Gibbs Free Energy
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
kinetic energy
the energy an object has due to its motion; useful to organisms; contribute to phenomena at all levels of organization in the universe
potential energy
stored energy that results from the position or shape of an object; useful to organisms; contribute to phenomena at all levels of organization in the universe
more complex molecule =
more potential energy = high enthalpy, low entropy
gibbs free energy
a measurement of the amount of energy that is available for a system (like a cell) to do work
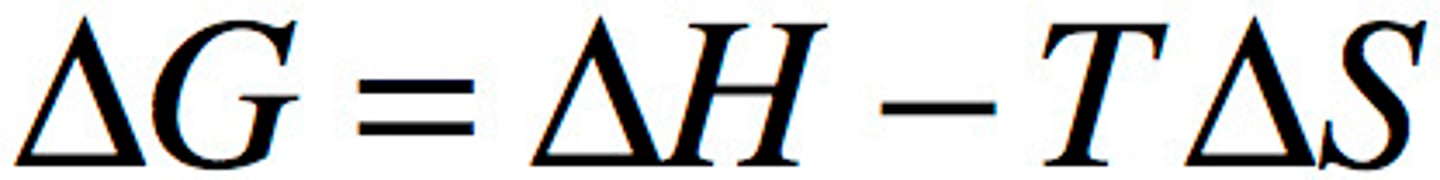
enthalpy
total energy stored in a system
entropy
a measure of the disorder of a system
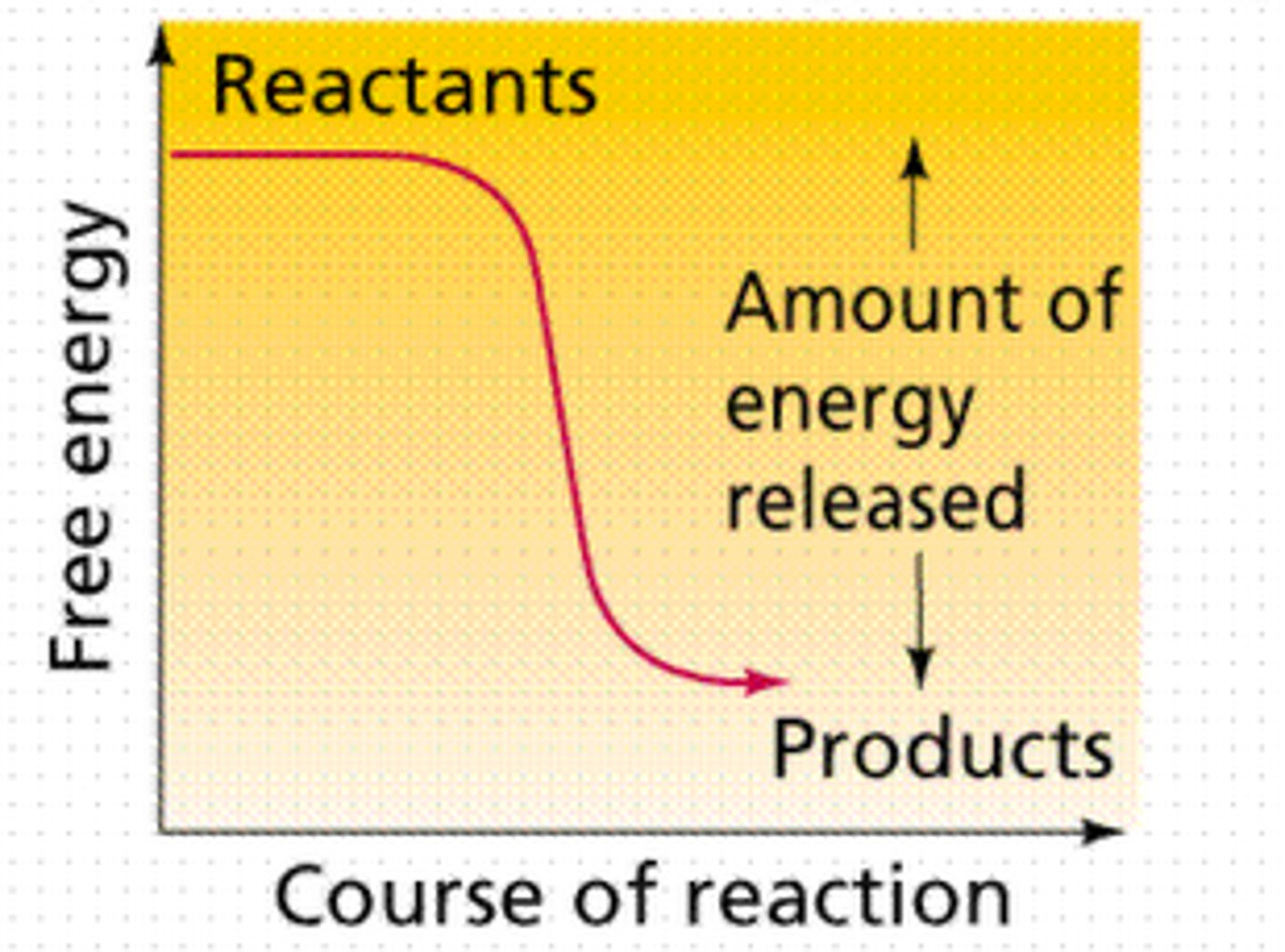
exergonic reactions
