Geometry Postulates
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Addition Property of Equality
if a=b and c=d, then a+c=b+d
Subtraction Property of Equality
if a=b and c=d, then a-c = b-d
Multiplication Property of Equality
If a = b, then ca = cb
Division Property of Equality
If a = b and c ≠ 0, then a/c = b/c
Substitution
If a=b, then either a or b may be substituted for the other in any equation
Reflexive
a = a
Symmetric
if a = b, the b = a
Transitive
If a = b and b = c, then a = c
Distributive Property
a(b+c) = ab+ac
Midpoint Theorem
if M is the midpoint of AB, then AM = ½ AB and MB = ½ AB
Definition of Midpoint
The two halves of the midpoint are equal to each other.
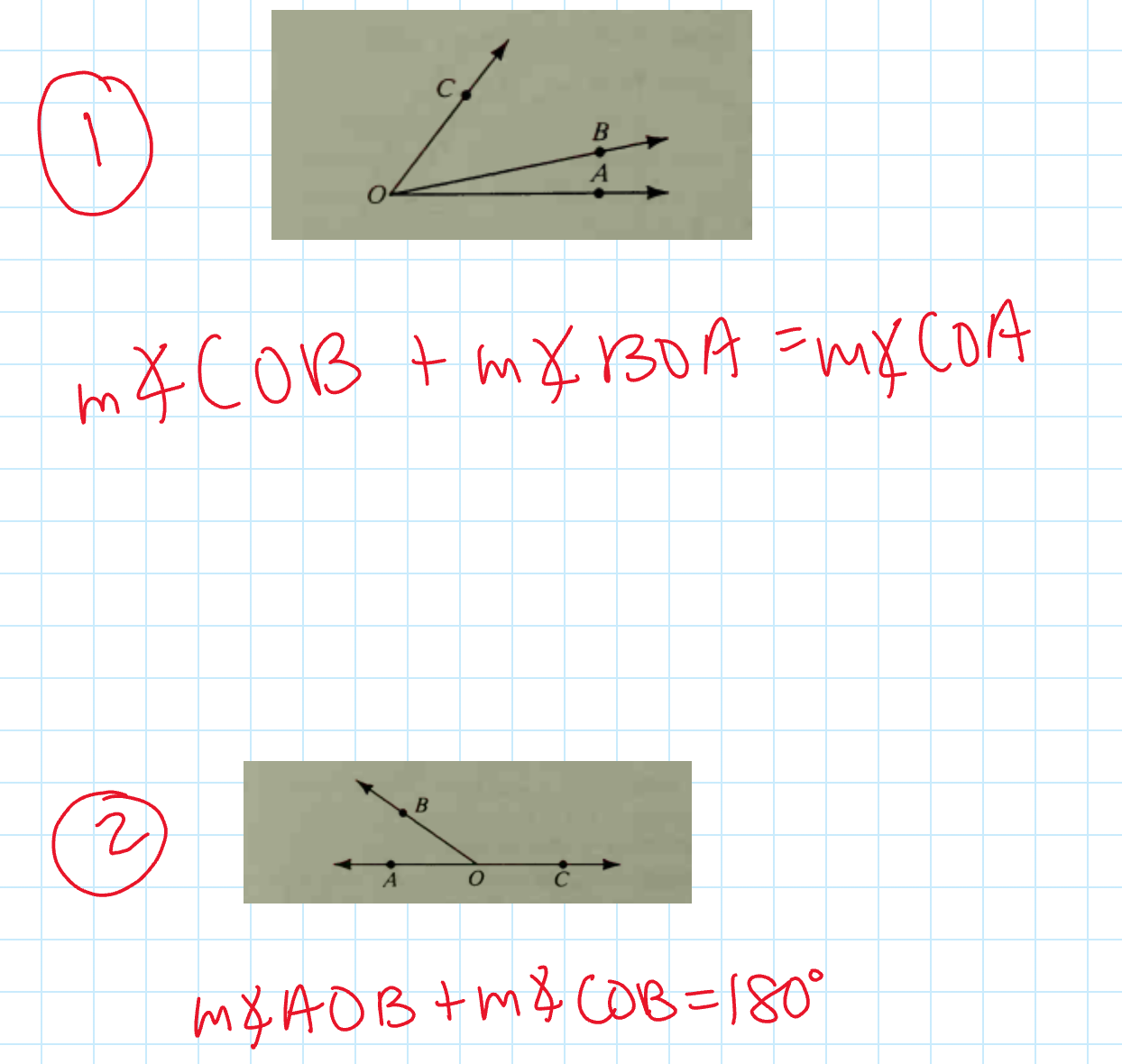
Angle Addition Postulate
Segment Addition Postulate
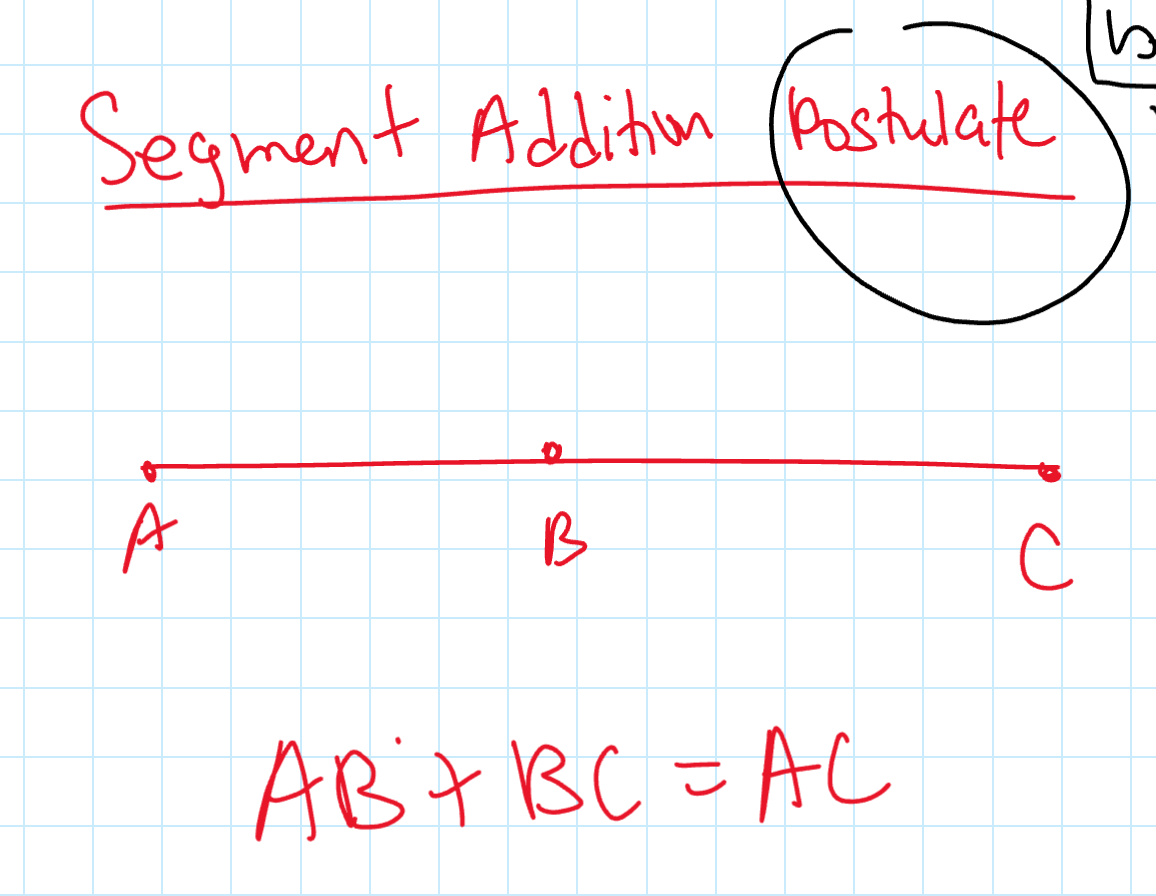
AB + BC = AC
Angle Bisector Theorem

Definition of Angle Bisector
divides an angle into two smaller, equal (congruent) angles
Def of Complementary Angles
Two angles that add up to 90 degrees
Def of Supplementary Angles
Two angles that add up to 180 degrees
Def of Perpendicular Lines
