METALS & ALLOYS
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
give examples of metals and alloys in dentistry
amalgam
cobalt chromium
stainless steel
gold
titanium
dental applications of metals and alloys
amalgams incl. Hg, Au alloys
inlays/ onlays: Pd alloys

what is a metal
metal: a crystalline material held together by metallic bonds
what are examples of crystal structure
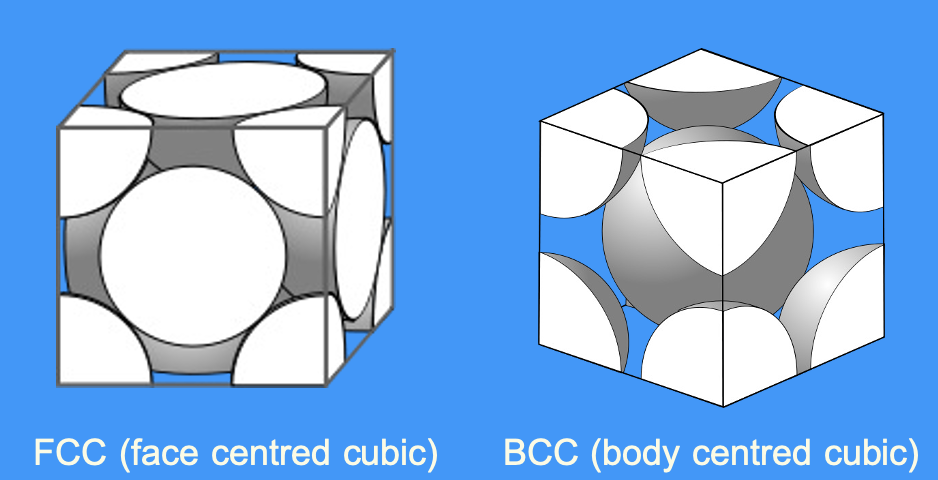
which crystal structure has a larger packing factor
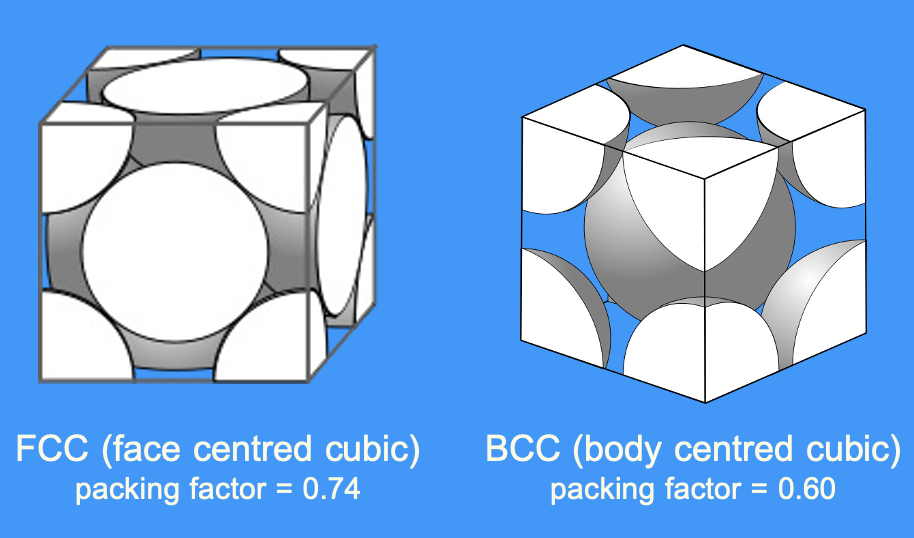
what does a bigger packing factor mean
bigger packing factor = denser metal
what is the correlation between grain size and material strength
smaller grains = stronger material
