pearson chatpers 11 - 15
1/171
Earn XP
Description and Tags
exam 3!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
172 Terms
Clusters of cell bodies in the CNS
Nuclei
Clusters of cell bodies in the PNS
Ganglia
Bundles of axons in the CNS
Tracts
Bundles of axons in the PNS
Nerves
Conduct electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body.
Axons
Receives electrical signals from other neurons
Dendrites
Integrates incoming signals and generates outgoing signal to axon.
Axon hillock
Releases neurotransmitters to communicate with other neurons.
Axon terminals
Maintains the cell's life functions and contains the nucleus.
Soma (cell body)
What structure contains the bulk of the neurolemmocyte's cytoplasm and organelles?
Neurolemma
What must be intact for a neuron to regenerate in the peripheral nervous system (PNS)?
Cell body
Regulation of heart rate, blood pressure, and digestive functions are carried out by the
autonomic nervous system
What forms the white matter of the spinal cord?
Myelinated axons
What specific part of the neuron communicates with a target cell and serves as the secretory region of the cell?
Axon terminals (synaptic knobs)
What cell type forms the myelin sheath in the central nervous system (CNS)?
Oligodendrocytes
Which division of the peripheral nervous system (PNS) carries signals from bones, joints, skin, and organs of vision to the central nervous system (CNS)?
Somatic sensory
The most common type of neuron in the human body is __________.
multipolar
The conducting region of the neuron is the __________.
axon
Neurons that transmit signals to the central nervous system
Sensory (afferent)
Neurons that carry signals from the central nervous system
Motor (efferent)
Neurons that process information within the central nervous system
Interneuron
Controls voluntary movements
Somatic
Related to the internal organs of the body
Visceral
Which neuroglial cells help form the blood-brain barrier?
Astrocytes
Which of the following are organs of the central nervous system?
Brain and spinal cord
The autonomic nervous system does not carry signals to __________.
skeletal muscle
Which of the following characteristics makes myelin such an excellent insulator for axons?
High lipid content
What type of neuron carries information toward the central nervous system (CNS)?
Afferent
Which of the following characteristics is not associated with neurolemmocytes?
Envelop parts of several axons with multiple processes
Which of the following effectors is controlled by the somatic motor division?
Skeletal muscle
What is the ciliated neuroglial cell that functions to circulate cerebrospinal fluid?
Ependymal cells
Bundles of axons known as tracts are part of the __________.
central nervous system (CNS)
What structure found in the peripheral nervous system (PNS) promotes regeneration of a damaged axon?
Neurolemmocytes
The majority of neurons are functionally classified as _________ neurons
interneurons
What neuroglial cells surround and support the cell bodies of neurons and have intertwined processes that link them with other parts of the neuron?
Satellite cells
What type of ion channel is always open?
Leak
What is the process of putting together all the excitatory and inhibitory stimuli that determine whether a neuron will or will not fire an action potential?
Neural integration
What is the period during an action potential when a nerve fiber cannot be stimulated to produce an additional action potential no matter how strong the stimulus?
Absolute refractory period
What ion triggers synaptic vesicles to release neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft?
Calcium
A series of measurements with a voltmeter show a neuron's membrane potential becoming more negative, from –70 mV to –85 mV. This neuron is experiencing a __________.
hyperpolarization phase
Influx of which of the following ions can cause an inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) to be produced?
Chloride ions
These channels open and close in response to changes in membrane potential.
Voltage-gated ion channels
These channels are always open.
Leakage channels
These channels open or close in response to the binding of a specific chemical molecule.
Ligand-gated ion channels
These channels open in response to physical deformation of the receptor, as in sensory neurons.
Mechanically gated ion channels
Which of the following events occurs when EPSPs arrive rapidly at a single synapse?
Temporal summation
Resting membrane potential is maintained by the Na+/K+ ATPase, which brings __________.
two potassium ions into the cytosol and three sodium ions into the extracellular fluid
What kind of conduction occurs when each section of the axolemma has to be depolarized to threshold in sequence along the entire axolemma for a current to spread down the length of the axon?
Continuous
Which type of fiber has the slowest conduction speed?
Type C
What term refers to a temporary change in the cell’s membrane potential that makes it less negative (or more positive)?
Depolarization
Which of the following events is most likely to trigger an action potential?
Excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP)
Which type of fiber has the largest diameter?
Type A
The influx of positive charges makes the membrane potential more positive and is known as __________.
depolarization
How many synaptic connections from different presynaptic neurons does an average neuron have?
