Multistore Model of Memory
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
what is memory?
an active information processing system that receives, encodes, stores, organises and receives
who created this model of memory?
Richard Atkinson and Richard Shiffrin (1968)
what does memory allow us?
it allows us to learn. it mentally represents our experiences without a stimulus being present. this includes visual, thoughts, spoken and sensory memory
what are the key processes in memory? (process 1)
encoding - the process that conerts information into a usuable form that can be stored and represented in the brain
what are the key processes in memory? (process 2)
storage - the retention of information in the memory system overtime for retrieval
what are the key processes in memory? (process 3)
consolidation - this is the process of strengthening newly formed memories traces transfered to the LTM
what are the key processes in memory? (process 4)
retrieval - this is how we can locate info stored in memory and bringing it into conciousness to complete cognitive tasks
what are the three stores of memory in multistore model?
the multistore model describes how memory is structured or built and the three stores are sensory memory, short term memory and long term memory
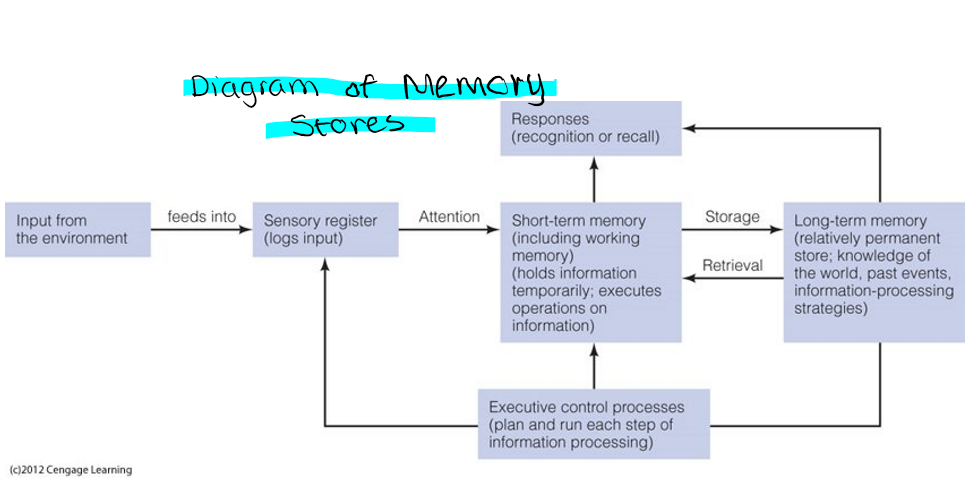
draw a diagram of the flow of the multistore model of memory and a small description
this flows through in a linear fashion, and is likened to an info processing model - memory is like a computer = imput-process-output.
our 5 senses detect the info, entering the sensory memory. if this info is attended to the info enters the STM and if this is rehearsed it enters the LTM for storage and retrieval
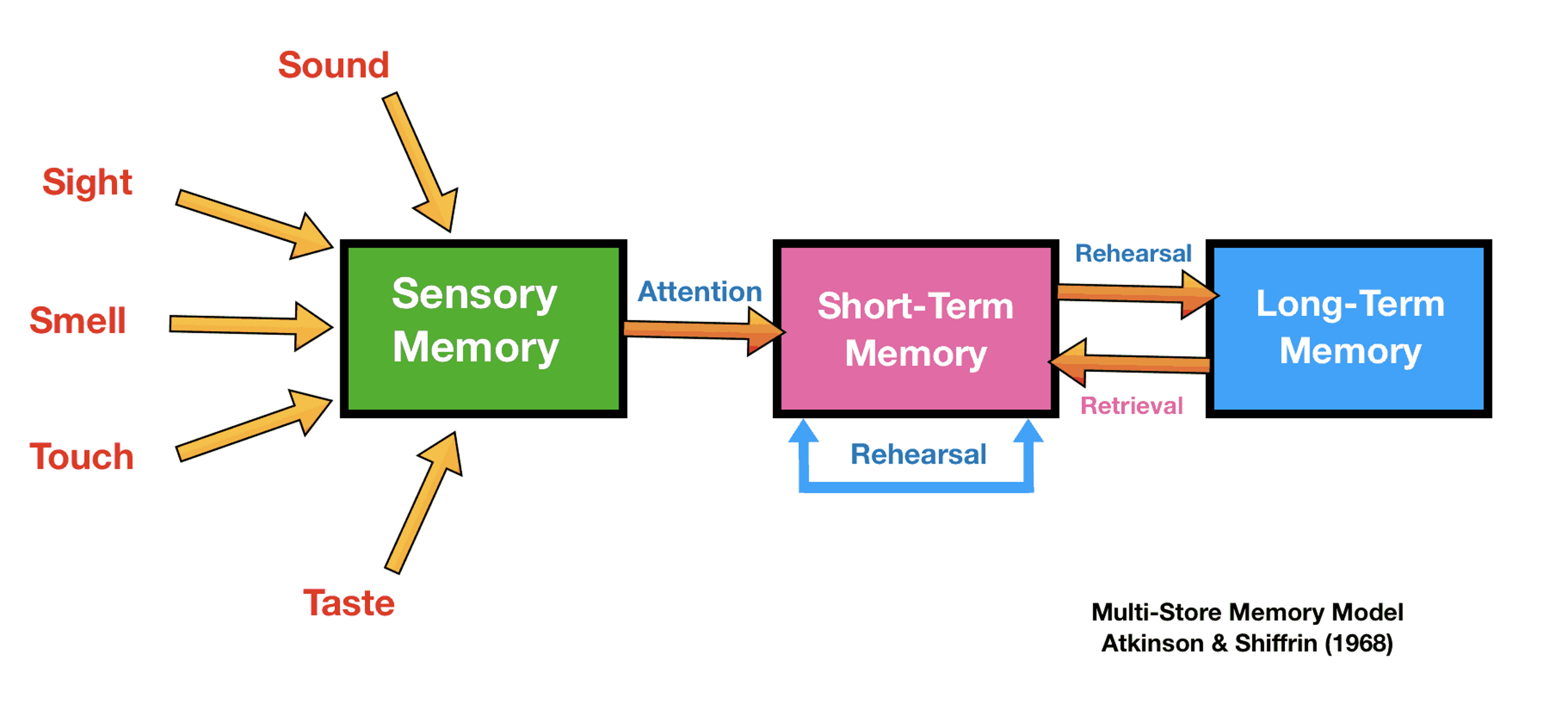
what are three differences in memory store?
capacity - how much info can be stored
duration - how long it can be stored for
function - what is done with stored info
describe sensory memory
duration - ¼ to ½ a second
capacity - all sensory experience
function - sensory info is encoded (conversion of sensory info to usable code so it can be understood by the brain. can be visual, acoustically or sematically/meaning)
steps - receives info from sensory organs and requires attention to continue. it can be either be sensory memory of iconic(visual) or echoic(auditory) input
memory is lost due to decay (just fades away)
