Muscles - Upper Limbs/Lower Limbs
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Triceps Brachaii m.
Action:
- prime mover: forearm extension
Description: large fleshy muscle of posterior humerus; three-headed origin

Contains three muscle heads:
1. long head
2. lateral head
3. medial head
Long head's origin = infraglenoid tubercle
Lateral head's origin = posterior humerus
Medial head's origin = distal radial groove on posterior humerus
Origin of Triceps Brachii m.
The three heads come together to insert onto olecranon process of ulna
So when we think about this muscle pulling/contracting it will pull elbow straight (extension) b/c attached to point of elbow
Insertion of Triceps Bracii m.
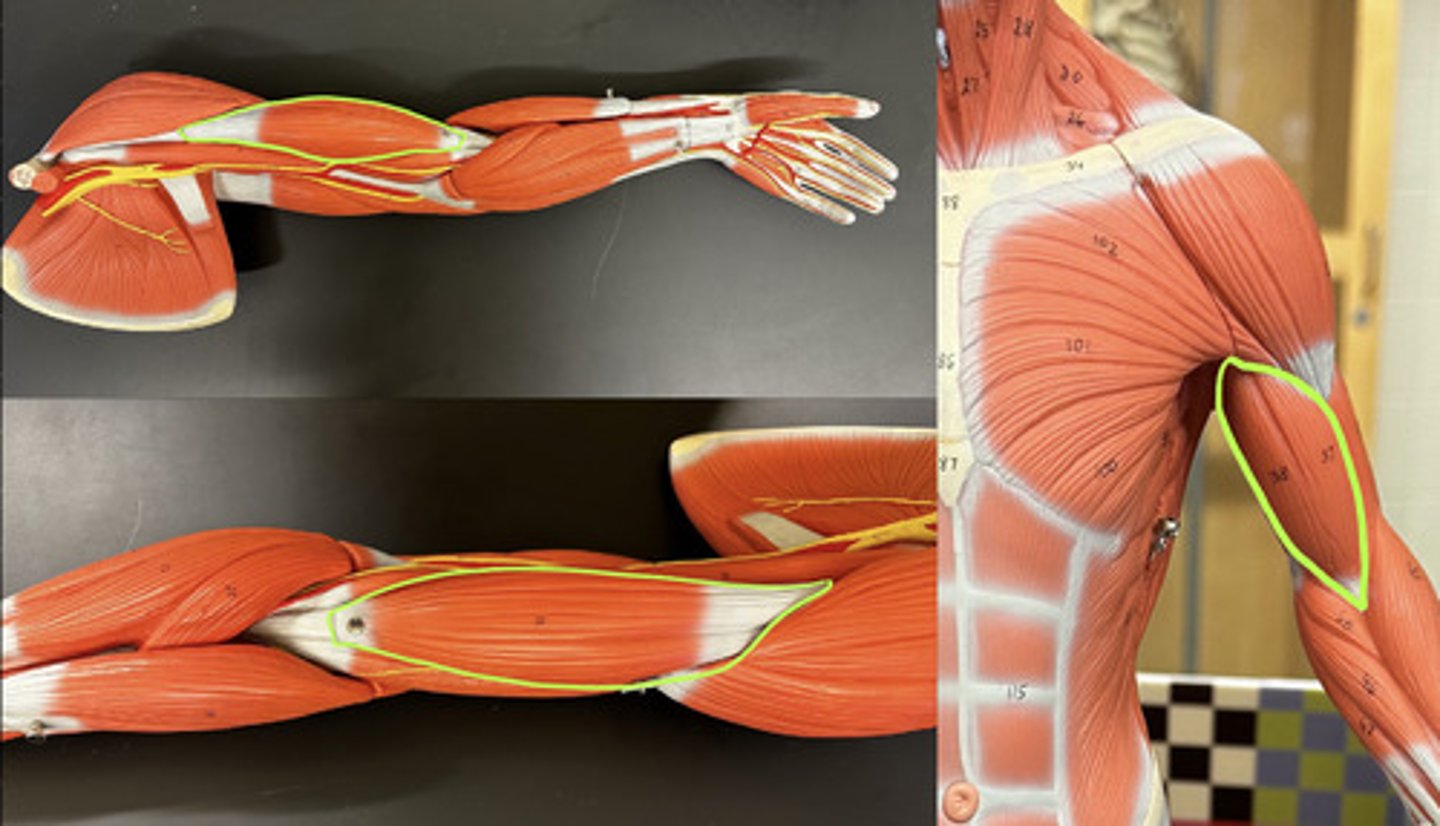
Biceps Brachii m.
Action:
- synergist of forearm flexion
- supinates forearm
Description: most familiar muscle of anterior humerus b/c this two-headed muscle bulges when forearm flexed
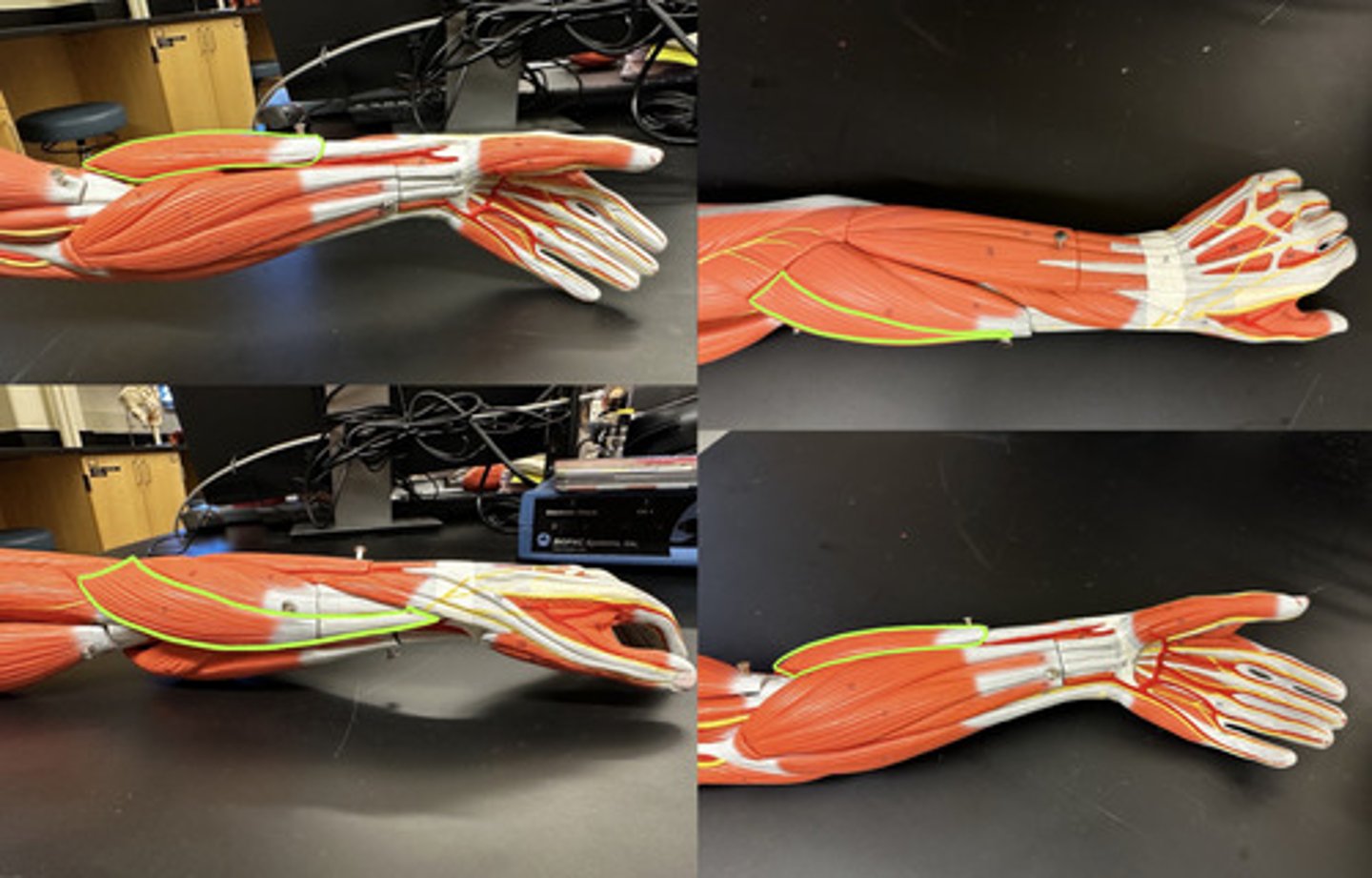
Brachioradialis m.
Action:
- Synergist in forearm flexion
Description: Superficial muscle of lateral forearm; forms lateral boundary of cubital fossa
Brachialis m.
Action:
- prime mover: forearm flexor
Description: Immediately deep to biceps brachii m.
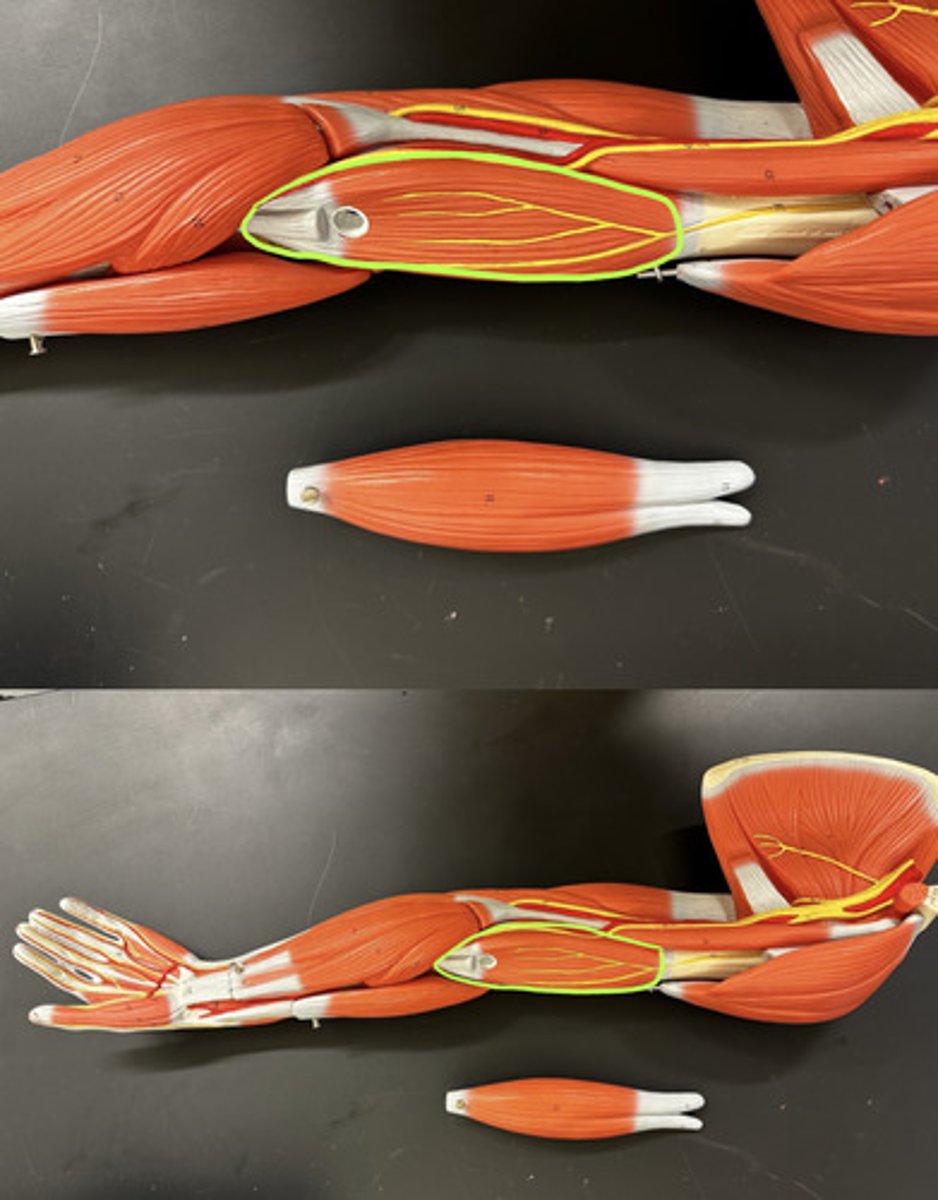
It is composed of muscle on the anterior portion of the forearm
These muscles then flex the fingers/digits
Thus, curling in fingers is flexion and the result of the muscles on the anterior side of the forearm
What is the forearm flexor compartment composed of?
