FA Davis Focused Questions With 100% correct answers already graded A+
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
The nurse is providing teaching to a client with cirrhosis. What topics should the nurse include in the teaching? Select all that apply.
A)Consuming adequate calories to minimize weight loss
B) Reducing calories to encourage weight loss
C) Monitoring use of medications that metabolize in the liver
D) Minimizing risk of bleeding with safe, careful self-care practices
E) Eliminating alcohol intake if alcohol is the cause of cirrhosis
A
C
D
E
The nurse is monitoring a client who is being treated for hepatic encephalopathy. Which diagnostic finding would indicate improvement of the client's condition?
A) Return of white blood cell count to within normal range
B) Chemistry profile within normal range
C) Decreased ammonia levels
D) Hemoconcentration
B
Outpatient treatment of fluid retention in clients with cirrhosis may be preferred for which reasons? Select all that apply.
A) Ability to better monitor dietary intake
B) Cirrhosis is not a chronic disease
C) More cost-effective
D) Decreases preventable rehospitalizations
E) Increases expectation of no exacerbations to manage
C
D
The nurse is caring for a client with cirrhosis. Which clinical manifestations should the nurse expect to observe? Select all that apply.
A) Altered mental status
B) Metabolic alkalosis
C) Altered respiratory status
D) Jaundice
E) Petechiae
A
C
D
E
Which mineral(s) are associated with congenital abnormalities that lead to the development of cirrhosis?
A) Iron and copper deficiency associated with iron deficiency anemia and Wilson's disease
B) Excess copper associated with Wilson's disease and excess iron associated with hemochromatosis
C) Increased iron associated with myelodysplasia
D) Iron deficiency associated with fetal alcohol syndrome
B
John has been diagnosed with cirrhosis of the liver following this infectious disease process. No immunization is available to prevent this chronic illness.
A) Hepatitis A
B) Hepatitis B
C) Hepatitis C
D) Hepatitis D
C
Paul is being treated for the second most common type of cirrhosis of the liver following a long history of alcoholism and accompanying malnutrition.
A) Wilson's Disease
B) Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH)
C) Laennec's Cirrhosis
D) Hepatitis C
C
Tanya has received a clinical diagnosis of a type of genetic cirrhosis. Client history reveals a metabolic disease affecting copper metabolism. Drag and drop the correct etiology.
A) Hepatitis C
B) Laënnec's cirrhosis
C) Biliary cirrhosis
D) Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)
E) Wilson's disease
F) Hepatitis A
G) Hepatitis B
H) Hepatitis G
E
Samuel has cirrhosis from cholangitis. He tells the nurse that the severe pruritus is very irritating.
A) Hepatitis C
B) Laënnec's cirrhosis
C) Biliary cirrhosis
D) Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)
E) Wilson's disease
F) Hepatitis A
G) Hepatitis B
H) Hepatitis G
C
Edna has a BMI of 40 and other comorbidities related to cardiac and respiratory dysfunction. The fat around her liver has led to her cirrhosis.
A) Hepatitis C
B) Laënnec's cirrhosis
C) Biliary cirrhosis
D) Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)
E) Wilson's disease
F) Hepatitis A
G) Hepatitis B
H) Hepatitis G
D
Brian has developed cirrhosis secondary to a fecal-oral virus he obtained when drinking contaminated water while camping years ago.
A) Hepatitis C
B) Laënnec's cirrhosis
C) Biliary cirrhosis
D) Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)
E) Wilson's disease
F) Hepatitis A
G) Hepatitis B
H) Hepatitis G
F
Joanne developed cirrhosis after a contaminated needle stick while working as a nurse. The virus she obtained could have been prevented if she had received the series of three immunizations and developed immunity.
A) Hepatitis C
B) Laënnec's cirrhosis
C) Biliary cirrhosis
D) Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)
E) Wilson's disease
F) Hepatitis A
G) Hepatitis B
H) Hepatitis G
G
Mark has cirrhosis from a little known and uncommon bloodborne virus. He became sick after multiple blood transfusions for his hemophilia.
