Biology Cell Structure Quiz
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Organelles
All cells have those four structures, but eukaryotic cells also have membrane-bound organelles
Organelles = "little organs"
Specialized structures within the cell that work together to help the cell function and survive
Organelles have different functions
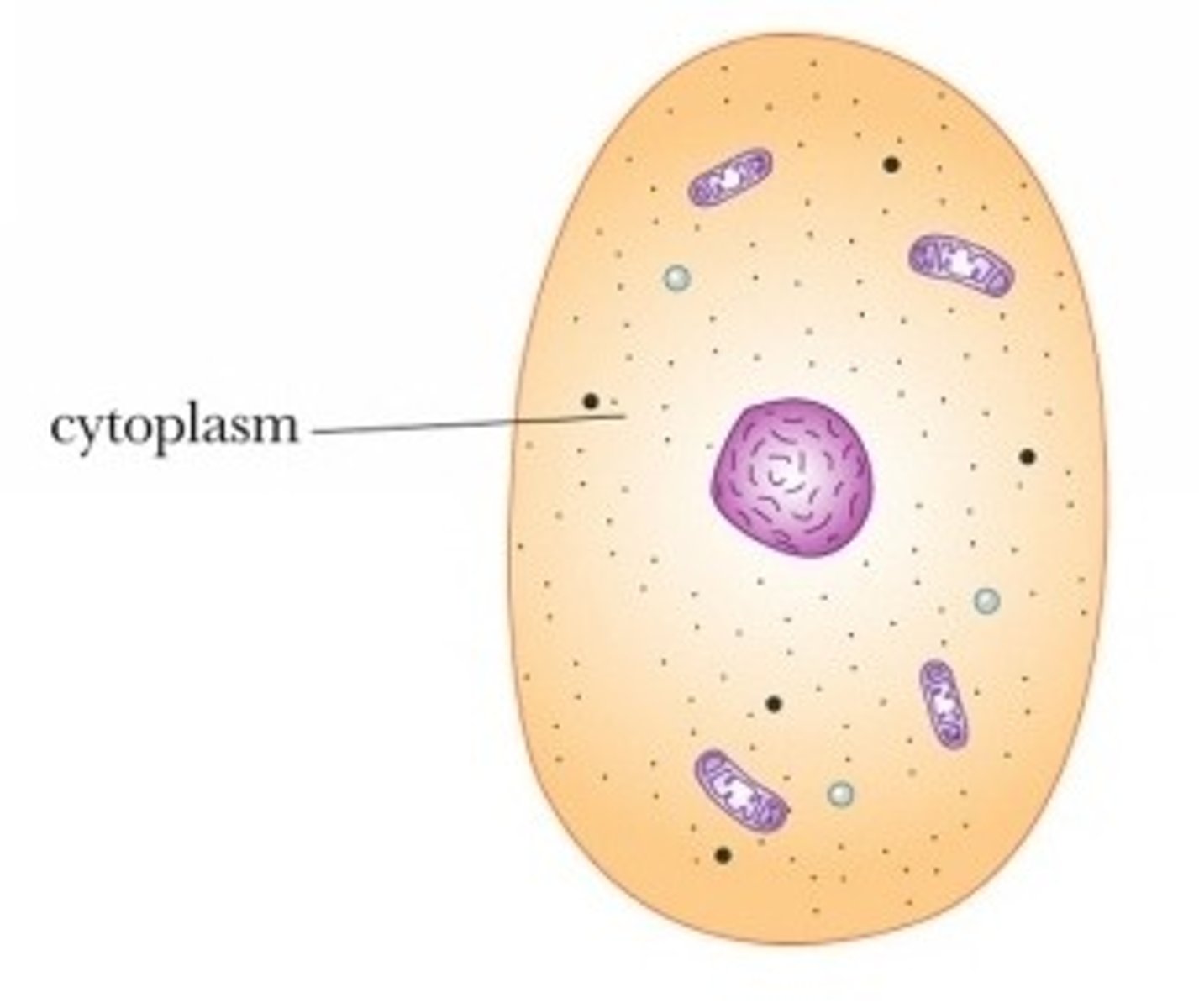
Cytoplasm
Structure
Jelly like substance
Mainly made up of water
Function
Holds everything in place
- It is all the empty space / filling
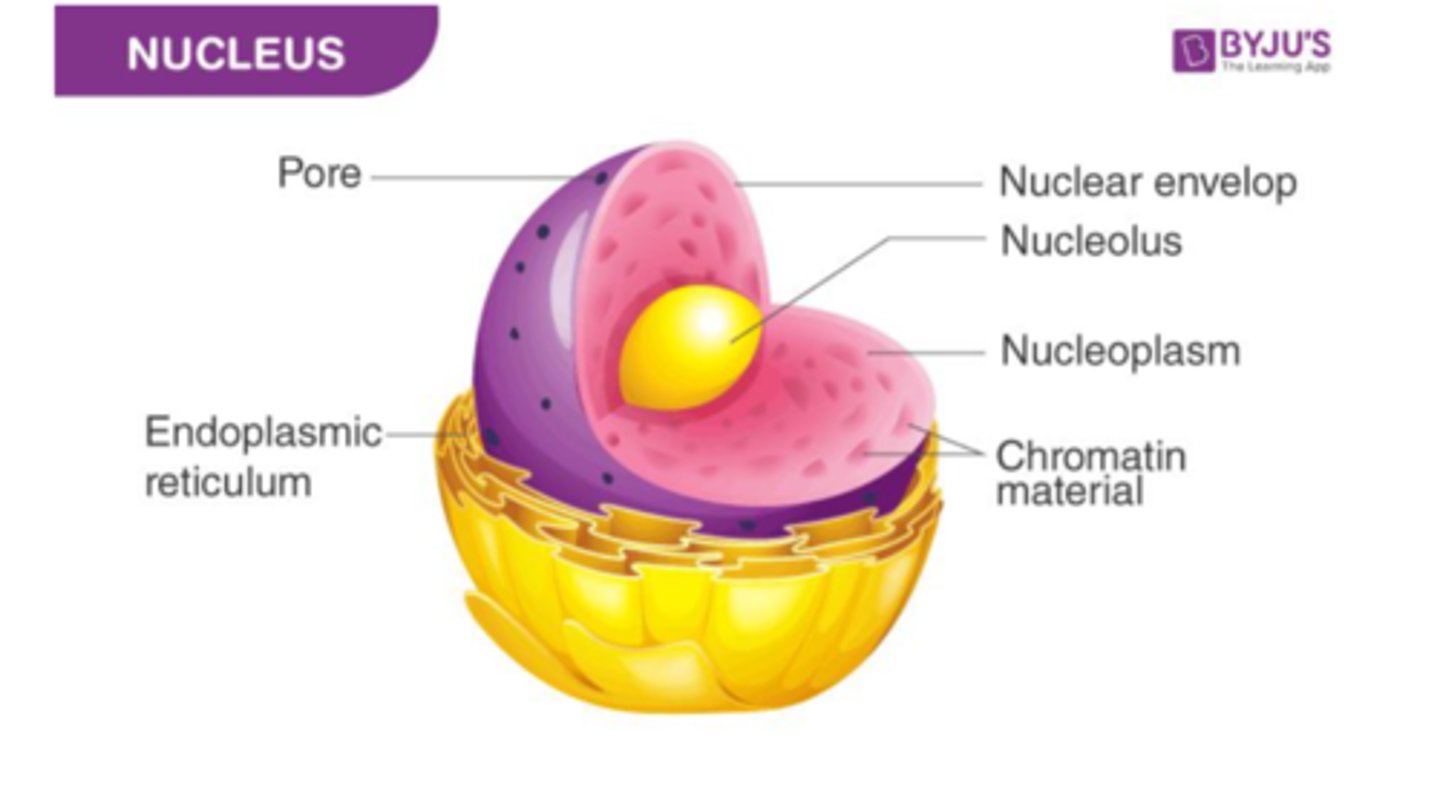
Nucleus
Structure
Contains genetic material (DNA stored as chromatin)
Chromatin looks like spaghetti
Only switches form to chromosomes in the last 10% of its life (during mitosis)
