Human Anatomy Lecture Exam 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/205
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:43 PM on 2/28/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
206 Terms
1
New cards
Joints
where two bones meet
fluid, cartilage, or fibrous tissue
Tradeoff flexibility & strength
fluid, cartilage, or fibrous tissue
Tradeoff flexibility & strength
2
New cards
Synarthrosis
no movement
3
New cards
Fibrous (Synarthrosis)
suture; surreal ligaments
and gomphosis; periodontal ligaments
and gomphosis; periodontal ligaments
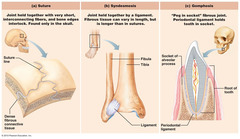
4
New cards
Cartilaginous (Synarthrosis)
synchondrosis
5
New cards
Bony fusion (Synarthrosis)
synostosis
6
New cards
Amphiarthrosis
some movement
7
New cards
Fibrous (Amphiarthrosis)
syndesmosis; between tibia and fibula, and between fibula and talus
8
New cards
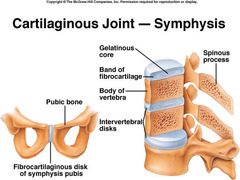
Cartilaginous (Amphiarthrosis)
Symphysis; pubis symphysis and intervertebral discs
9
New cards
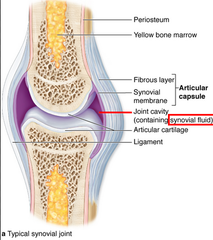
Diarthrosis
free movement
10
New cards
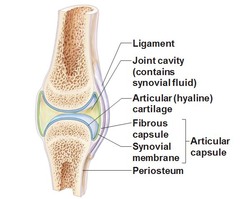
Synovial joints
Have fibrous joint capsule, synovial membrane, articulate cartilages, and joint cavity containing synovial fluid
11
New cards
Synovial joints make up
Accessory structures, blood vessels, and nerves
12
New cards
Synovial fluid
lubricates articular cartilages & reduces friction and nourishes articular cartilage; shock absorber
13
New cards
Linear motion
Movement in a straight line.
14
New cards
Rotation
circular movement around an axis such as the shoulder joint
15
New cards
Angular motion
the motion of a body about a fixed point or fixed axis
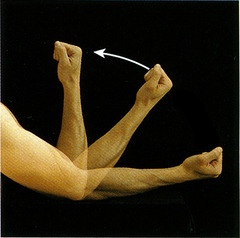
16
New cards
Circumduction
the circular movement at the far end of a limb
17
New cards
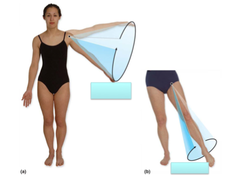
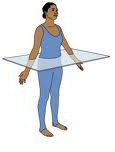
Transverse plane
horizontal division of the body into upper and lower portions
18
New cards
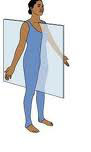
Sagittal plane
divides body into left and right
19
New cards
Frontal plane
Divides the body into front and back portions.