It is composed of muscles on the posterior portion of the forearm
These muscle then extend the fingers/digits
Thus, extending fingers outward is extension and the result of the muscles on the posterior side of the forearm
What is the forearm extensor compartment composed of?
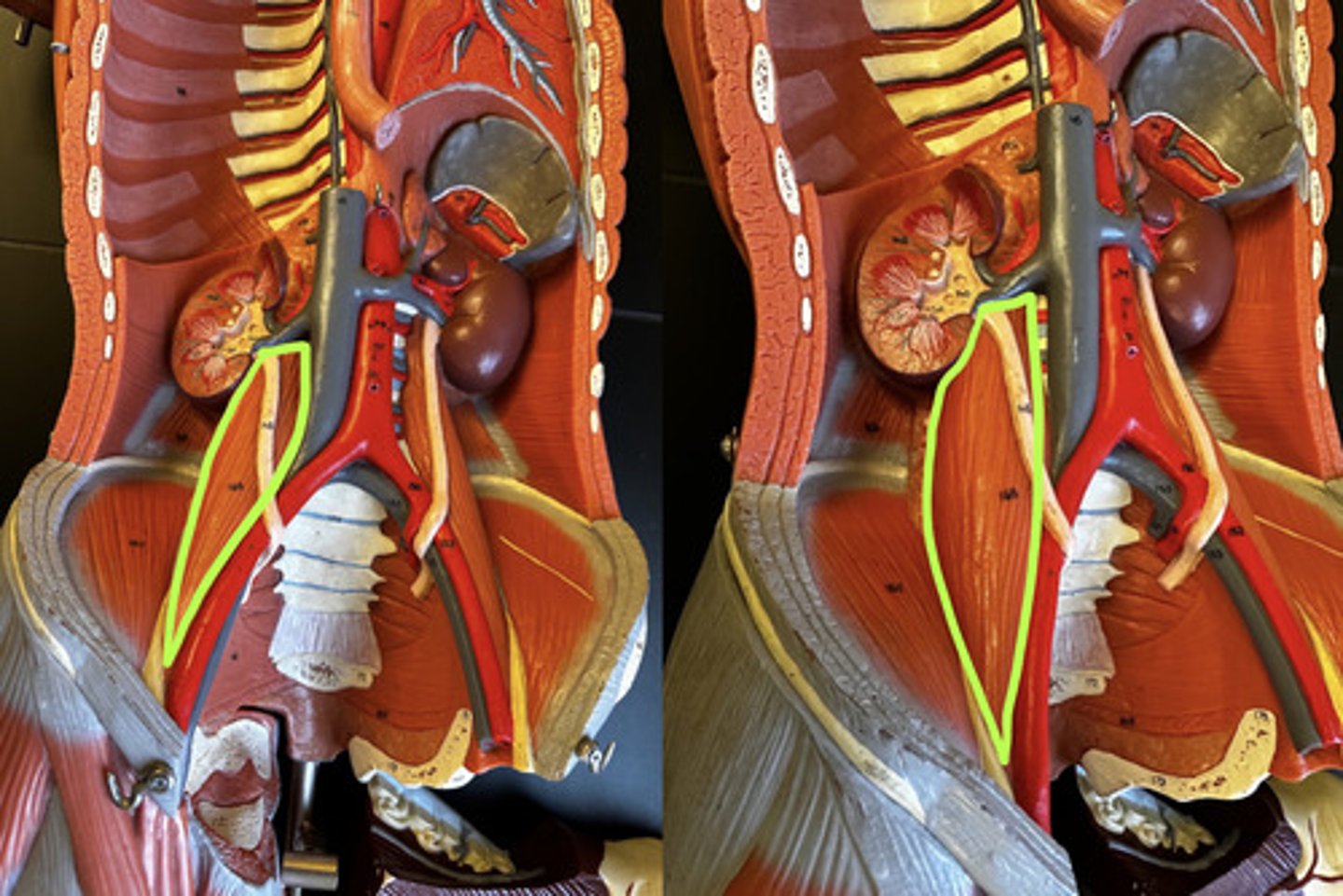
- Iliacus m.
- Psoas major m.
What muscles make up the Iliopsoas m.
Ilipsoas m.
Action:
- prime mover: flex trunk at hip joint
- prime mover: flex thigh/hip
- lateral flexion of vertebral column (specifically psoas m.)
Description: composed of two closely related muscles; fibers pass under inguinal ligament to insert into femur via a common tendon; iliacus is more lateral

iliacus m.
Action:
- prime mover: flex trunk at hip joint
- prime mover: flex thigh/hip
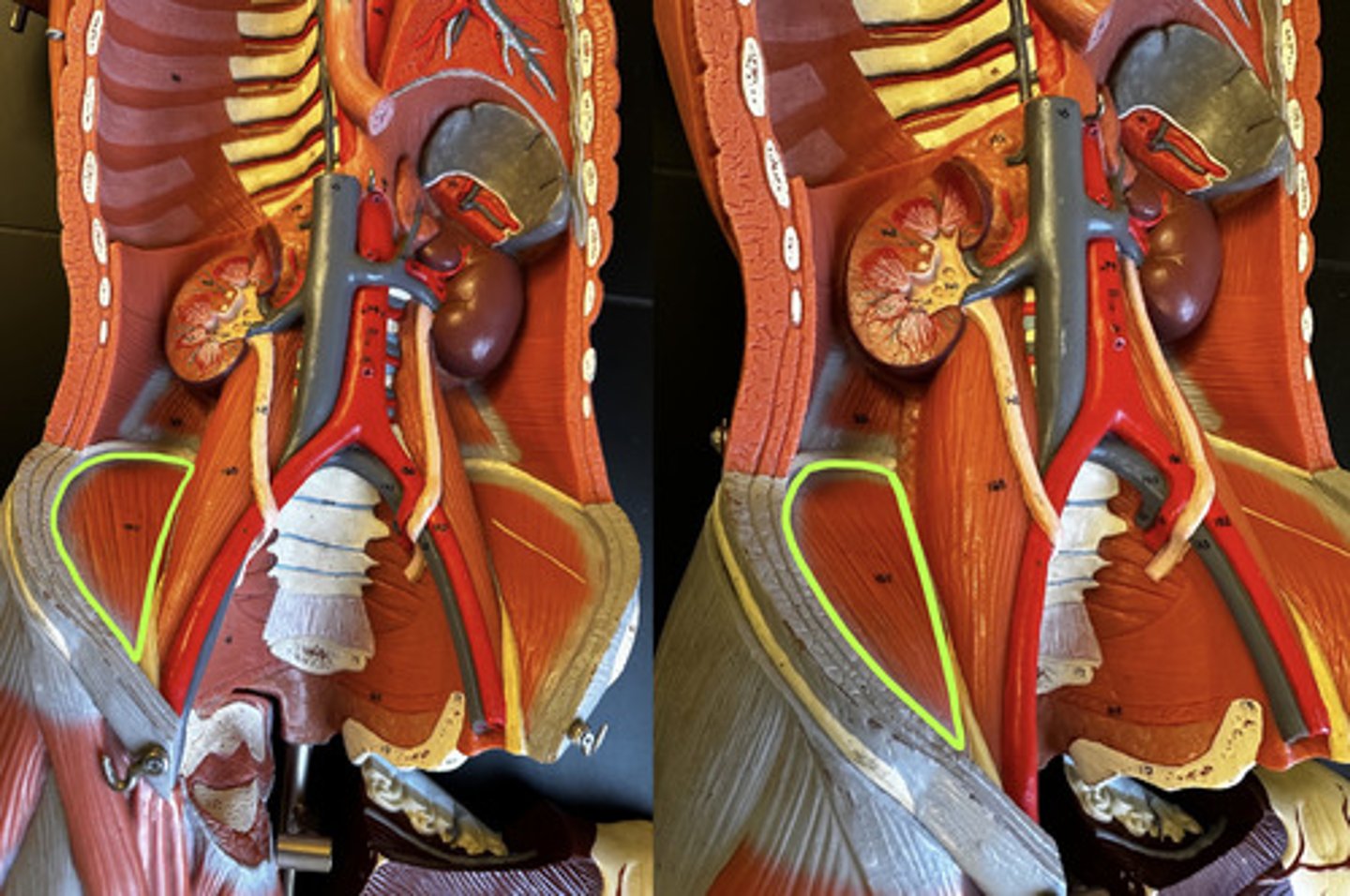
Psoas major m.
Action:
- prime mover: flex trunk at hip joint
- prime mover: flex thigh/hip
- lateral flexion of vertebral column
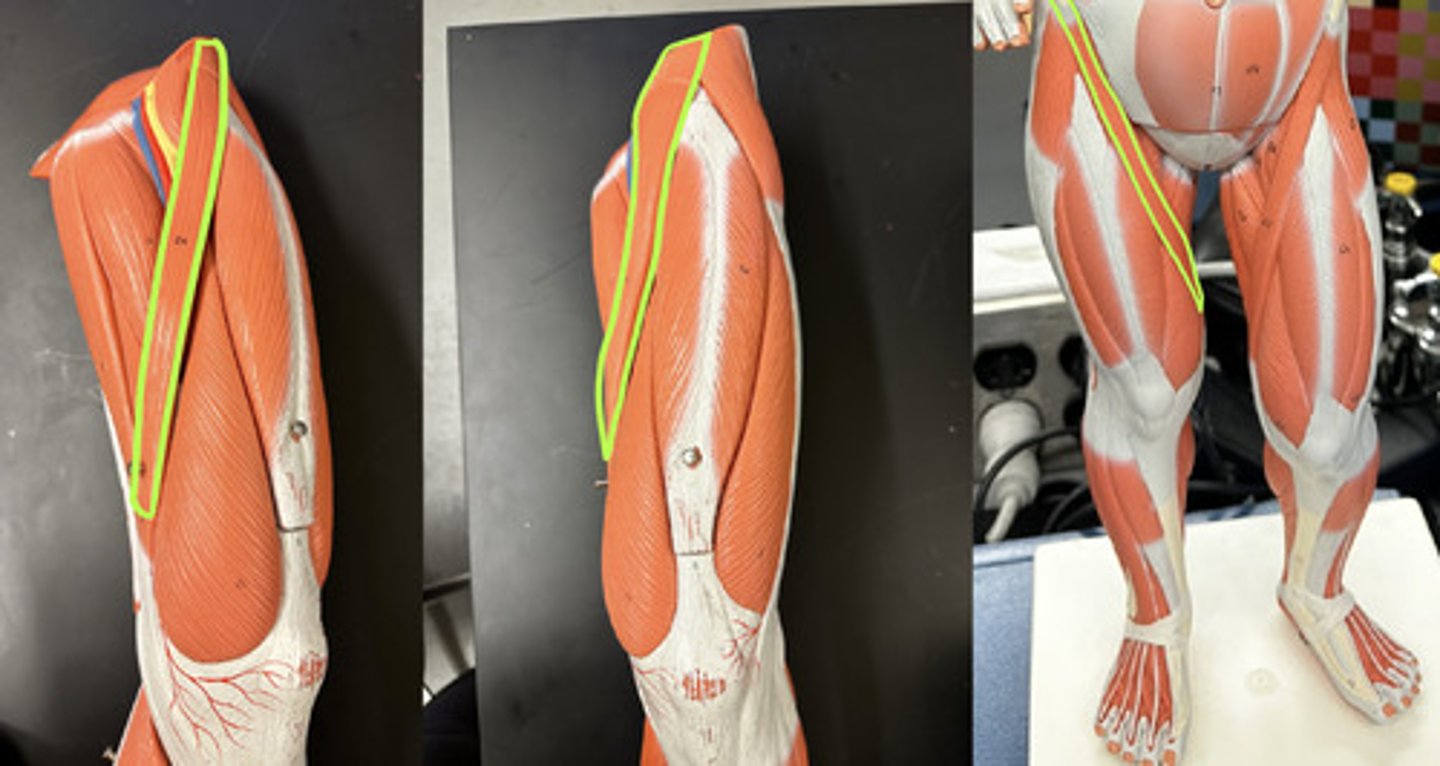
Sartorius m.