A) Hepatitis C
B) Laënnec's cirrhosis
C) Biliary cirrhosis
D) Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)
E) Wilson's disease
F) Hepatitis A
G) Hepatitis B
H) Hepatitis G
H
In cirrhosis, alterations in blood and lymph flow can lead to what end organ effect of the liver?
A) Increased perfusion as a result of ascites
B) Increased pressure leading to increased vascularity
C) Cellular changes leading to malignancy
D) Necrosis
D
The nurse is caring for a client with cirrhosis. What should the nurse monitor as signs of worsening of the disease? Select all that apply.
A) Petechiae
B) Increased appetite
C) Laryngitis
D) Pedal edema
E) Jaundice
A
D
E
Which behavioral finding would the nurse anticipate finding in a client with cirrhosis who has hepatic encephalopathy?
A) Intact short-term memory
B) Intact long-term memory
C) Personality changes
D) Clear speech articulation
C
Which finding is typically associated with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis cirrhosis?
A) Clinical obesity
B) Alcoholism
C) Evidence of metabolic disease
D) History of hepatitis
A
Alcoholism is associated with which type of cirrhosis?
A) Laënnec's
B) Congenital
C) Metabolic
D) Biliary
A
Which type of liver cirrhosis is caused by the intake of alcohol?
A) Micronodular cirrhosis
B) Laënnec's cirrhosis
C) Wilson's disease cirrhosis
D) Hemochromatosis cirrhosis
B
The nurse is teaching a group of pre-school teachers about hepatitis A. Which is true? Select all that apply.
A) It can cause chronic infection.
B) It can last up to 8 weeks.
C) It can be spread only by blood and body fluids.
D) It can cause mild symptoms, or sometimes the patient may remain asymptomatic.
E) It can cause an elevation in the levels of antihepatitis A immunoglobulin M.
B
D
E
Which clinical manifestation is most likely caused by the accumulation of ammonia and toxins in the blood?
A) Ascites
B) Portal hypertension and varices
C) Hepatic encephalopathy syndrome
D) Hepatorenal syndrome
C
Which clinical manifestation detected in the patient with cirrhosis is directly associated with accumulation of ammonia?
A) Pruritus
B) Altered mental status
C) Altered blood pressure and edema
D) Petechiae and bleeding
B
Which point regarding hepatitis B infection indicates a need for further instruction?
A) "It has an incubation period of about 45 to 60 days."
B) "Its route of transmission is the fecal-oral."
C) "It can be prevented by vaccination."
D) "It results in chronic infection."
B
Which abnormal laboratory value associated with liver failure is correct? Select all that apply.
A) Albumin level is decreased.
B) Total bilirubin level is elevated.
C) Platelets are increased.
D) Partial thromboplastin time is prolonged.
E) Ammonia level is decreased.
A
B
D
The nurse is caring for a patient with known hepatitis B. A second type of hepatitis is discovered. What type of hepatitis would it be?
A) Hepatitis A
B) Hepatitis C
C) Hepatitis D
D) Hepatitis E
C
The nurse is educating a high-risk community group about hepatitis. Which statement regarding nonviral forms of hepatitis indicates a need for further instruction?
A) "They may result in jaundice."
B) "They can be treated by pegylated interferon injections."
C) "They may result in hepatomegaly."
D) "They can be caused by ingestion, inhalation, or injection of toxins or drugs."
B
Which statement by a nursing student regarding liver cancer indicates a need for further instruction?
A) "Hemochromatosis is a risk factor for liver cancer."
B) "Secondary liver cancer originates from the liver."
C) "Radiofrequency ablation is a mode of treatment for liver cancer."
D) "Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization is a mode of treatment for liver cancer."
B
Which actions are most appropriate when caring for a patient with liver cancer? Select all that apply.
A) Administer nerve blocks locally and directly into the nerves of the abdomen.