20
New cards
Monoaxial
type of joint in which the bone can move in only one plane
21
New cards
Biaxial
movement in two planes; ribs and wrist
22
New cards
Triaxial
movement in three planes; shoulder, hip
23
New cards
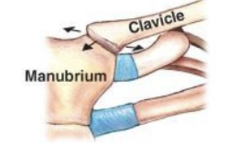
Plane Joint
monaxial, slight linear motion
Example: sternoclavicular and acromioclavicular joints, intercarpal and intertarsal joints, vertebrocoastal joints, and sacro-iliac joints
Example: sternoclavicular and acromioclavicular joints, intercarpal and intertarsal joints, vertebrocoastal joints, and sacro-iliac joints
24
New cards
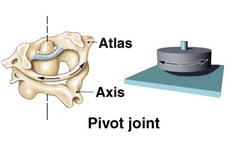
Pivot joint
monoaxial, rotation
Examples: Atlanto-axial joint and proximal radio-ulnar joint
Examples: Atlanto-axial joint and proximal radio-ulnar joint
25
New cards
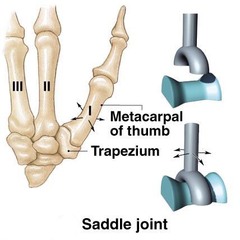
Saddle joint
biaxial, angular motion
Example: first carpometacarpal joint
Example: first carpometacarpal joint
26
New cards
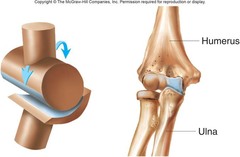
Hinge joint
angular motion in a single plane, monaxial
Example: elbow joint, knee joint, ankle joint, and interphalangeal joint
Example: elbow joint, knee joint, ankle joint, and interphalangeal joint
27
New cards
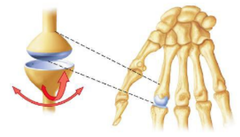
Condylar joint
biaxial, angular motion
Example: Metacarpophalangeal joints 2 to 5, radiocarpal joint, and metatarsophalangeal joints
Example: Metacarpophalangeal joints 2 to 5, radiocarpal joint, and metatarsophalangeal joints
28
New cards
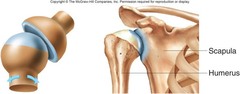
Ball and socket joint
Triaxial, angular motion, circumduction, & rotation
Example: shoulder joint and hip joint
Example: shoulder joint and hip joint
29
New cards
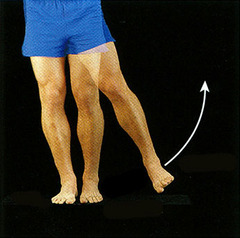
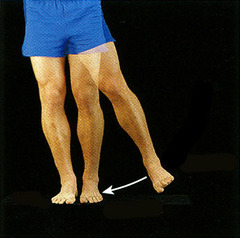
Abduction
Movement away from the midline of the body (away from longitudinal axis)
30
New cards
Adduction
Movement toward the midline of the body (towards the longitudinal axis)
31
New cards
Flexion
Decreases angle between bones; "bends forward"
32
New cards
Extension
Increases angle between bones; "bends backwards"
33
New cards
Hyper extension/flexion
beyond normal limits
34
New cards
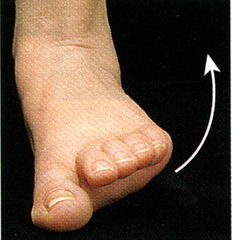
Eversion
moving the sole of the foot outward at the ankle
35
New cards
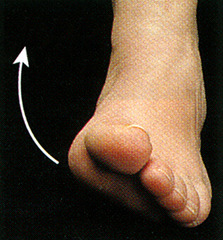
Inversion
Turning the sole of the foot inward
36
New cards
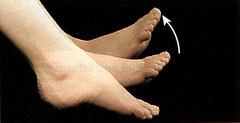
Dorsiflexion
bending of the foot or the toes upward
37
New cards
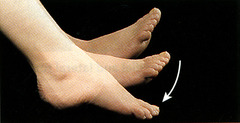
Plantar flexion
bends the foot downward at the ankle
38
New cards
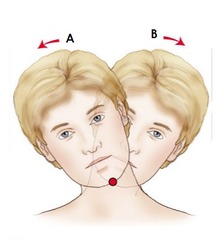
Lateral flexion
Side-bending left or right
39
New cards
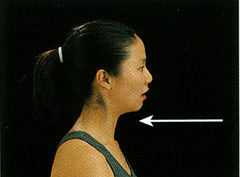
Retraction
moving a body part backward and parallel to the ground
40
New cards
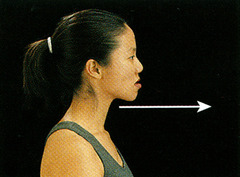
Protraction
moving a body part forward and parallel to the ground
41
New cards
