b9
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
Abiotic factors
Non-living factors in an ecosystem
Biotic factors
Living factors in an ecosystem
Percolation
movement of water through the soil to the ground water
Quadrats
Square frames used in field-work techniques
Mutualism
Organisms living closely together for mutual benefit
Random sampling
Sampling method done with quadrats
Systematic sampling
Sampling method done with belt transects
Parasite
Organism feeding on another while living together
Non-indigenous species
Organisms not naturally found in an area
Reforestation
Replanting forests after destruction
Potable
Water safe for drinking
Combustion
Process releasing carbon dioxide into the atmosphere
Photosynthesis
Process removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere
Desalination
Producing drinking water from salty water
Chlorine
Added to water to kill pathogens
Filtration
Process to remove large solids from water
population
all the organisms of a particular species in that habitat
habitat
where an organism lives
ecosystem
the interaction of a community of living organisms with the non-living parts of their ecosystem
community
all the population of different species that live together in a habitat
interdependence
all species depend on other species in some way for survival
interspecific competition
competition between different species
intraspecific competition
competition between members of the same species
competition
the struggle between organisms to survive in a habitat with limited resources
abundance
how many organisms there are
distribution
where the organisms are
what are quadrats used for
measure abundance
what are transects used for
measure how distribution changes
what is a transect
a line through a habitat along which organisms are sampled
biodiversity
variety of living things on earth or in a particular ecosystem
why is biodiversity important
keeps ecosystem stable, we need pollinators for food, need certain species for medicine, jobs , tourism and cultural aspects
fertiliser
substance added to soil in order to supply plants with nutrients
leaching
nutrients are washed from the soil by water
eutrophication
-nutrients from fertiliser enter lakes and rivers by leaching
-stimulates rapid algae growth which blocks light from reaching plants below
- lack of light kills plants
- decomposers eat dead plant matter
- decomposers aerobically respire ( less oxygen )
- lack of oxygen kills fish and other aerobic organisms
what are the bacteria that feed on dead plants called
saprobiotic bacteria
dangers of non-indigenous species being added to habitat
spread disease, ruin ecosystem as they may outcompete indigenous species
mutualism examples
oxpeckers and hippos , cleaner fish and sharks , nitrogen fixing bacteria and plants
what percentage of energy and biomass is passed on at each stage
10
what affects rate of decomposition
oxygen availability, temperature, water content
trophic level
position of an organism in a food chain
why is only 10% of biomass passed on at each stage of a food chain