Surrounded by nuclear envelope / membrane with pores that control what goes in and out
Function
Protect the DNA that controls the activities of the cell
Controlling protein production
ONLY RNA CAN LEAVE NUCLEUS, NOT DNA
Nucleolus
Structure
Inside the nucleus
Function
Makes rRNA, which makes up ribosomes
Without nucleolus, no ribosomes => no proteins
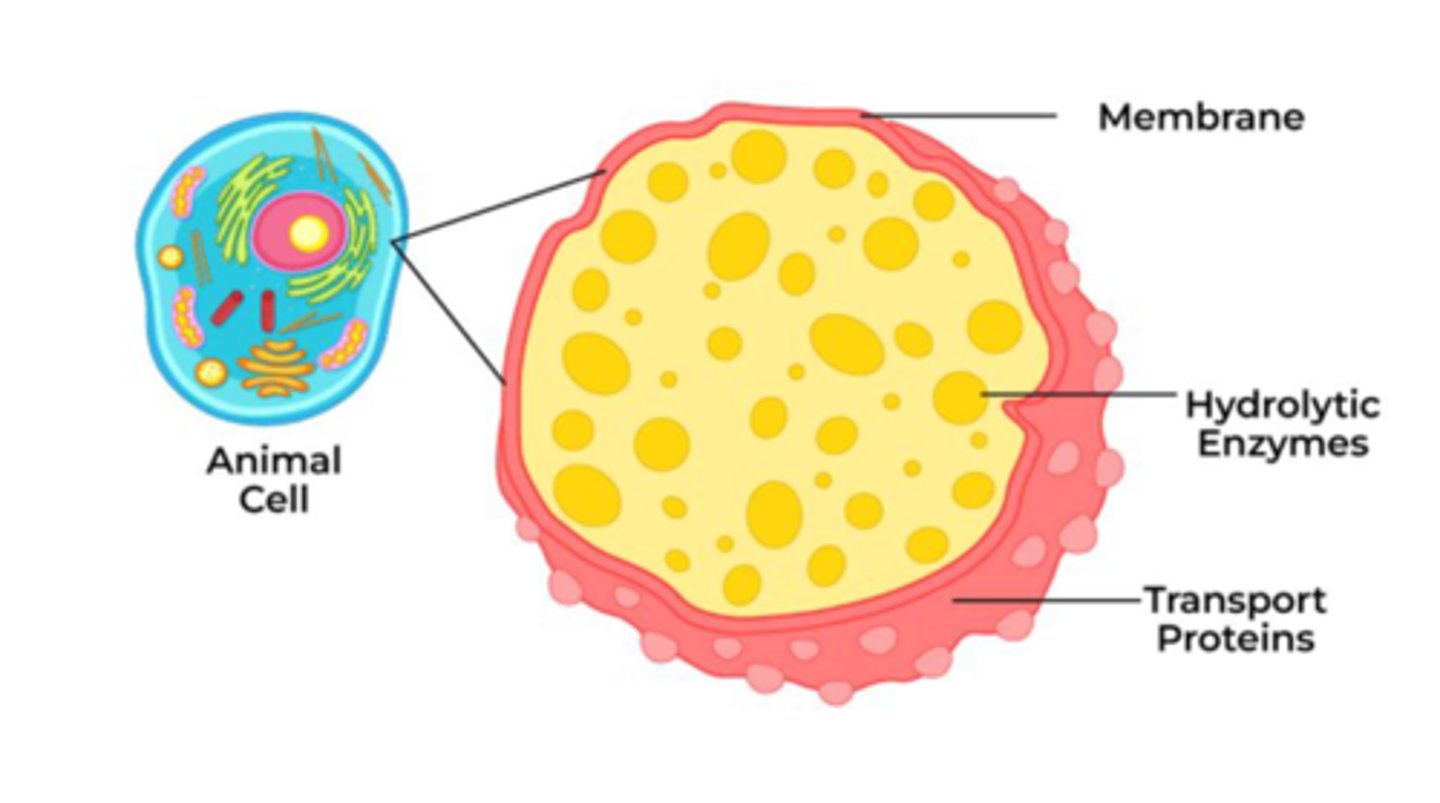
Lysosomes
Structure
Contains enzymes
Organic catalyst that speeds up chemical reactions
Functions
Break down dead materials (food, bacteria, old parts of the cell, etc.)
Clean-up system
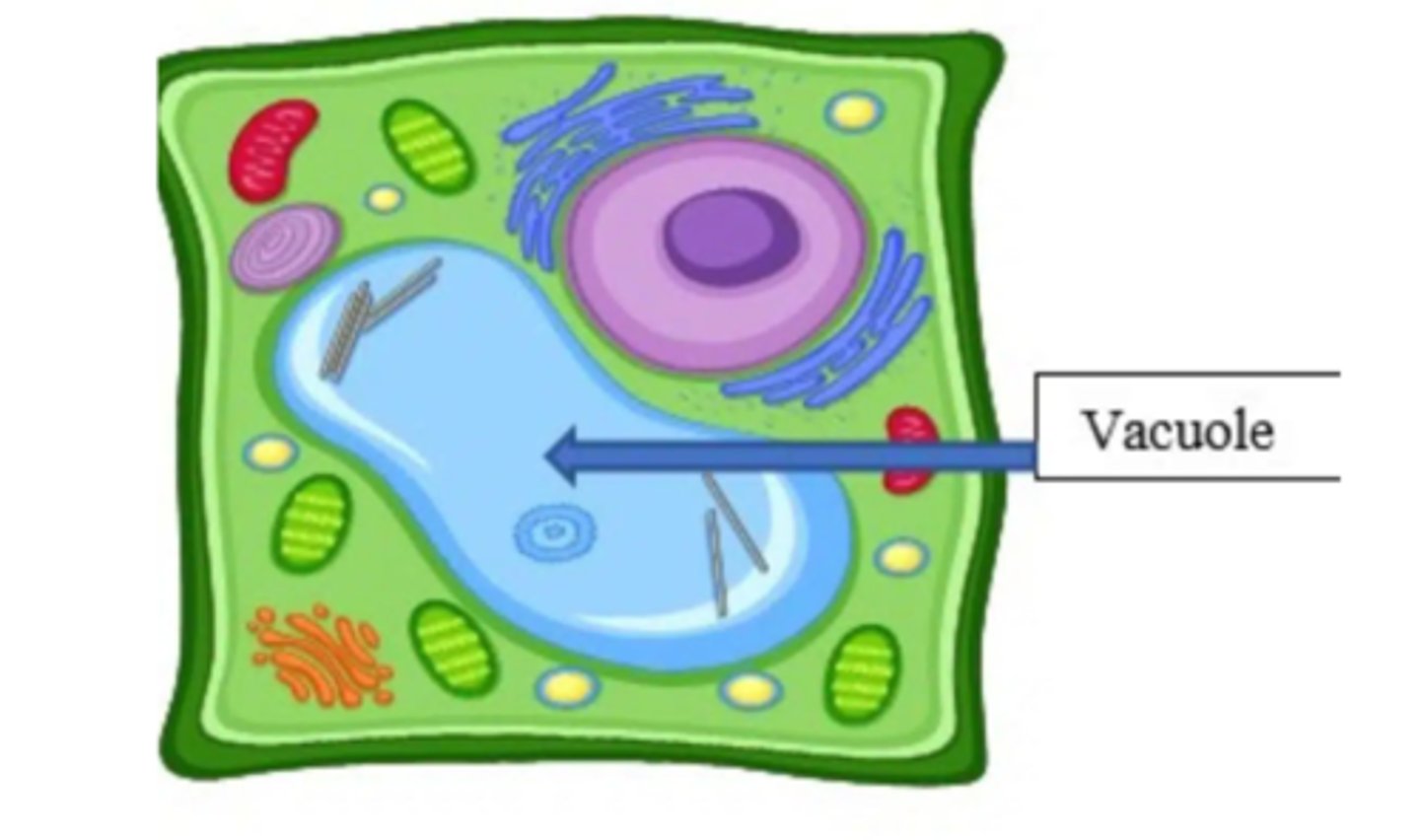
Vacuoles
Structure
Small and numerous in animal cells
One large central one in plant cells
Function
Storage (water, nutrients, waste, etc.)