10,000
The majority of synapses in the nervous system are __________.
chemical
Which type of channel opens in response to a chemical binding to a receptor on the channel?
Ligand-gated
What is the resting membrane potential of a typical neuron?
–70 mV
During saltatory conduction, action potentials are generated __________.
only at nodes of Ranvier of myelinated axons
How many neurotransmitters operating in the human nervous system have been identified?
More than 100
Which neurotransmitter is the most important inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain?
GABA
Which of the following neurotransmitters is not a type of catecholamine?
Acetylcholine
What do neurotransmitters that bind ionotropic receptors directly control?
The movement of ions into or out of the postsynaptic neuron
Which of the following pairs of neurotransmitters are strictly inhibitory?
Glycine and GABA
Cholinergic synapses use the neurotransmitter __________.
acetylcholine
What change in membrane potential is caused when glycine and GABA stimulate the opening of chloride ion channels?
Hyperpolarization
What are the main types of neurotransmitter receptors
| |
Metabotropic |
What is thought to be one of the major neurotransmitters involved in mood regulation, motor behaviors, feeding behaviors, and daily rhythms and is a common target in the treatment of depression?
Serotonin
Which of the following descriptions best characterizes a converging circuit?
Axon terminals from multiple input neurons join onto a single postsynaptic neuron.
The same __________ can have different effects depending on the properties of the __________.
neurotransmitter; receptor
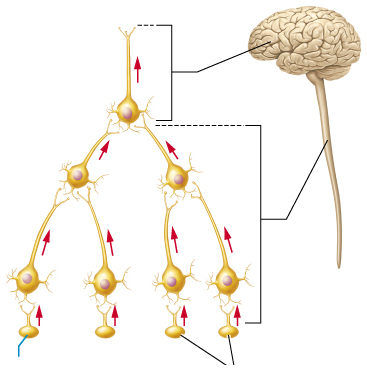
What does this image depict?
Converging circuit
Which circuit type is characterized by multiple input neurons converging onto a single postsynaptic neuron?
Converging circuit
What is considered to be the most important excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain?
Glutamate
The _________ regulates homeostasis, the autonomic nervous system, the endocrine system, and the sleep/wake cycle.
hypothalamus
What functional brain system participates in memory, learning, emotion, and behavior?
Limbic system
Imbalances to temperature homeostasis, weight loss, a decrease in cognitive abilities, hallucinations and even death may all be caused by:
sleep deprivation.
Bundles of white matter in the cerebrum are known as __________.
tracts
What structure(s) of the brain is/are concerned directly with the maintenance of homeostasis?
hypothalamus
reticular formation
The primary visual cortex is located in the:
occipital lobe.
While playing Frisbee with your friends, you are able to track it in the air when it is your turn to catch it because of your:
parietal association cortex.
During development of the nervous system, the telencephalon will become the:
cerebral hemispheres.
What provides a link between the nervous system and the endocrine system?
Hypothalamus
The cerebellum functions in __________.
the planning and coordination of movement
The most important part of the brain in terms of our immediate survival is the:
brainstem
What component of the diencephalon secretes the hormone melatonin?
Pineal gland
Which of the following structures is not part of the limbic system?
Caudate nucleus
The deep grooves in the cerebrum are known as:
fissures.
Dreams occur during which stage of sleep?
REM
Cognition is best described as __________.
recognizing, processing, planning, and responding to stimuli
Nearly all stimuli destined for the cerebral cortex must first pass through the ________.
thalamus
What type of fiber carries information from the frontal lobe of the right cerebral hemisphere to the occipital lobe of the same cerebral hemisphere?
Association fibers
Integrative functions are carried out by the:
central nervous system.
Which of the following structures connects the brain to the spinal cord?
Brainstem
The ability to produce language is a function of _________, whereas the ability to understand language is a function of _________.
Broca’s area; Wernicki’s area
The cerebellar cortex is extensively folded causing the white matter to resemble tree branches and thus is called the:
arbor vitae.
It is in the medulla oblongata that corticospinal tracts __________, meaning that the motor fibers originating from the right cerebral cortex descend through the left side of the spinal cord, and vice versa.
decussate
Which brain nucleus serves as the body's 'master clock'?
Suprachiastmatic nucleus
Our conscious processes, such as planning movement, interpreting incoming sensory stimuli, and complex higher functions, are all functions of the:
cerebral cortex (neocortex)
The central sulcus separates the:
parietal and frontal lobes.
An elevated ridge on the surface of the cerebrum is known as a __________.
gyrus
Which parts of the brain are involved in the storage of long-term memory?
Hippocampus | |
Amygdala | |
Frontal lobe |