Honors Biology Unit 2
1/47
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Covalent bonds
atoms sharing a set of electrons in their outer shell
tugging marker example
2 or more atoms held together by a covalent bond form a molecule
molecule
a group of atoms
polar covalent bond
electrons are shared unequally between the two atoms
polar molecule
one negative side (near the oxygen) and one positive side (near the hydrogen) to the overall molecule bc the negatively charged electrons are held more tightly by the oxygen than the hydrogen atoms
molecule with an unequal distribution of charge, resulting in the molecule having one positive and one negative side
hydrophilic
love water
non-polar molecule
electrons are shared equally and they don’t have any poles
hydrophobic
hate water
hydrogen bond
attraction between two adjacent water molecules because of the slightly positive and negative attraction
weak
enable water to have unique properties
makes water attracted to itself and other polar molecules
without it water would boil at -80 c and freeze at -100 c
reactant
a substance that takes part in and undergoes change during a reaction.
cohesion
water molecules are attracted to themselves
adhesion
water molecules are attracted to other polar substances
surface tension
a liquid with a high resistance to an object
evaporative cooling
uses evaporation to help cool the air
solute
substance being dissolved in the liquid
solvent
substance doing the dissolving (usually a liquid)
solution
when one substance is dissolved in another
pH
the concentrations of H+ ions in a certain solution
pH scale
each step on the pH scale is a factor of 10
1-10
1 = very acidic
5-6 = slightly acidic
7 = neutral
8-10 = slightly alkaline
12-14 = very alkaline
acid
a substance that forms higher concentrations of H+ ions in a solution than water does (an a lower concentration of OH-)
taste sour
neutralize bases
corrode metal
pH less than 7
base
a substance that forms lower concentrations of H+ ions in a solution than water does (and higher concentrations of OH-)
slippery
neutralize acids
alkaline
higher than 7 pH
neutral
equal amount of H+ and OH- ions
matter
anything that takes up space and has mass
chemical element
cannot be broken down into other substances
single bond
sharing one set (1 marker)
double bond
sharing two sets (2 markers)
carbohydrates
CHO! - carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
sucrose
structure: monomer: monosaccharides, polymer: polysaccharides
functions: structure (cell walls, exoskeletons), fast energy source
the 6 most common elements in living things
SPONCH!
S - sulfur
P - phosphorus
O - oxygen
N - nitrogen
C - carbon
H - hydrogen
Proteins
CHON - carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen
hair, sucrase
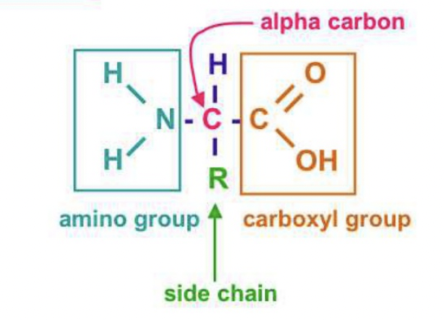
structure: monomer: amino acids
function: protein channels in cell membranes, enzymes like sucrase, structural like hair, antibodies, hormones
Monomer: amino acid
Polymer: polypeptides
Lipids
CHO - carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
phospholipid: special lipid that creates cell membranes, one bent, outside hydrophobic
structure: varies based on function, hydrophobic (hate water)
functions: create cell membranes, long term energy storage, hormones, steroids, insulation
1 glycerol, 1-3 fatty acid chains
long hydrocarbon chains are the signature of lipids
cholesterol, steroid
Nucleic Acids
DNA & RNA
CHONP - carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus
structure: monomer: nucleotide, nucleic acids
function: codes for proteins
The Unique Properties Of Water
capillary action (creep up thin tubes)
ex: food coloring example - slide 12
high surface tension
ex: water striders can walk on water
it has a high heat of vaporization
takes more heat energy to cause water to evaporate
water resists temperature change
beach is hot but water is cold bc water absorbs the heat energy before it changes temperature
water expands when it freezes
means that ice is less dense than liquid water, so float
Water is a
universal solvent!
