Photochlorination of Alkanes (Halogenation)
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What is the name of the process alkanes undergo to form halogenoalkanes?
Free-radical substitution.
What is homolytic fission?
When the covalent bond breaks evenly, and each bonded atom receives one of the electrons, forming free radicals.
What is a free radical?
Any species with an unpaired electron.
How do you represent a free radical species?
Free radicals are usually represented with a single dot next to the atom with the lone pair of electrons.
Describe one characteristic of free radicals.
Free radicals are highly unstable and very reactive.
What is heterolytic bond fission?
When the covalent bond breaks unevenly, and one of the bonded atom receives the shared pair of electrons.
What does heterolytic bond fission produce?
Heterolytic fission forms oppositely charged ions.
The atom that takes the shared pair of electrons becomes the negative ion (anion).
The other atom becomes the positive ion (cation).
State the 3 stages of the free-radical substitution reaction of halogens and alkanes.
Initiation
Propagation
Termination
What is the initiation stage?
The bond in a diatomic halogen molecule is broken by homolytic bond fission under UV light to form 2 free radicals.
Example: Cl2 → 2Cl·
What is the propagation stage?
Free radical species react with an alkane molecule and get substituted into the molecule, forming more radicals.
Explain the propagation stage for the free-radical substitution reaction between methane and chlorine.
In the first propagation step, a chlorine free radical reacts with methane, removing a hydrogen atom from methane. This gives hydrochloric acid and a methyl free radical.
Cl· + CH4 → CH3· + HCl
In the second propagation step, the methyl free radical reacts with chlorine gas (Cl2). One of the chlorine atoms becomes a free radical, and the other combines with the methyl free radical to form the alkyl halide (chloromethane) product.
CH3· + Cl2 → CH3Cl + Cl·
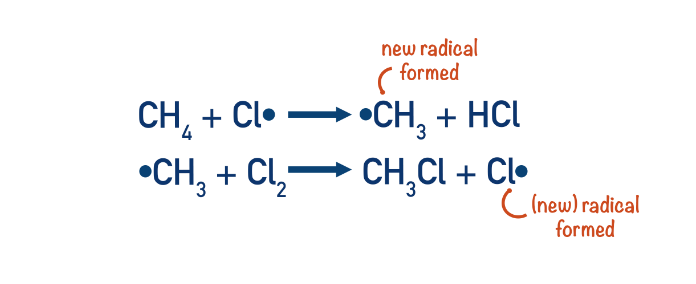
Why is the propagation stage described as a chain reaction?
For every chlorine free radical that goes in at the beginning, a new one is generated at the end.
Example:
1) Cl· + CH4 → CH3· + HCl
2) CH3· + Cl2 → CH3Cl + Cl·
What is the termination stage?
Free radicals react with each other to create a covalent bond and terminate the chain.
The product formed is stable, and no new free radicals are formed, so the chain reaction ends.
Give examples of termination stage reactions.
CH3· + Cl· → CH3Cl
CH3· + CH3· → C2H6
Cl· + Cl· →Cl2