Set 8: Sors Filtr Theeree
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Source-filter theory
a theory of speech acoustics that analyzes the vocal tract as a series of band-pass filters.
A basic scientific framework for understanding the sounds that are coming out of the vocal tract.
Source – origin (we’ll start with glottis)
Filter(s) – shape the noise: high pass / low pass / band pass
High-pass vs. Low pass filter
High pass -> frequencies higher than x can pass
e.g., 300 Hz High Pass Filter à frequencies higher than 300 Hz allowed through
Low pass is the opposite
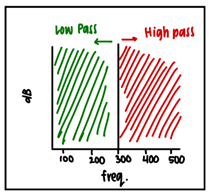
Band-pass filter
lets frequencies within a range through
Whan the high and low cut-off frequencies of a bandpass filter are equal, we can talk about the center frequency of a filter
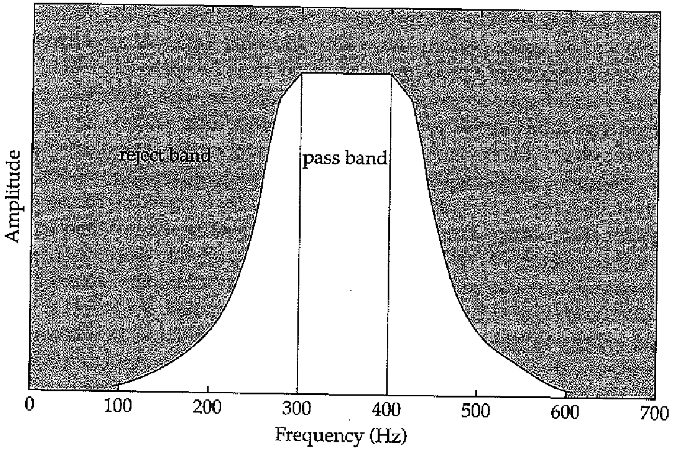
Explain the concepts of skirts
You get this shape b/c nothing is perfect or absolute – some things beyond the filter will squeeze through
Center Frequency
When the high and low cut-off frequencies of a bandpass filter are equal, we can talk about the center frequency of a filter.
This is how we model the vocal tract
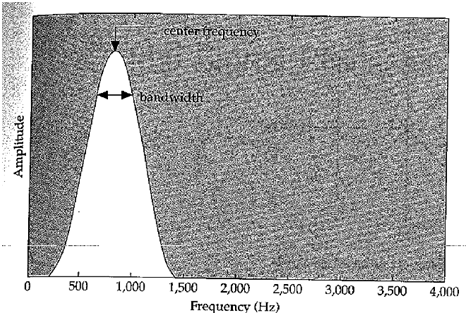
Bandwidth
The range around the Center Frequency: 50% higher + 50% lower
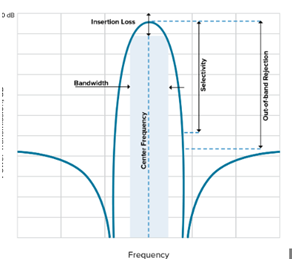
What happens to the bandwidth when you lower the energy?
Lowering the energy à higher spread of bandwidth
Harmonics
Harmonics are properties of the source (which creates the pressure wave)
Whole number multiples of F0
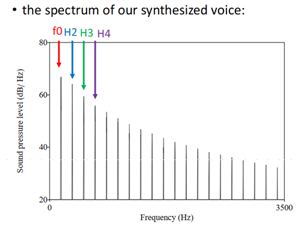
Glottal Source
The glottal source provides a complex (quasi-)periodic signal
Pulsating air with all these harmonics
The glottal source thus produces the fundamental frequency and an
infinite number of harmonics.
Resonance
• All objects oscillate at greater amplitude in response to certain
frequencies. This is the natural resonance of that object.
• In speech, we are talking about the column of air in the vocal tract.
• The natural resonance is based on the size of that vocal tract.
• We model this as a tube.
Natural resonance of speech
Natural resonance of speech is based on size and shape of vocal tract.
Speech can be imagined as a column of air in the Vocal Tract
How do we estimate the resonance frequencies of a tube?
we estimate it based on the tube’s length

Ruben’s Tube
A Ruben’s tube is a long tube filled with gas and perforated with small holes along the top, with a speaker attached to one end.
When sound waves travel through the tube, they create pressure variations that cause the flames emerging from the holes to rise and fall in a pattern corresponding to the standing wave inside the tube.
These flame patterns make the normally invisible sound pressure distribution visually observable.

How is Ruben's Tube similar to the vocal tract?
Ruben’s tube is similar to the vocal tract because both act as resonant tubes in which standing waves form at certain frequencies, shaping the pattern of pressure variations inside.
In the vocal tract, these pressure patterns correspond to formants, while in Ruben’s tube they appear as flame height patterns that visually reveal the same underlying resonant behavior.
Node
Pressure maximum and minimum velocity
Antinode
atmospheric pressure, maximum velocity

How do we model the vocal tract
we model it as a series of bandpass filters
What is the lowest natural frequency of a tube
it is one that has a wavelength 4 times the length of the tube
What are resonant frequencies
The physical properties of the filter (tube); these are the frequencies that the tube wants to amplify

What are formants
formants are amplified frequency bands with increased energy (naturally high amplitude) in the output spectrum. These usually correspond with the resonant frequencies of the vocal tract, but they are technically different.
This is what comes out of the output spectrum one we combine the source + filter
The harmonics under the RFs get amplified
The fundamental frequency is redundantly present in the speech spectrum. How?
Resonance Frequencies vs Formants
Resonance frequencies refer to the specific frequencies that a filter, such as the vocal tract, naturally amplifies, while formants are the actual bands of amplified frequencies observed in the speech output.
Are R1 and H1 related to each other?
NO
H1 is a harmonic that comes from the noise source.
R1 is a property of the filter
Half Wavelength Resonator
a tube or system that resonates most strongly when its length equals one-half of the wavelength of the sound frequency inside it
A tube closed at both ends is called a half-wavelength resonator because its boundary conditions require pressure antinodes at both ends, and the simplest standing wave that satisfies this pattern is one where the distance between the two antinodes equals half of a wavelength, making its fundamental resonance correspond to λ/2.
¼ Wavelength Resonator
The lowest natural frequency of the tube is one that has a wavelength 4x the length of the tube