Action:
- helps with flexing, abducting, and laterally rotating thigh
- also helps flex leg
Description: Strap-like superficial muscle running obliquely across anterior surface of thigh to knee
Adductor magnus m.
Action:
- Prime mover: adduction of hip
- medically rotates thigh (result of combined actions of seven muscles)
- synergist for thigh flexion
Description:
Large muscle mass forming medial aspect of thigh; arise from front of pelvis and insert at various levels on femur
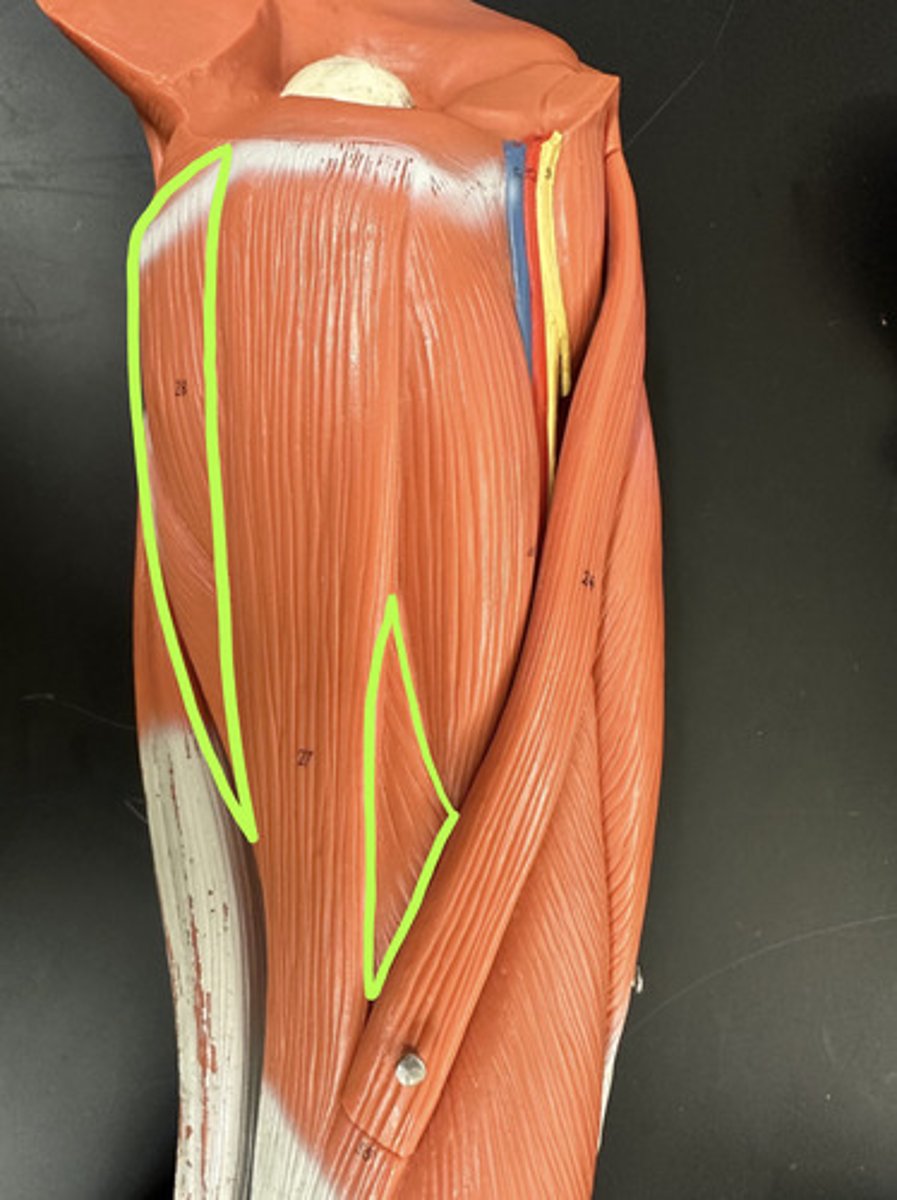
Adductor longus m.
Action:
- synergist for adduction of hip
- synergist for thigh flexion
- medically rotates thigh (result of combined actions of seven muscles)
Description:
Large muscle mass forming medial aspect of thigh; arise from front of pelvis and insert at various levels on femur
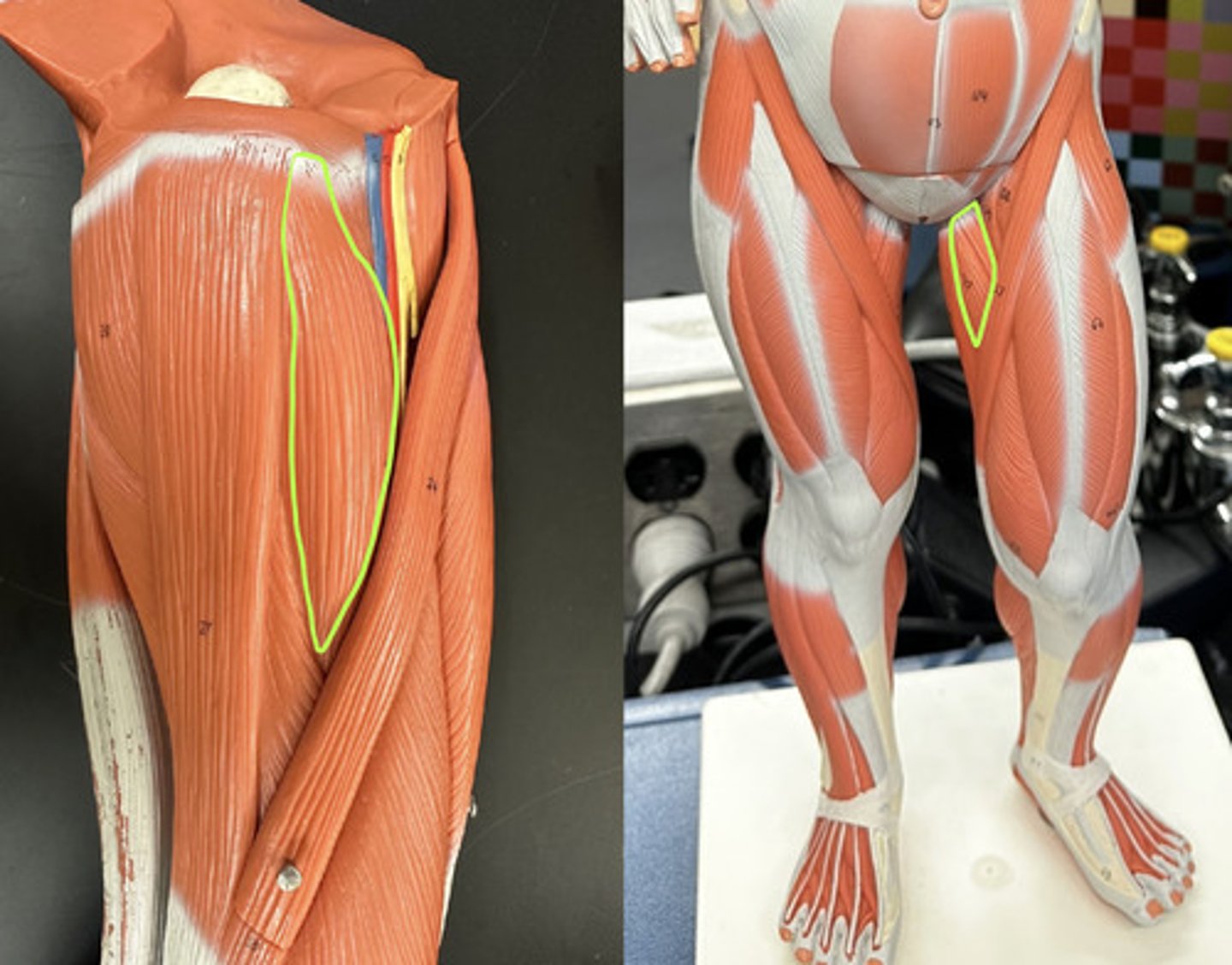
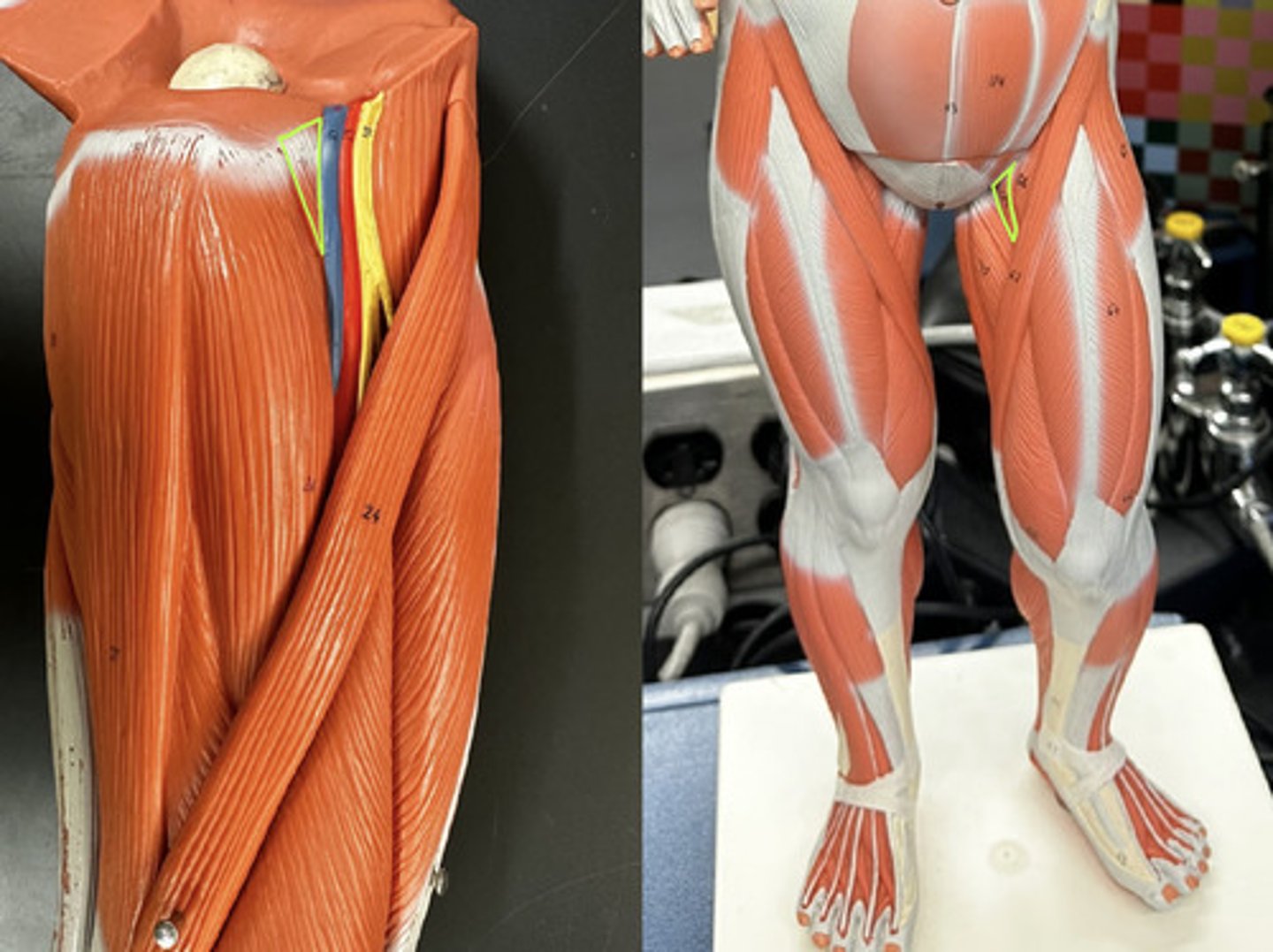
Pectineus m.
