Lecture 4 brainstem and corpus callosum
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
Corpus callosum
white matter structure
C-shaped nerve fiber bundle connecting the left and right halves of the brain
Transfers information b/w hemispheres
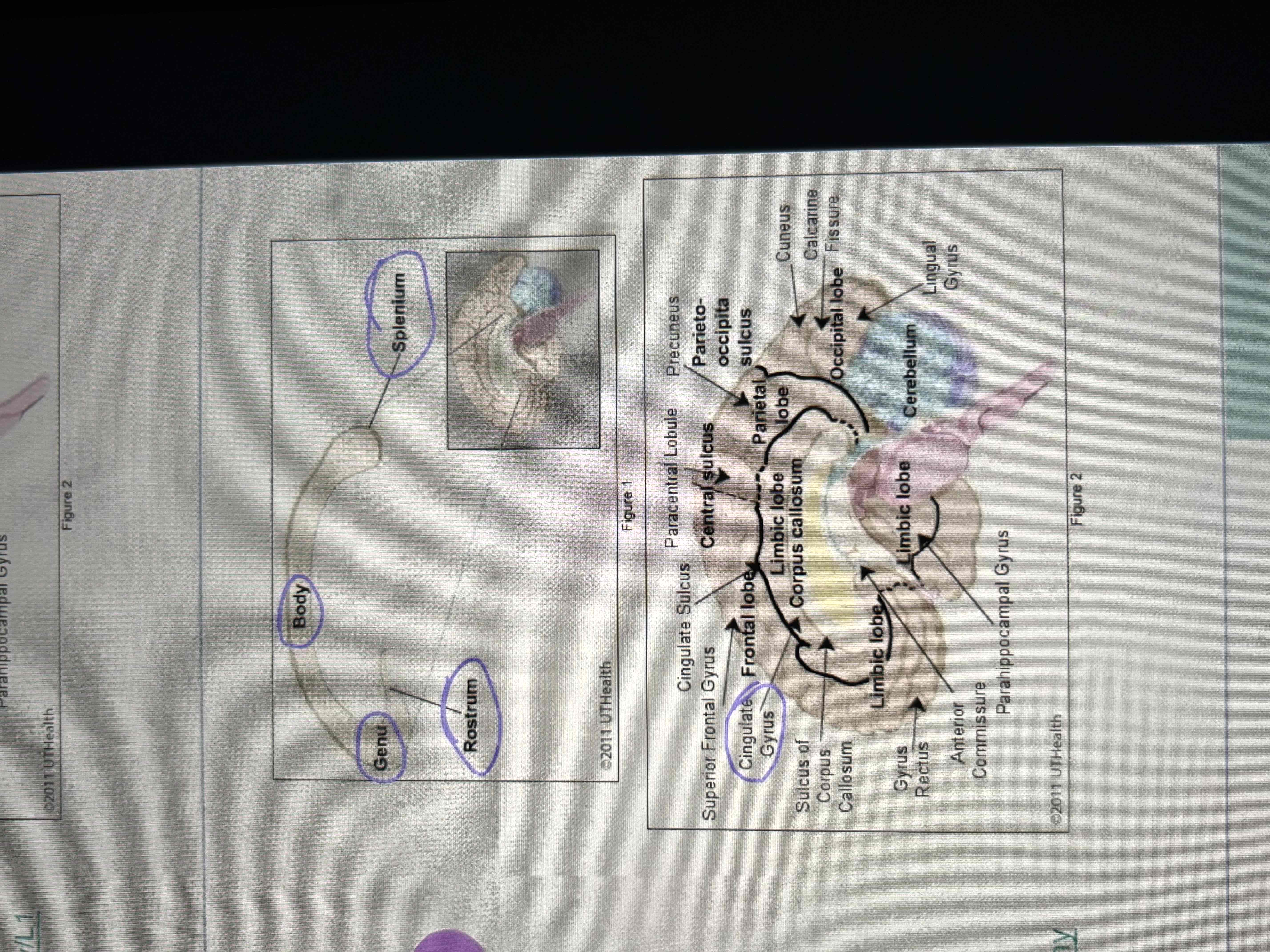
Corpus Callosum Parts
1. rostrum
2. Genu
3. Body
4. Splenium
Cingulate gyrus sits above
Septum pellucidum sits below
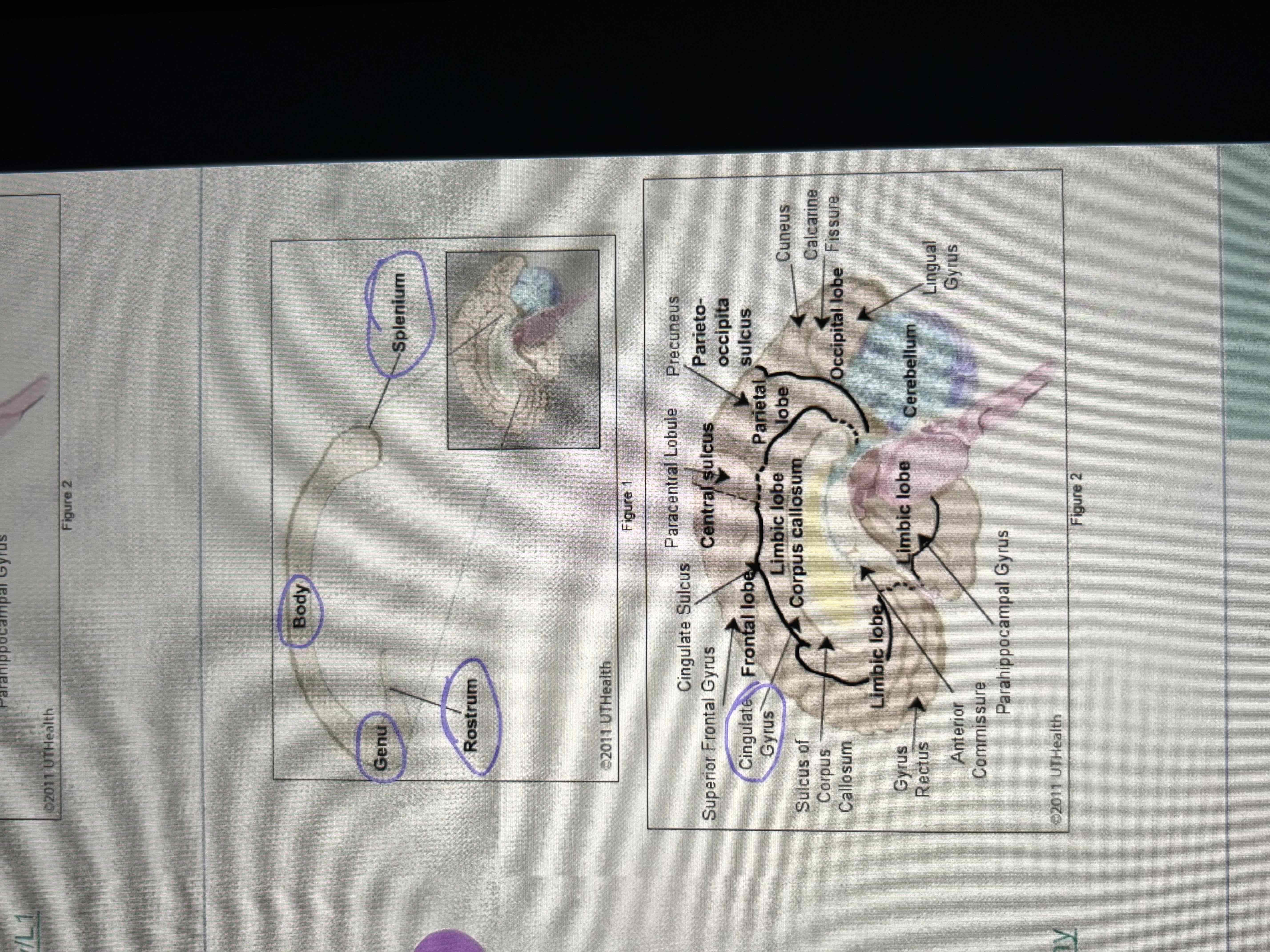
Limbic lobe (system)
functional grouping of structures along the medial and inferior aspects of the cortex
Involved in long term memory and learning, drive related behavior, olfaction, and emotional function
Contains: cingulate gyrus, parahippocampal gyrus (uncus), subcallosal gyrus, hippocampus
