B7 CM Heme/Onc Exam 2
1/753
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Tumor suppressor genes 🤝 me during exam week: doing absolutely nothing.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
754 Terms
•collect and return interstitial fluid, including plasma protein to the blood, and thus help maintain fluid balance
•defend the body against disease by producing lymphocytes
•absorb lipids from the intestine and transport them to the blood
what are the principal functions of the lymphatic system?
thoracic duct
all lymphatics for the rest of the body drain into the:
lymphatic duct
all lymphatics for the right upper quadrant drain into the:
virchow's node
Supraclavicular node enlargement by metastatic carcinoma
chylothorax
presence of chyle in the pleura, caused by disruption or dysfunction in the flow of chyle through the thoracic duct
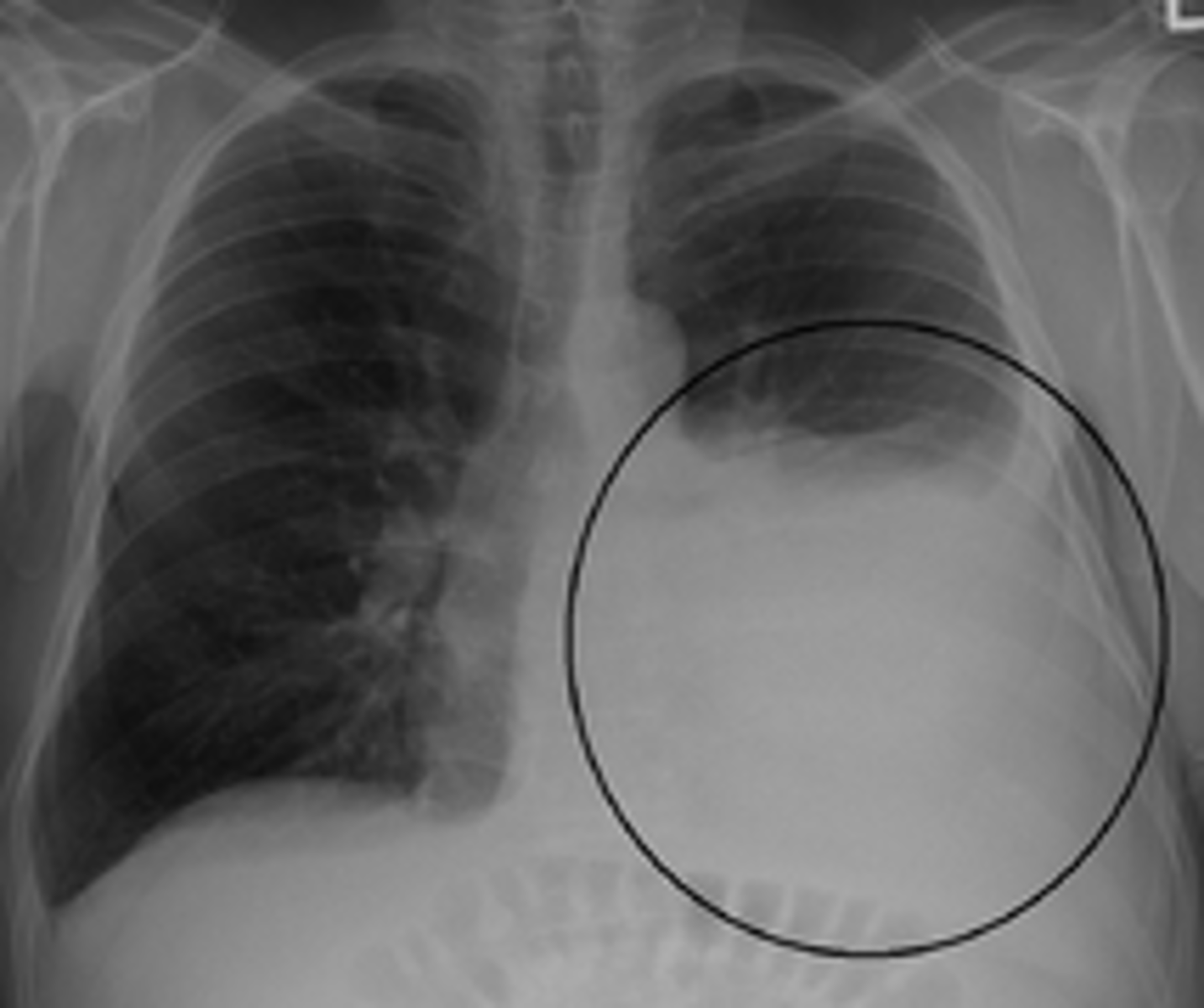
malignancy, benign tumors, lymphatic disorders
nontraumatic causes of chylothorax
iatrogenic from surgery
traumatic causes of chylothorax
chyle
white or pale yellow substance in lymph that contains fatty substances absorbed by the lacteals
dyspnea without chest pain, as chyle does not invoke an inflammatory response
presentation of chylothorax
-thoracentesis with pleural fluid analysis
-milky appearance, predominantly lymphocytes