Action:
- synergist for adduction of hip
- synergist for flexion of hip
- medically rotates thigh (result of combined actions of seven muscles)
Description: Overlies adductor brevis on proximal thigh

Gracilis m.
Action:
- synergist for adduction of hip
- synergist for flexion of leg
- medially rotates leg
Description: Strap-like superficial muscle of medial thigh
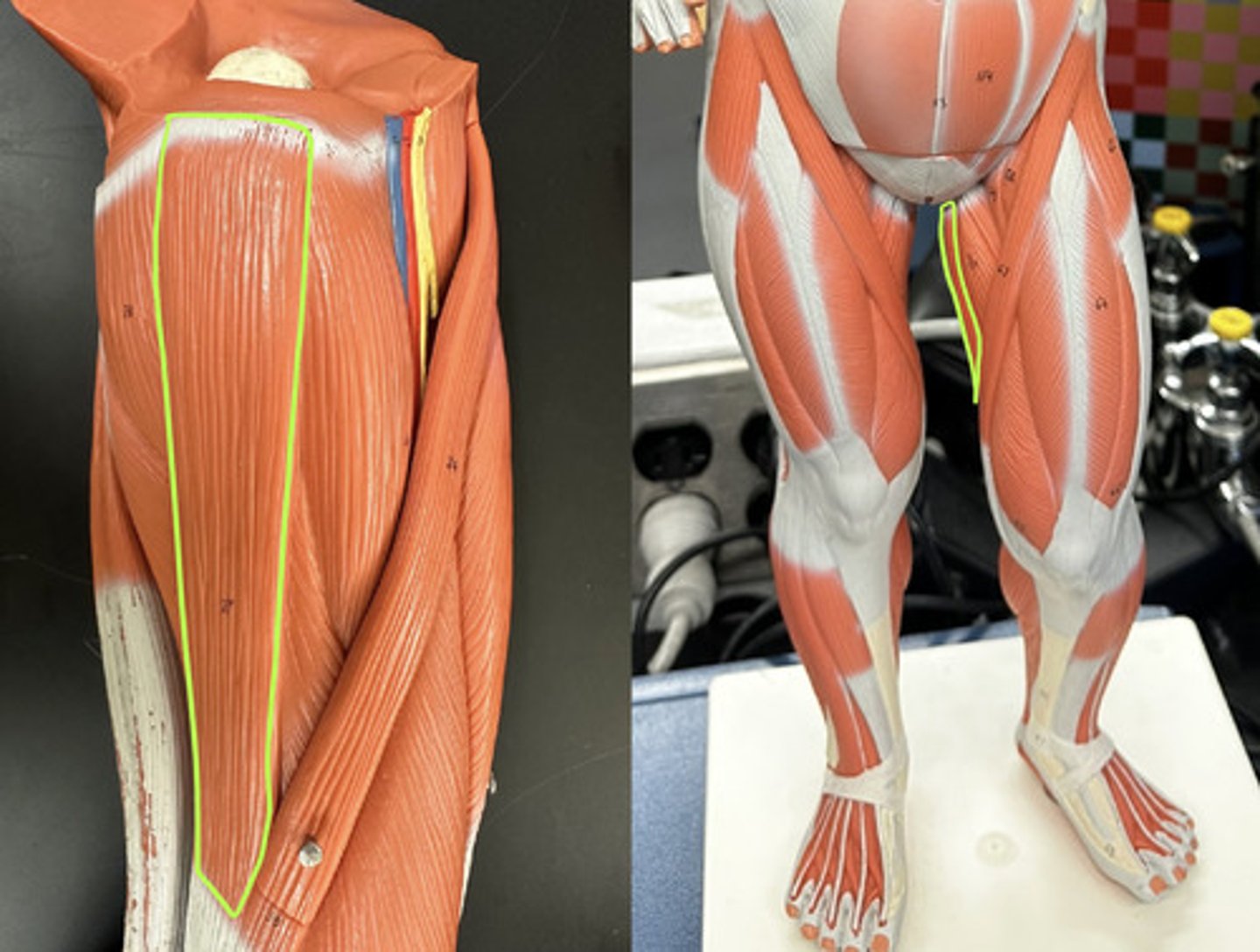
"quad" = meaning four muscle all working together
Include:
- Rectus femoris m.
- Vastus lateralis m.
- Vastus medialis m.
- Vastus intermedius
they all work together, acting on the knee, to causing extension of the knee/leg
What muscles make up the Quadriceps femoris m.?
Rectus femoris m.
Action:
- leg extension
- synergist for thigh flexion (can act on the thigh b/c its origin is on the hip bone, so it can act on the hip bone, only one of the quads that does this!)
Description: Superficial muscle of thigh; runs straight down thigh; only muscle of group to cross hip joint
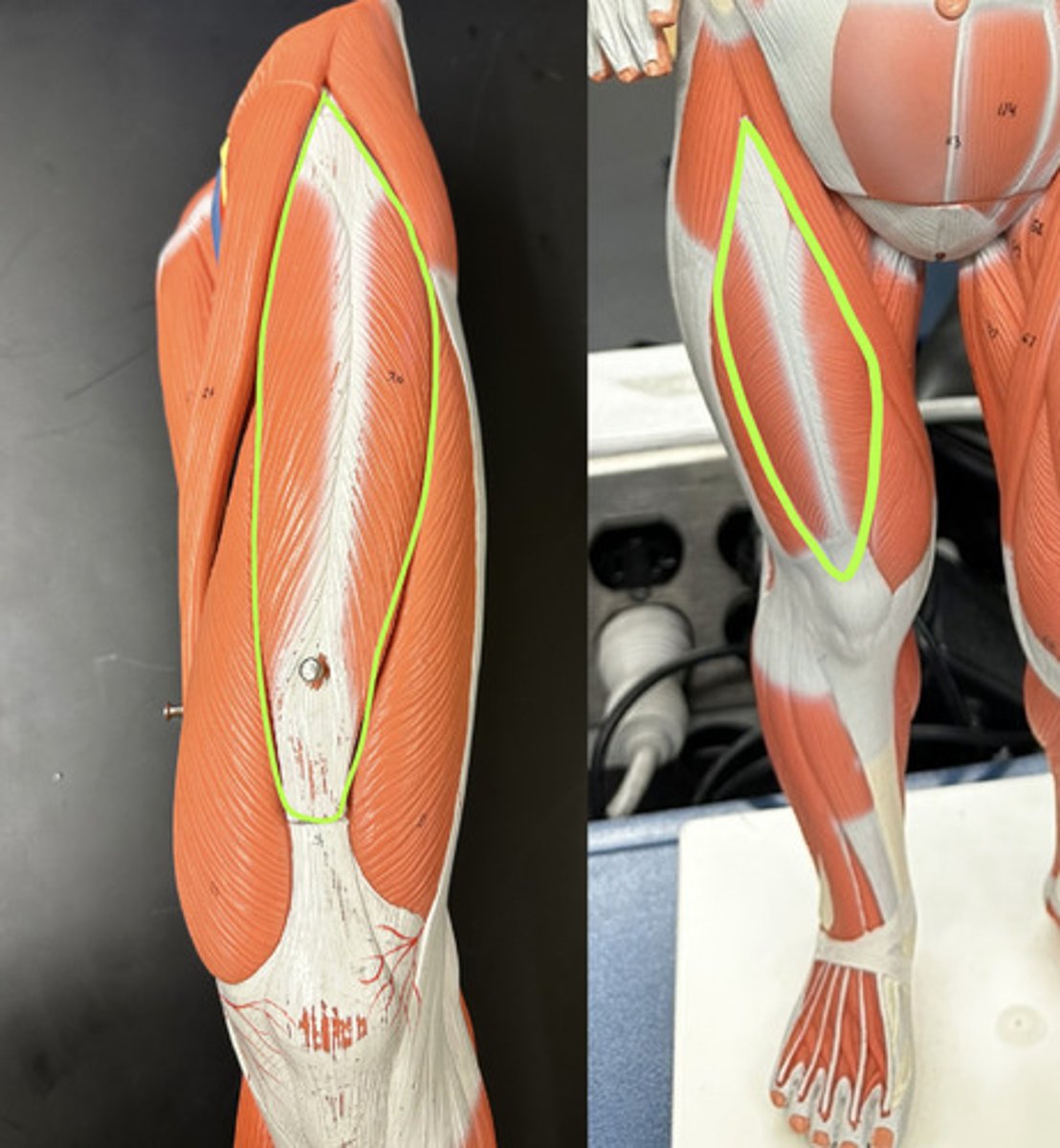
Has two tendons:
1. Straight tendon
2. Reflected tendon
Straight tendon origin = anterior inferior iliac spine
Reflected tendon = groove superior to acetabulum (or superior margin of acetabulum)
Origin of Rectus femoris m.
Two tendon insert onto tibial tuberosity of tibia
they do so via the patellar tendon to the patella (so tendon b/c muscle to bone), and then from the patella to the tibial tuberosity via the patellar ligament (so ligament b/c bone to bone)
Insertion of Rectus femoris m.
