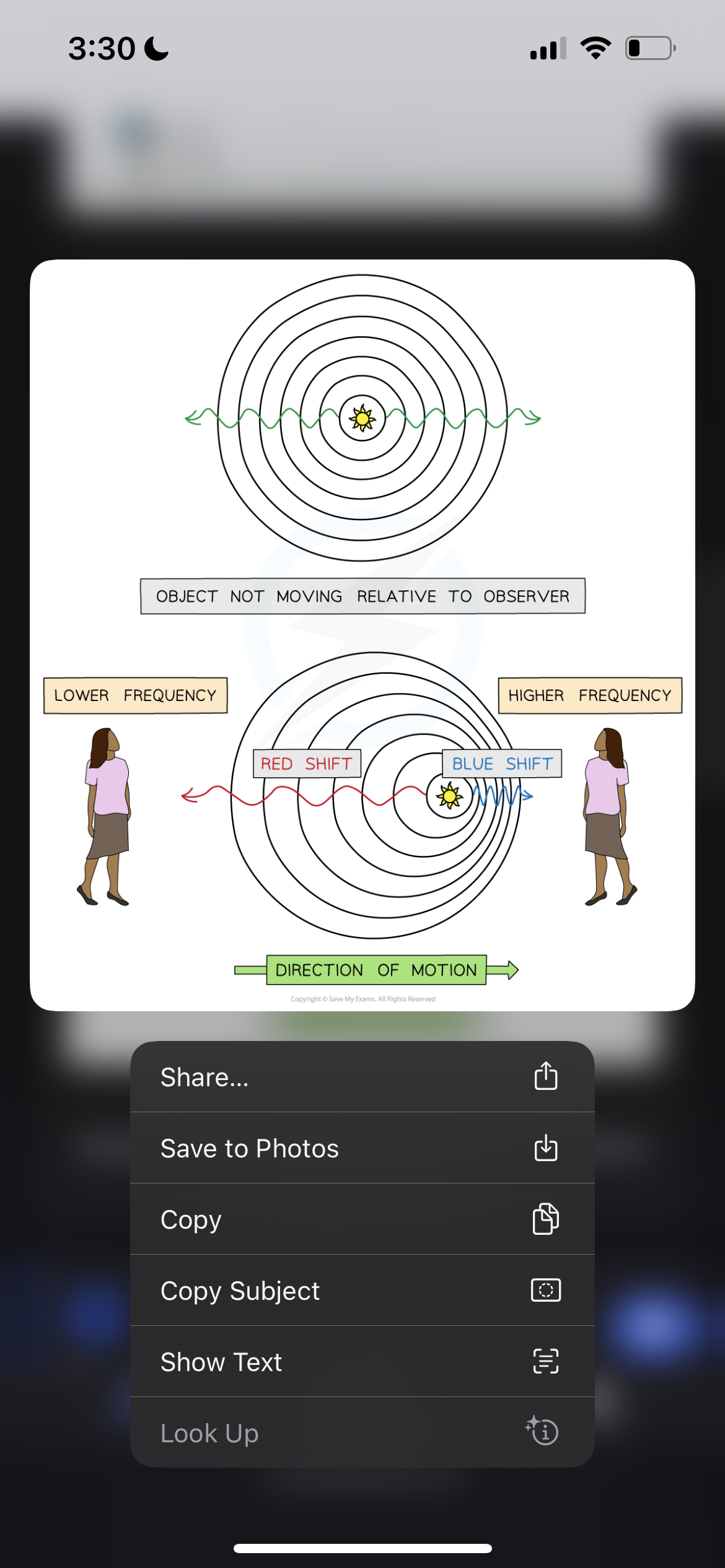
Light coming from the sun compared to light coming from a distant galaxy
Light from a star that is moving towards an observer will be blueshifted and light from a star moving away from an observer will be redshifted
Describe how red shift proves the Big Bang right
The diagram also shows that the light coming to us fromdistant galaxies is redshifted
The lines on the spectrum are shifted towards the red end
This indicates that the galaxies are moving away from us
If the galaxies are moving away from us it means that the universe is expanding
The observation of redshift from distant galaxies supports the Big Bang theory
Another observation from looking at the light spectrums produced from distant galaxies is that the greater the distance to the galaxy, the greater the redshift
This means that the further away a galaxy, the faster it is moving away from us
Describe the Big Bang
Around 14 billion years ago, the universe began from a very small region that was extremely hot and dense
Then there were a series of explosions, which we call the Big Bang
This caused the universe to expand, cooling as it does so, to form the universe we currently observe
Each point expands away from the others
This is seen from galaxies moving away from each other, and the further away they are the faster they move
As a result of the initial explosions, the universe continues to expand
What is the evidence of the Big Bang
By observing the light spectrums from supernovae in other galaxies there is evidence to suggest that distant galaxies are receding (moving further apart) ever faster
These observations were first made in 1998
The light spectrums show that light from distant galaxies is redshifted, which is evidence that the universe is expanding – the galaxies are moving away from us - and, indeed, each other
This is what happens in an explosion
Matter is first densely packed and as it explodes it, it moves out in all directions getting further and further from the source of the explosion
Some matter will be lighter and travel at a greater speed, further from the source of the explosion
Some matter will be heavier and travel at a slowerspeed, closer to the source of the explosion
If you were to travel back in time and compare the separation distance of the galaxies they would become closer and closer together until the entire universe was a single point
If the galaxies were originally all grouped together at a single point and were then exploded we would see a similar effect
The galaxies that are moving fastest would move the furthest - the distance they move would be proportional to their speed
The galaxies that are moving slowest would move the least
What are the observations not understood about the universe
Evidence from the rotation and motion of galaxiessuggests that there is much more matter in the Universe than we are able to account for
This unseen matter is given the name dark matterand its nature is not currently known
Measurements of the expansion of the Universe using supernovae suggest that the Universe is starting to expand at a faster rate
It has been suggested that this accelerated motion is caused by dark energy pushing everything in the Universe apart
If gravity is present everywhere in the Universe, it might be expected that everything will one day become closer together, but that is the opposite of what we see
This is another reason why dark energy is a possible solution which could be counteracting gravity and expanding the Universe instead
How does the earth gravitational force affect motion of satellites
gravitational force causes the satellite to accelerate towards the earth
This changes the direction of motion but not speed
So changes the velocity of the satellite
How does red shift prove the Big Bang theory