Central Vacuole
PLANT CELLS ONLY
Structure
Massive central structure
Function
Storage center (mostly water & nutrients)
Pressure increases rigidity
Folds in on itself
Pressure inside central vacuole goes down => loses rigidity
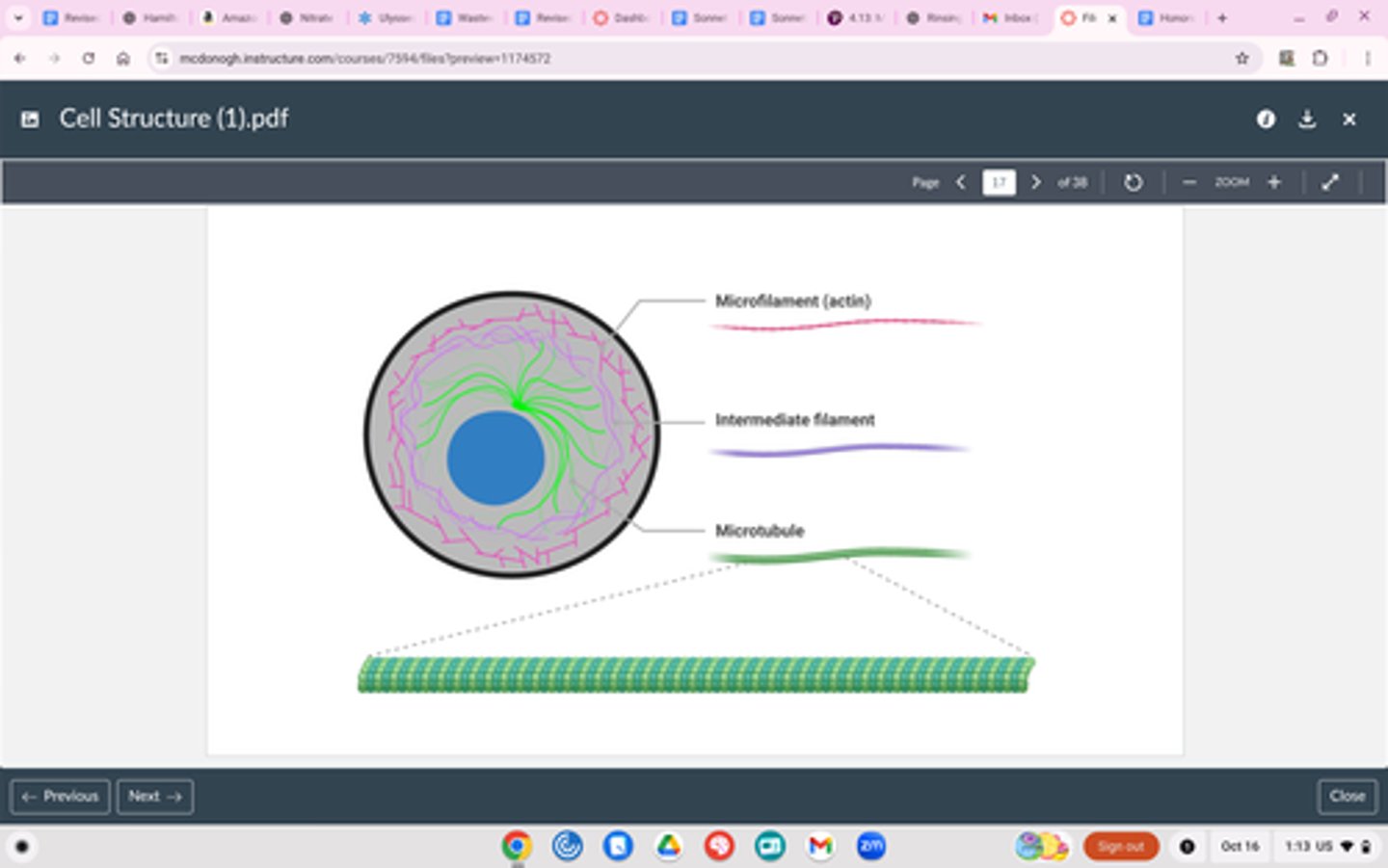
Cytoskeleton
Structure
Thread-like fibers (Microtubules, Actin filaments, and more)
Made of proteins
Usually not pictured in cell diagrams
Function
Gives cell shape
Ability to move organelles around
Provide structural support for animal cells that don’t have cell walls
Centrioles / Centrasomes
ANIMAL CELLS ONLY
Structure
Made of microtubules