-high protein, no glucose, pH 7.4-7.8
-high TGs
diagnostic findings of chylothorax
-fragment of tumors
-infected material
what materials are most commonly spread via the lymph vessels to spread malignancy?
malignancy
if pt presents with lymphadenopathy, what should always be on your ddx?
-strep pharyngitis
-cellulitis or inflammatory conditions of the skin (bug bite, tinea, cat scratch disease)
-inguingal adenopathy of STI: chancre, HSV
-EBV
common etiologies of explained/likely explained lymphadenopathy
tender anterior cervical LAD
lymphadenopathy associated with strep pharyngitis
lymphagitis
infection of lymph vessel walls that occurs in some acute pyogenic infections in which the microbes in the lymph draining from the area infect and spread along the walls of lymph vessels
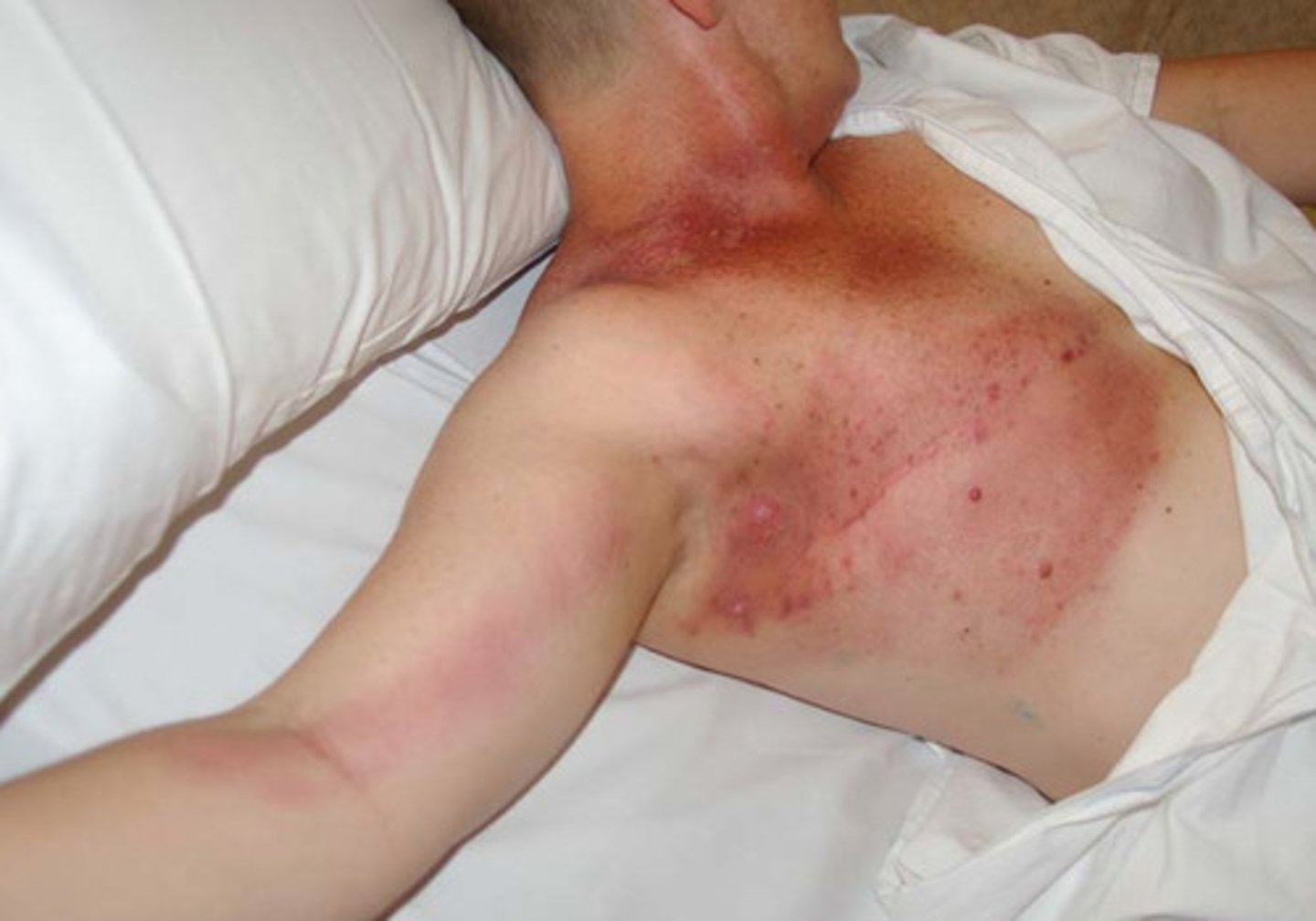
bilateral posterior cervical LAD
adenopathy associated with EBV
EBV
what disease?
-rash will develop in 90% who are treated with amoxicillin
Primary HIV infection
What disease?
-cause of explained lymphadenopathy
-mucocutaneous ulceration
-rash (48-72 hours after onset of fever)
CMV
What disease?
-mild form of EBV mono
-Elevated LFTs more common
-cause of explained lymphadenopathy
toxoplasmosis
What disease?
-Fever and LAD without pharyngitis
-No pharyngitis,
-Normal LFTs
-cause of explainable lymphadenopathy
