APES: Biodiversity + Conservation
1/71
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
weather
local area’s short term temperature, precipitation, humidity, + other physical conditions measured over hours or days
3 Main Factors Affecting Heat and Moisture in Air Circulation
Properties of air, water, and land
Uneven heating of the earth’s surface
Rotation of the earth on its axis
Coriolis Effect
Perceived deflection of wind movement caused by Earth’s rotation
Directions of the Coriolis Effect
North=right/clockwise
South=left/counter-clockwise
Prevailing winds
Global winds that blow predominantly from certain directions due to the Coriolis Effect and uneven heating of the Earth's surface
Fairly constant
Thermocline
Boundary between waters of different temperatures
results from different densities (caused by temp.)
El Nino/ENSO
trade winds weaken/reverse direction
warm water towards South American coast
less upwelling
decreased fish populations
more ran in Western Hemisphere, drought in Easter HemisphereEl Niño is an abnormal climate pattern characterized by the warming of surface waters in the Pacific Ocean, leading to significant weather changes and disruptions in marine ecosystems.
La Nina
increased upwelling of South American coast
cools coastal surface water
more Atlantic hurricanes
colder winters in NE US, warmer winters in SE US
Rain shadow effect
one side of a mountain receives significantly more rainfall than the other
causes a dry area on the leeward side due to descending dry air having lost moisture in order to pass over top of mountain
Greenhouse effect
warming of Earth's surface due to the trapping of heat by greenhouse gases in the atmosphere
allows solar radiation in but prevents some of the outgoing heat from escaping
4 major natural gases causing greenhouse effect
water vapor
methane
carbon dioxide
nitrous oxide
Biomes
large terrestrial regions characterized by similar climate, soil, plants, and animals regardless of location
Types of Forest Biomes
Tropical, temperate, taiga
Major types of grasslands
tropical grasslands (savannas)
praries
temperate grasslands
steppe
Tropical rainforest location and characteristics
along the equator
from 30N to 30S
year round warm temp, high humidity, lots of rain
broadleaf evergreens
high PP and biodiversity
poor soil quality
Temperate deciduous forest location and characteristics
30N-60N and 30S-60S
moderate temperatures with seasons
broadleaf deciduous trees
nutrient rich soilT
Taigas/boreal forest location and characteristics
northern regions just south of Arctic tundra
long, dry, cold winters
conifers
waxy, needle shaped leaves on trees
low plant diversity
acidic and nutrient poor soils
Ecological roles of mountains
habitat for endemic species
regulate earth’s climate
melting snowpack provides surface water
Tropical grassland/savanna location + characteristics
Easter Africa, parts of South America and Australia
warm temperatures, alternating warm and dry seasons
large grazing herbivores - gazelles, zebras
plants have deep roots for groundwater supplies
Temperate grassland location + characteristics
Mid/Western US and Canada, parts of South American and Russia
rainfall determines tall/shortgrass prarie
cold winters, hot/dry summers
high productive cropland
fires in summer/fall that eliminate competing species
Arctic tundra
Northern regions of Canada, Asia, Europe
dominated by lichens and moss
treeless plains
covered with snow and ice
permafrost
very dry, similar to deserts
trop
Tropical desert locations and characteristics
surface areas have little vegetation
rocks and stand
high daytime temperatures
Temperate desert location and characteristics
Southwest US
more precipitation that tropical
drought resistant shrubs, cacti, succulents
high daytime + low night time temperatures
Cold desert locations and characteristics
Great Basin, Gobi Desert
sparse vegetation
cold winters
Temperature
measure of movement of particles
Dissolved oxygen
amount of oxygen dissolved in water
cooler and faster moving waters have higher DO
N
Nutrient load
measure of nutrients in water
phosphate and nitrates
S
Turbidity
measure of cloudiness of water caused by suspended sediments
Salinity
concentration of dissolved salts
Ecological benefits of oceans
habitat and nursery areas
moderate climate
absorb CO2
reduce storm impact (estuaries, mangroves)
E
Economic benefits of oceans
food resources
oil, natural gas, mineral resources
transportation routes
areas for recreation
Plankton
drifters
bottom trophic levels
phytoplankton, sunfish
Zooplankton
drifting heterotrophs
protozoa, crustaceans, krill
Nekton
strong swimming organisms that live in the water column, such as fish and squid, capable of moving independently of water currents.