diagram showing metal microstructure
metals: usually polycrystalline structure consisting of grains and grain boundaries
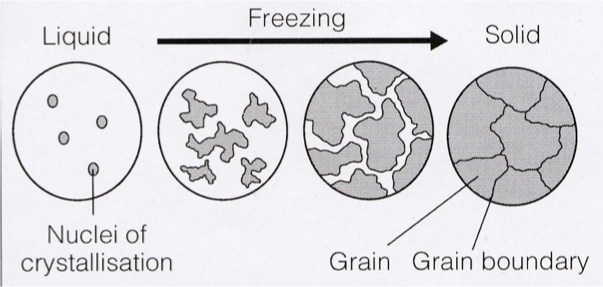

how does metal need to be prepared to view the microstructure under the microscope
metal must be etched with acid
etching creates grain contrast depending on the crystallographic orientation
what pure metals are used in dentistry
gold
platinum
titanium
state the types of alloy structures
when metals are mixed they can form multiple different mixed structures:
substitutional solid solutions
interstitial solid solutions
intermetallic compounds

outline substitutional solid solution
the different atoms have the same valency
with the same crystal structure i.e. body centred plus body centred and face centred plus face centred
their atomic size is within 15%
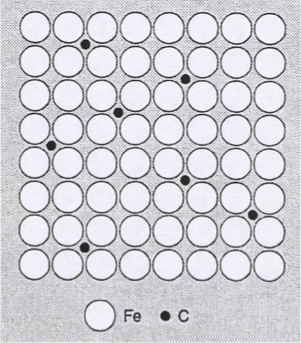
outline interstitial solid solution
solute atom ≤ solvent atom
the solute (smaller) atoms occupy the space between the solvent (larger) atoms
distortion of the lattice occurs to accommodate the extra atoms
outline intermetallic compound
formed when two or more metals combine with a discrete composition or stoichiometric ratio
what is an example of an intermetallic compound
dental amalgam
alloy contains a silver/ tin compound: Ag3Sn
also contains a copper/ tin compound: Cu6Sn5
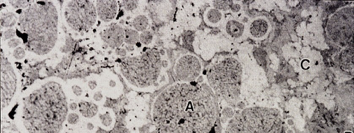