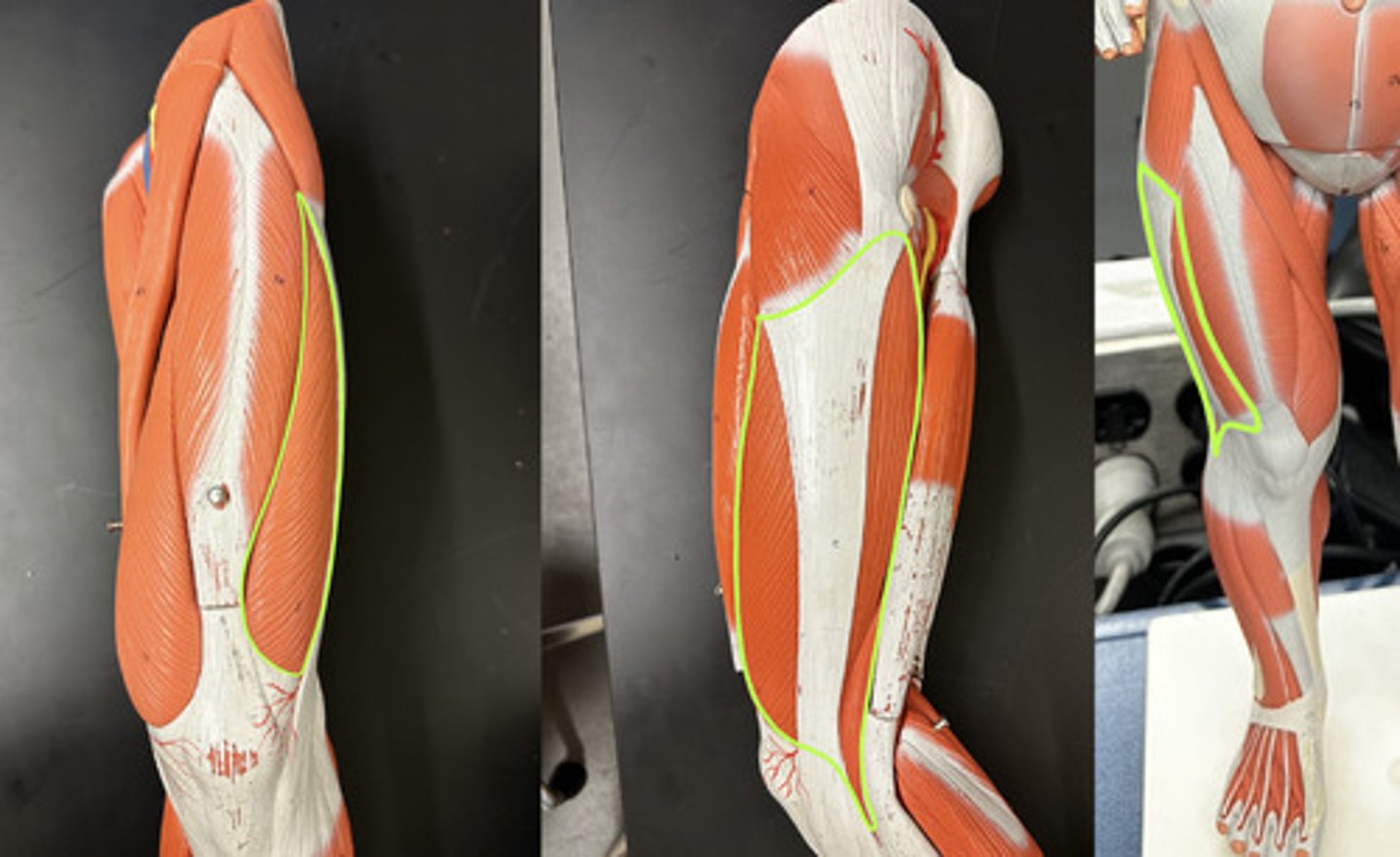
Vastus lateralis m.
Action:
- leg extension
- stabilizes knee
Description: Forms lateral aspect of thigh; intramuscular injection site
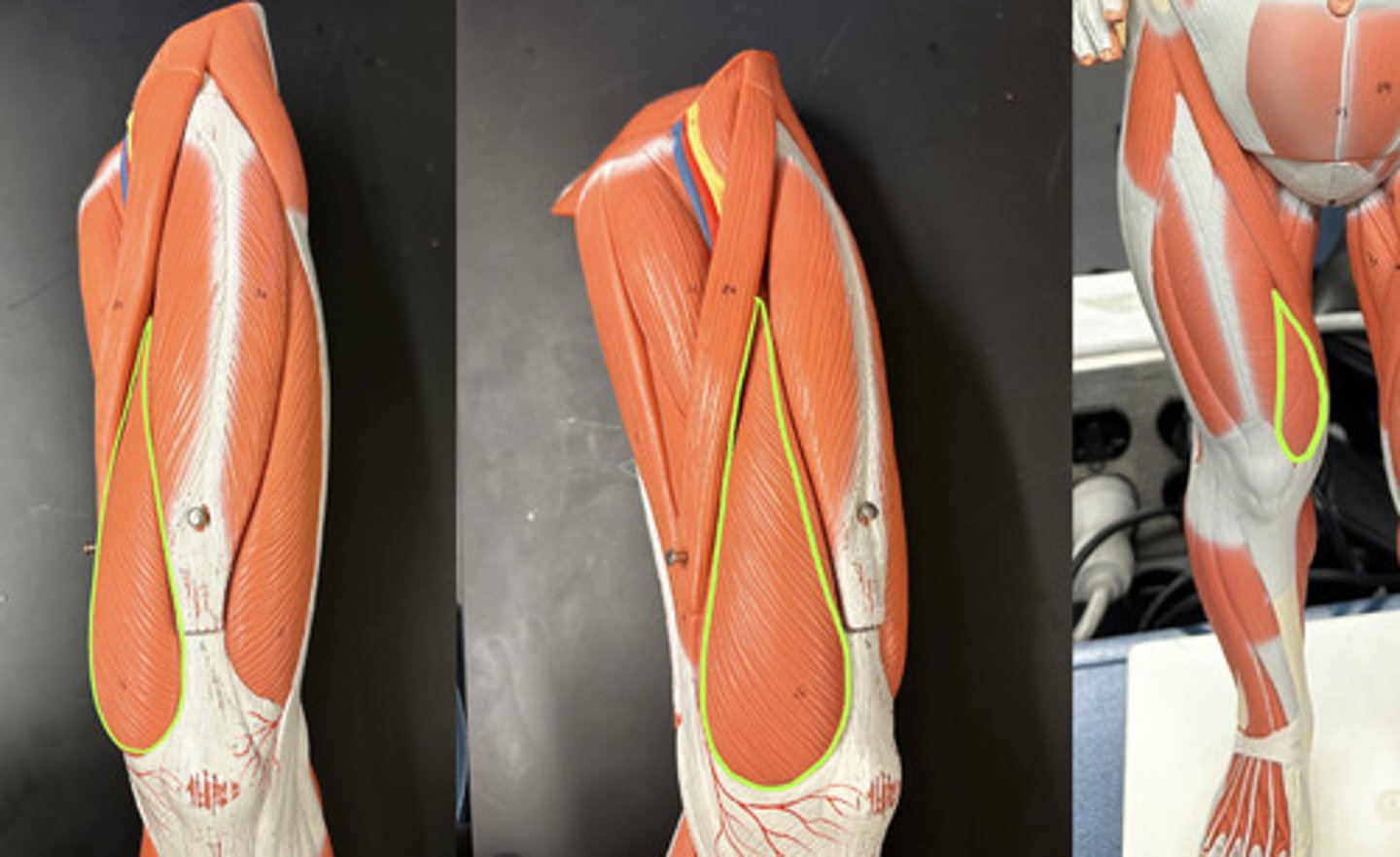
Vastus medialis m.
Action:
- leg extension
- stabilizes patella
Description: Forms inferomedial aspect of thigh
Vastus Intermedius m.
Action:
- leg extension
Description: obscured by rectus femoris; lies between vastus lateralis and vastus medialis on anterior thigh
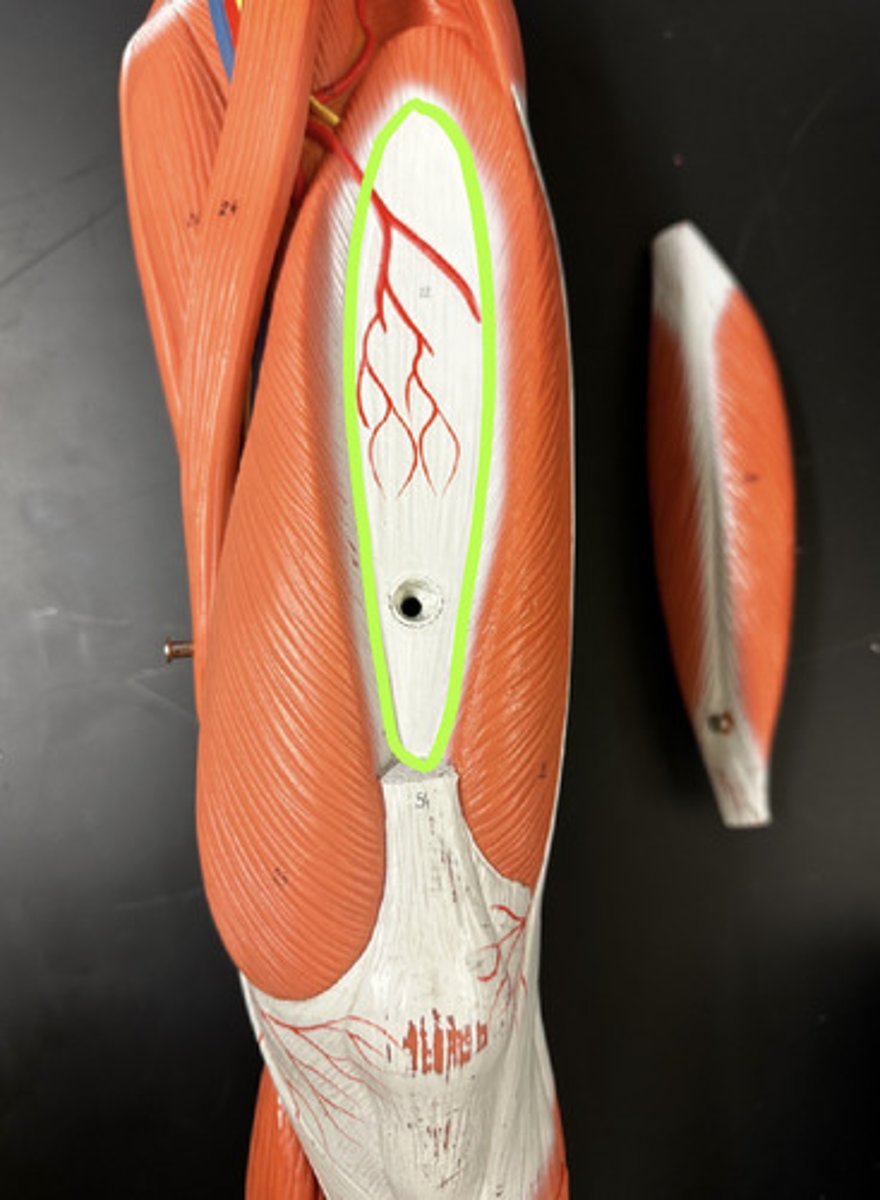
Tensor fasciae latae m.