Two lines that Intersect to form Right Angles
If two lines are perpendicular, then they form congruent adjacent angles

If two lines for congruent adjacent angles, then the lines are perpendicular
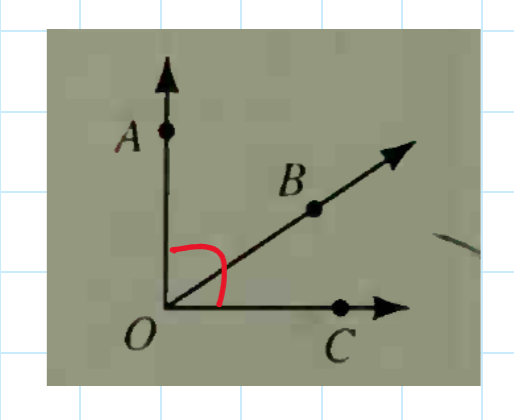
If the exterior sides of two adjacent acute angles are perpendicular, then the angles are complementary
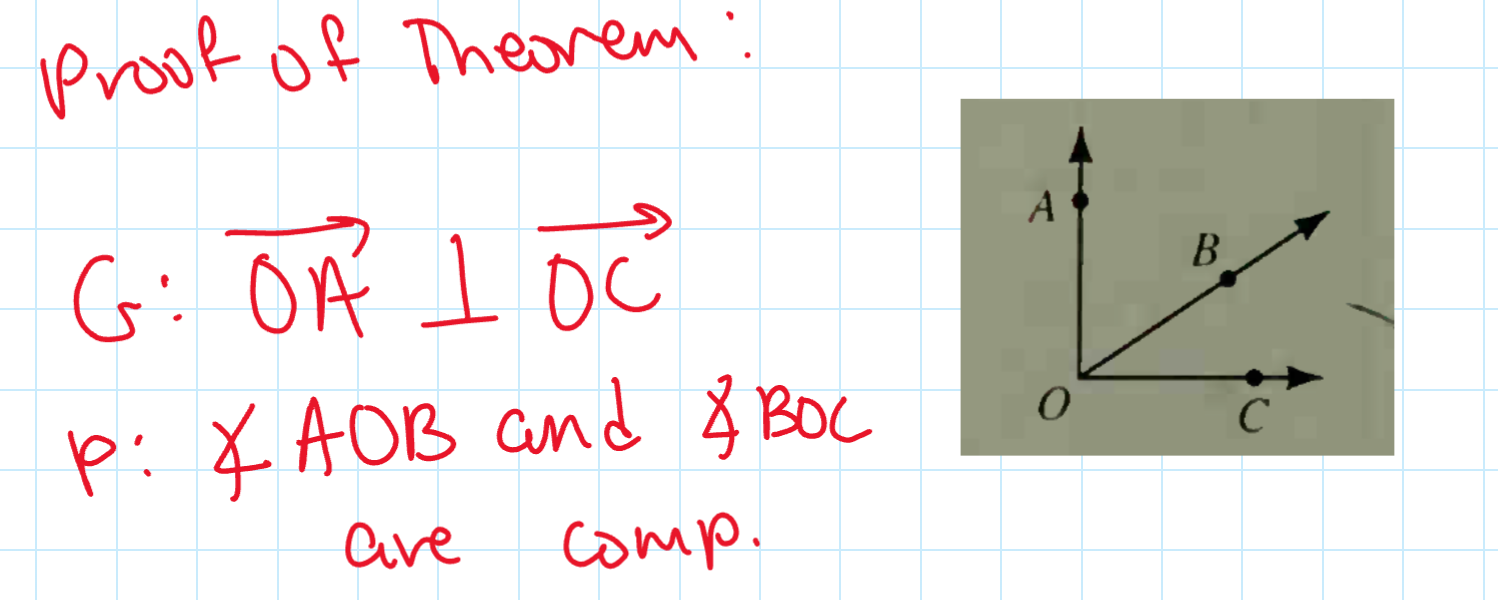
If two angles are supplements of congruent angles, then the angles are congruent

If two angles are complements of congruent angles, then the two angles are congruent