B) Include plenty of fluids and protein-rich foods in the diet.
C) Administer antibiotics and antipyretics to the patient .
D) Keep the lower extremities at a lower level.
E) Administer nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications to the patient.
A
C
E
A nursing student is listing the types of hepatitis that are transmitted through infected blood and body fluids. Which example listed by the nursing student indicates a need for further instruction?
A) Hepatitis C
B) Hepatitis D
C) Hepatitis E
D) Hepatitis G
C
Which clinical manifestation is found in stage I hepatic encephalopathy? Select all that apply.
A) Slurred speech
B) No response to painful stimulus
C) Reversal of day and night sleep patterns
D) Impaired writing
E) Mood swing
A
C
D
Which type of hepatitis is considered a chronic illness?
A) Hepatitis C
B) Hepatitis D
C) Hepatitis E
D) Hepatitis G
A
The nurse is caring for this patient with acute hepatis. The skin coloring on the left is from a week ago and the coloring on the right is from today. Which additional assessment finding would be consistent with this assessment?
A) Yellow halos in field of vision
B) Hunger
C) Clay colored stools
D) Decrease in serum bilirubin levels
C
Which type of hepatitis can be prevented by vaccine?
A) Hepatitis B
B) Hepatitis C
C) Hepatitis E
D) Hepatitis G
A
The patient a nurse is caring for is scheduled for a test in which a diagnostic tool uses a contrast media to inject into the bile duct of the liver of a patient . What is this test?
A) Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD)
B) Liver biopsy
C) Endoscopic retrograde
D) cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
E) Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography
E
A nurse is discussing the precautionary measures that need to be taken to prevent further complications with a patient who has hepatitis. Which statement made by the patient indicates a need for further discussion?
A) "I should continue taking acetaminophen as I have in the past."
B) "I should take supplements of vitamin A, D, E, and K."
C) "I should take small, frequent meals that are low in fat."
D) "I should maintain a proper balance of rest and exercise."
A
Which clinical manifestation is a nurse most likely to observe in a patient with liver trauma?
A) High hemoglobin
B) Decreased respiratory rate
C) Elevated liver enzymes
D) High blood pressure
C
Which action performed by a nurse while taking care of a patient with cirrhosis puts the patient at increased risk of complication?
A) Providing electrolyte replacements such as potassium
B) Administering diuretics
C) Increasing amounts of protein in the diet
D) Restricting sodium and fluid intake as ordered
C
A nurse is assessing a patient who has experienced cirrhosis and subsequent decreased immune status. Which is the nurse most likely to document in the patient's record?
A) Risk for injury and bleeding
B) Altered nutrition less than body requirements
C) Fluid volume deficit
D) Impaired skin integrity
D
Which patient is demonstrating signs of stage 2 hepatic encephalopathy?
Patient A: Slurred speech, impaired writing, and lethargy
A) Patient A:Slurred speech, impaired writing, and lethargy
B) Patient B: Increased drowsiness, disorientation, and mood swings
C) Patient C: Severe confusion, rigid extremities, and increased deep tendon reflexes
D) Patient D: Nonresponsive for painful stimuli
B
The nurse is teaching a patient with a liver disorder about nutritional intake. Which statement made by the patient indicates the need for further teaching?
A) "I should limit my daily fat intake."
B) "I should fulfill my daily calorie requirement."
C) "I should eat small and frequent meals."
D) "I should increase the protein content of my diet."
D
The nurse is assessing the laboratory findings of a patient with suspected liver failure. Which laboratory findings support the nurse's suspicion? Select all that apply.
A) Decreased albumin
B) Decreased ammonia
C) Prolonged prothrombin time
D) Decreased alkaline phosphatase
E) Prolonged partial thromboplastin time
A
C
E
A patient is hospitalized as the result of an injury in the abdominal area. The computed tomography scan reveals a penetrating trauma of the liver. For which complication should the nurse monitor after the patient's treatment?