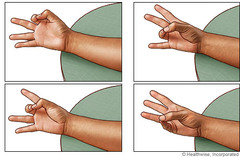
Opposition
Movement of the thumb to touch the fingertips
42
New cards
Reposition
return back to normal (anatomical position)

43
New cards
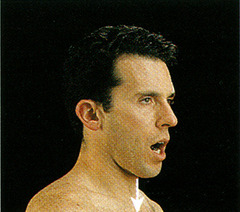
Depression
lowering a body part
44
New cards
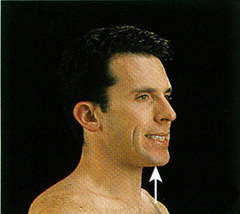
Elevation
raising a body part
45
New cards
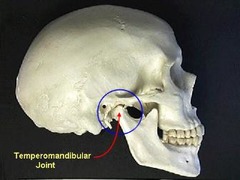
temporomandibular joint (TMJ)
2 synovial cavities in same space
Very loose
Allows for chewing
Plane & hinge
Very loose
Allows for chewing
Plane & hinge
46
New cards
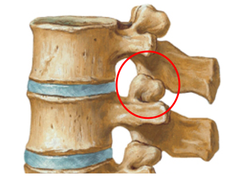
zygapophyseal joints
articular processes between vertebra
Limits Flexion, Extension, Rotation, and Lateral flexion
Limits Flexion, Extension, Rotation, and Lateral flexion
47
New cards
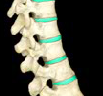
Intravertebral disc
Vertebral endplate, anulus fibrosus, and nucleus pulposus
48
New cards
Intravertebral ligaments
Ligamentum flavum, posterior longitudinal ligament, interspinous ligament, supraspinous ligament, and Anterior longitudinal ligament
49
New cards
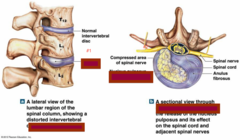
Herniated/ bulging disc
a rupture of the nucleus pulpous through the annular wall of the disc and into the spinal canal
50
New cards
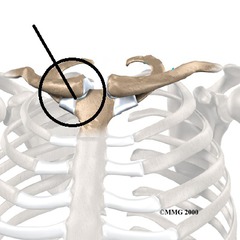
Sternoclavicular joint
only joint for axial and upper appendicular
two synovial cavities
two plane joints
two synovial cavities
two plane joints
51
New cards
Glenohumeral joint
ball and socket
greatest range of motion
triaxial
greatest range of motion
triaxial
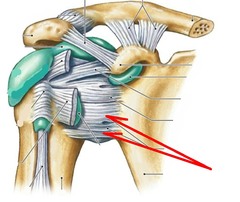
52
New cards
Elbow joint
3 joints w/in one capsule
53
New cards
2 hinge joints: flexion/extension
Humberto-ulnar: strongest; trochlea & tronchlear notch
Humeroradial: more flexible; capitulation & head of radius
Humeroradial: more flexible; capitulation & head of radius
54
New cards
1 pivot joint
proximal radio-ulnar
55
New cards
Proximal & distal radio-ulnar joints
pivot joints
allow rotation
allow rotation
56
New cards
proximal radio-ulnar joint
head of radius & radial notch of ulna
57
New cards
Annular & quadrate ligament
stabilize proximal joint
58
New cards
Distal radio-ulnar joint
Ulnar notch of radius & head of ulna
59
New cards
Radio-ulnar ligament & interosseous membrane
stabilize distal joint
allows for supination and pronation
allows for supination and pronation
60
New cards
Wrist joint
radiocarpal joint & intercarpal joints
61
New cards
Condylar joints
Flexion/Extension, Adduction/Abduction, Circumduction
example: radiocarpal joint
example: radiocarpal joint
62
New cards
Saddle joints
Flexion/Extension, Adduction/Abduction; Opposition; Circumduction
carpometacarpal joint of thumb
carpometacarpal joint of thumb
63
New cards
Plane joint
intercarpal joints and carpometacarpal joint of little finger
64
New cards
Femur joint
ball and socket joint
fat pad absorbs shock
fat pad absorbs shock
65
New cards