Function
Appear during cell division
Help cell divide by pulling chromosomes apart
Fishing rods connected to chromosomes that reel them apart
Mitosis and miosis
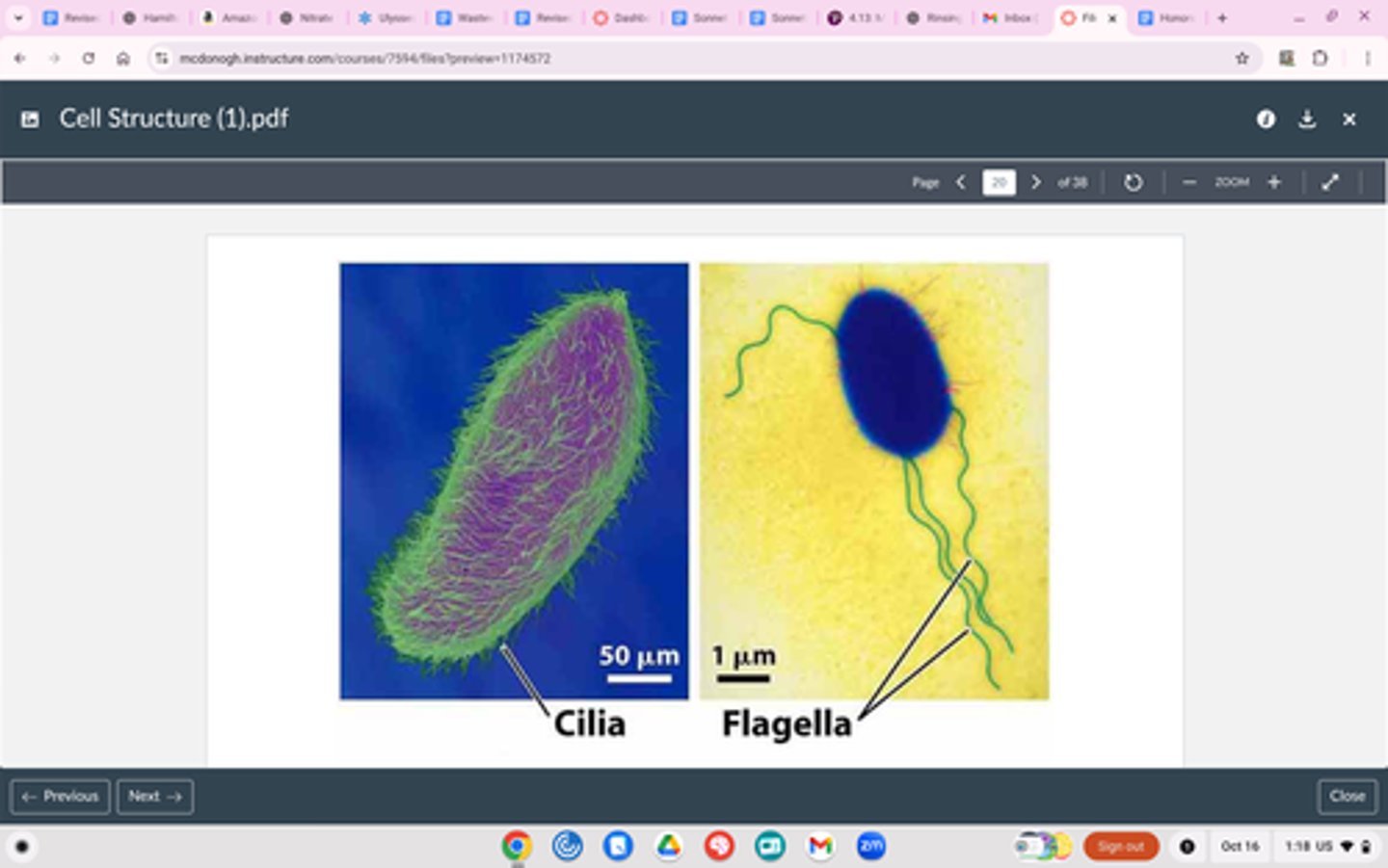
Cilia and Flagella
Structure
Cilia: shorter, more numerous, hair like structures
Flagella: longer and fewer tail-like structures (1-3)
Outside cell surface (both)
Function
Cilia: Move fluid across cell surface
Flagella: Move entire cell
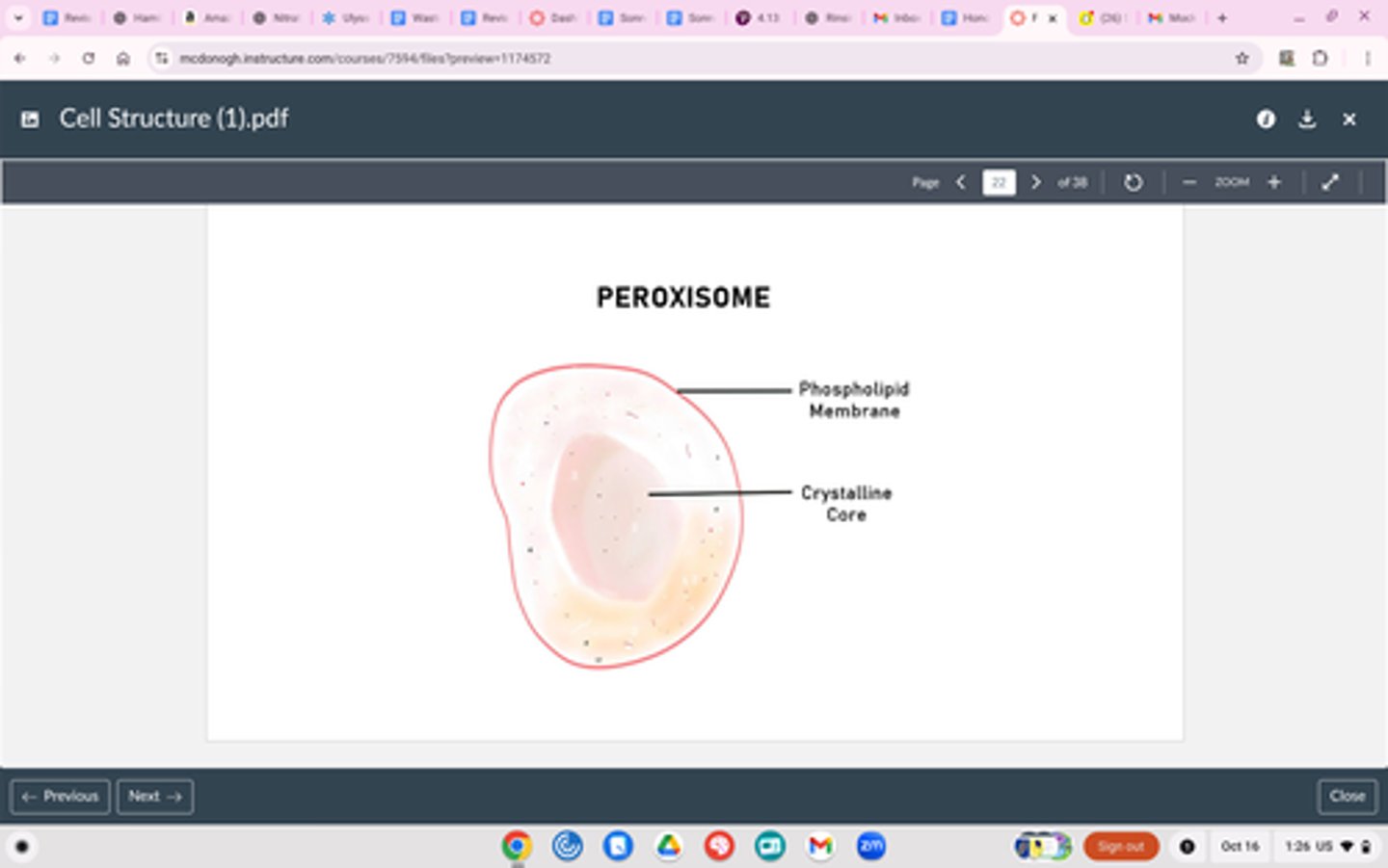
Peroxisome
Structure
Small, free floating in cytoplasm
Function
Breakdown of lipids, detoxification (breakdown of hydrogen peroxide with catalase)
