Chapter 14: Innate Immune Response
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
The interior deep tissues of the body are generally ____, meaning free of microbes.
sterile
The three general components of the ____ immune system are first-line defenses, sensor systems, and effector actions.
innate
With respect to the body's borders, the contents of the digestive tract are ______.
outside the body;
The digestive tract is a tube that runs through the body but is in contact with the external environment, and is thus regarded as being "outside".
The epithelial cells that line the exposed surfaces of the body are tightly packed together and rest on the ______ membrane.
basement
Lysozyme breaks down peptidoglycan, a common component of the cell wall of bacteria. What effect would this have on most bacterial cells?
It would leave cells susceptible to lysis due to osmotic pressure imbalances.
The deeper interior tissues of the body are generally laden with helpful symbiotic bacteria.
False;
Indeed, the deeper interior tissues of the body are generally sterile, except during infections.
Catalase, an enzyme produced by some species of bacteria, ______.
1) destroys peroxidase enzymes
2) creates H2O and O2 as breakdown products
3) breaks down hydrogen peroxide
4) breaks a substrate down into antimicrobial compounds
2) creates H2O and O2 as breakdown products
3) breaks down hydrogen peroxide
Innate immunity includes ______.
1) transducing particles
2) antibodies
3) sensor systems
4) effector actions
5) first-line defenses
3) sensor systems
4) effector actions
5) first-line defenses
Some areas of the body have populations of microbes living on cell surfaces. Select each area that would have normal microbiota.
1) Large intestine
2) Muscle tissue
3) Skin
4) Brain
5) Vagina
1) Large intestine
3) Skin
5) Vagina
The first-line defenses of innate immunity are ______.
the body's borders
If a person develops an infection, the number of disease-fighting cells in the bloodstream will ______.
increase because they are recruited from reserves in the bone marrow
The exposed surfaces of the body are lined by ______ cells.
epithelial
A ____ is any type of white blood cell with noticeable cytoplasmic granules.
granulocyte
Lysozyme, an enzyme that degrades peptidoglycan in bacteria, can be found ______.
1) in saliva
2) in phagocytic cells
3) in tears
4) in the mucus of the small intestine
5) in fecal matter
1) in saliva
2) in phagocytic cells
3) in tears
4) in the mucus of the small intestine;;
-This enzyme is one of many in saliva in the oral cavity.
-Lysozyme is sometimes used inside of phagocytic cells to help break down peptidoglycan of ingested microbes.
-This enzyme is one of the secretions in tears that lubricate and cleanse the surface of the eye.
-There are cells that produce this enzyme to help protect the tissues around the small intestine from microbes.
What is the main role of neutrophils?
Phagocytosis
Peroxidase enzymes can be found in phagocytic cells.
True;
This is one of the sets of enzymes used to degrade bacteria ingested by phagocytes.
In addition to phagocytosis, neutrophils kill microbes by ______.
releasing destructive enzymes
The population of microbes that routinely grow on the body surfaces is the normal ____ , or flora.
microbiota
Monocytes travel in the ____, , while macrophages are more differentiated, larger, and reside in tissues, including the liver, spleen, lymph nodes and lungs.
blood
The cells of the immune system ______.
move from one part of the body to another via the body's circulatory systems
Dendritic cells provide a link between the innate and adaptive immune systems by ______.
engulfing material and degrading it, then presenting it to the adaptive system cells
The general term for any type of white blood cell with noticeable cytoplasmic granules is ______.
granulocyte
Without lymphocytes, we wouldn't be able to ______.
mount an adaptive immune response
______ are also called polys, polymorphonuclear leukocytes, or PMNs.
Neutrophils
Immune cells communicate with each other through surface receptors, adhesion molecules, and chemical signals known generally as ____
cytokines
Neutrophils can release their cell contents to form NETs, an acronym that stands for neutrophil ______.
extracellular traps
A molecule that can bind to a given surface receptor is called a ______ for that receptor.
ligand
Monocytes are normally found in various tissues of the human body, including lungs, liver, and brain.
False;
Monocytes travel in the blood. What do we call the further differentiated form of a monocyte that is in the tissues?
Match each type of cytokine's mode of action with the description of that trait.