Knee ligaments prevent
hyperextension or hyperflexion
extensive adduction or abduction
extensive adduction or abduction
66
New cards
Cruciate ligaments
allow locking and unlocking of the knee; stand for long periods
67
New cards
Knee joint
works as a hinge joint;
ligaments, menisci, tendons, bursa, & fat pad all stabilize this joint
ligaments, menisci, tendons, bursa, & fat pad all stabilize this joint
68
New cards
Anterior cruciate ACL
Locks knee in extended position
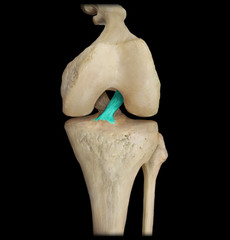
69
New cards
Medial & lateral menisci
shock absorbers
lateral stability
increase surface area of joint
changes shape to support articular surface
lateral stability
increase surface area of joint
changes shape to support articular surface
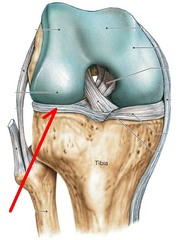
70
New cards
ligaments that stabilize the knee joint
fibular collateral ligament, popliteal ligaments, posterior cruciate ligament, anterior cruciate ligament, tibial collateral ligament, patellar ligament
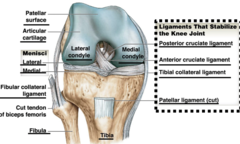
71
New cards
Talocrural joints
Hinge: talus, tibia & fibula
72
New cards
Tibiotalar joint
hinge, main joint, bears body mass; supported by:
proximal tibiofibular joint (plane joint),
distal tibiofibular joint (fibrous syndesmosis), and
fibulotalar joint (fibrous syndesmosis)
proximal tibiofibular joint (plane joint),
distal tibiofibular joint (fibrous syndesmosis), and
fibulotalar joint (fibrous syndesmosis)
73
New cards
Condylar joints
metatarsophalangeal joints
74
New cards
Hinge joints
Interphalangeal joints
75
New cards
Plane joints
Talonavicular joint, Intertarsal joints, Tarsometatarsal joints, and Calcaneocuboid joint
76
New cards
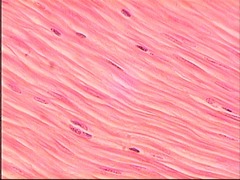
Smooth muscle
Non-striated, can replicate; hyperplasia, reflex arcs or myogenic
77
New cards
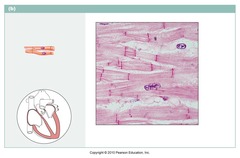
Cardiac muscle
Myogenic, branched, scar tissue, pumps blood
78
New cards
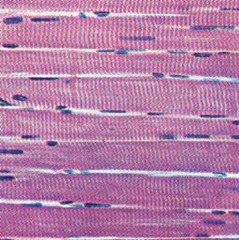
Skeletal muscle
multinucleate, pulls on bones, voluntary or reflex arc, hypertrophy
79
New cards
Muscle tissues share 4 basic properties
Excitability, Contractility, Extensibility, and Elasticity
80
New cards
Excitability
ability to respond to stimuli; undergo Action Potentials
81
New cards
Contractility
ability to shorten & exert tension
82
New cards
Extensibility
contract over a range of resting lengths
83
New cards
Elasticity
recoil to original length
84
New cards
Skeletal muscle
Produces movement, Maintain posture & body position, Support soft tissue, Regulate entering & exiting of material; found in some sphincters, and Maintains body temperature; shivering thermogenesis
85
New cards
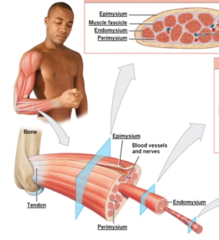
Connective tissues of Skeletal Muscle (organ)
epimysium, Muscle fascicle, Endomysium, and Perimysium
86
New cards
Connective tissues of Muscle Fascicle (bundle of cells)
Perimysium (A), Muscle fiber (B), and Endomysium (C)