A) Pneumonia
B) Tachycardia
C) Abdominal pain
D) Low blood pressure
A
Which condition can be treated with Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt [TIPS]?
A) Ascites
B) Portal hypertension
C) Hepatic encephalopathy
D) Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis
A
Which of the following blocks acid secretion in the last step of production in the stomach?
A) H2RAs
B) PPIs
B
Which of the following is used to treat H. pylori in addition to GERD?
A) H2RAs
B) PPIs
A
In which of the following does tolerance to medication is likely to occur?
A) H2RAs
B) PPIs
A
Which of the following provides quicker onset of action to provide relief?
A) H2RAs
B) PPIs
A
Which of the following has a longer duration of action?
A) H2RAs
B) PPIs
B
Which of the following decreases acid production of parietal cells?
A) H2RAs
B) PPIs
A
Which of the following include generic names such as cimetidine, famotidine, and ranitidine?
A) H2RAs
B) PPIs
A
Which of the following interfere with the absorption of ketoconazole, ampicillin, iron, and digoxin.
A) H2RAs
B) PPIs
B
Which of the following include generic names such as lansoprazole and omeprazole?
A) H2RAs
B) PPIs
B
Which client is most likely to be at risk for developing gastroesophageal reflux disease?
A) 38-year-old male who is a vegetarian
B) 25-year-old pregnant woman
C) 18-year-old female who likes to eat several small meals a day
D) 44-year-old male who has no reported comorbidities
B
Which foods should be avoided in a client who has already been diagnosed with gastroesophageal reflux disease? Select all that apply.
A) Chocolate
B) Beer
C) Caffeinated coffee
D) Peppermint gum
E) Broth or consommé
A
B
C
D
Which of these symptoms would the nurse expect to find in a client with gastroesophageal reflux disease? Select all that apply.
A) Atypical chest pain
B) Sleep issues
C) Adult-onset asthma
D) Elevated temperature
E)Laryngitis
A
B
C
E
In working with clients who have been diagnosed with gastroesophageal reflux disease, which statement is accurate related to the use of proton pump inhibitors as therapeutic treatment?
A) It is also useful in the treatment of H. pylori.
B) The client is encouraged to increase fluid intake while taking this therapy to prevent dehydration from occurring.
C) It leads to resolution of clinical condition after two months of therapy.
D) Tolerance is unlikely.
D
Which medication option would have a longer duration of action in treating the clinical condition of gastroesophageal reflux disease?
A) Proton pump inhibitors
B) Antacids
C) Corticosteroids
D) Opioid analgesics
A
Which medication can help to decrease the gag reflex if administered to a patient with stomatitis?
A) IV acyclovir
B) Viscous lidocaine
C) Nystatin
D) Histamine receptor agonists
B
A nurse is teaching a patient with stomatitis about the precautionary measures that can promote rapid healing. Which comments by the patient indicate a need for further teaching? Select all that apply.
A) "I should use a hard-bristled toothbrush to clean the mouth"
B) "I should apply water soluble lubricants for lips and mouth"
C) "I should remove dentures and other oral appliances if pain persists."
D) "I should limit intake of protein-rich foods in the diet"
A
C
D
Which clinical manifestations should a nurse look for in a patient with type II hiatal hernia? Select all that apply.
A) Feeling full after eating
B) Regurgitation
C) Chest pain like angina
D) Feeling of suffocation
E) Belching
A
C
D
Which action taken by the nurse may cause aspiration in a patient with oral cancer?
A) Providing elixir form of medications
B) Instructing the patient to refrain from talking when eating
C) Lowering the head of the bed
D) Assessing the patients ability to swallow
C
Which is true regarding leukoplakia?
A) It is a malignant lesion found commonly on the mandibular mucosa.
B) It occurs mostly in newborns
C) It is more prevalent in women than men
D) It looks like nonremovable, slightly raised, sharply rounded white plaques.