Action:
- steadies trunk
- synergist in abduction of the hip
- medial rotation of hip (result of combined actions of seven muscles)
- synergist in hip flexion
Description: enclosed between fascia layers of thigh
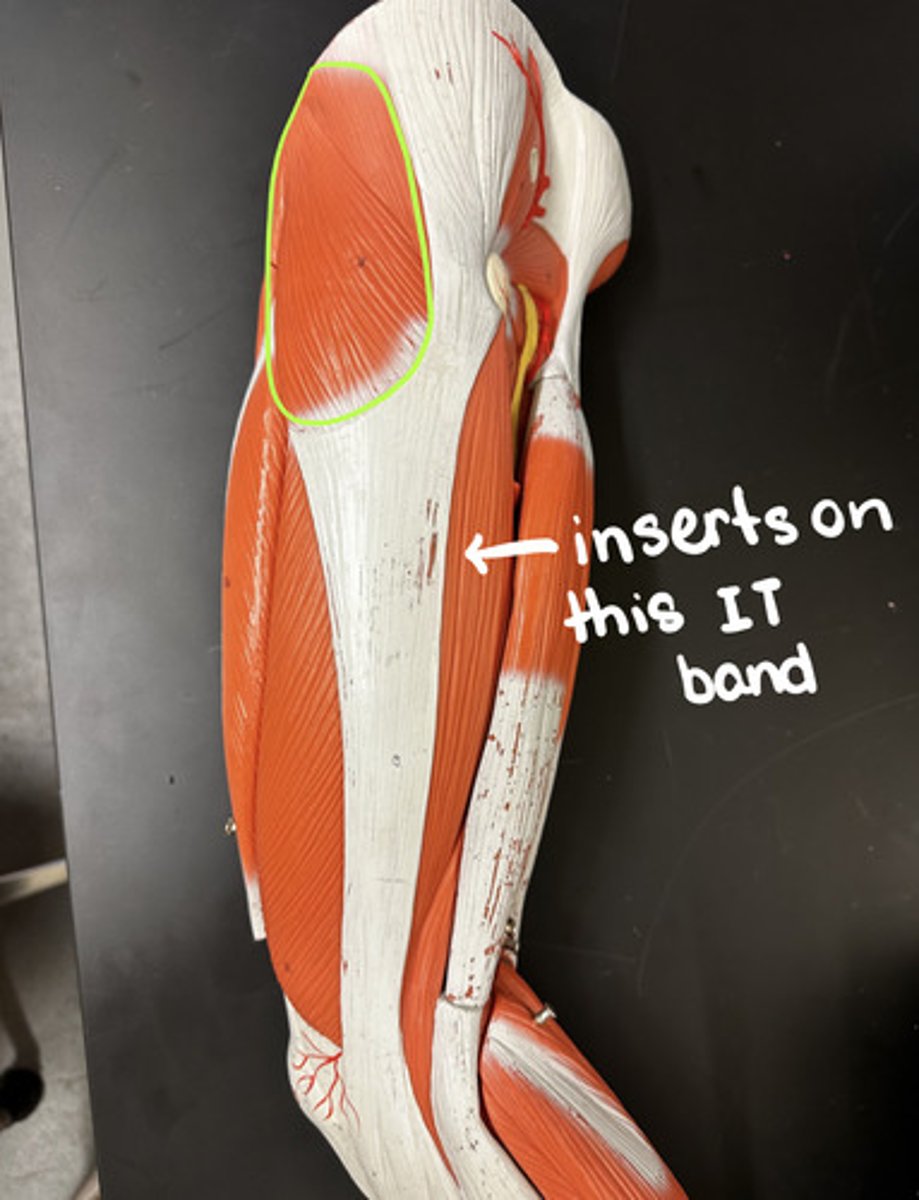
Gluteus maximus m.
Action:
- prime mover: hip extension
Description: largest and most superficial of gluteal muscles (which form buttock mass); intramuscular injection site
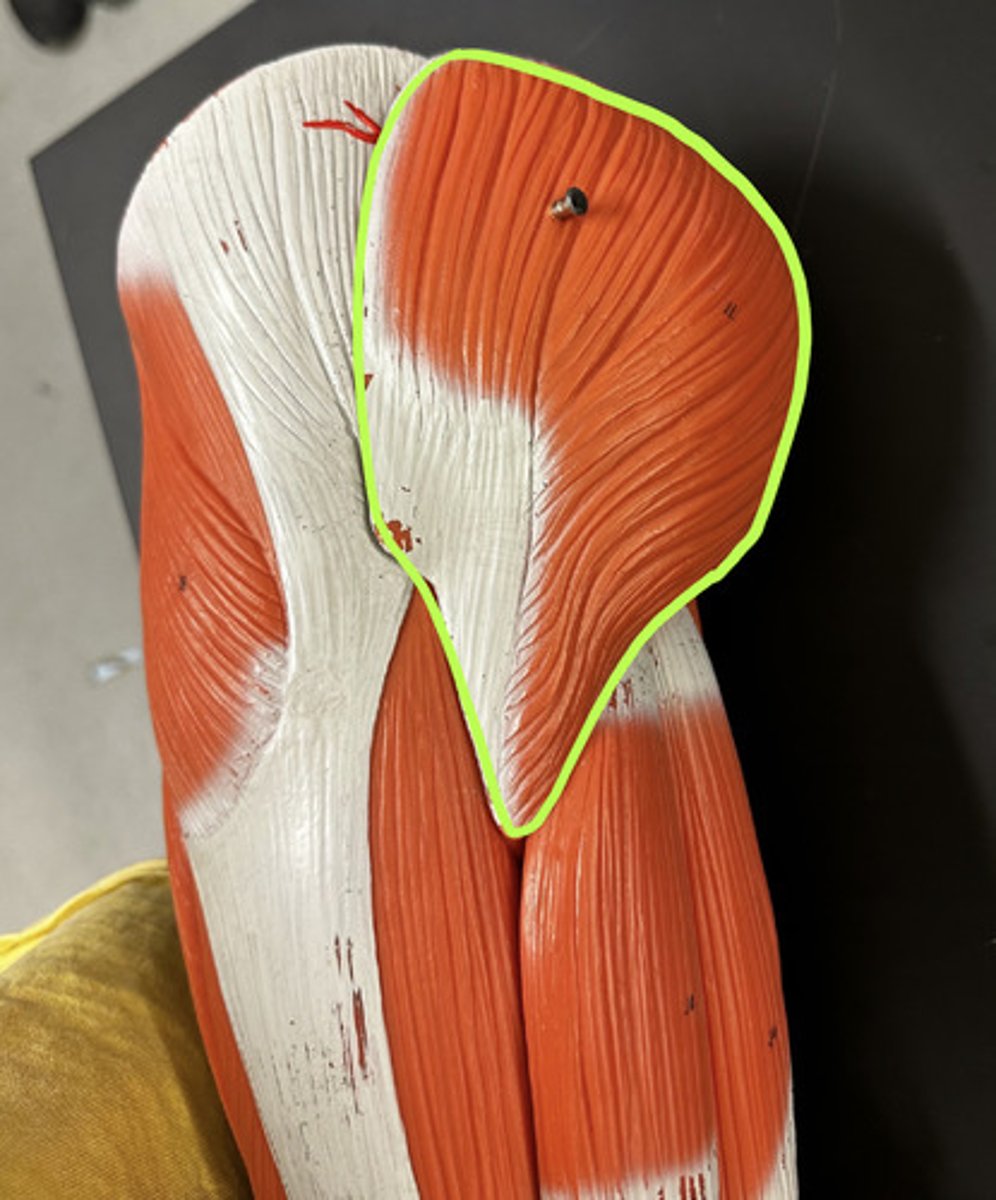
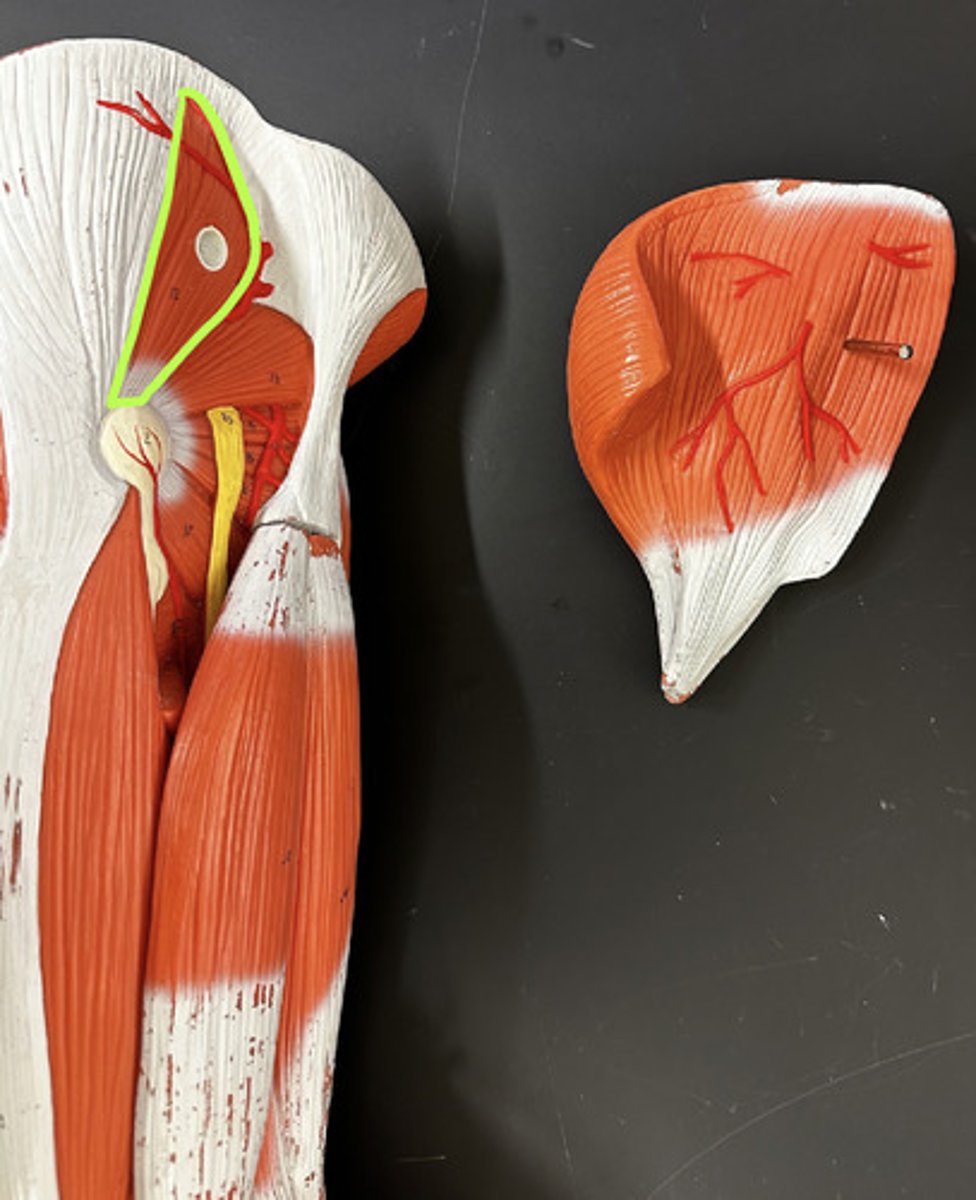
Gluteus medius m.
Action:
- prime mover: hip abduction
- medial rotation of hip (result of combined actions of seven muscles)
Description: partially covered by gluteus maximus; intramuscular injection site
Group of 3 muscles (one muscle has 2 heads, and all the others have 1 head → so you can actually think of the hamstrings as 4 muscles)
Include:
- Biceps femoris m. (two heads!)
- Semitendinosus m.
- Semimembranosus m.
they all work together, acting on the knee, to causing flexion of the knee/leg
What muscles make up hamstrings?
Biceps femoris m.