organisms don’t eat all of their food, some material isn’t absorbed, most biomass is used to release energy for processes
nitrogen cycle steps without plants and animals
nitrogen fixation , nitrification , denitrification
nitrogen cycle with plants and animals steps
nitrogen fixation , nitrification , assimilation , decomposition , nitrification , denitrification
nitrogen fixation
nitrogen fixing bacteria turn nitrogen gas into ammonium.
what can lightning do in terms of nitrogen fixation
lightning can turn nitrogen gas into nitrates
decomposition in nitrogen cycle
dead plants and animals and waste products are decomposed into ammonia
nitrification
nitrifying bacteria turns ammonia into nitrites then nitrates
denitrification
denitrifying bacteria turn nitrates into nitrogen gas
assimilation
plants take up nitrates and make proteins
water cycle
water from sea evaporates and transpiration , water vapour rises and condensed and forms clouds , precipitation , percolation
sedimentation
remove smaller bits as they pass through a bed of sand and gravel
carbon cycle
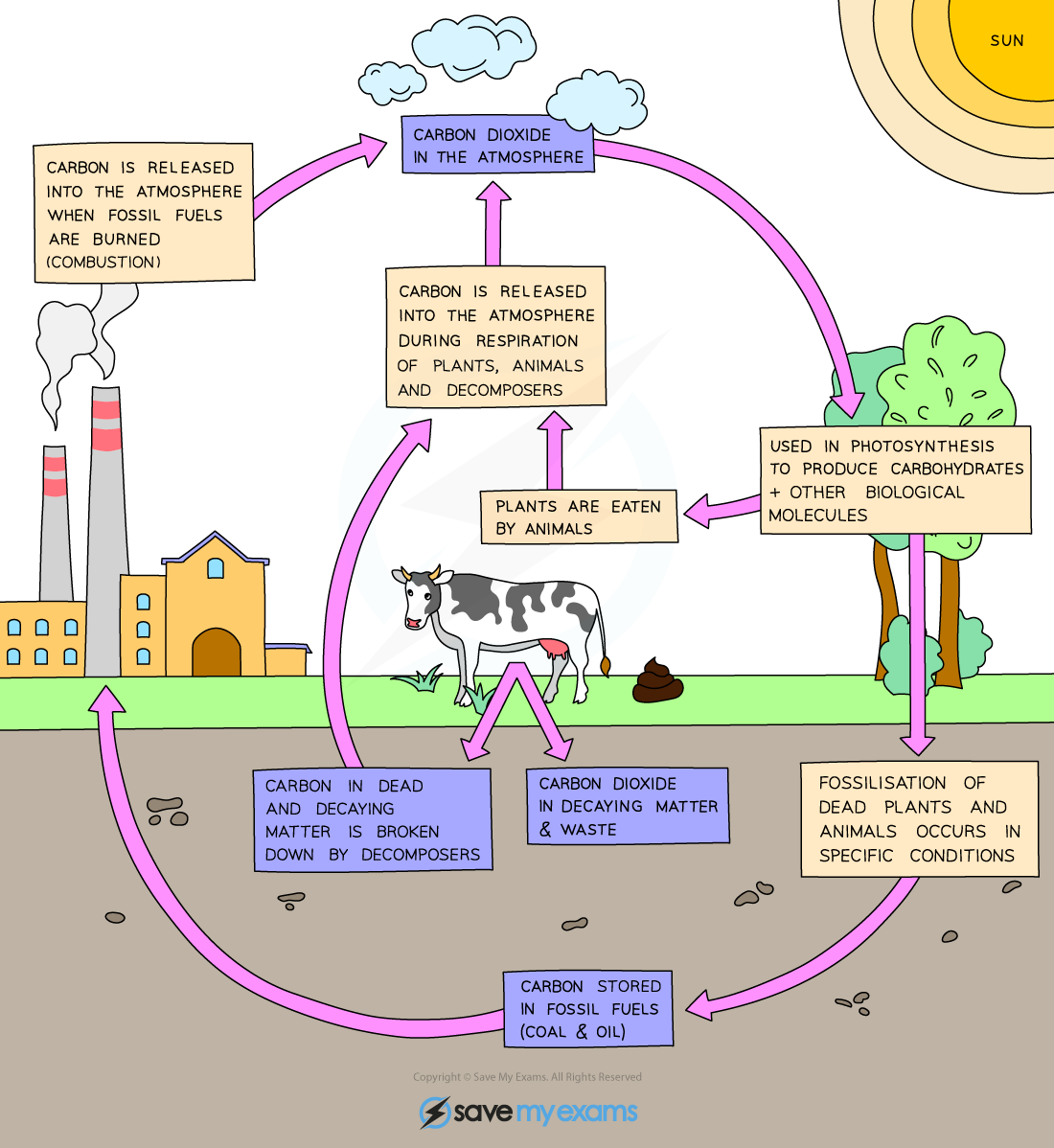
photosynthesis takes carbon dioxide
animals eat plants storing carbon
plants and animals respire
plants and animals decompose releasing carbon
plants and animals fossilise storing carbon
carbon is released in combustion
what are 2 carbon sinks
oceans , sedimentary rock
rate of decay
change in mass / time
decomposers
break down matter at microscopic level
detritivores
small animals that break down large matter to increase surface area for decomposers
factors affecting decay
temperature, water , availability of oxygen
how does temperature affect decay
optimum temp for enzymes
how does water affect decay rate
water is needed for essential biological processes and enzyme reactions
how does availability of oxygen
oxygen is needed for aerobic respiration
4 methods of preserving food
freezing, removing water , reducing oxygen , irradiating foods to kill bacteria
reverse osmosis
salt water moves through partially permeable membrane at high pressure
negative human impacts on biodiversity
overfishing, eutrophication by fertilisers, introduction of non-indigenous species
sustainable fishing methods
maximum catch per year
larger holes in nets to let small fish escape
no fishing during breeding seasons or near breeding grounds
types of conservation and maintenance of biodiversity
conserving species, reforestation
methods of conserving endangered animals
protect habitat
breeding programs
method of conserving endangered plants
seed banks - store seeds of rare species
what are indicators of air pollution
absence of lichens or crusty lichens
indicators of clean air
blackspot fungus on roses and bushy lichens
indicator of water pollution
bloodworms and sludge worms
indicator of clean water environment
freshwater shrimps and stoneflies
Food security
Having enough food to feed a population
Biological factors threatening food security
Population , changing diets , environmental changes , pests and pathogens , conflicts , price