Benthos
bottom dwellers
crabs, lobsters, oysters
feed on detritus (marine snow)
Coastal zone
high tide mark to edge of continental shelf
warm, rich in nutrients
high net PP (lots of sunlight)
contains 90% of all marine species
Estuaries
freshwater rivers meet salty ocean
bays, inlets, sounds, salt marshes, mangrove forests
high productive because of large nutrient inputs from rivers + lots of sunlight
Intertidal
influenced by tides
different types: sloping, rocky
organisms have adaptations for wave activity and exposure during low tides
Coral Reefs
very diverse ecosystems in warm waters
very sensitive
need clear water
Euphotic zone
top ocean layer
lots of phytoplankton
supports large predatory fish
Bathyal zone
mid level ocean layer
little sunlight, no photosynthetic organisms - aphotic
Abyssal zone
no light - aphotic
very nutrient rich (marine snow)
Lentic zones
still freshwater
lakes, inland wetlands, ponds
Lotic zones
moving freshwater
rivers, streams
Littoral zone
shadow zone closest to shore
lots of sunlight + nutrients
emergent and submergent plants
Limnetic zone
upper layer of lake away from shore
lots of phytoplankton
make up base of food chain
supply most DO for aerobic consumers
Profundal zone
midlevel zone
little sunligh
low DO and nutrients
Benthic zone
bottom zone
mostly decomposers
Oligotrophic
lakes with low nutrient levels and limited primary productivity
Mesotrophic
lakes with high concentrations of nutrients and high levels of net primary productivity
Ecological services of wetlands
recharge groundwater system
habitat
nursery for aquatic species, spawning ground for fish
filtering toxins + excess nutrients
reducing flood and erosion
River zones
Source zone, transition zone, floodplains
Habitat fragmentation
large habitats are divided into smaller, isolated patches, affecting species survival and ecosystem functioning
increases edge habitat
Laws to protect endangered species
Endangered Species Act of 1973
identify and protect species at risk for extinction
Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES)
bans selling, hunting, or capturing threatened or endangered species
Old growth forest
not affected by human activities or natural disasters in 200+ years
Secondary growth forests
form from secondary succession after land was cleared (logging, volcanoes, fires, etc.)
Clear cutting
remove all trees in one go
Selective cutting
specific trees onlys
Strip cutting
take out a strip, allow to regrow, take out strip next to previous one
Silviculture
regenerating a forest after a disturbance
can speed up process
Rangelands
unfenced land used for grazing livestock and wildlife, often managed for sustainable use and biodiversity.
Pastures
fenced grasslands for livestock grazing, often improved through planting forage species.
In which of these biomes does fire serve the role of building deep topsoils and minimizing the establishment of trees?
A) Tundra
B) Tropical rain forests
C) Tall grass praries
D) Taiga
E) Saltmarshes
C) Tall grass prairies.
Characteristics that would lead to a non-native organism’s becoming invasive in a new environment would include which of the following characteristics
I. High reproductive rate
II. Short lived
III, Generalists
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and III only
E) I, II, and III
D: Invasive species are often characterized by a high reproductive rate and generalist habits, allowing them to thrive in various environments and outcompete native species.