Difference between these and lysosomes, peroxisomes breaks down harmful molecules and lipids, while lysosomes break down ENTIRE organelles
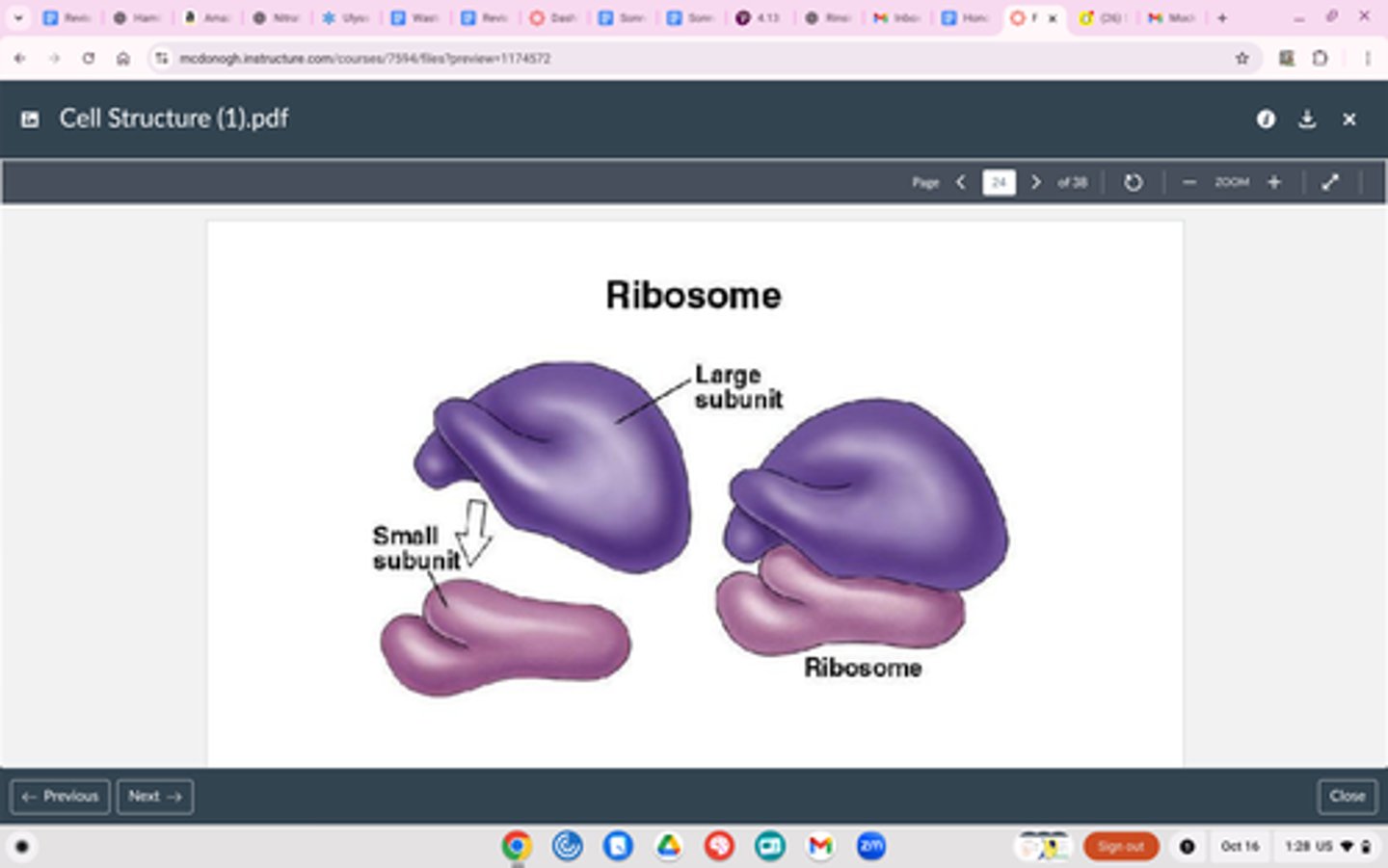
Ribosomes
Structure
Made of proteins and rRNA
Located on rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER) & floating in cytoplasm
Function
MAKE PROTEINS
^ proteins are synthesized right between the large and small sub-unit
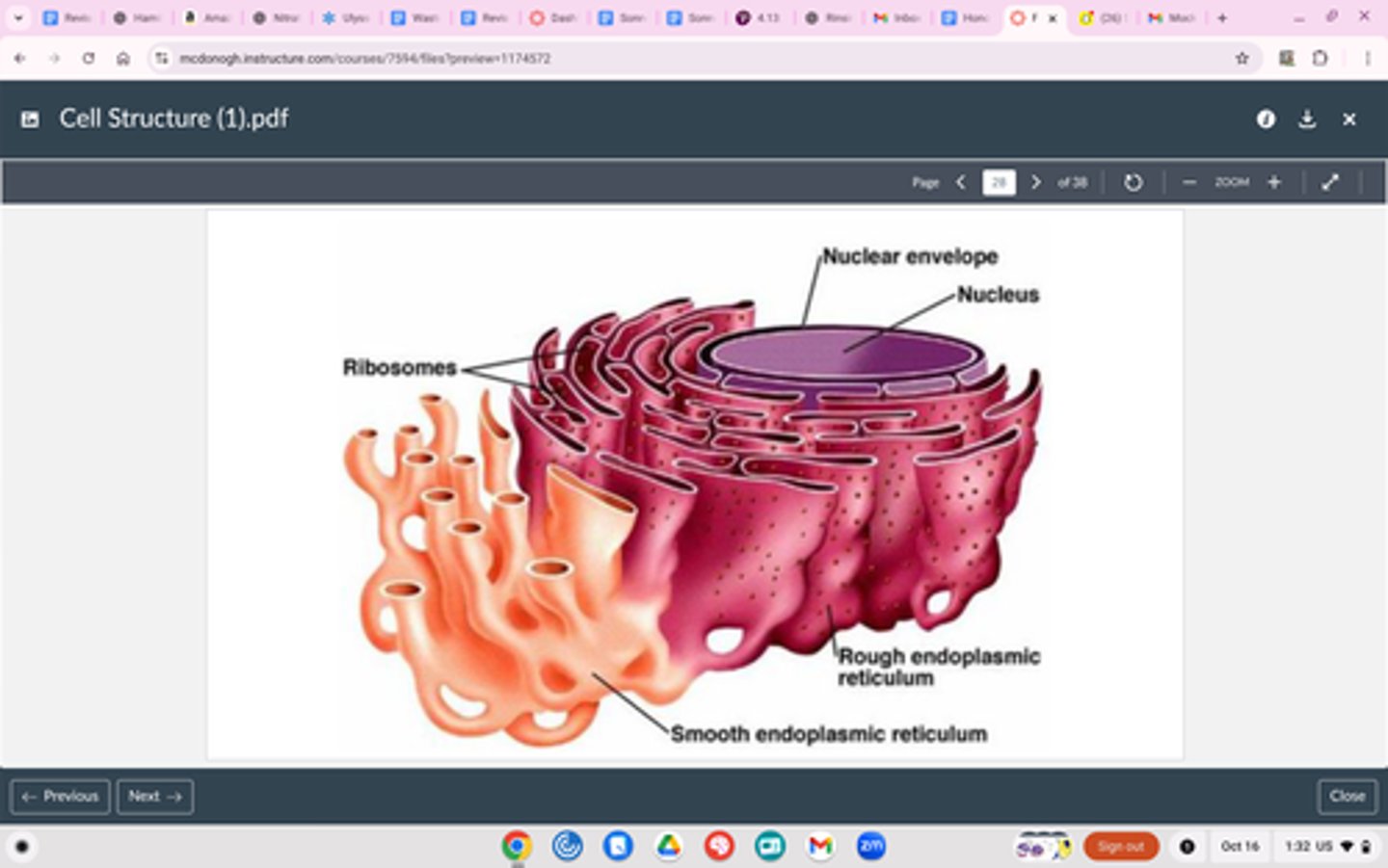
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Structure
Internal membrane system
Function
Depends on type: smooth vs. rough
Rough ER
Structure
