Biology operons/bacteria/viruses
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
1
New cards
bacteria
single celled prokaryotes
2
New cards
circular
bacteria have singular _____ chromosome
3
New cards
Naked DNA
DNA not associated with histones or histone-like proteins.
4
New cards
Plasmid
A small ring of DNA that carries accessory genes separate from those of the bacterial chromosome
5
New cards
horizontal gene transfer
The transfer of genes between organisms in a manner other than traditional reproduction.
6
New cards
vertical gene transfer
transmission of genes from the parental generation to offspring via sexual or asexual reproduction
7
New cards
sources of variation
mutation, transformation, transduction, conjugation, transposons
8
New cards
spontaneous mutation
a random change in the DNA arising from errors in replication that occur randomly
9
New cards
E. Coli
example of a spontaneous mutation
10
New cards
transformation
process in which one strain of bacteria is changed by a gene or genes from another strain of bacteria; pick up foreign DNA wherever
11
New cards
R plasmids
carry genes for antibiotic resistance
12
New cards
swapping
resistant genes are on plasmids that are ____ between bacteria
13
New cards
transduction
phage viruses carry bacterial genes from one host to another
14
New cards
conjugation
bacteria sex
15
New cards
conjugation
the direct transfer of DNA between two cells that are temporarily joined
16
New cards
conjugation
"male" extends sex pilli and attatches to "female" bacterium
17
New cards
transposons
(jumping genes) short strands of DNA capable of moving from one location to another within a cell's genetic material
18
New cards
transposon
cut and paste
19
New cards
retrotransposon
copy and paste
20
New cards
Bacterial metabolism
Bacteria need to respond quickly to changes in their environment
21
New cards
feedback inhibition
product acts as an allosteric inhibitor
22
New cards
gene regulation
the turning on and off of genes
23
New cards
build
if bacterium has enough tryptophan then it doesnt need to make enzymes used to _____ tryptophan
24
New cards
digest
If bacterium encounters new sugar like lactose, then it needs to start making enzymes used to ____ lactose
25
New cards
operon
group of genes operating together
26
New cards
promoter
specific region of a gene where RNA polymerase can bind and begin transcription
27
New cards
operator
Region of DNA that controls RNA polymerase's access to a set of genes with related functions; binding site of repressor protein
28
New cards
repressor protein
a regulatory protein that binds to an operator and blocks transcription of the genes of an operon
29
New cards
repressible operon
transcription is usually on, but can be inhibited (repressed) when a specific small molecule binds allosterically to a regulatory protein (example tryptophan)
30
New cards
repressible
tryptophan is a ____ operon
31
New cards
synthesis pathway model
When excess tryptophan is present, it binds to tryp repressor protein & triggers repressor to bind to DNA, blocks (represses) transcription
32
New cards
Inductible operon
When substance is present - turn on operon
33
New cards
digestive pathway model
When lactose is present, binds to lac repressor protein & triggers repressor to release DNA, induces transcription
34
New cards
allosteric inhibition
lactose is an _____ regulator of repressor protein
35
New cards
Inductible
default setting is off
36
New cards
repressible
default setting is on
37
New cards
CAP
ust bind to cAMP to activate transcription of the lac operon by RNA polymerase
38
New cards
cAMP
When glucose levels decline in E. coli, catabolite activator protein (CAP) is bound by ____to promote transcription of the lac operon.