generalized or localized
with an unexplained lymphadenopathy , must determine if it is:
generalized lymphadenopathy
> 2 noncontiguous LN regions without an explanation
CBC, CXR, HIV, (+/- monospot)
initial testing if you find unexplained generalized lymphadeopathy
supraclavicular > neck > axilla > groin
most to least likely nodes of lymphadenoapthy
allopurinol, atenolol, captopril, cephalosporins, gold, hydralizine, imatinib, penicillin, phenytoin, sulfonamides
select drugs that can cause lymphadenopathy
determine if it is likely cancer
-if no, follow up in 3-4 weeks for changes
-if yes, biopsy
work up if you find an unexplainable, localized lymphadenopathy?
-age over 40
-size >2cm
-duration over 1 month
risk factors pointing to malignancy in unexplained localized lymphadenopathy
abnormal
supraclavicular lymphadenopathy is always
malignant than infectious (vice versa if <20 years old)
A mass in the neck of a patient greater than 40 years old is much more likely to be
biopsy (preferably core)
-image according to results of biopsy if malignancy is found
first step in work up of unexplained axillary adenopathy is
NO!! If it ends up being breast cancer, and excisional biopsy decreases the yield of a sentinel lymph node biopsy and may unnecessarily commit the patient to an axillary lymph node dissection.