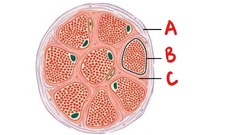
87
New cards
Connective tissues of Muscle Fiber (cell)
Sarcolemma (B), Myofibril (C), Endomysium (G), and Myosatellite cell (H)
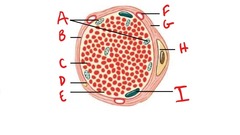
88
New cards
Muscle fiber (cell)
Myosatellite cell, Myofibril, Sarcolemma, Nuclei, Muscle fiber, Sarcoplasm
Mitochondria, Sarcolemma, Myofibril, Thin filament, Thick filament, Triad, Sarcoplasmic reticulum, T tubules, Terminal cisterna, Sarcoplasm, and Myofibrils
Mitochondria, Sarcolemma, Myofibril, Thin filament, Thick filament, Triad, Sarcoplasmic reticulum, T tubules, Terminal cisterna, Sarcoplasm, and Myofibrils
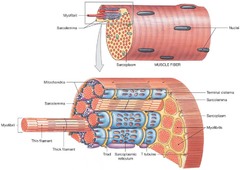
89
New cards
myofilaments to muscle
Myofilaments -> Sarcomere -> Myofibril -> Muscle fiber -> Fascicle -> muscle
90
New cards
Myofilaments
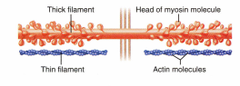
91
New cards
Sarcomere
smallest contractile unit of muscle
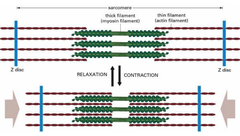
92
New cards
Myofibril
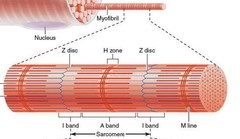
93
New cards
Muscle Fiber
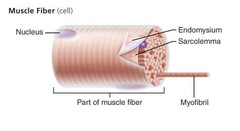
94
New cards
Fascicle
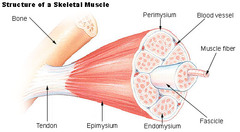
95
New cards
Muscle
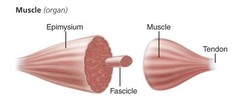
96
New cards
Sarcomere Structure
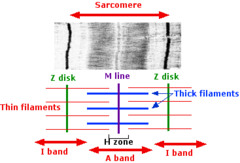
97
New cards
Sliding filament theory
(1) Rigor is a transient site
(2) ATP binding dissociates myosin from actin. The cross-bridge can now go through a cycle o a new G-actin molecule
(3) Myosin ATPase hydrolizes ATP to ADP and Pi. Energy from the reaction is transferred to the cross-bridge. ADP and Pi remain bound to myosin.
(4) The myosin head moves to the cocked position and binds to a G-actin molecule.
(5) Myosin attachment to actin triggers rapid Pi release and the power stroke. The actin filament is moved about 10 nm towards the center of the sarcomere.
(6) The myosin head and unbinds ADP and remains tightly bound to actin (rigor).
(2) ATP binding dissociates myosin from actin. The cross-bridge can now go through a cycle o a new G-actin molecule
(3) Myosin ATPase hydrolizes ATP to ADP and Pi. Energy from the reaction is transferred to the cross-bridge. ADP and Pi remain bound to myosin.
(4) The myosin head moves to the cocked position and binds to a G-actin molecule.
(5) Myosin attachment to actin triggers rapid Pi release and the power stroke. The actin filament is moved about 10 nm towards the center of the sarcomere.
(6) The myosin head and unbinds ADP and remains tightly bound to actin (rigor).
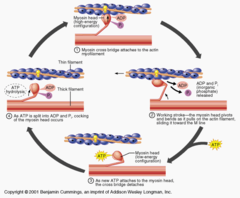
98
New cards
Action potential (AP)
rapid change in membrane potential over surface of cell
99
New cards
Excitable cells that have action potential
Muscles, Sensory cells, Neurons, and some endocrine cells
Excitable cells may secrete a signaling molecule due to AP
Excitable cells may secrete a signaling molecule due to AP
100
New cards
Skeletal muscles are stimulated via
reflex arcs and voluntary motor units