How do environmental changes affect food security
Extreme weather conditions and environmental changes due to climate change can cause decreased yield
How can cost affect food security
Agricultural inputs can be expensive . Costs are passed on to the consumer making food more expensive
Sustainable farming methods
Making enough food for current population while ensuring that future generations ability to make enough food isn’t affected
food web
show interdependence of ecosystem
3 types of food pyramids from producer to tertiary consumer
pyramids of number, pyramid of biomass, pyramid of energy transfer
how do changing diets affect food security
makes feeding populations more difficult. drives demand and makes food more expensive
why is the carbon cycle important
to cycle carbon which is a component of all organic molecules and to sustain life
why is the water cycle important
distributes freshwater around the world
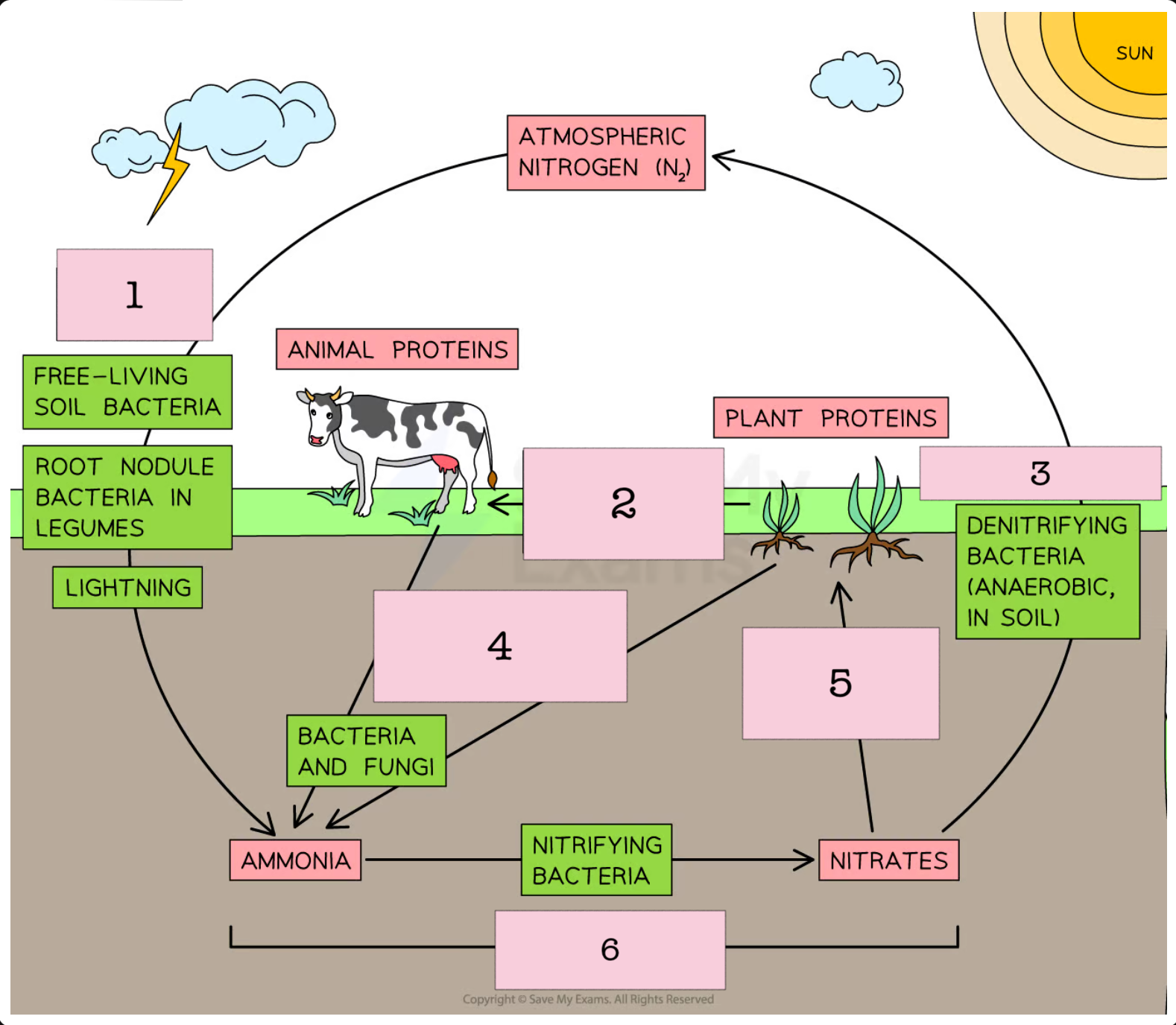
nitrogen fixation
feeding
denitrification
decomposition
assimulation
nitrification
how does oxygen availability affect decay
increases it as oxygen is needed to respire
decomposition / decay
breaking down and digestion of biological material by organisms called decomposers
what microorganisms are decomposers
bacteria , fungi, detritus feeders
uses of decomposition
compost
what is compost
natural fertiliser which recycles materials back into the soil
what are the conditions for compost making
mesh sides to increase oxygen, moist and warm conditions generated by the decomposers, insulation
how to slow down decomposition
low temperatures, sterile conditions, vacuum pack food, dry foods
what is a sustainable alternative of fossil fuels that are non-renewable
biofuel
benefits of fishfarming
can produce lots of fish for humans in small spaces. maximises yield
negatives of fish farming
attracts predators which may get caught in nets, spread of disease in and outside fish farm, eutrophication can occur ,
if fish escape they may cause problems as they’re indigenous
how do plants take up nitrates by assimilation
taken up using active transport in root hair cell
what are nitrates used for
making amino acids and proteins , proteins are used to build plant cells
3 ways concentration of nitrates in the soil can be increased
artificial fertiliser, crop rotation, nitrogen fixing and nitrifying bacteria
how does lightning help make nitrates
the heat and pressure of lightning combines oxygen and nitrogen in the atmosphere
how could deforestation affect the water cycle
water vapour in atmosphere would decrease as there is less trees and transpiration
why might CO2 levels fluctuate in a year
during winter , trees have less leaves so less photosynthesis occurs
more fossil fuels are being burned in winter
consequence of no carbon cycle
less organic molecules for future organisms to build their biomass with as there’s finite number of atoms
how do clouds form
warm air rises with water vapour and as the air cools , the water vapour condenses