D
A nurse is reviewing the risk factors that may increase the risk for developing esophageal cancer. Which risk factor listed indicates a need for further training?
A) Nutritional deficiency
B) Barrett's esophagus
C) Weight Loss
D) GERD
C
Which is true regarding xerostomia? Select all that apply.
A) It may be also termed as wet mouth as it increases the flow of saliva in the mouth.
B) It occurs in patients receiving significant radiation exposure to the salivary glands during radiotherapy
C) It is a symptom of several diseases as well as a side effect of many different medications.
D) It decreases the risk of contracting candidiasis and developing stomatitis.
E) It may be caused by removal of the salivary glands, dehydration, and diabetes.
B
C
E
Which is true regarding H2 receptor antigen antagonists in treating gastroesophageal reflux disease? Select all that apply.
A) Some patients may develop a tolerance
B) They have a delayed onset of action and a longer duration of action
C) They Reduce acid production longer than antacids but are slower to take effect
D) They are more effective in suppressing gastric acid secretion than proton pump inhibitors
E) They decrease acid production of parietal cells in the stomach lining by blocking histamine 2 at one of the first steps of acid production
A
C
E
Which is true of the action of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) in treating gastroesophageal reflux disease?
A) They block gastric acid production
B) They increase gastric pH
C) They increase gastric emptying
D) They are short-acting medications that decrease gastric acid production
A
The nurse performs an assessment and sees this. What could cause this condition?
A) Excessive oral hygiene
B) Immune suppression
C) Allergic reaction
D) Excess milk intake
B
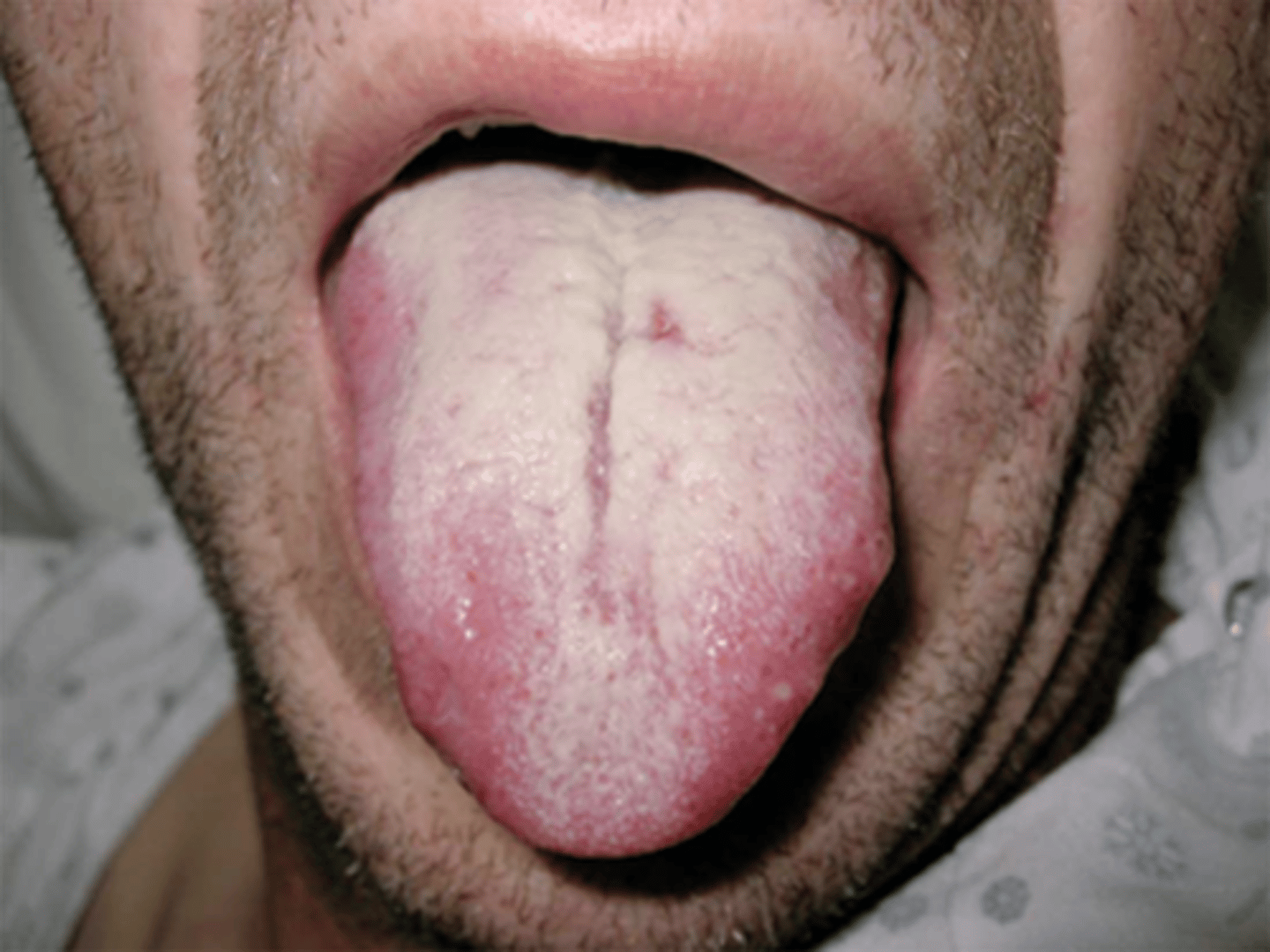
The nurse is providing nutrition education to Kaitlin, a 35-year-old female client who has a clinical diagnosis of irritable bowel syndrome. Which options should the nurse include with dietary teaching to help manage exacerbation of symptoms? Select all that apply.