what does this image show
microscopic view of amalgam
define the term ‘phase’
phases: a homogenous physically distinct part of a system that is separated from other parts by a definite physical boundary
the different crystal structures are called phases
images of different alloys
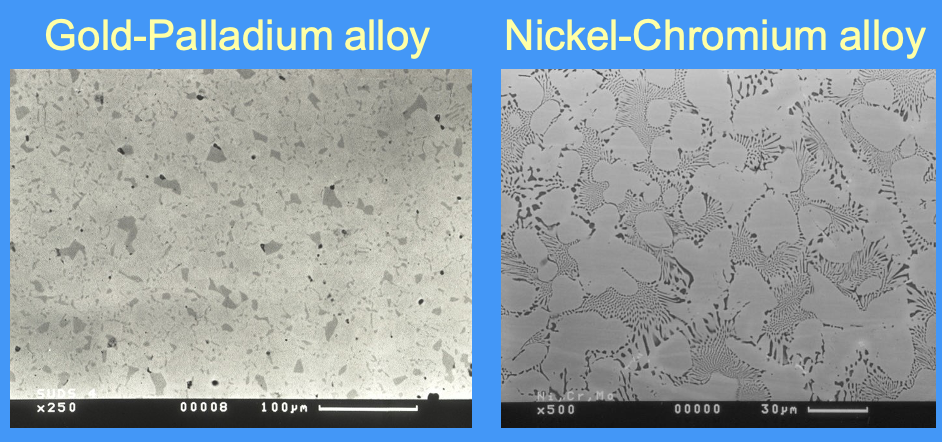
how many phases does an alloy consist of
an alloy can consist of single or multiple phases
phases can have distinctly different compositions
phases can have different crystalline structures
metals summary
metals are held together by metallic bonds - these can be weak or strong
metals are polycrystalline and can take up many crystal forms
what do the phases in an alloy depend on