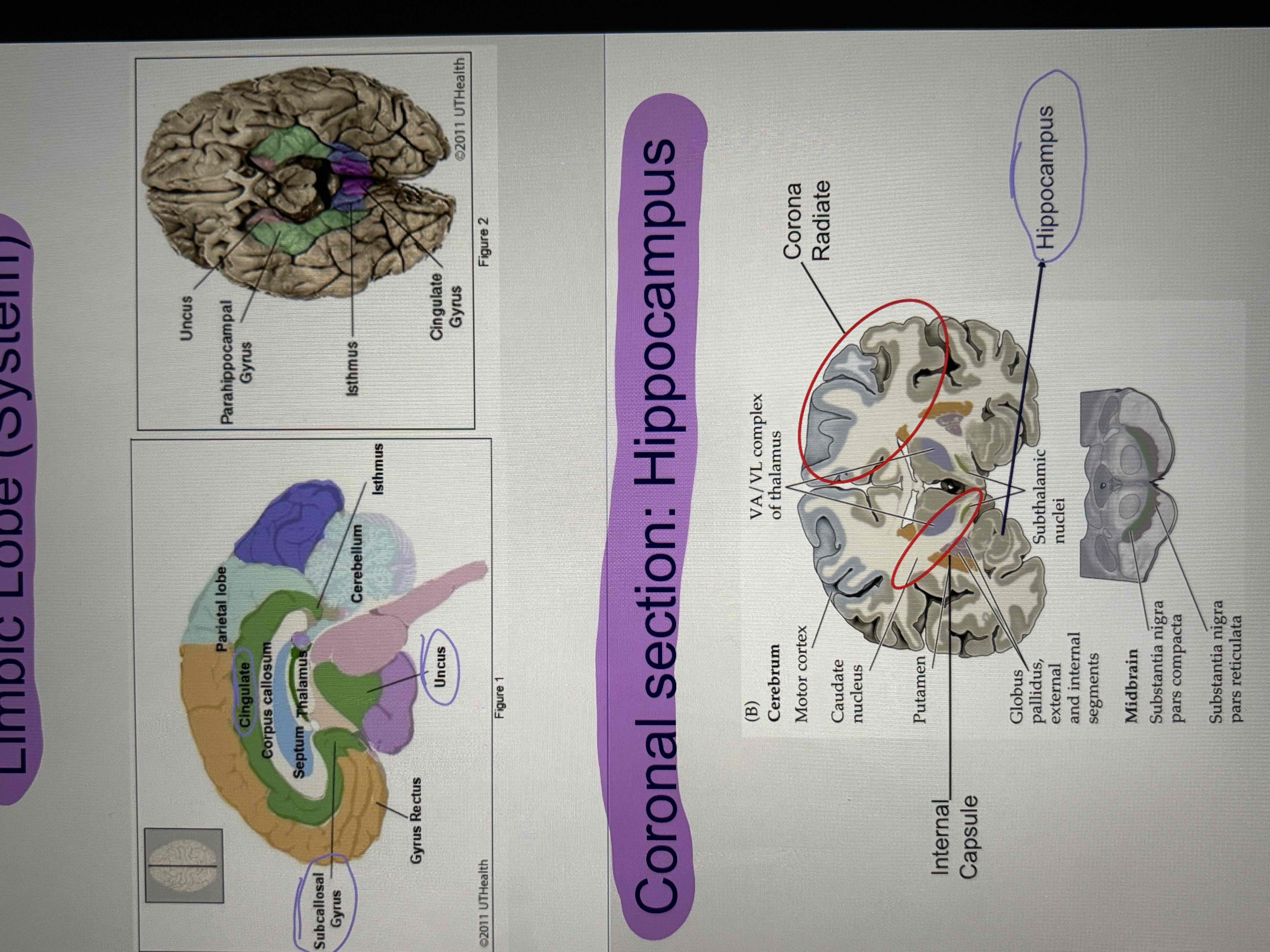
Insular lobe
forms the “floor” of the lateral sulcus, sitting deep to the frontal and temporal lobes
Involved in a variety of functions, including pain and autonomic regulation, as well as taste, auditory, and vestibular processing
Brainstem
mesencephalon- midbrain
Rhombencephalon:
metencephalon: pons and cerebellum
Myelencephalon: medulla
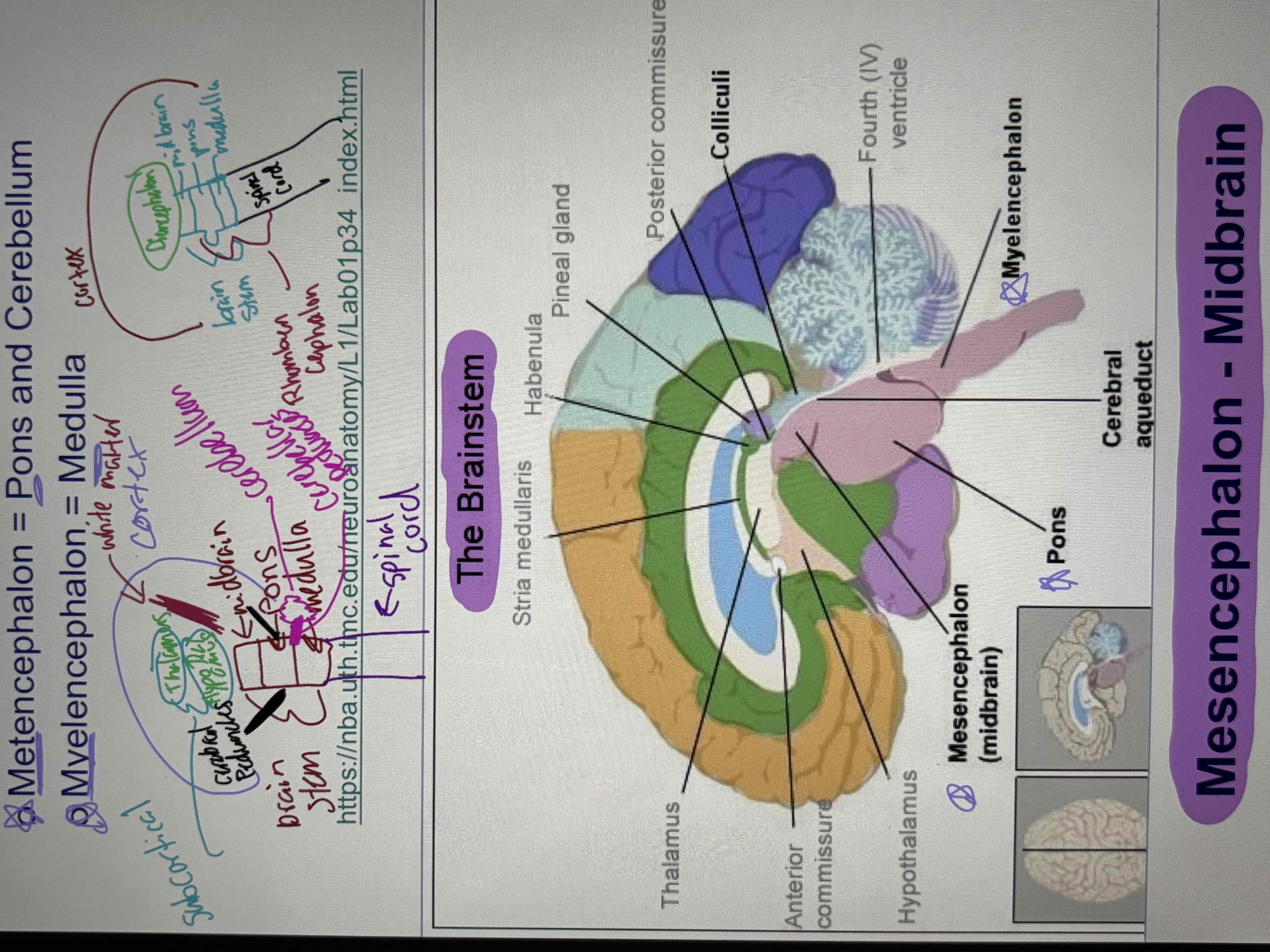
Mesencephalon- midbrain
The base of the midbrain consists of the cerebral peduncles, which contain nerve fibers descending from the cerebral cortex.
Cranial nerve nuclei- 3rd (oculomotor), 4th (trochlear) and part of the 5th (reigning) are located in the midbrain tegmentum.