39
New cards
cAMP
when levels of this become high levels of glucose are low
40
New cards
CAP
when glucose levels increase in E. Coli, ____ detatched from the Lac operon, turning it off
41
New cards
Gene regulation
bacteria preform ___ _____ in order to conserve energy
42
New cards
epigenetics
the study of influences on gene expression that occur without a DNA change
43
New cards
DNA packing
coiling and folding of DNA in each chromosome
44
New cards
nucleosomes
"beads on a string", 1st level of DNA packing, histone proteins
45
New cards
packing
degree of ___ DNA regulates transcription (ex. "lightly packed around histones=no transcription, genes turned off)
46
New cards
Methylation
addition of a methyl group, blocks transcription factors,genes turned off
47
New cards
acetylation
addition of acetyl group, unwinds DNA, enables transcription
48
New cards
transcription initiation
RNA polymerase binds to promoter
49
New cards
promoter
specific region of a gene where RNA polymerase can bind and begin transcription, nearby control, base rate
50
New cards
enhancer
A DNA sequence that recognizes certain transcription factors that can stimulate transcription of nearby genes, distant control, high rate
51
New cards
transcription complex
the completed assembly of transcription factors and RNA polymerase II bound to the promotor
52
New cards
post transcriptional control
Alternative RNA splicing, variable processing of exons creates a family of proteins
53
New cards
regulation of mRNA degredation
Life span of mRNA determines amount of protein synthesis, mRNA can last from hours to weeks
54
New cards
RNA interference
technique to silence the expression of selected genes in nonmammalian organisms; uses synthetic double-stranded RNA molecules matching the sequence of a particular gene to trigger the breakdown of the gene's messenger RNA
55
New cards
siRNA
short segments or RNA, bind to mRNA, create sections of double stranded mRNA, 'death tag' for mRNA, triggers degradation
56
New cards
gene silencing
A gene that is not expressed owing to epigenetic regulation.
57
New cards
control of translation
block initiation of translation stage, regulator proteins attach to 5' end, prevent attachment of ribosomal subunit and initiator tRNA, block translation
58
New cards
protein processing