the phases in an alloy depend on composition and temperature
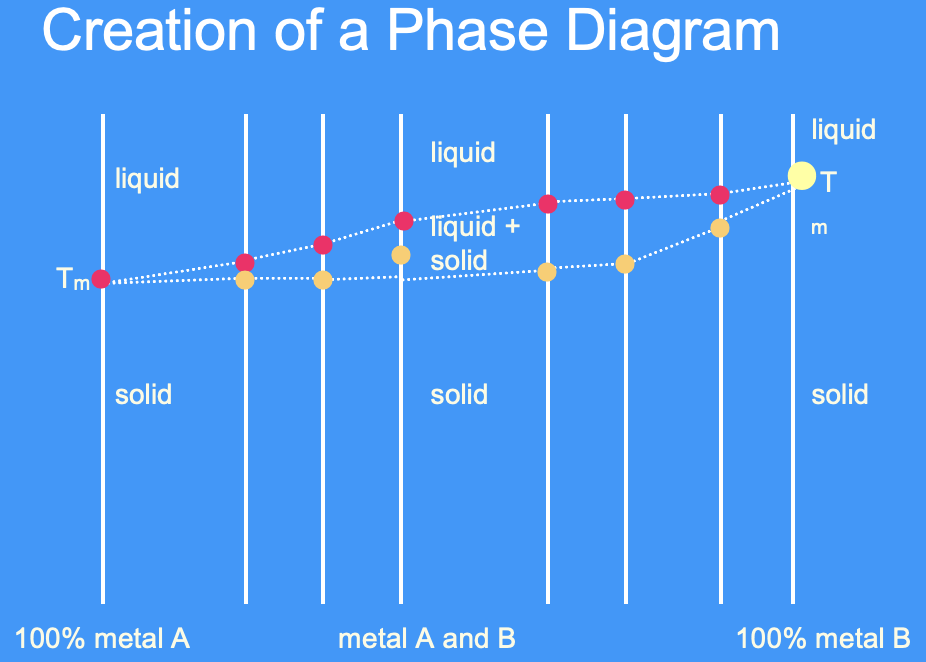
what is a phase diagram
a phase diagram is a graphical representation of the phases in an alloy with different compositions and temperatures/ a means of representing the structure of alloys as a function of composition
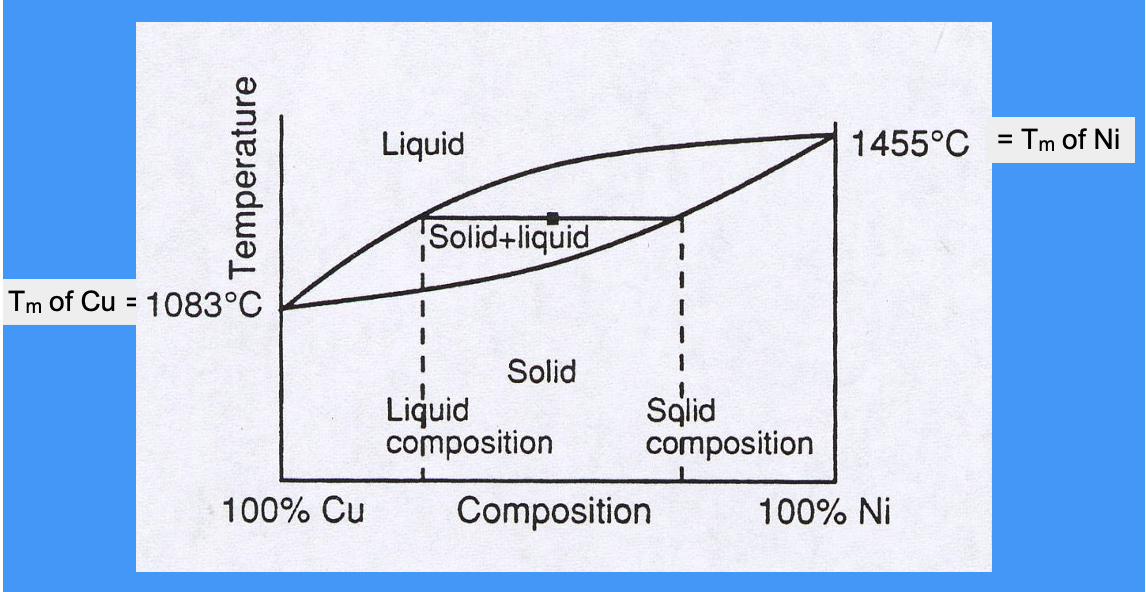
phase diagram for Cu and Ni
copper and nickel are totally soluble in each other
either vertical line is pure copper/ nickel
this is a binary phase diagram
alloys can be solid and liquid over a range of temperatures
graph showing transitions in pure metals
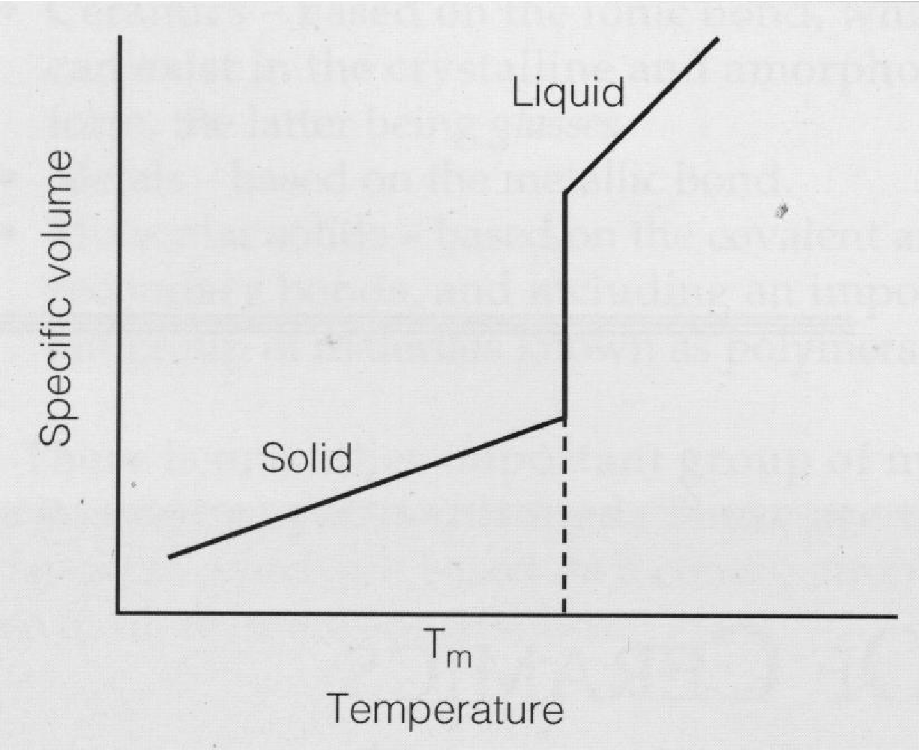