1) Local
2) Regional
3) Systemic
1) Local --> Acting only on the very few cells in the immediate vicinity of the cytokine's release
2) Regional --> Acting on a variety of cells in the general vicinity of the cytokine's release
3) Systemic --> Acting throughout the organism, and not restricted to a particular area
____ cells function as sentinel cells, engulfing material in tissues and taking it to adaptive immune system cells for inspection.
Dendritic
Chemicals that are secreted by certain cells of the immune system and which act at low concentrations to cause effects on other cells, are known as ____
cytokines
____ are responsible for adaptive immune responses and include two major groups: B cells and T cells.
Lymphocytes
Adhesion molecules can be thought of as the ______ of the cell, allowing, for example, endothelial cells lining blood vessels to bind passing phagocytic cells.
hands
How do immune cells communicate with each other?
1) via cytokines
2) via adhesion molecules
3) via surface receptors
4) via antibodies
1) via cytokines
2) via adhesion molecules
3) via surface receptors
Pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) detect ______.
signs of microbial invasion;
PRRs don't bind cytokines because cytokines are produced by our own cells.
What are possible outcomes of a ligand binding to its receptor on a cell's surface?
1) The internal portion of the receptor becomes modified.
2) A response is triggered in the cell, initiating some change.
3) The cell will change the receptor so the ligand will no longer bind to it.
1) The internal portion of the receptor becomes modified.
2) A response is triggered in the cell, initiating some change.
The pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) of an innate immunity cell allow that cell to tailor its response according to the general category of pathogen by determining ______.
the assortment of the pathogen's MAMPs
A cytokine is ______.
secreted by a specific cell type and binds to a receptor on target cells, causing a response in that target cell such as growth or death
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) can be found ______ of macrophages.
1) on ribosomes
2) on the cell surface
3) in endosomes
4) in phagosomes
5) in the nucleus
2) on the cell surface
3) in endosomes
4) in phagosomes
Cytokines are analogous to the ______ of a cell.
voice
Specific TLRs (toll-like receptors) anchored in endosomes and phagosomes typically detect ______ that indicate microbial origin.
nucleic acids
An example of adhesion molecules in action occurs when ______ cells are needed in the tissues. The ______ cells lining the blood vessels make adhesion molecules to "grab" these cells from the blood.
phagocytic; endothelial
PRRs in a cell's cytoplasm enable the cell to monitor ______ for signs of invasion.
its own internal contents
A family of proteins called ____ _____ receptors (PRRs) allow the body's cells to recognize and bind to a wide variety of ligands found in many pathogens.
pattern recognition
When a cell's cytoplasmic PRRs detect viral RNA, the cell responds by synthesizing and secreting a(n) ______.
interferon
If a macrophage's pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) detect bacterial products, then that macrophage will produce ______.
pro-inflammatory cytokines
The primary end outcome of activation of the complement system is ______.
removal and destruction of invading microbes;
There are other outcomes as well, but this is the primary effect of activation of the complement system.
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are present on or in which of the following sentinel cells?
1) macrophages
2) nerve cells
3) muscle cells
4) dendritic cells
1) macrophages
4) dendritic cells
The three pathways of complement activation converge at the formation of ______ convertase.
C3
TLRs (toll-like receptors) in endosomes and phagosomes detect ______.
1) long molecules of double-stranded RNA
2) peptidoglycan fragments from bacterial cell walls
3) transfer RNA that carries the amino acid phenylalanine
4) nucleotide sequences that are relatively common in bacterial DNA
1) long molecules of double-stranded RNA
4) nucleotide sequences that are relatively common in bacterial DNA
The name of the alternative pathway of complement activation reflects the fact that it ______.
was not discovered first
Most host cells have PRRs in their ____ , allowing the cells to screen their own internal contents for signs of invasion.
Need help? Review these concept resources.
cytoplasm
C3b is both a product and a trigger for the alternative complement cascade. How can this occur?
C3 is unstable and can spontaneously split into C3a and C3b at a low rate.
Specifically, interferons are ______.
cytokines that can induce antiviral effects
The complement pathway that is activated by binding of C3b to cell surfaces is the _______.
alternative pathway.
The complement system is a series of ______ that circulate in the ______.
proteins; blood and extracellular fluid
Protective outcomes of activation of the complement system include ______.