Which of the following non-point pollution types is most likely to cause cultural eutrophication in lake ecosystems?
A) Oil from parking lots
B) Fertilizer from agricultural fields, golf courses, and lawns
C) Heavy metals from mining practices
D) The natural flow of topsoil into the water in wilderness areas
E) Pesticides from agricultural fields, golf courses, and lawns
B) Fertilizer from agricultural fields, golf courses, and lawns
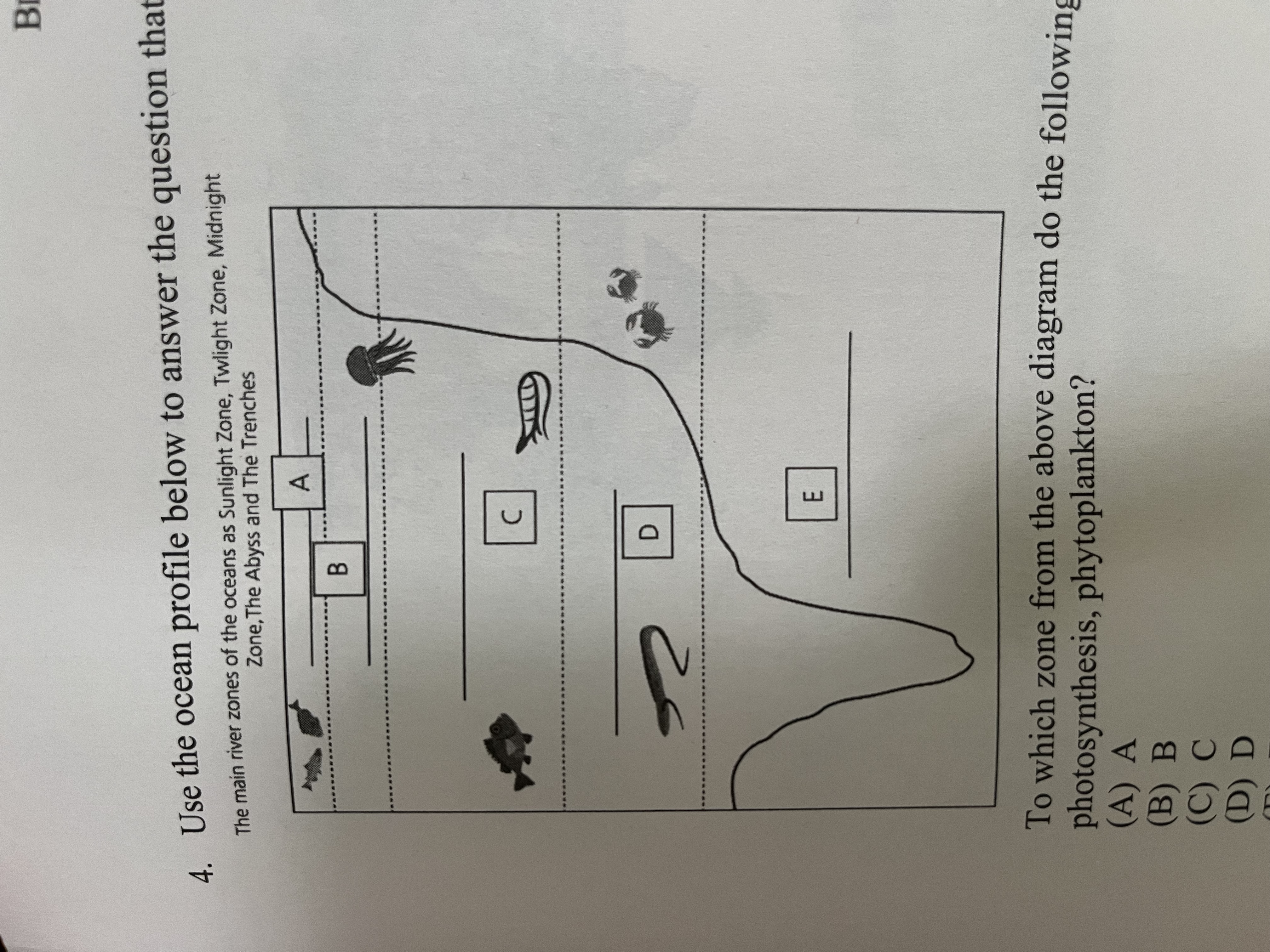
Use the ocean profile below to answer the question that follows:
To which zone from the above diagram do the following terms apply: Photosynthesis, phytoplankton?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E)E
A, where sunlight penetrates and supports photosynthesis, primarily involving phytoplankton
All of the following are associated with an El Nino event EXCEPT:
A) Decreased upwelling events
B) suppressed thermocline in the Pacific Ocean
C) increased Atlantic coast hurricanes
D) torrential rain and flooding in Peru
E) Drought in Indonesia and Australia
C) increased Atlantic Ocean hurricanes

Which terrestrial biome would be most likely to be found in the shaded region on the map below?
A) Chaparral
B) Temperate rainforest
D) Deciduous forest
D) Taiga
E) Cold desert
D) Taiga, characterized by coniferous forests and cold climate.
The land area that delivers recharge to smaller tributary streams that flow into larger rivers is called the:
A) Watershed
B) Source zone
C) Flood plain
D) Delta
E) Estuary
A) Watershed, which is the land area that drains rainwater and snowmelt into a common waterway, such as a stream or river.
Oceanic currents act as a conveyor belt system, creating a connected loop of deep and shallow ocean currents that transfers warm and cold water between the tropics and the poles. The strongest influence on this system of ocean currents is due to
A) upwelling currents that bring cold nutrient-rich water from the bottom to the top
B) the rotation of the earth on its axis
C) Differences in water density due to temperature and salinity concentration
D) atmospheric convection causing large inputs of freshwater into the ocean by precipitation
E) location of continents that help determine direction and flow of ocean currents
C) Differences in water density due to temperature and salinity concentration
The most biologically diverse areas of the ocean include coral reeds and estuaries. All of the following characteristics are reasons why these ecosystems can support such a high level of diversity EXCEPT
A) they are areas of high primary productivity
B) both ecosystems have abundant nutrient flow that supports phytoplankton populations
C) Coral reeds and estuaries receive an abundant amount of sunlight
D) Both ecosystems provide plenty of habitat space for organisms
E) These ecosystems do not have commercially important species, therefor human impact on biodiversity is limited
E) These ecosystems do not have commercially important species, therefore human impact on biodiversity is limited, is incorrect as human activities often significantly affect these ecosystems
Use the diagram below to sequence the stages the lake is going through
A) Autotrophic, mesotrophic, eutrophic
B) Autotrophic, oligotrophic, mesotrophic
C) Eutrophic, oligotrophic, mesotrophic
D) Oligotrophic, mesotrophic, eutrophic
E) Mesotrophic, eutrophic, autotrophic
D) Oligotrophic, mesotrophic, eutrophic describes the stages a lake undergoes from low nutrient levels to high nutrient levels, impacting its productivity and ecosystem health