Action:
- leg flexion
- synergist in extension of hip/thigh
Description: most lateral muscle of group; arises from two heads
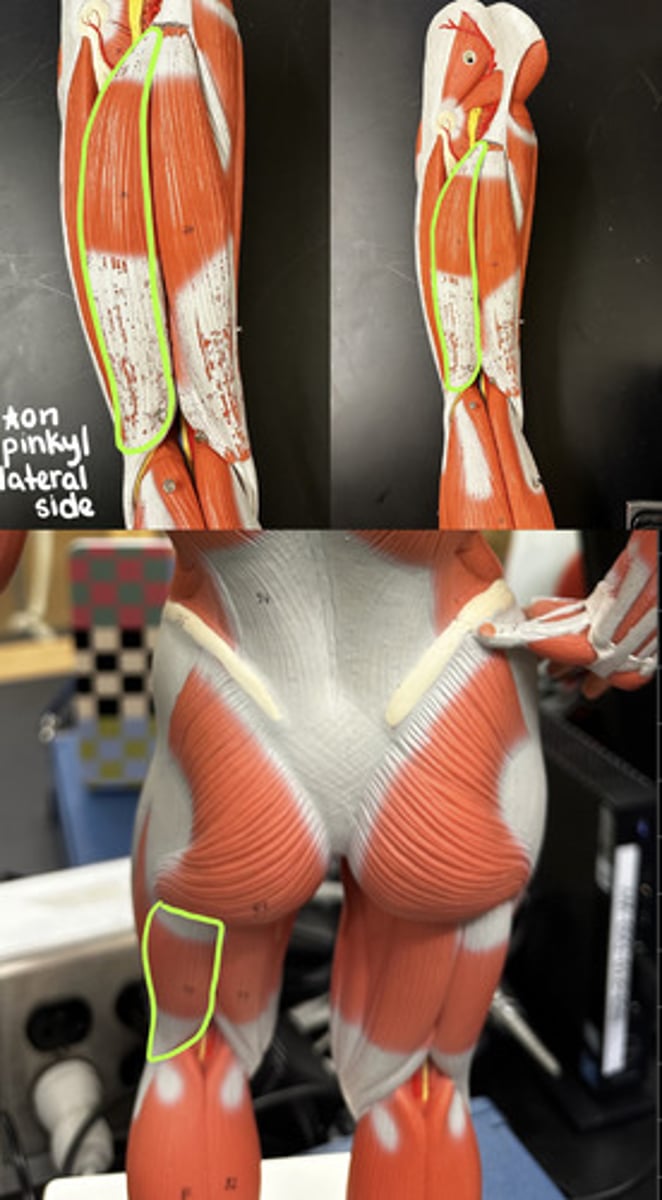
Has two heads:
1. Long head
2. Short head
Long head origin = ischial tuberosity of ischium
Short head origin = linea aspera of femur and distal femur
Origin of Biceps femoris m.
Inserts on head of fibula and lateral condyle of tibia
comes down on side of knee, so that it can act on knee!
(keep in mind: fibula non-weight bearing, so only function is muscle attachment)
Insertion of Biceps femoris m.
Semitendinosus m.
Action:
- synergist in thigh extension
- flexes leg
Description: medial to biceps femoris
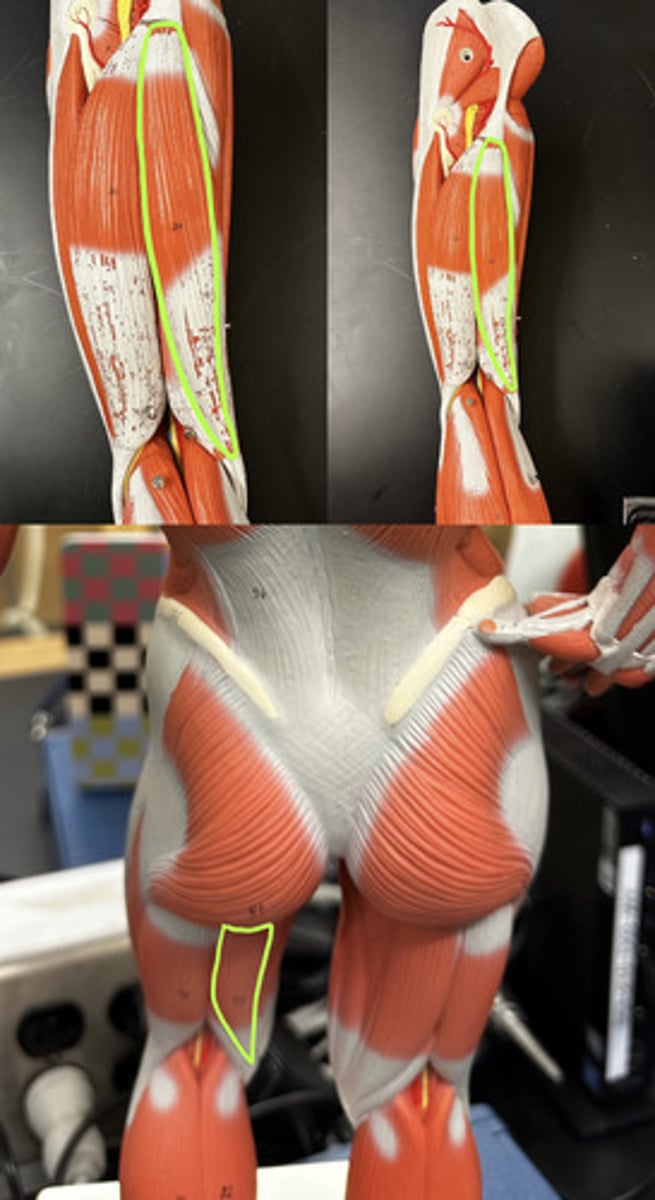
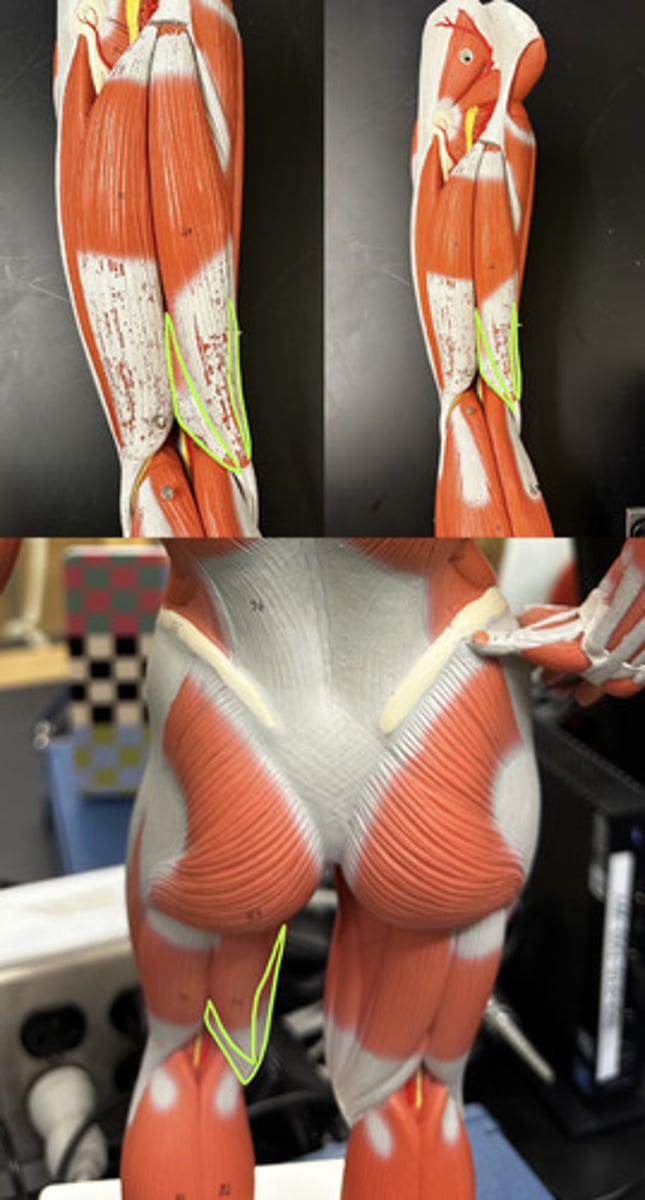
Semimembranosus m.
Action:
- synergist in thigh extension
- flexes leg
Description: deep to semitendinosus m.
It is composed of muscle on the posterior portion of the leg
These muscles then flex the toes/digits
(specifically flexing the toes, because ankle only flexes and does not extend, so when we talk about flexion and extension we aren't talking about ankle joint b/c it can't extend, but the toes can extend and flex!)
Thus, curling toes inward is flexion and the result of the muscles on the posterior portion of the leg
What is the leg flexor compartment composed of?
It is composed of muscle on the anterior portion of the leg
These muscles then extend the toes/digits
(specifically flexing the toes, because ankle only flexes and does not extend, so when we talk about flexion and extension we aren't talking about ankle joint b/c it can't extend, but the toes can extend and flex!)
Thus, lifting toes up is flexion and the result of the muscles on the anterior portion of the leg
What is the leg extensor compartment composed of?
Gastrocnemius m.
Action:
- prime mover: plantar flexes foot
Description: superficial muscle of pair; two prominent bellies
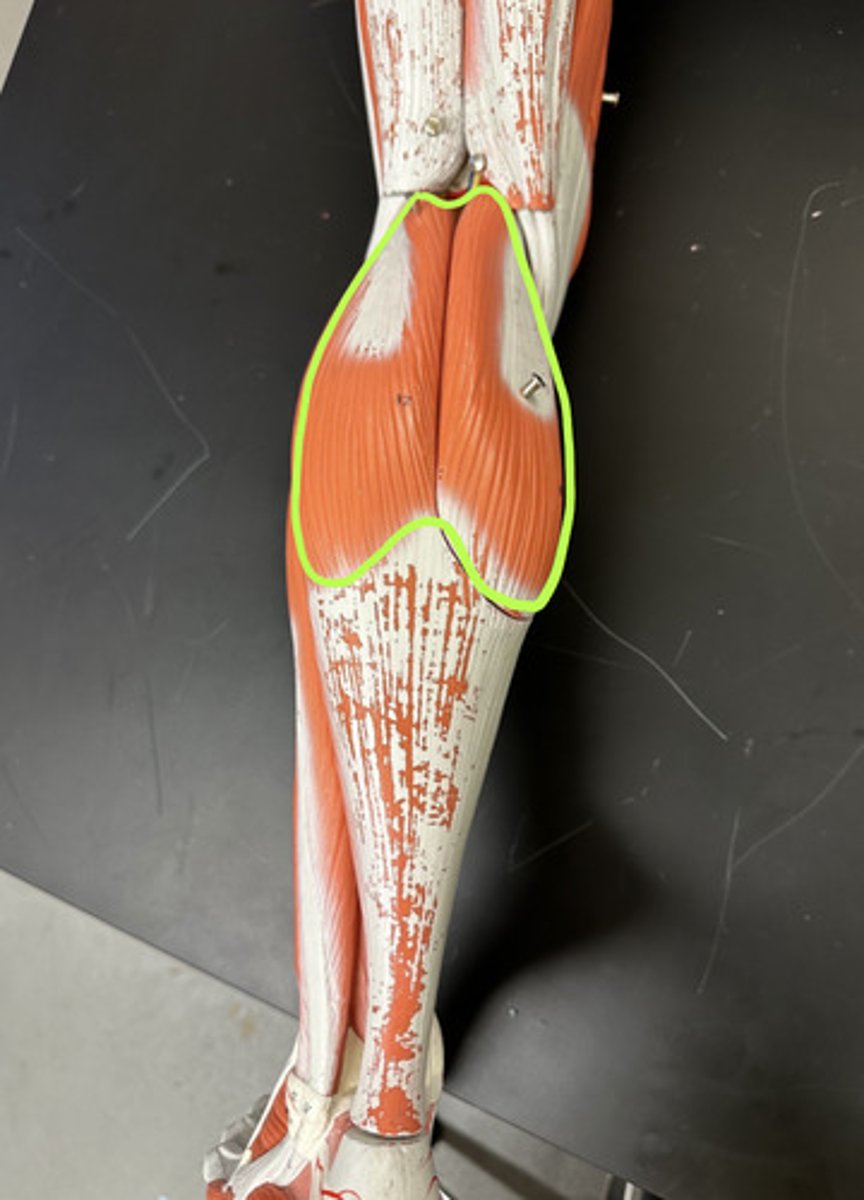
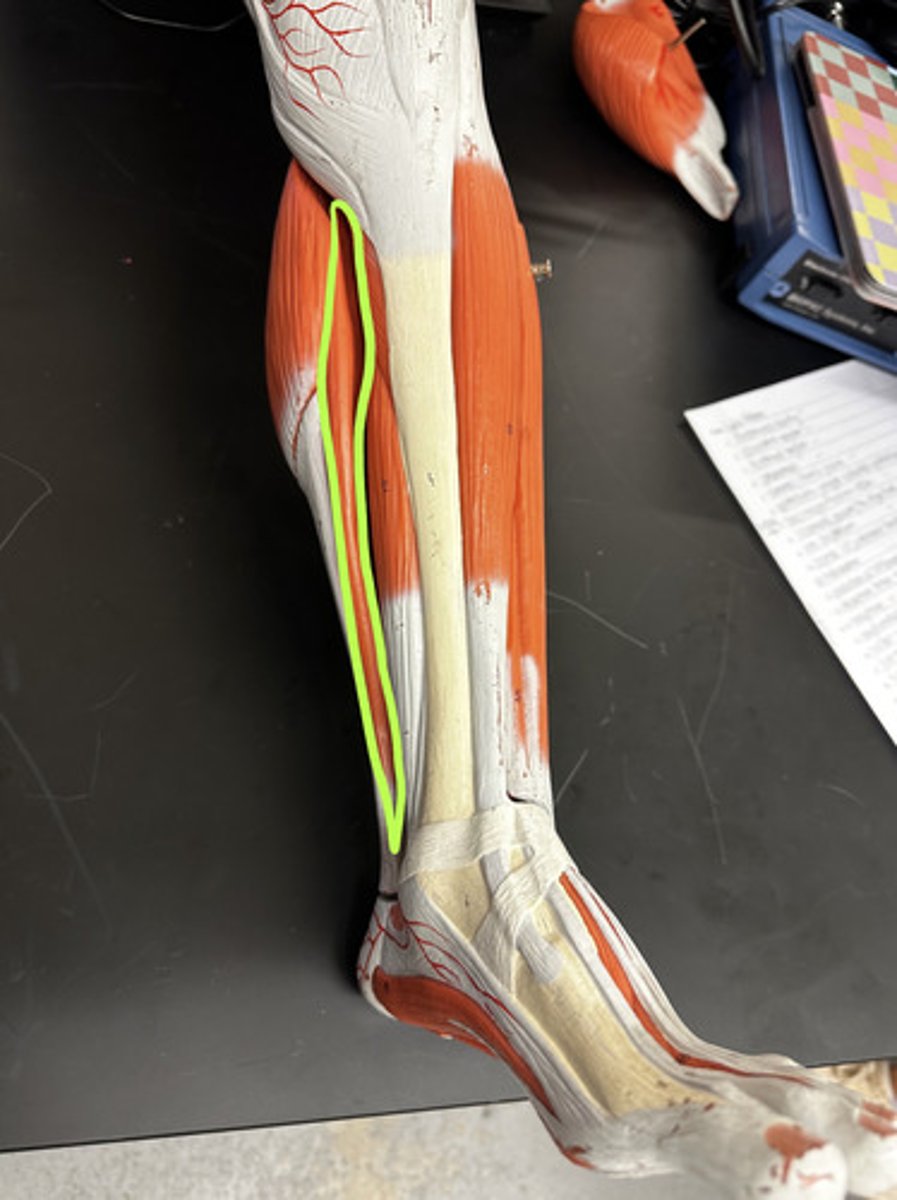
Soleus m.