folding, cleaving, adding sugar groups, targeting for transport
59
New cards
protein degradation
ubiquitin tagging, proteasome degradation
60
New cards
proteasome
organelle that degrades proteins
61
New cards
ubiquitin tagging
mark unwanted proteins with a label "death tag"
62
New cards
emerging virus
viruses that "jump" host, switch species, ebola, sars, bird flu
63
New cards
cells
viruses are not ___
64
New cards
virus
DNA or RNA enclosed in a protein coat
65
New cards
chaperonin
A protein molecule that assists in the proper folding of other proteins.
66
New cards
parasites
lack enzymes for metabolism, lack ribosomes for protein synthesis, need host "machinery
67
New cards
Viral genomes
may be composed of DNA or RNA and may be single- or double-stranded
68
New cards
capsid
Outer protein coat of a virus
69
New cards
capsid
crystal like protein shell, 1-2 types of proteins, many copies of same protein
70
New cards
viral envelope
a lipid bilayer that envelops some viruses, can be derived from host cell membrane
71
New cards
host
virus DNA/RNA enters ____ cell
72
New cards
assimilation
viral DNA/RNA takes over host, reprograms host cell to copy viral nucleic acid and build viral proteins
73
New cards
self assembly
nucleic acid molecules and capsomeres then self-assemble into viral particles and then exit cell
74
New cards
capsomeres
protein subunits that make up capsids
75
New cards
lysis
destruction
76
New cards
rabiees
can infect all mammals
77
New cards
human cold
only cells lining upper respiratory tract of humans
78
New cards
HIV
binds only to specific white blood cells
79
New cards
bacteriophages
viruses that infect bacteria
80
New cards
lytic lifecycle
reproduce virus in bacteria, release virus by rupturing bacterial host
81
New cards
lysogenic lifecycle
integrate viral DNA into bacterial DNA, reproduce with bacteria
82
New cards
restriction enzymes
recognize and cut up foreign DNA
83
New cards
phages
viruses that infect bacteria
84
New cards
retroviruses
have to copy viral RNA into host DNA, enzyme is reverse transcriptase, RNA---> DNA---> mRNA
85
New cards
reverse transcriptase
a polymerase that catalyzes the formation of DNA using RNA as a template
86
New cards
HIV
envelope with glycoproteins for binding to specific WBC, capsid containing 2 RNA strands and 2 copies of reverse transcriptase