Has ribosomes on surface
Hugs the nucleus (closest thing to it
Function
MAKES PROTEINS
Smooth ER
Structure
No ribosomes on surface
Attached to outer side of ER
Function
Makes lipids
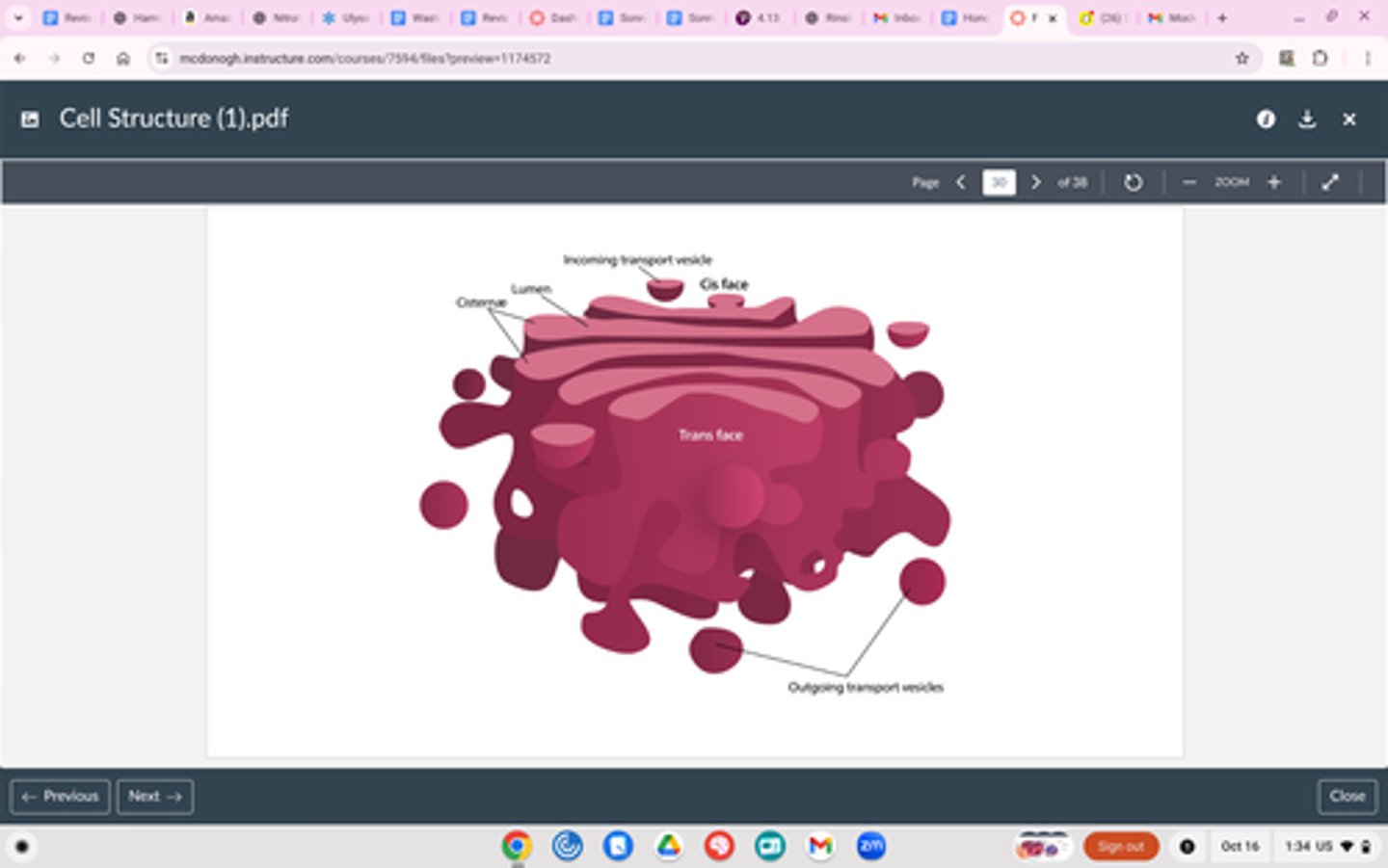
Golgi Apparatus
Structure
Folded membrane
Function
Gets vesicles (containers) of proteins from ER
Processes, sorts and ships proteins where they are needed
Could be inside or outside of the shell
Postal service - gets proteins where they need to go
^ enters through cisface => travels through apparatus => leaves through transface
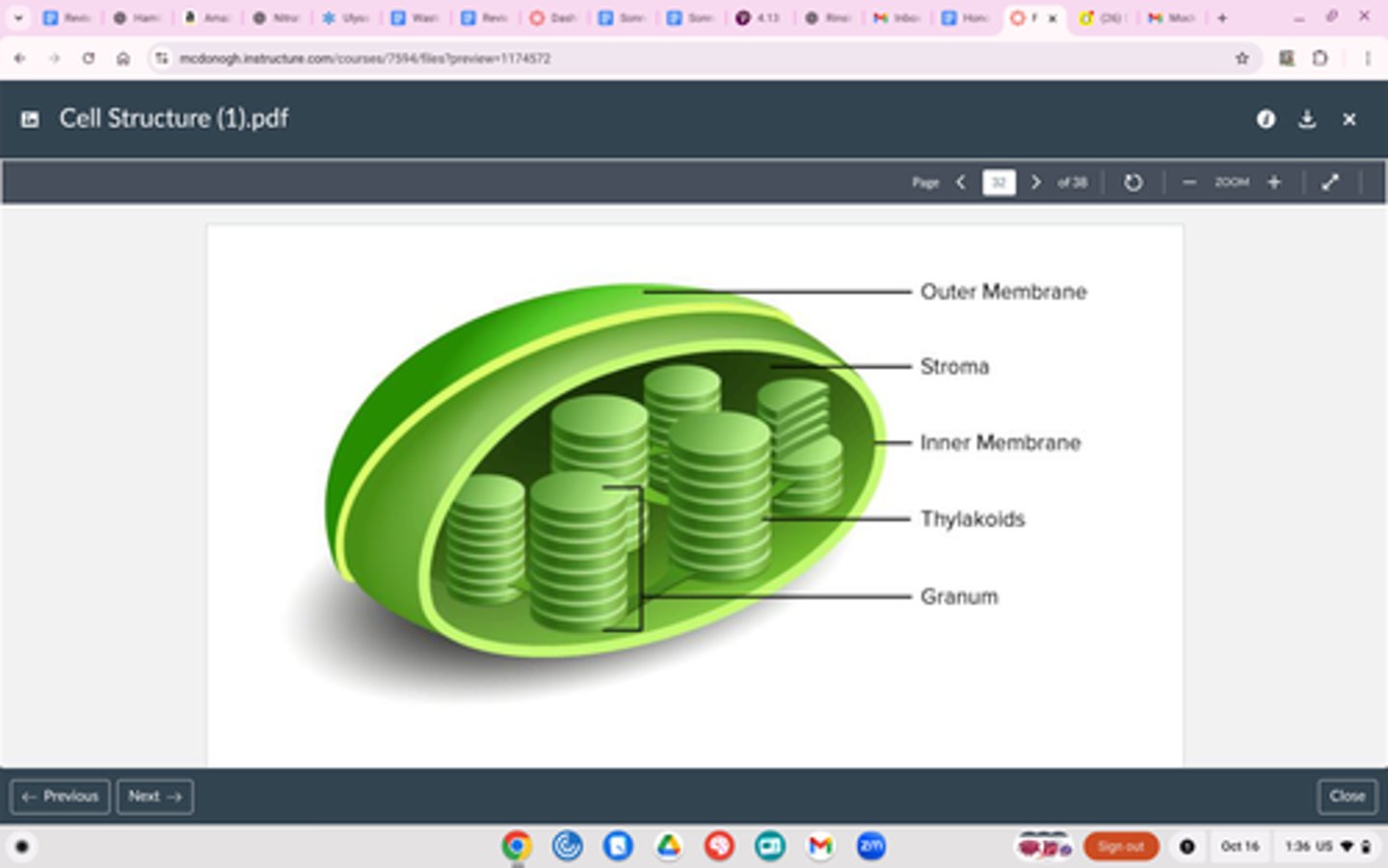
Chloroplasts
PLANT CELLS ONLY