A) Maintain a minimum intake of caffeine to prevent caffeine withdrawal
B) Include a consistent level of fiber in the diet (30 to 40 grams per day) to maintain stool bulk
C) Limit intake of carbonated beverages to one can a day
D) Increase daily fluid intake to 6 to 8 glasses of water
E) Ingest gas-forming foods only every other day to prevent cumulative effects
B
D
Kaitlin asks about using alternative therapies to relieve clinical symptoms of IBS. Which suggestions should the nurse make? Select all that apply.
A) Herbal tea
B) Ginger
C) Fennel
D) Peppermint
E) Garlic
A
B
C
D
Kaitlin has provided the nurse with a food diary to help identify possible food triggers for IBS. Which diet entry poses a concern? Select all that apply.
A) Egg substitute omelet for breakfast
B) Diet sodas at lunch time
C) Bran cereal for breakfast
D) English breakfast decaffeinated tea for breakfast
E) Apple as an afternoon snack
B
E
Kaitlin expresses concerns that she wants to lose weight. What recommendations should the nurse make to help her attain this goal without exacerbating her IBS?
A) Limit caloric intake to 1,500 calories a day for 1 month
B) Maintain a regular meal schedule
C) Begin an all-liquid diet to stimulate weight loss
D) Include processed frozen foods as meal replacements
B
Kaitlin reports clinical symptoms that affect her enjoyment of meals. Which symptoms are associated with IBS?
A) Eructation and dyspepsia
B) Hiccups and indigestion
C) Dizziness and feelings of satiety
D) Urge to void
A
Kaitlin asks the nurse about stress management to help control her symptoms. Which suggestions should the nurse make? Select all that apply.
A) Take a daily walk
B)Go to church every week
C) Consider a group yoga class
D) Find a massage therapist
E) Take 15 minutes each day to meditate
A
C
D
E
Kaitlin tells the nurse "I know this sounds crazy, but my stomach feels better when I suck on a peppermint candy." How should the nurse reply?
A) Peppermint has no impact on your intestinal functioning.
B) Peppermint is an antispasmodic and has anti-inflammatory properties.
C) Peppermint is a laxative, which increases motility.