87
New cards
budding
Asexual reproduction in which a part of the parent organism pinches off and forms a new organism
88
New cards
protease
enzyme that digests protein
89
New cards
chemokines
A chemical secreted by blood vessel endothelium and monocytes during an immune response to attract phagocytes to an area
90
New cards
cancer viruses
Viruses disrupt the normal growth and division of cells in a host, cause abnormal growth and create tumours
91
New cards
oncogenes
cancer causing genes
92
New cards
prions
infectious proteins
93
New cards
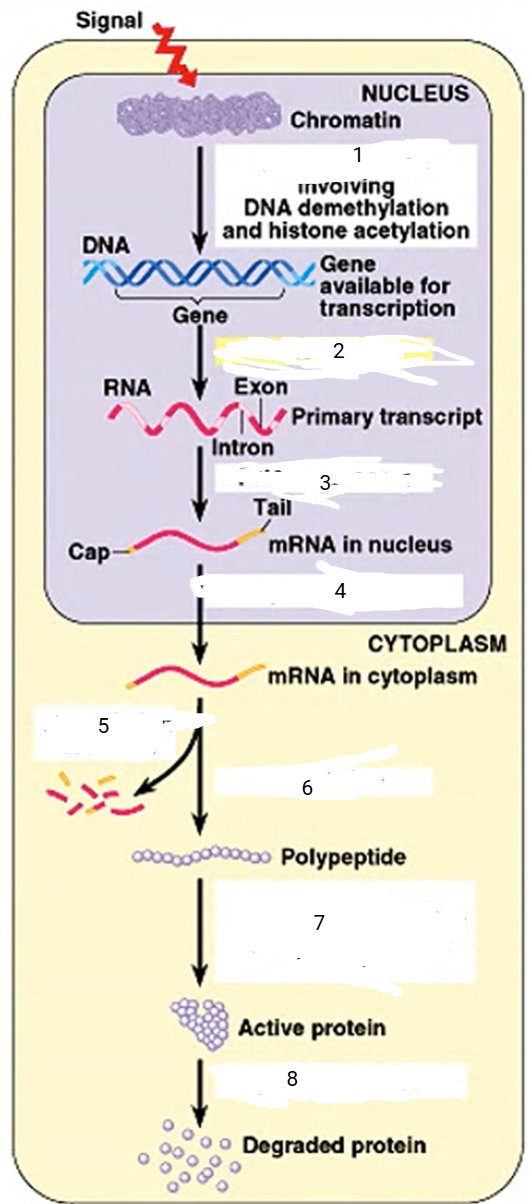
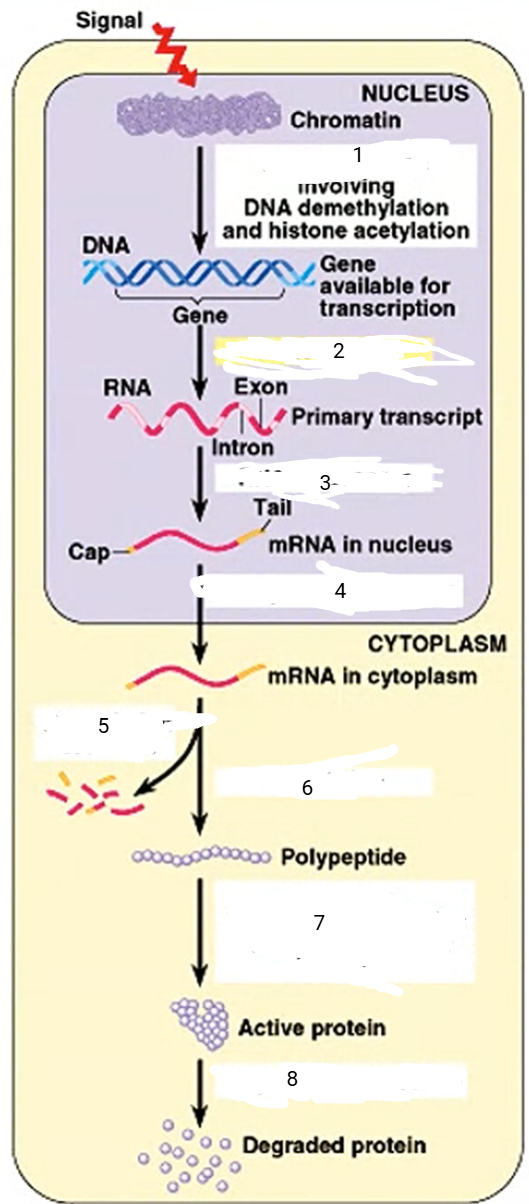
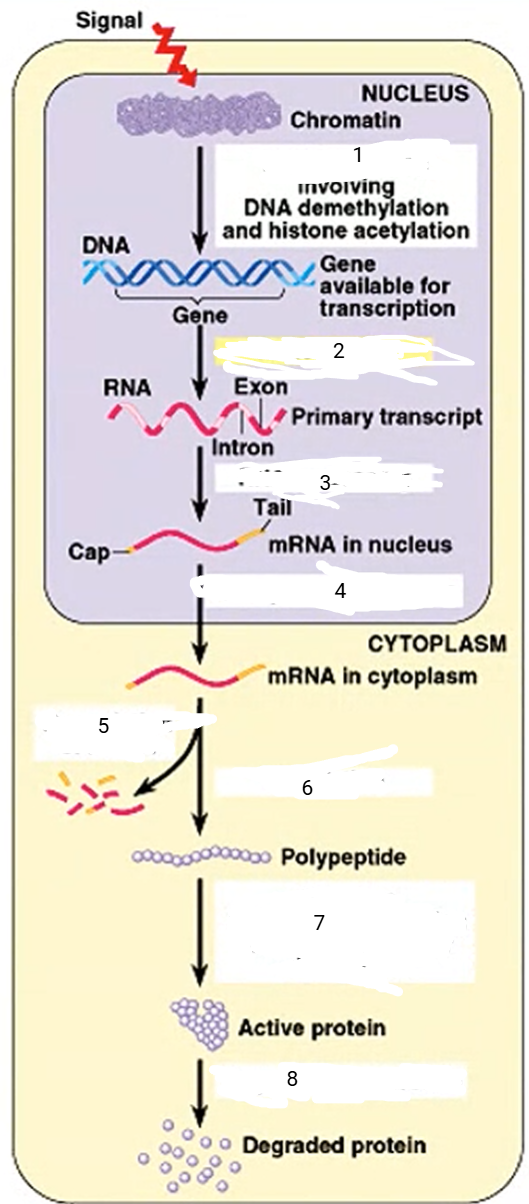
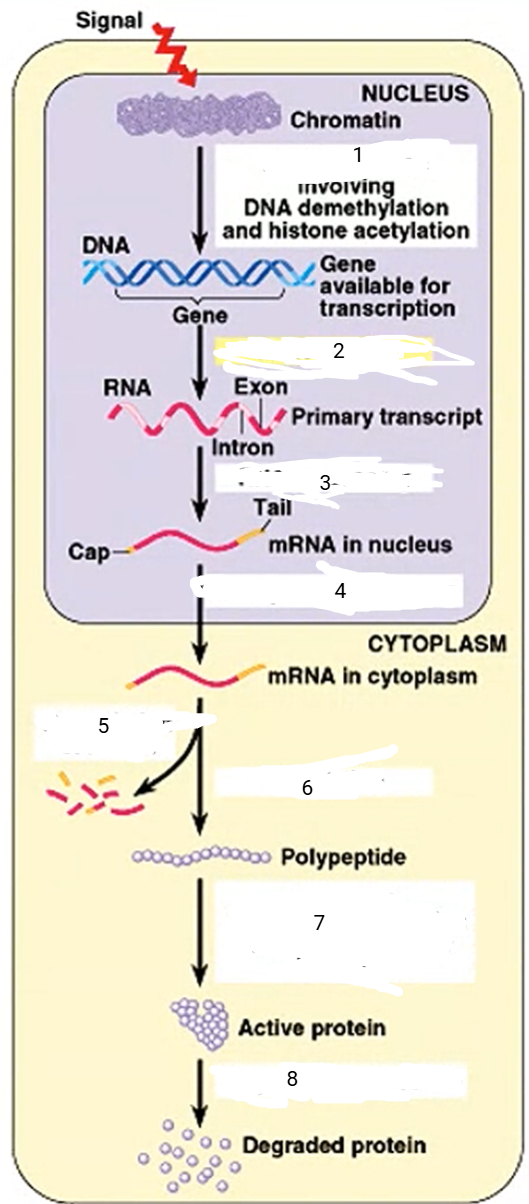
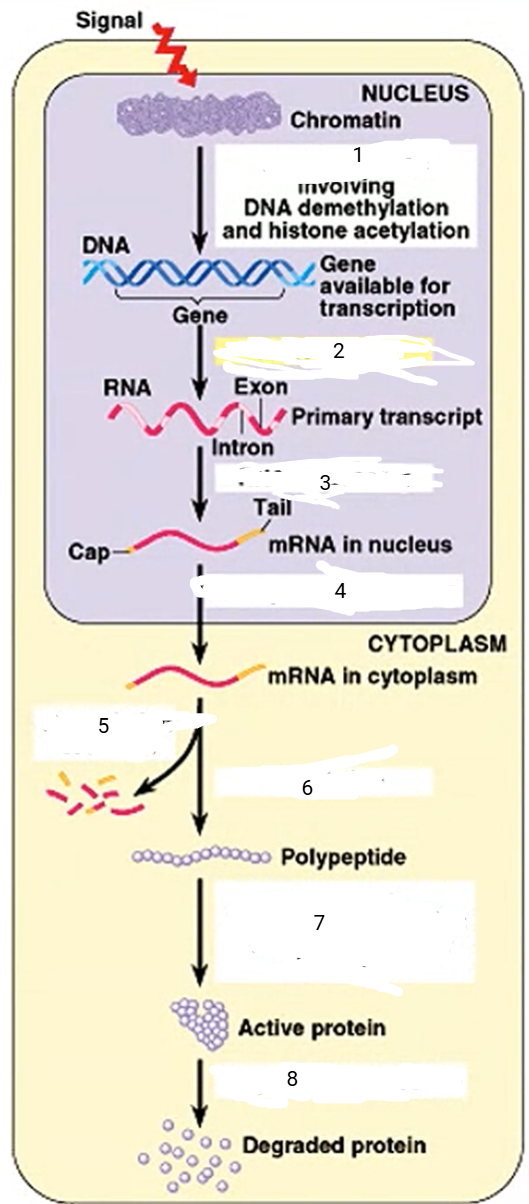
DNA unpacking
1
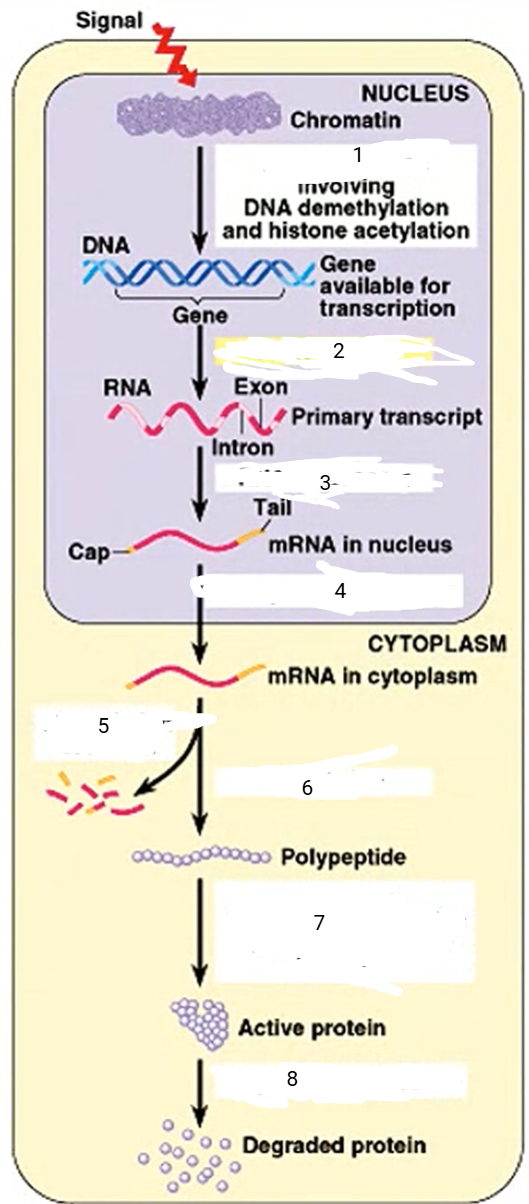
94
New cards
transcription
2
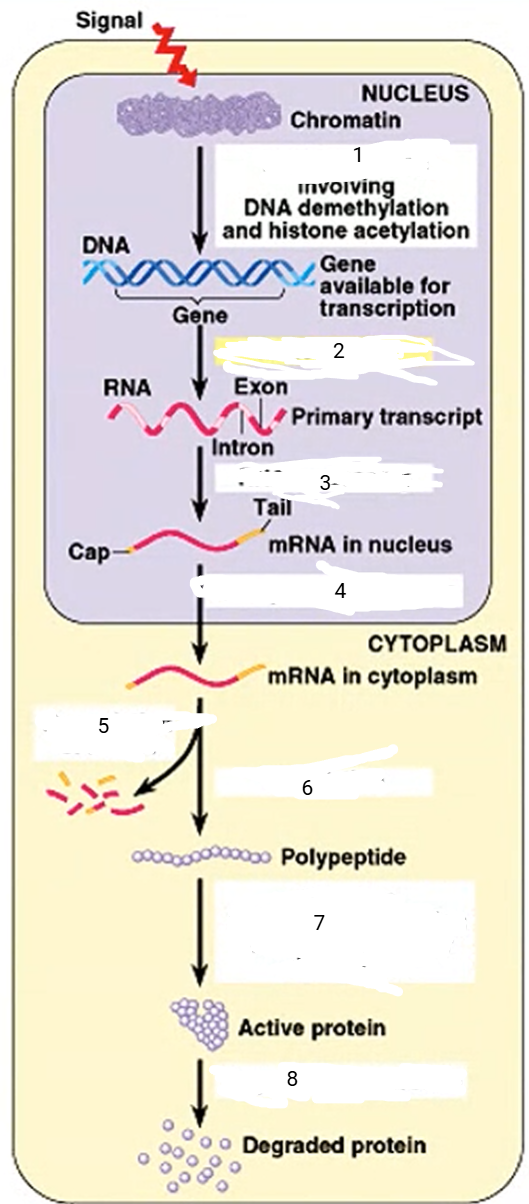
95
New cards
RNA processing
3
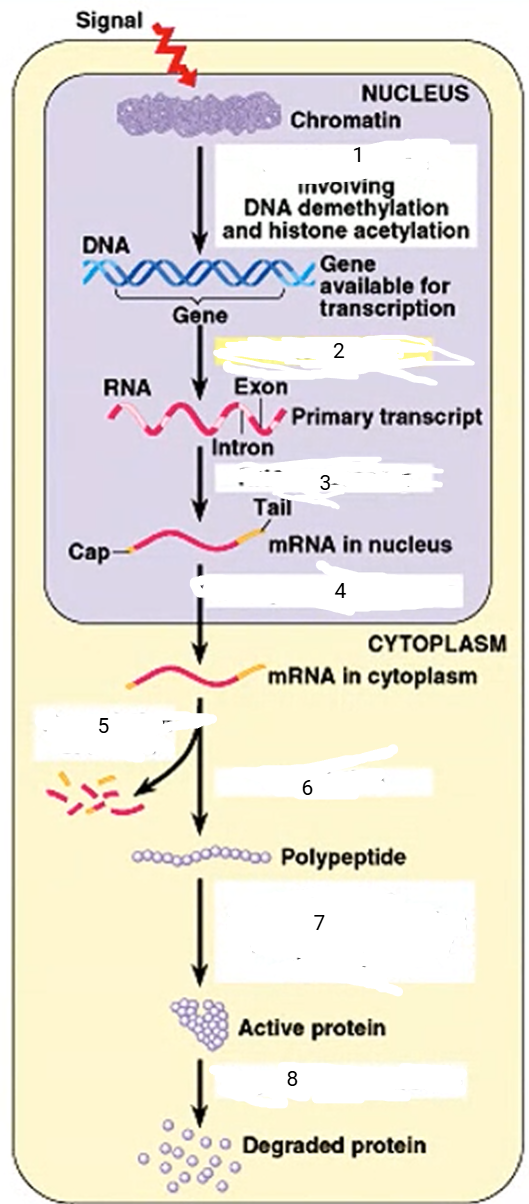
96
New cards
transport to cytoplasm
4
97
New cards
mRNA degradation
5
98
New cards
translation
6
99
New cards
cleavage, transport to destination
7
100
New cards
protein degradation
8