Should you perform an excisional biopsy to start with unexplained axillary adenopathy?
inguinal lymph nodes
primary lymph drainage of anus and genitalia, and distal 1/3 of vagina is
inguinal adenopathy
lymphadenopathy often palpable in healthy people without cancer
-Often palpable in healthy people without cancer perhaps because chronic trauma and infection is so common in the LE; also common in obese pts
Contrast cross-sectional CT
initial study of choice for adult pts with neck mass
normal: hypoechoic cortex and echoic central hilum
abnormal: centrally hypoechoic, lost its hilum
normal vs abnnonrmal LN on ultrasound
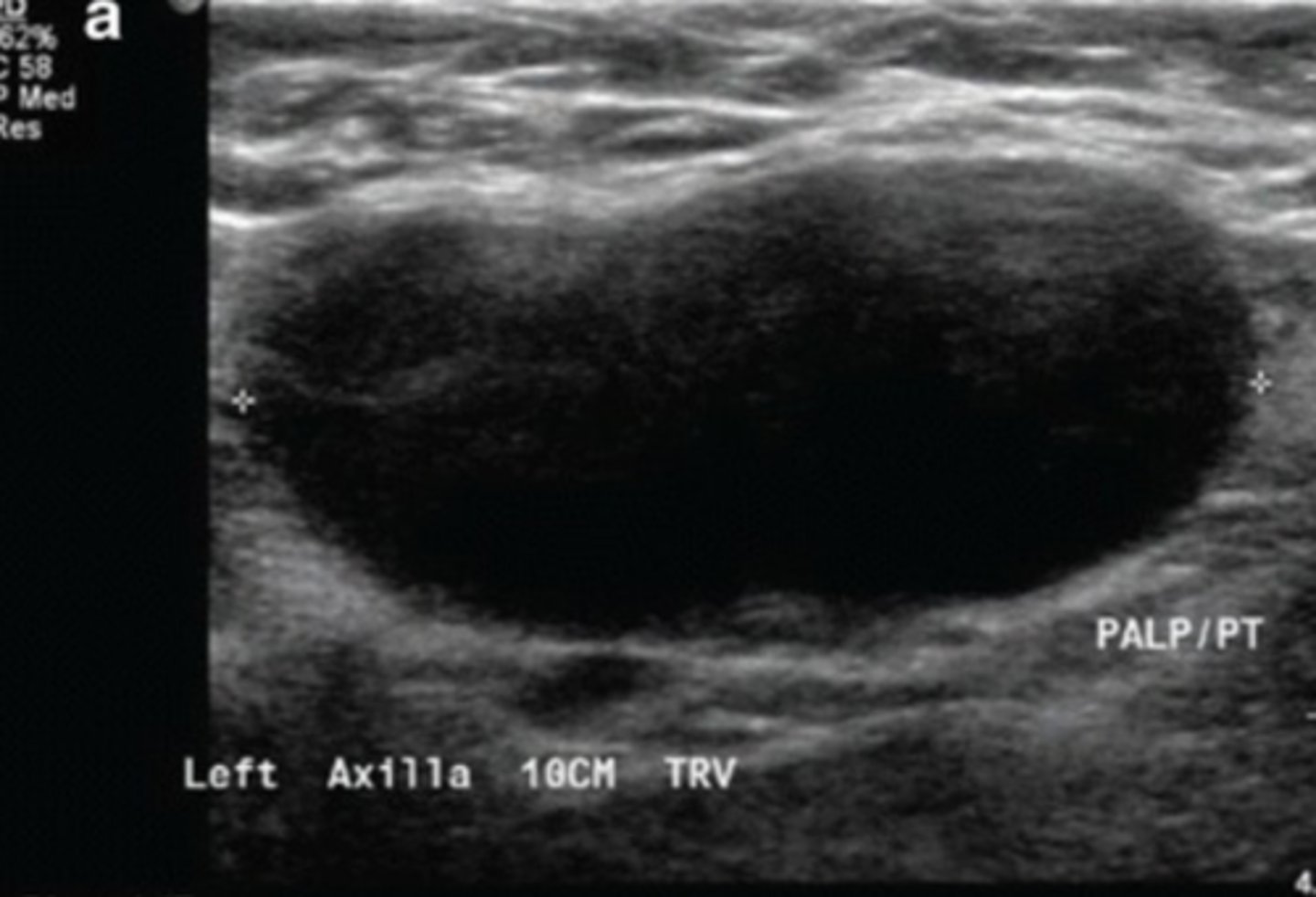
•Size (location & context dependent)
•Morphology (loss of hilum)
•Enhancement
•Invasion (aka extracapsular extension)
things to assess on imaging in work up of lymphadenopathy
▪Currently not sufficient for establishing a diagnosis of cancer
disadvantage of liquid biopsy
useful in the following when additional tissue biopsy is not feasible but diagnosis is already established
▪Identifying therapeutic targets
▪Selecting patients at risk of recurrence
▪Monitoring response to therapy
indications for liquid biopsy of lymphadenopathy
-high false negative rate!