The red nucleus in the substantial nigra, two prominent nuclei, are also found in the midbrain tegmentum.
The superior and inferior colliculi, found in the tectum, are involved in visual and auditory functions respectively.
Rhombencephalon- metencephalon (pons and cerebellum)
pons is composed of two parts, the Pontine tegmentum (dorsal) and the basilar pons (ventral).
At the level of the pons, the cerebral aqueduct has expanded to form the fourth ventricle.
The cerebellum is situated posterior to the pons and forms part of the roof (tectum) of the fourth ventricle.
The basilar pons contain ascending and descending tracts.
The pontine tegmentum contains the nuclei of the cranial nerves: 5th (trigeminal), 6th (abducens), 7th (facial), and the 8th (vestibulocochlear) nerves
Rhombencephalon- myelencephalon (medulla)
The medulla lies between the pons and the spinal cord
It is continuous with the spinal cord just above to foramen magnum in the first spinal nerve
The posterior surface of the medulla forms the bottom, half of the fourth ventricle floor
The medulla also has ascending and descending tracts
The medulla contains, the cranial nerve nuclei from the 9th (glossopharyngeal), 10th (vagus), 11th (accessory), and 12th (hypoglossal) nerves, which regulate respiration, swallowing, sweating, gastric, secretion, cardiac, and vasomotor activity.
Medulla had pyramids and olives, and the inferior cerebellar peduncles.