Structure
Three parts: Thylakoid, grana (stacks of Thylakoids) and stroma (fluid)
Double membrane (two phospholipid bilayers on top of each other)
Function
Where photosynthesis happens
Converts energy from the sun into sugar (glucose)
Intake light energy => converts into sugar
Autotrophs
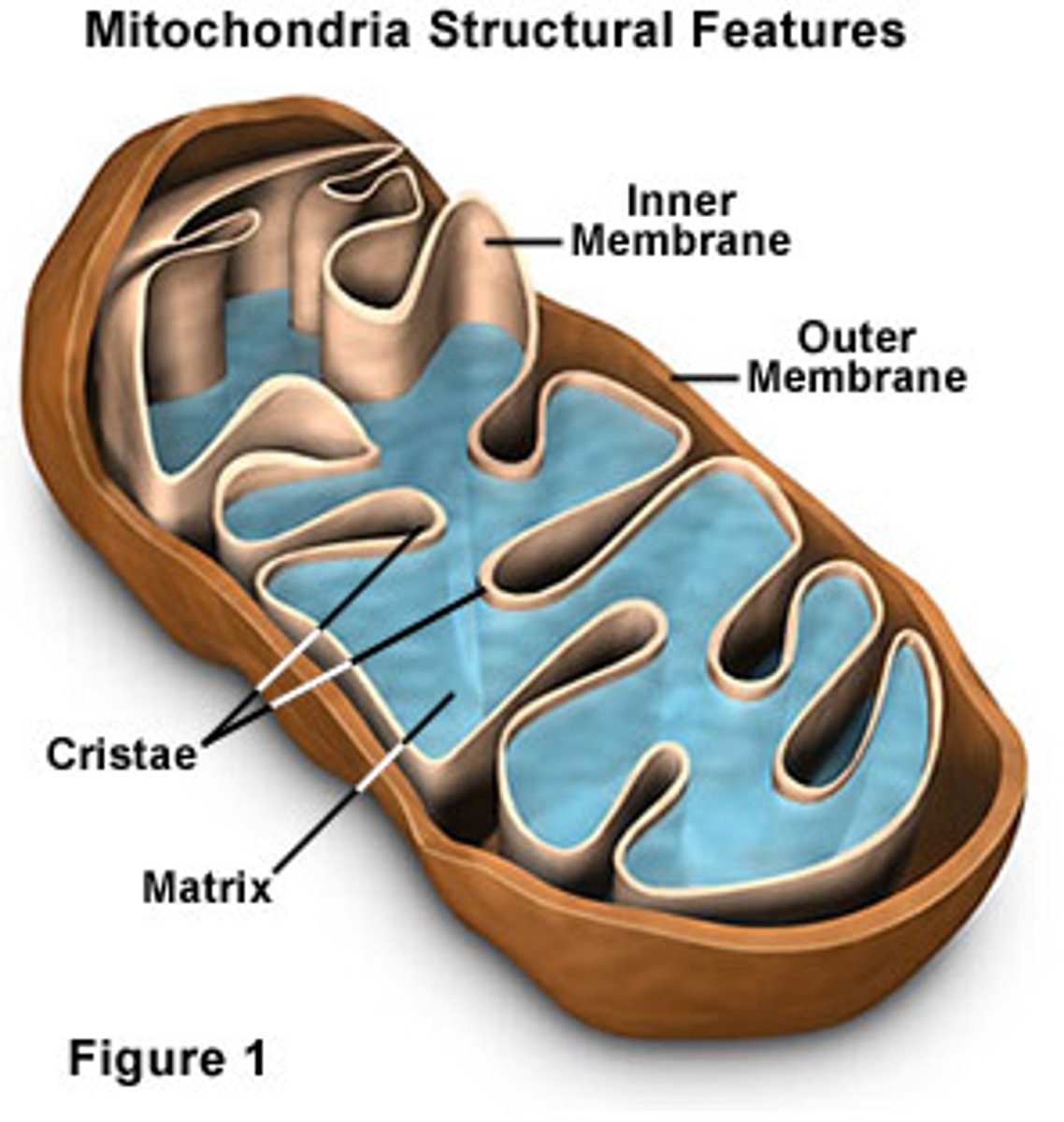
Mitochondria
POWERHOUSE OF THE CELL
Structure
Two parts: Inner membrane and matrix (fluid)
Double membrane
Inner membrane has special function
Matrix is the space that the fluid takes up
Function
Where cellular respiration happens
Breaks down food to release energy as ATP (energy currency)