-lack of tissue architecture
-limited material
-generally not sufficient info for establishing initial diagnosis
disadvantage of FNA in evaluating lymphadenopathy
core biopsy
what type of biopsy?
•14 to 20 gauge needle
•Typically under image guidance
•Provides enough tissue for special testing and some information on nodal architecture
•Allows for placement of clips/markers into area of interest
more painful, hematomas can form, generally safe tho
disadvantage of core biopsy
•Excisional - entire abnormal LN is removed
•Incisional - part of abnormal LN is removed
what is the difference between excisional and incisional biopsy
•Allows for assessment of nodal architecture
•Preferred biopsy when lymphoma is suspected
advantages of open biopsy
open biopsy
biopsy type that is generally better to avoid if you think you are dealing with a carcinoma
-removes sentinel node, risk of seeding the skin
lymphedema
▪An accumulation of excessive proteins, edema, chronic inflammation, and fibrosis in tissues secondary to the impairment of the lymph vessels.
Chronic condition, generally not cured
▪congenital absense or anomaly of the lymphatic system
pathophysiology of primary lymphedema
obstruction or interruption of lymphatic system
ex: malignancy, infection, trauma, cancer treatment
pathophysiology of secondary lymphedema
-highest risk associated with axillary dissection + axillary radiation
-lowest risk with sentinel biopsy alone
determinant of risk of lymphedema in breast cancer treated pts
•Psychosocial
•Skin infection
•Lymphangiosarcoma: Stewart-Treves syndrome
complications of lymphedema
do NOT overtreat the axilla!
-avoid excisionnal biopsy in initial workup, perform sentinel node biopsy in clinically negative axilla, neoadjuvant therapy for positive axilla
best way to management treatment relatedd lymphedema
-monitoring, elevation, exercist
-compression therapy
-physiotherapy
conservative management of lymphedema
•Lymphatic bypass procedures
•Excision
•Liposuction
surgical management of lymphedema consnists of
•Synthesis of immunoglobulin G (IgG), properdin (an essential component of the alternate pathway of complement activation), and tuftsin (an immunostimulatory tetrapeptide)
immune functions of the spleen
>12 cm across
size definition of splenomegaly
•No symptoms in some cases
•Pain or fullness in the left upper abdomen that may spread to the left shoulder
•Early satiety
•Anemia
•Fatigue
•Frequent infections
•Thrombocytopenia
•Easy bleeding
symptoms associated with an enlarged spleen
ultrasound
best imaging for monitoring size of spleen
•Biopsy is generally not performed due to risk of bleeding
can I biopsy the spleen?