D) Peppermint has antinausea affect and can improve stomach irritation.
B
Kaitlin tells the nurse she feels she is losing her friends because her dietary restrictions and symptoms are preventing her from socializing. What might the nurse suggest?
A) Allow for cheat meals
B) Find an online support group
C) Find new friends
D) Ignore restrictions when out with friends
B
As the nurse continues to monitor Kaitlin’s progress, which laboratory findings might be observed? Select all that apply.
A) Hypokalemia
B) Hyperglycemia
C) Elevated BUN
D) Decreased creatinine
E) Hypernatremia
A
C
E
A client with irritable bowel syndrome is instructed to begin using a food diary. The client is unclear as to why a food diary is needed. What is the basis of the nurse's explanation?
A)Flare-ups of the disease process are associated with increased caloric intake.
B) Food selection should be based on following a low-sodium, low-fat diet.
C) Excess fluid intake can lead to exacerbations of the disease.
D) Certain foods can act as triggers and cause flare-ups of the disease.
D
Which ingredients should be avoided in food selection for a client who has irritable bowel syndrome? Select all that apply.
A) Sodium
B) Fructose
C) Sorbitol
D) Dextrose
E) Lactose
B
C
D
E
Which herbal therapy would aid in the expulsion of flatulence in a client diagnosed with irritable bowel syndrome?
A) Ginger
B) St. John's Wort
C) Garlic
D) Echinacea
A
The nurse is providing teaching to a client with irritable bowel syndrome. Along with teaching the client about proper nutrition, what other topics should the nurse address? Select all that apply.
A) Smoking cessation
B) Keeping daily activity low, exercising only as necessary
C) Sleeping seven to eight hours each night
D) Limiting alcohol intake
E) Investigating alternative therapies
A
C
D
E
Which members of the interdisciplinary team would a nurse include in discharge planning for a client who has been diagnosed with irritable bowel syndrome? Select all that apply.
A) Nutrition counseling
B) Psychological therapy
C) Support group
D) Hospice
E) Ostomy support group
A
B
C
A nurse is discussing postsurgery care techniques for a patient with a hernia. Which techniques are appropriate? Select all that apply.
A) Inspect the incision for signs and symptoms of infection and report any concerns to the primary healthcare provider.
B) Avoid heavy lifting for several weeks.
C)Promote atelectasis and venous thromboembolism (VTE).
D) Avoid deep breathing and early ambulation.
E) Splint the surgical site with pillows while coughing.
A
B
E
Which is true of ulcerative colitis? Select all that apply.
A) Complications such as hemorrhage and nutritional deficiencies may occur.
B) It occurs anywhere in the gastrointestinal tract from mouth to anus.
C) Weight loss rarely occurs.
D) Granuloma is common.
E) Stools are frequent and watery with blood and mucus
A
C
E
Which describes a patient with internal hemorrhoids that prolapse upon defecation and must be reduced manually?
A) Grade I
B) Grade II
C) Grade III
D)Grade IV
C
In which way are external hemorrhoids diagnosed?
A) Anoscopy
B) Visual inspection
C) Digital examination
D) Sigmoidoscopy
B
In which diagnostic study does the patient swallow a pill to capture the image of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract to assess for colorectal cancer?
A) Lower GI series
B) Wireless capsule endoscopy
C) Virtual colonoscopy
D) Sigmoidoscopy
B
Which interventions should a nurse implement for a patient after colorectal surgery? Select all that apply.
A) Take vital signs of the patient every 48 hours
B) Monitor white blood cell count every day for the first few days
C) Check if the urine output is at least 10mL/hr during the first 24 hrs
D) Check if the stoma is reddish pink and moist
E) Ensure that the patent does not receive food and water per order
B
D
E
Which nursing action, when caring for a patient with abdominal trauma, may result in further complications?
A) Administering IV fluids to the patient
B) Removing objects emerging from the wound
C) Promoting hemodynamic stability
D) Obtaining samples for a CBC, serum electrolytes, and urinalysis
B
The nurse is assessing for appendicitis at McBurney's point. Which location is this?