1) inflammatory response
2) cell lysis
3) phagocytosis
4) antibody production
5) opsonization
1) inflammatory response
2) cell lysis
5) opsonization
C3 convertase ______.
1) splits complement component C3
2) forms part of the membrane attack complex
3) forms at the convergence of the three pathways of complement activation
4) is the final product of the complement activation cascade
splits complement component C3
forms at the convergence of the three pathways of complement activation
Microbes that have been opsonized are easier to engulf because phagocytes have ____ for opsonin proteins such as C3b on their surface.
receptors
As its name suggests, the alternative pathway of complement activation serves as a back-up in case the other complement activation pathways fail.
false;
The name reflects that it was not discovered first; it actually provides vital early warning that an invader is present.
Opsonization resulting from the complement cascade is ______.
the coating of a microbial cell surface with opsonins, in this case, C3b
In the alternative pathway, the C3 convertase is composed of ______ and other activated (cleaved) complement system proteins.
C3b
Which of the complement activation pathways is most likely to act inappropriately, and therefore require regulation, and why?
Alternative pathway;
This pathway can be triggered by C3 spontaneously breaking down into C3a and C3b. Therefore, this pathway could act when it shouldn't.
The alternative complement pathway is triggered ______.
when C3b binds to foreign cell surfaces to start the complement cascade
If macrophages cannot rapidly clear invading microbes, those phagocytic cells produce cytokines that ______.
recruit neutrophils
Opsonization, inflammatory response, and lysis of foreign cells are three protective outcomes of the ______.
complement system
A pathogen that is able to avoid fusion of lysosomes with phagosomes can ______.
avoid destruction by phagocytes
Why does opsonization make a microbe easier for a phagocyte to ingest?
Because phagocytes have receptors for opsonin proteins on their surface.
____ is an activated complement molecule that can serve as a strong chemoattractant for phagocytic cells.
C5a
____ means coating a microbial surface with proteins or other molecules, making it easier for it to be engulfed by a phagocytic cell.
Opsonization
A phagocyte binds directly to a bacterial cell when ______.
the cell's receptors bind to mannose on the bacteria
Which of the following are mechanisms that either prevent complement protein activation or protect host cells from activated complement proteins?
1) Microbial surfaces lack proteins that bind and inactivate C3b
2) Proteins on host cells bind and inactivate C3b
3) Inactivated C3b is not an effective opsonin
4) Proteins that inactivate C3b don't affect C3a
2) Proteins on host cells bind and inactivate C3b
3) Inactivated C3b is not an effective opsonin
A ____ is a vesicle that surrounds and encloses a particle brought into a phagocytic cell by phagocytosis.
phagosome
When microbes enter through a minor skin wound, resident ______ in the tissues destroy them. If these microbes are not rapidly cleared, the resident cells secrete _______ to recruit _______ for extra help.
macrophages; cytokines; neutrophils
Macrophages are scavengers. As such, not only do they engulf and destroy foreign invaders, but they also ______.
engulf and recycle dead cells and debris
Understanding the steps of phagocytosis is important medically because ______.
many pathogens are able to evade one or more of them
Macrophages have a lifespan of weeks to months. To replace them, ______ leave the bloodstream and differentiate into new macrophages.
monocytes
Which one of the following items would not be a chemoattractant for phagocytic cells?
C3b
____ ______, a type of cell specialized for phagocytosis, need the assistance of helper T-cells to become fully activated, showing an example of the cooperation between the innate and adaptive response systems.
Macrophages
When a phagocyte encounters something too large to engulf, it will ______.
release its toxic contents into the surrounding area as a means to degrade the particle
A macrophage usually kills microbes by ______, while a neutrophil can additionally kill by ______.
ingesting microbes and destroying them internally; releasing toxic granule components
Indirect binding of a phagocyte to a bacterial cell occurs when ______.
the cell's receptors first bind to opsonins that have coated the bacterial cell
The best analogy for the macrophages' role is that of ______.
police officers who routinely protect city streets
In response to tissue damage or introduction of microbes into normally sterile body sites, ____ occurs. The purpose of this is to contain the site of damage, localize the response, eliminate the invader, and restore tissue function.
inflammation
What is the lifespan of macrophages?
weeks to months
The inflammatory process involves a cascade of events that results in dilation of blood vessels, leakage of fluid from those vessels, and migration of leukocytes out of the bloodstream and into the tissues.