energy is released; polymers into monomers, catabolic; spontaneous; G is negative
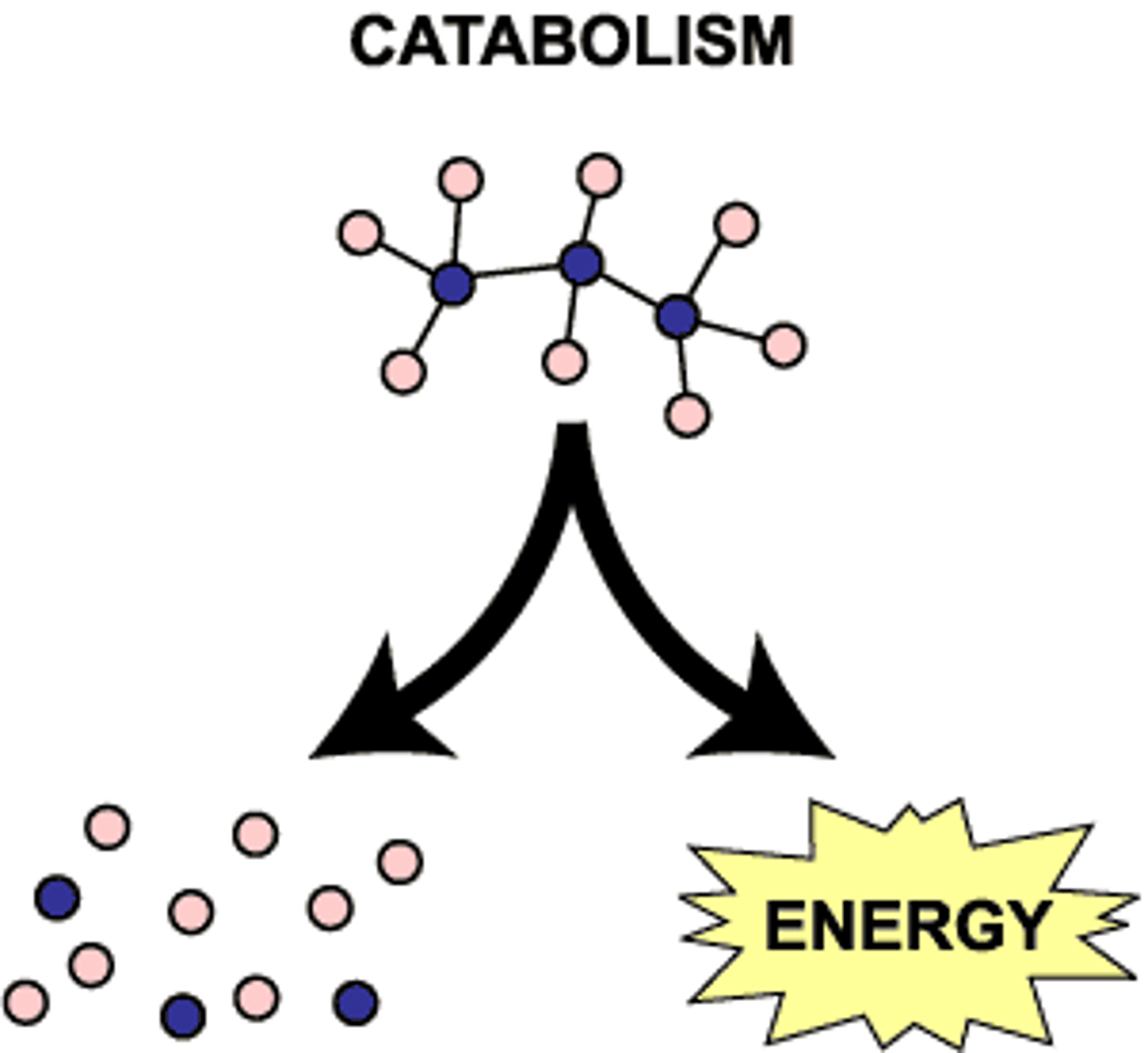
catabolic
a process in which large molecules are broken down
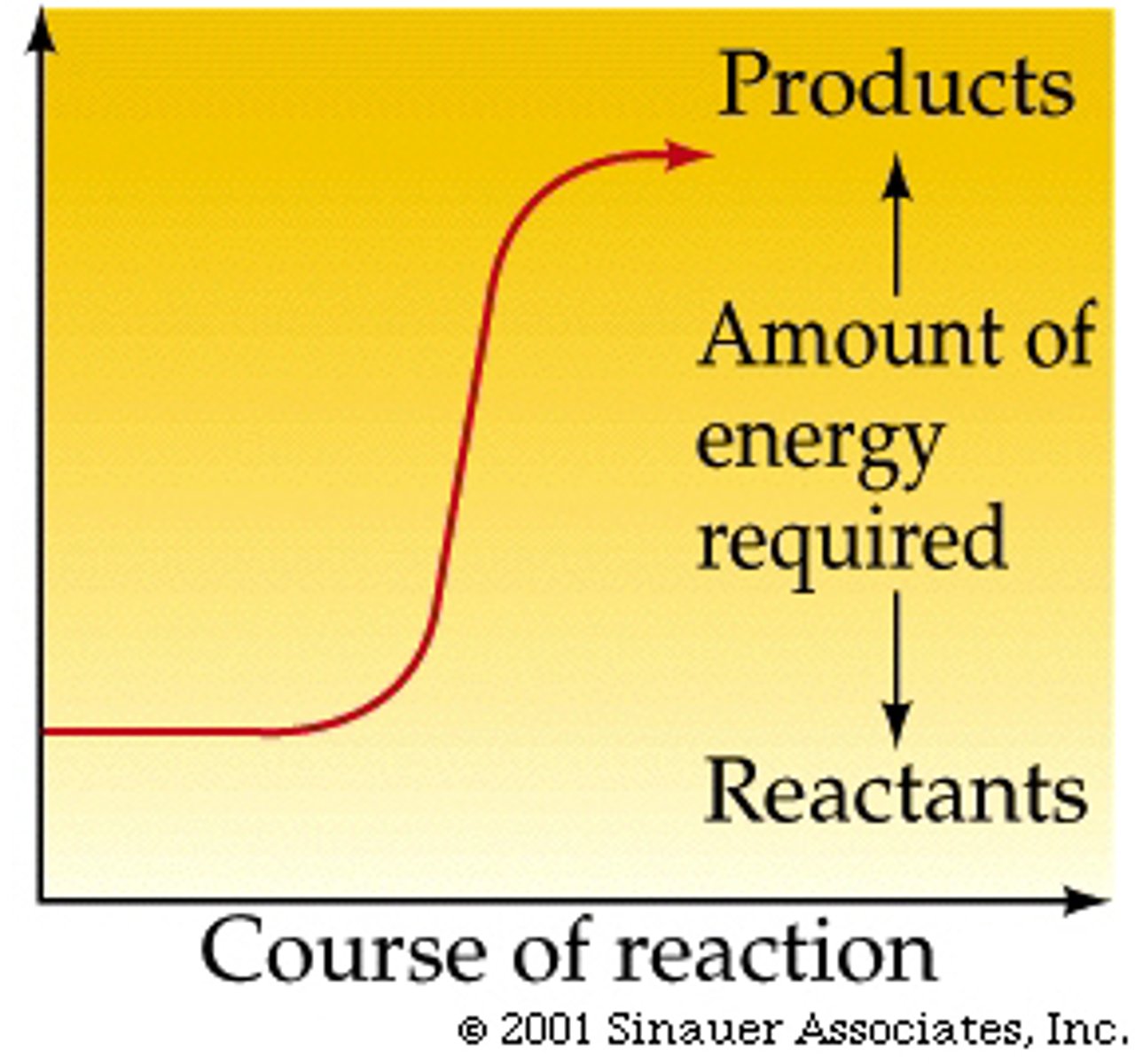
endergonic reactions
require energy input to occur; monomer into polymer, anabolic; not spontaneous; G is positive
anabolic
a process in which large molecules are built from small molecules