Action:
- prime mover: plantar flexes foot
Description: deep to gastrocnemius m.
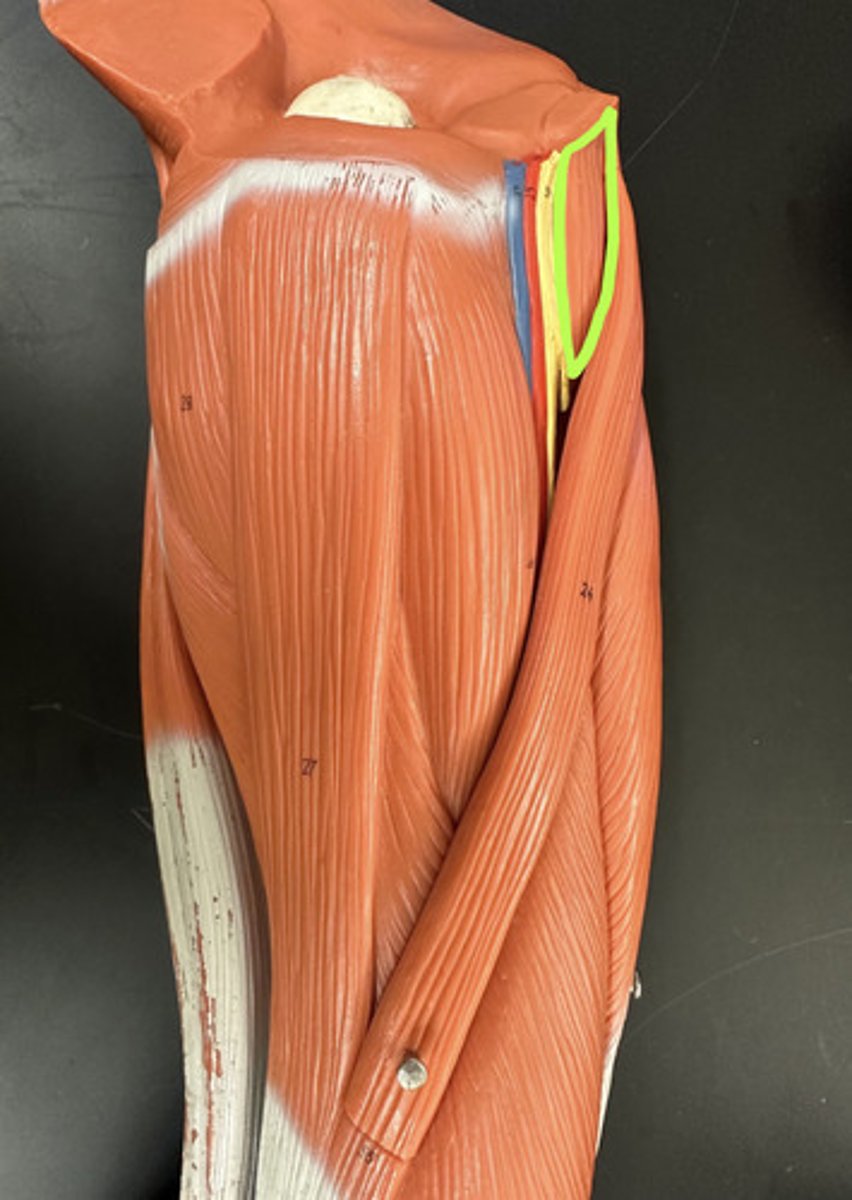
It is a two-headed flexor muscle
1. Long head
2. Short head
Long head origin = supraglenoid tubercle and lip of glenoid cavity on scapula
Short head origin = coracoid process of scapula
What is the origin of Biceps brachii m.?
Two-headed muscle inserts by a common tendon onto the radial tuberosity of radius
Radius on lateral side of forearm, so bicep crosses elbow to get to radial tuberosity, meaning it will act on elbow causing elbow/forearm flexion and supination
What is the insertion of Biceps brachii m.?
Tibialis anterior m.
Action:
- Prime mover: dorsiflexion
Description: superficial muscle of anterior leg; parallels sharp anterior margin of tibia
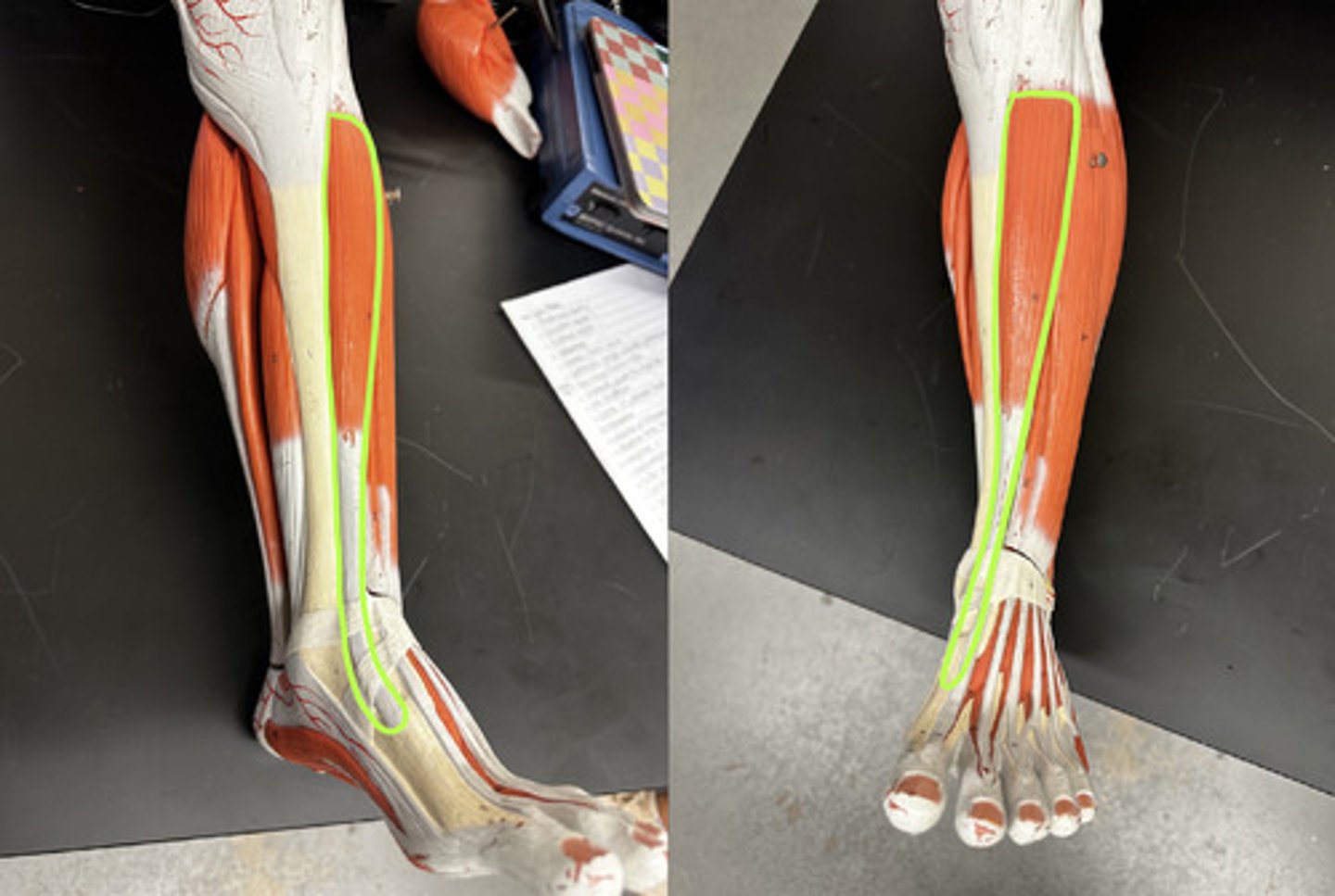
Originates on:
1. Lateral condyle of tibia
2. Upper 2/3 of tibia
3. Interosseus membrane (piece of CT between tibia and fibula , it helps connect the two bones together and stabilize them)
What is the origin of Tibialis anterior m.?
Insertes on:
1. inferior surface of medial cuneiform
2. metatarsal I
This means the muscle will be move ankle, b/c it crosses over it
What is the insertion of Tibialis anterior m.?