Chapter XIX: The Gravitational Field
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
theres an equation in this chapter that i need to put on my cheat sheet- its not in these flashcrad s
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Why does modern physics reject the idea of action at a distance for gravitational force?
Because all forces are now understood to operate through fields, not direct contact across empty space.
What is a gravitational field?
A physical field created by a mass (like Earth) that causes other masses to accelerate toward it.
How does a gravitational field relate to the motion of a falling object?
The field causes the object to accelerate, rather than the Earth pulling it directly.
How does the strength of the gravitational field change with distance?
It diminishes with distance, following a definite law (like Newton’s inverse square law).
What unique property distinguishes gravitational fields from electromagnetic ones?
The acceleration they cause is independent of the body’s material or physical state.
What does it mean that all objects fall the same in a gravitational field (in vacuum)?
Their acceleration is identical, regardless of mass or composition—this is the equivalence principle in action.
According to Newton’s law, how is force related to mass and acceleration?
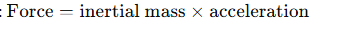
According to gravitational theory, how is force related to the gravitational field?
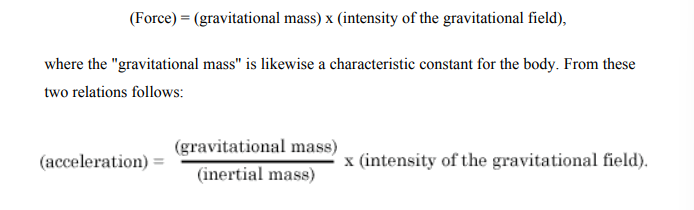
What must be true if all bodies accelerate the same in a gravitational field?
Gravitational mass must equal inertial mass for all bodies.
What important equivalence does Einstein draw from gravitational and inertial mass being equal?
That inertia and weight are manifestations of the same property of matter.