water’s polarity allows it to dissolve many types of solutes
Dissociation of water molecules
water molecule (2 hydrogen, 1 oxygen) split to form negative hydroxl ion (alkaline) and positive hydrogen ion (acidic)
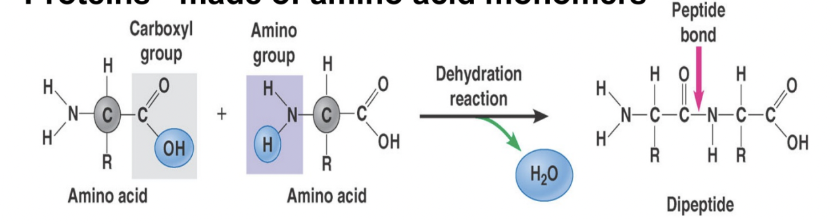
dehydration synthesis
clicks monomers together to form longer polymers
happens by removing an O and H atom off one monomer, and an H atom off another, and clicking those together to form water, which floats away
two monomers now have space to bond
hydrolysis
“water breaking”
breaks monomers off a polymer chain
happens by adding a water molecule to a bond. the O and H from the water bond to the side of one monomer, and the other H from the water bonds to the other monomer. this breaks them apart
the polymer is now shorter
glucose
6 carbon
12 hydrogen
6 oxygen
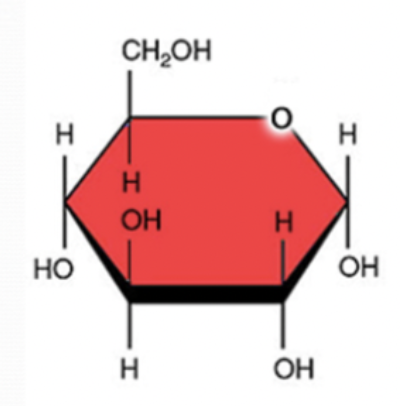
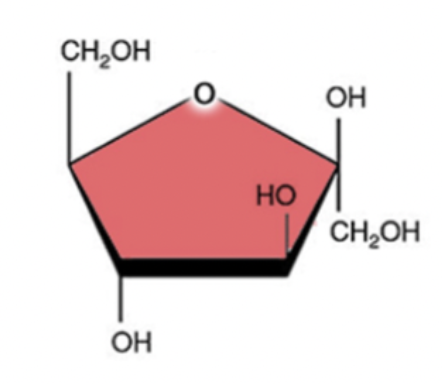
fructose
5 carbon
10 oxygen
6 oxygen
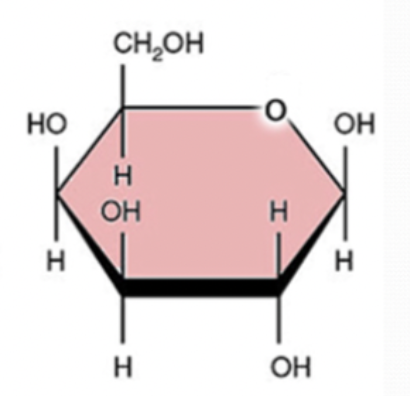
galactose
6 carbon
12 hydrogen
6 oxygen
lactose
glucose + galactose
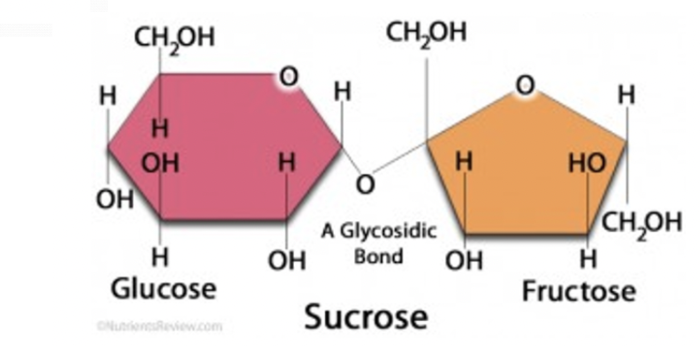
sucrose
glucose + fructose
Polysaccharides
Starch
this carb/polysaccharide is found in plants. it is used by plants and animals for energy
Glycogen
this carb/polysacc is found in animal muscles. it is how animals store sugars
Cellulose
this carb/polysacc is found in plants. it is used by plants for structure (cell walls, tree trunks). animals cannot digest it, it is fiber in our diet
maltose
glucose + glucose
Phospholipids
a special lipid that creates cell membranes
2 fatty acid chains, one is bent bc double bonded carbon
with a polar head that is hydrophobic
makes up the cell membrane
Amino Acids
polysaccharide equation
reactant
the substance present at the start of an experiment
product
substance produced in a chemical reaction