ATP is the physical energy
Mitochondria produces almost all of the energy for a cell and an organism
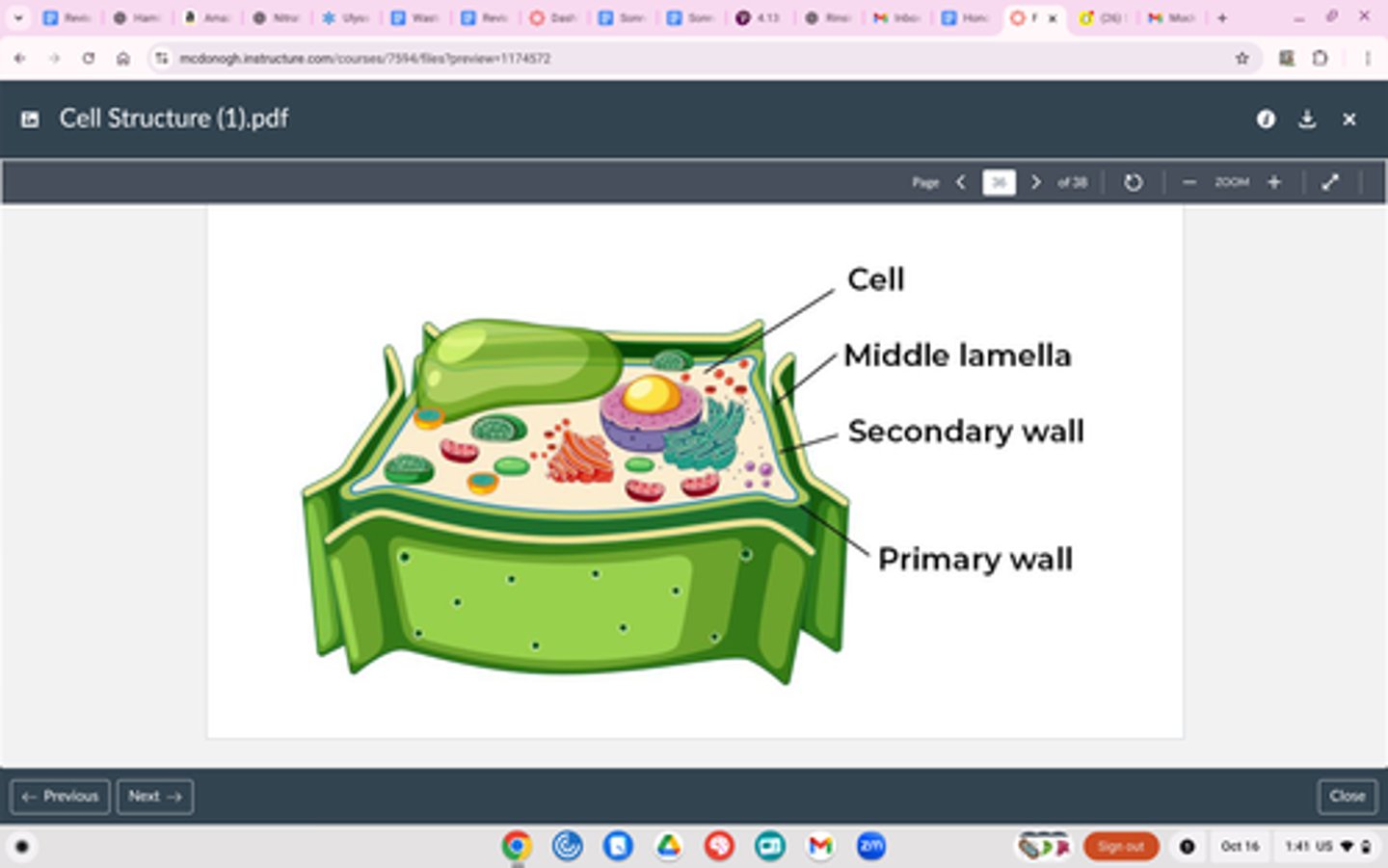
Cell Wall
PLANTS AND FUNGI ONLY
Structure
Made of cellulose (plants), chitin (fungi)
Function
Protect and maintain shape
^Cell wall is outside of cell membrane
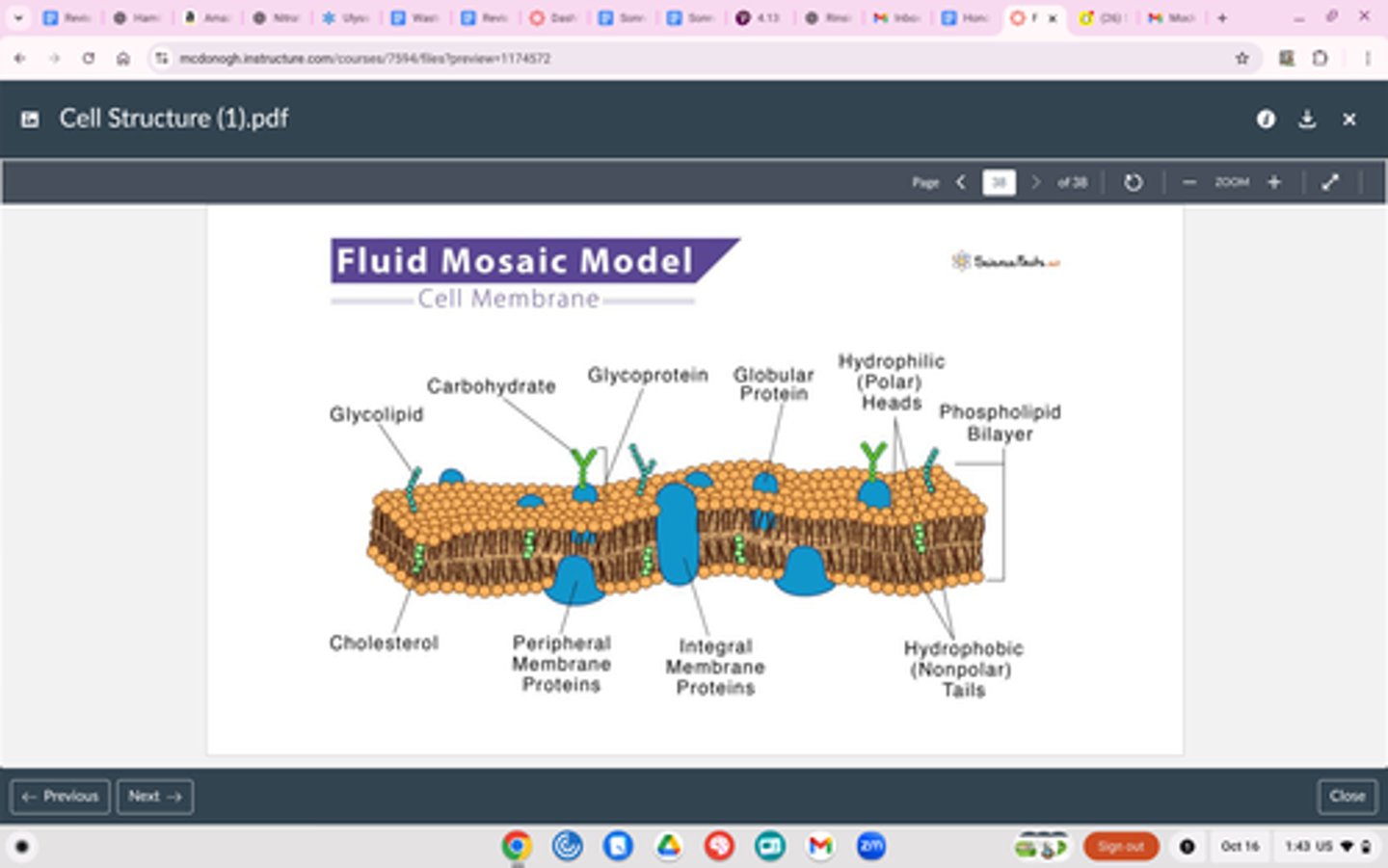
Cell (Plasma) Membrane (Phospholipid Bilayer)
Structure
Surrounds the outside of all cells
Made of two layers of phospholipids
Has embedded proteins
Function
Control what goes in and out of the cell
"Fluid-Mosaic Model" - composed of many parts that move around freely