decribe short term memory
duration - it lasts for 0-30 seconds
capacity - 7 ± 2 items
function - it rehearses info so it can be consolidated and transferred into the LTM
encoding is mainly auditory (lasts longer than iconic)
it can be lost due to new info coming along (displacement) or fades away (decay)
describe long term memory
duration - unlimited
capacity - unlimited
function - info that has been consolidated is stored so it can be retrieved at a later date when needed
encoding - sematic
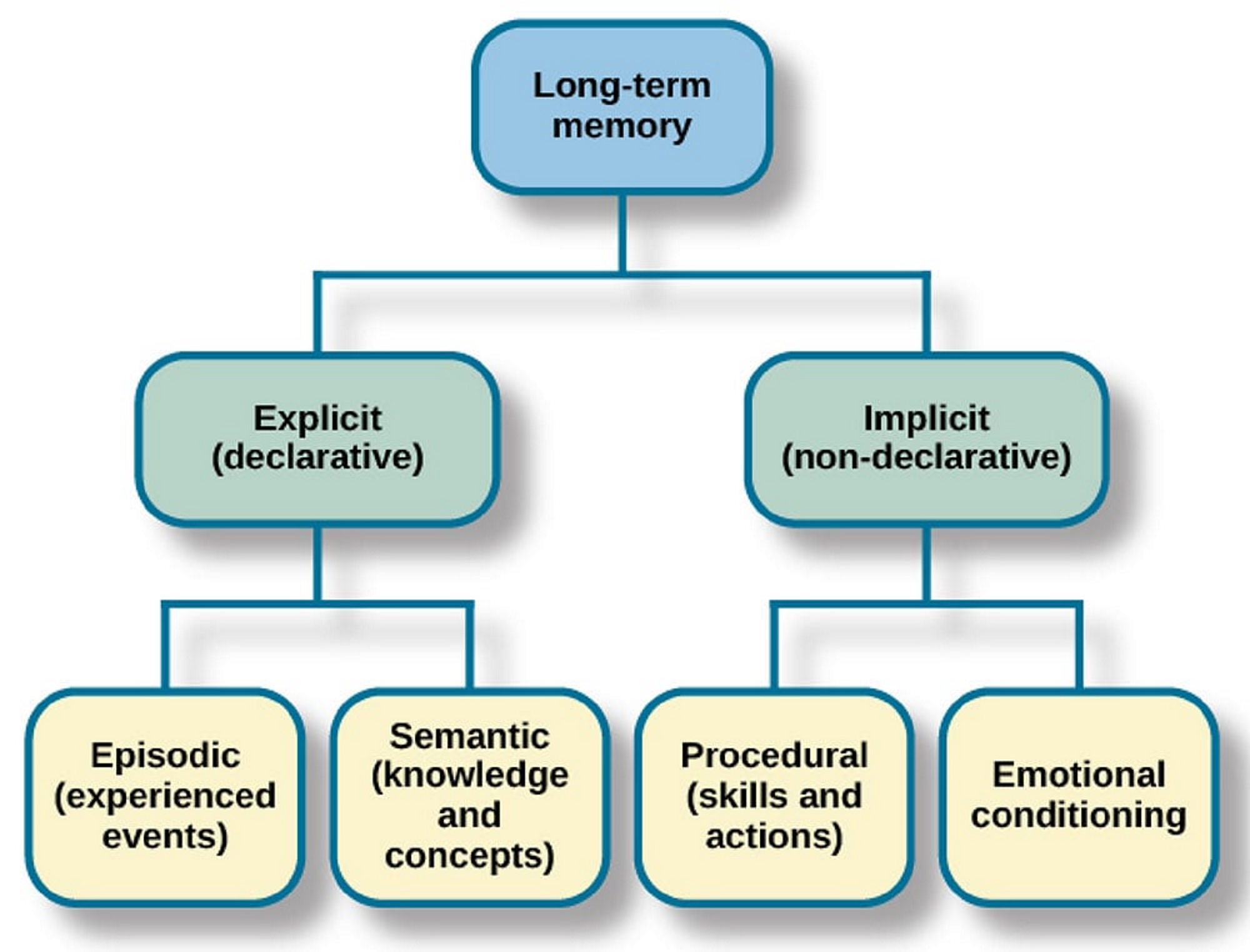
what are the two types of LTM?
procedural (non declarative/implicit) - refers to the change in behaviour or performance that results of prior experience that is remembered unconciously. it is the memory of “how to” perform tasks
declaritive (explicit) - long term storage of facts and events which needs concious effoort
what are the two forms of declaritive memory?
episodic - associated with episodes or events that have been experienced
sematic - associated with general facts of the world
draw a diagram of the LTM memory model
draw a diagram of the memory stores in Atkinson and Shiffrins (1968) multistore model of memory