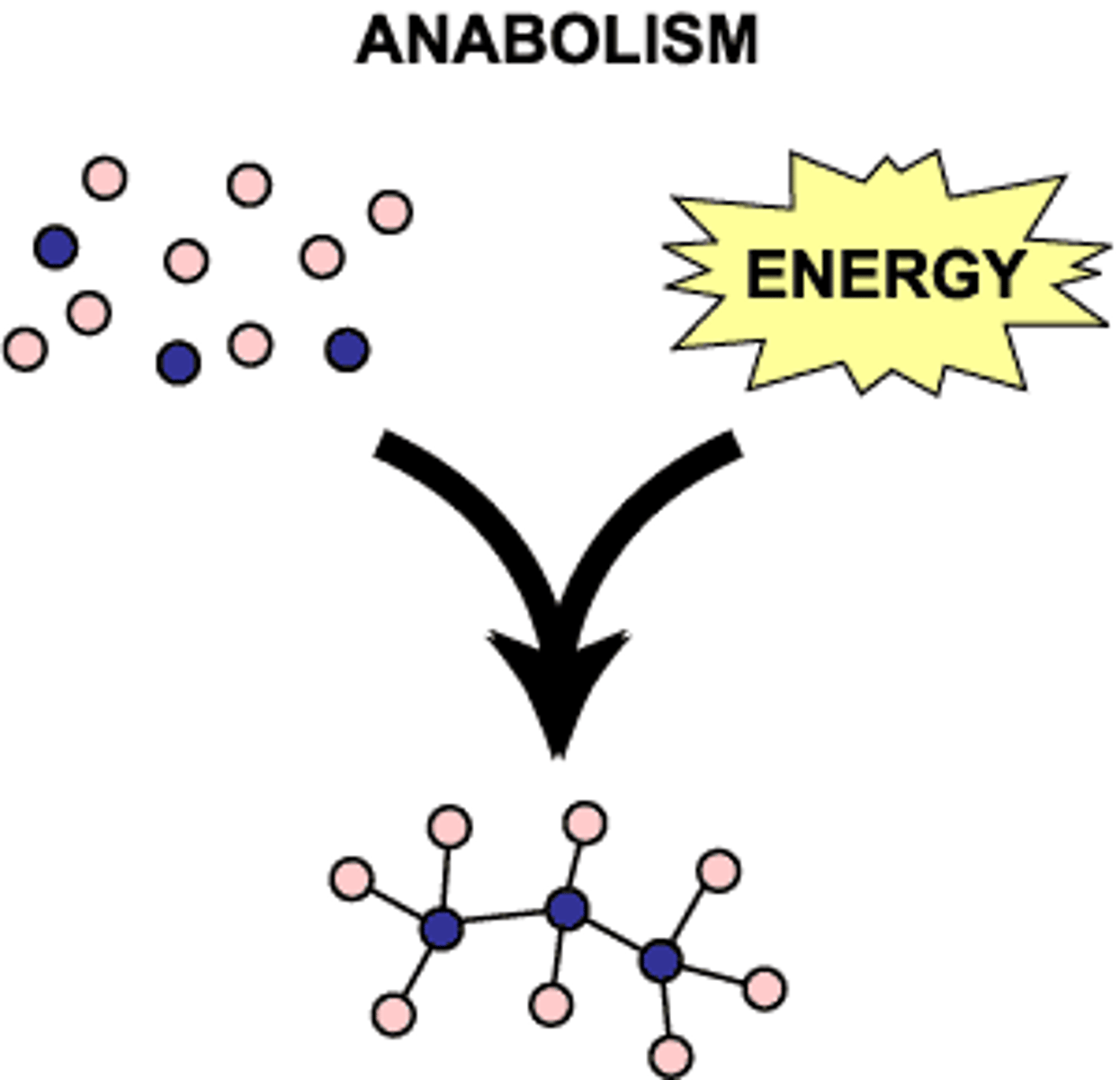
life is highly ordered
organisms use the energy they convert to power cellular processes that decrease their overall entropy; increases entropy of the surroundings
life requires...
energy input
spontaneous reaction
A reaction that will proceed without any outside energy
∆H
enthalpy
∆T
change in temperature
∆G
change in free energy
∆S
change in entropy