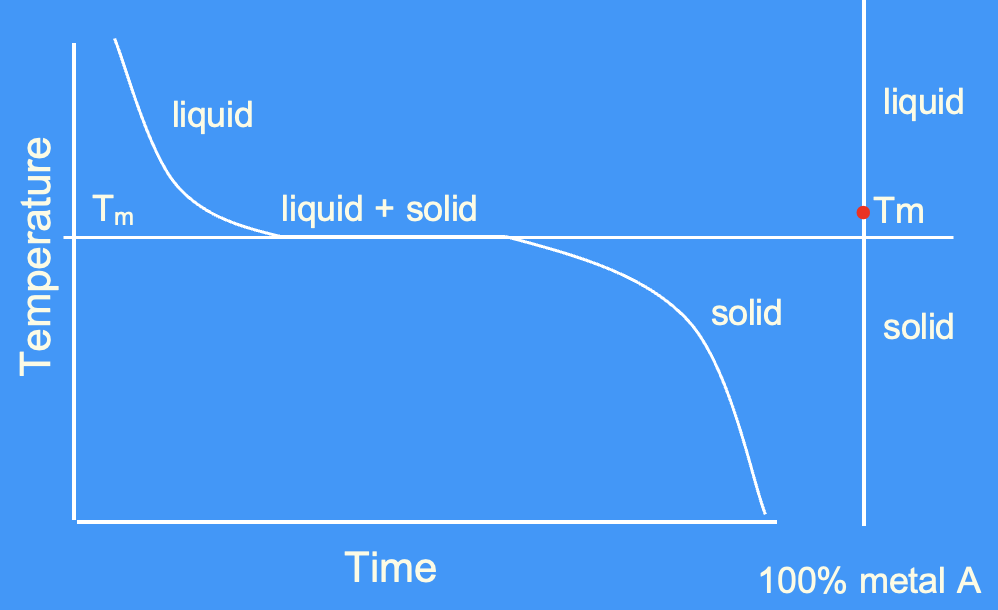
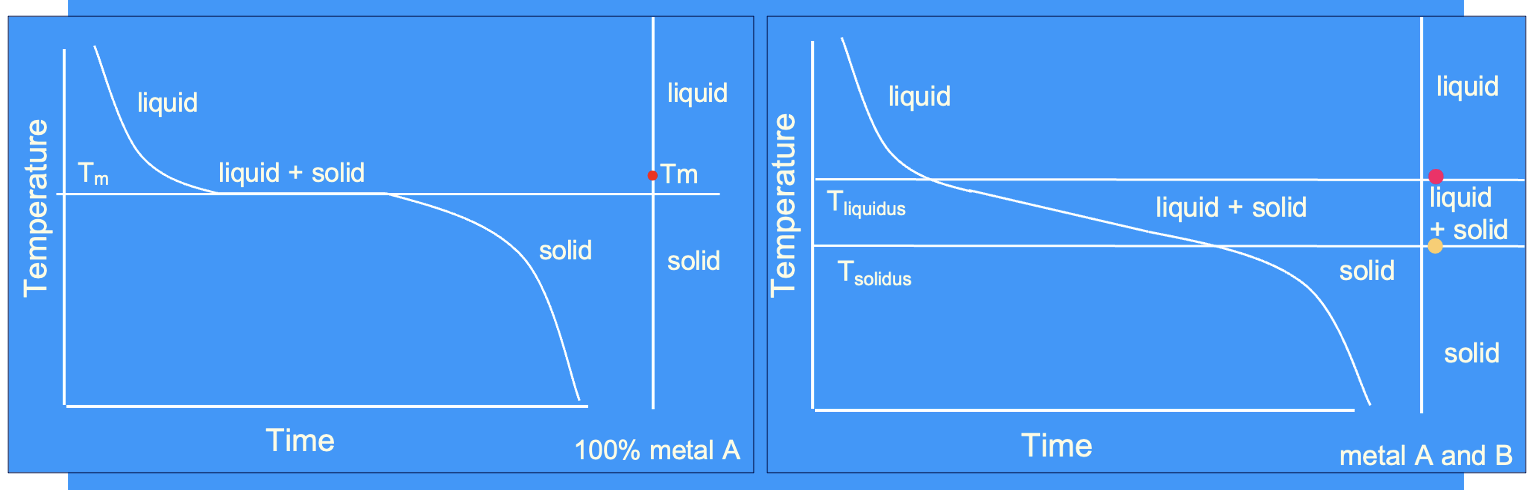
cooling curve for a pure metal
only achieve solid + liquid at one precise temperature in a pure metal (at Tm) - unlike an alloy
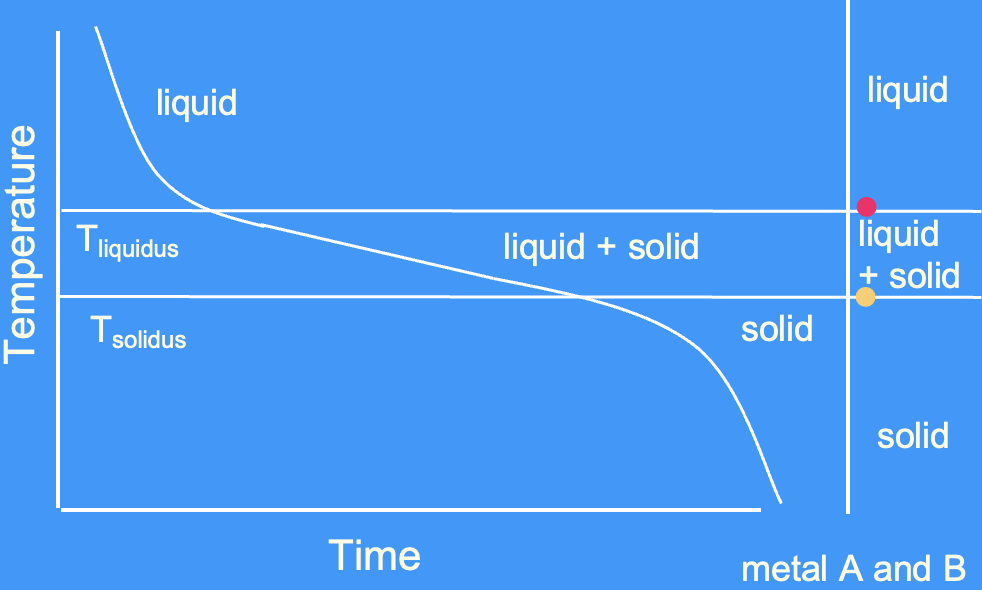
cooling curve for an alloy
achieve solid + liquid over a range of temperatures - unlike a pure metal
pure metal VS alloy cooling curve
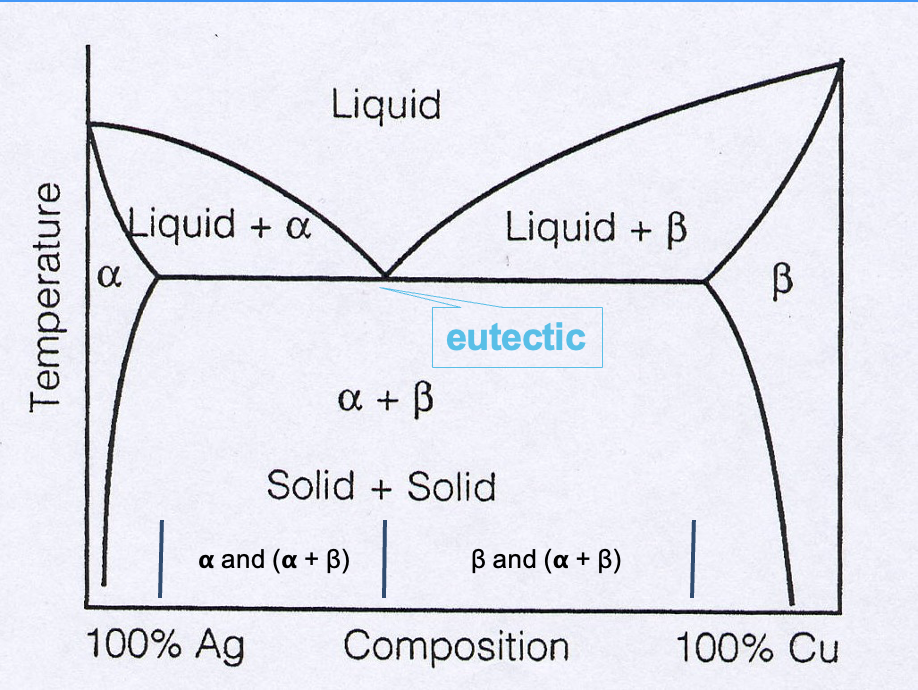
eutectic phase diagram for Ag and Cu
in alpha and beta area, Ag and Cu are fully soluble in each other
what is the eutectic point
eutectic point: alloy acts like a pure metal
this will only be at one specific composition
there is no solid-liquid region, straight from liquid » solid