True
Macrophages have limited killing power until they become ______ macrophages.
activated
During inflammation, ____ system proteins leak out into tissues to become cleaved and activated and attack microbes.
complement
Which descriptions are true for neutrophils but not macrophages?
1) They release granule contents and DNA strands to entrap and destroy microbes.
2) They have more killing power.
3) They are always present in the tissues, whether slow wanderers or stationary.
4) They have a longer life span in the tissues.
1) They release granule contents and DNA strands to entrap and destroy microbes.
2) They have more killing power.
The four basic functions of inflammation include all of the following EXCEPT ______.
1) elimination of the invader
2) restoration of tissue function and capability at the damaged site
3) recruitment of the full spectrum of adaptive immune responses to the area
4) localization of the immune response
5) containment of the site of damage
recruitment of the full spectrum of adaptive immune responses to the area;
While innate cells and responses are usually brought into an area of inflammation, adaptive cells are not.
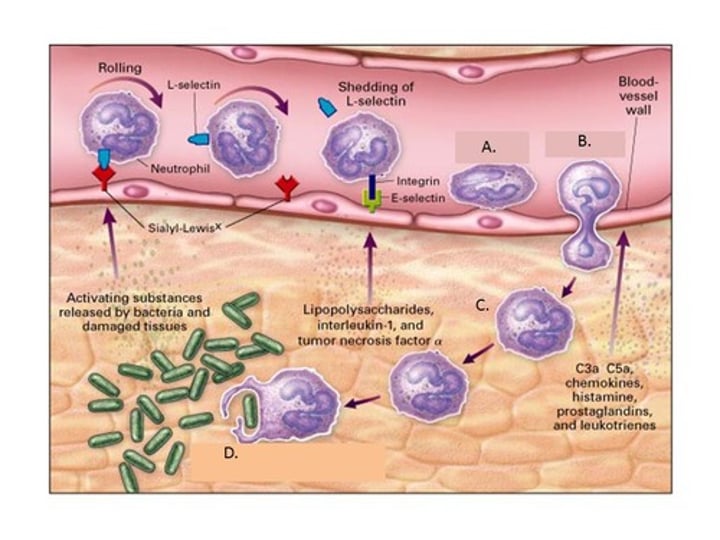
Diapedesis is ______.
the squeezing of leukocytes out of the blood vessels and into an inflamed or infected area
In an inflammatory response, the diameter of local blood vessels increases due to the action of the chemical ____ and other inflammatory mediators, slowing blood flow in the area. At the same time, changes in the endothelial cells that line the capillaries create small gaps in the normally ____ junctions between the cells, allowing more fluid to leak from the blood vessels into the tissue.
histamine; tight
What are features of the inflammatory response?
1) It can help eliminate an invading microbe.
2) It occurs as a result of a cell undergoing apoptosis.
3) It can damage host tissues.
1) It can help eliminate an invading microbe.
3) It can damage host tissues.
The main reason that blood proteins and phagocytic cells can enter infected tissues during the inflammatory response is that ______
changes in the cells lining the blood vessel walls allow the items to leave the bloodstream and enter the infected area;
Inflammation is a strong inducer of changes in the endothelial lining, allowing such items to leave the blood.
Why might it be a good thing for a host to kill an infected self cell?
If it's harboring an infectious agent, killing the cell may prevent adjacent cells from also becoming infected by that infectious agent.
Fever is ______.
1) the body's response to cold temperatures
2) an important host defense mechanism
3) a strong indication of infectious disease
4) the body's response to high temperatures
2) an important host defense mechanism
3) a strong indication of infectious disease
The process in which leukocytes squeeze between the endothelial cells to enter infected or inflamed tissues is referred to as
diapedesis
A negative consequence of inflammation can result when ______ and toxic products from ______ are inevitably released, damaging our own tissues.
enzymes; phagocytes
In humans and other animals, sacrificing "self" cells may ______.
1) eliminate cells no longer needed
2) limit the spread of an infection
3) remove susceptible cells a pathogen might otherwise infect
1) eliminate cells no longer needed
2) limit the spread of an infection
Human body temperature is kept around 37oC by a temperature-regulation center in the ____
hypothalamus/brain