A) RUQ
B) RLQ
C) LUQ
D) LLQ
B
A client with a history of chronic pancreatitis presents to the hospital for admission. The nurse should expect to find which clinical manifestations on assessment? Select all that apply.
A) Decreased respiratory rate
B) Stable blood pressure
C) Clay-colored stools
D) Epigastric and left upper quadrant pain
E) Steatorrhea
C
D
E
What clinical markers are used in the evaluation of Ranson’s Criteria when determining the severity of acute pancreatitis? Select all that apply.
A) White blood cell count greater than 16,000/mL
B) Rise in hematocrit level greater than 10%
C) Fluid sequestration greater than 3 L
D) Glucose greater than 200 mg/dL
E) Age less than 20 years
A
D
What nutritional concern will the nurse expect to find in a client who has chronic pancreatitis?
A) Weight gain
B) Denies nausea
C) Weight loss
D) Stabilized weight pattern with different food preferences
C
The nurse is caring for a client with acute pancreatitis. What complications should the nurse monitor for in the critical client? Select all that apply.
A) Hemorrhage
B) Gallstone development
C) Multiple organ failure
D) Pleural effusion
E) Osteoporosis
A
C
D
The nurse is providing client teaching on pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy. What should the nurse tell the client this therapy is used to treat?
A) Decreased insulin level
B) Inflammation and obstruction
C) Pseudocyst
D) Malnutrition and malabsorption
D
Select the correct statements for each question when managing the client with chronic pancreatitis. Select all that apply.
Oral pancreatic enzymes
A) Do not chew to prevent disruption of enteric coating
B) Deliver following ingestion of meals
C) Provided in extended-release capsules
D) Helps digest fats and proteins
E) Must be taken with to meals
F) Must be swallowed whole for therapeutic dose
A
C
D
E
F
Select the correct statements for each question when managing the client with chronic pancreatitis. Select all that apply.
Dietary and alcohol intake with chronic pancreatitis
A) Avoid coffee and caffeine for prevention of gastric distress
B) Low-fat diet required for malabsorption of fats
C) Alcohol should be avoided to minimize pancreatic inflammation
D) Maintain a diabetic diet for glycemic control
E) Increased caloric intake too combat weight loss
F) Total parenteral nutrition for nutritional support
A
B
B
E
F
Select the correct statements for each question when managing the client with chronic pancreatitis. Select all that apply.
Pain
A) Opioids provide best pain relief
B) Non-opioids should be avoided
C) Described as persistent and recurring
D) Described as right lower quadrant abdominal pain
E) Focused over epigastric region
F) Pain secondary to impaired pain receptors
A
C
E
Select the correct statements for each question when managing the client with chronic pancreatitis. Select all that apply.
Pancreatic Enzyme Replacement Therapy (PERT)
A) Provides glycogen and amylase
B) Provides amylase, lipase, and protease
C) Used in the treatment of acute pancreatitis
D) Helps to aid in absorption of nutrients
E) Causes weight loss which helps to normalize insulin levels
F) Used to correct problems of malabsorption and malnutrition
B
D
F
Select the correct statements for each question when managing the client with chronic pancreatitis. Select all that apply.
Gastrointestinal prophylaxis therapy for chronic pancreatitis
A) Used to restore normal bowel function
B) Helps decrease gastric acid secretion
C) Relies on histamine blockers
D) Relies on proton pump inhibitors
E) Increases bulk of stools
F) Assists in normalization of bowel frequency
B
C
D
Select the correct statements for each question when managing the client with chronic pancreatitis. Select all that apply.
Lab findings with chronic pancreatitis
A) Elevated amylase and lipase levels
B) Decreased alkaline phosphatase
C) Decreased bilirubin
D) Elevated glucose level
E) Decreased potassium level
F) Elevated sodium level
A
D