primary
sarcoidosis is considered a ______ cause of splenomegaly
RhoGAM
drug highly associated with splenomegaly
neutrophilia
most common form of leukocytosis
viral (EBV)
most common infectious cause of lymphocytosis
Drugs
Addisons/allergy
Worms
Neoplasia
DAWN
mnemonic to rremember the most common causes of eosinophilia
CML
most common neoplasm causing basophilia
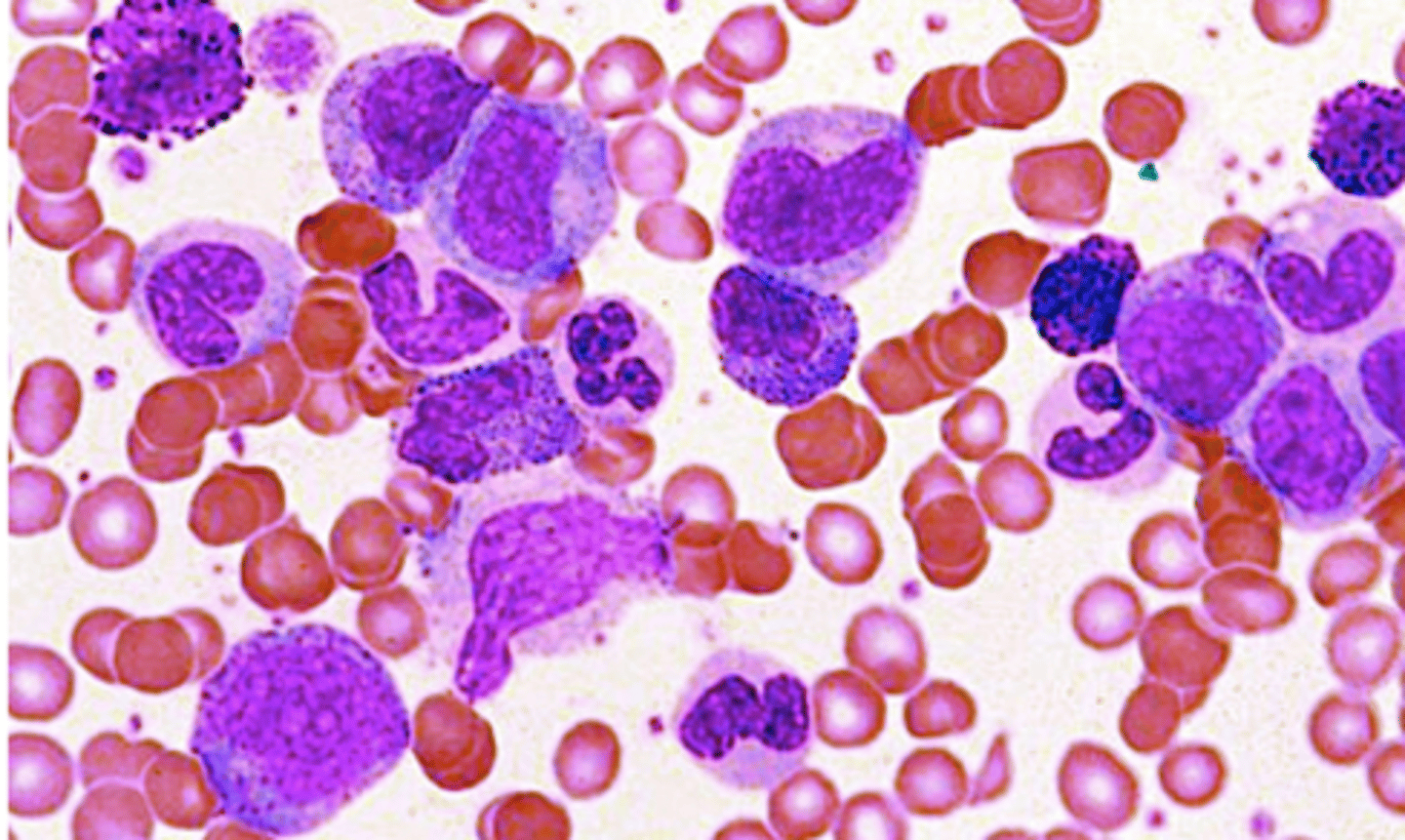
-marked increase in neutrophils >50000
-left shift
-severe infection, trauma, bone marrow infiltration
-looks like leukemia
define criteria of a leukemoid reaction
acute myeloid leukemia
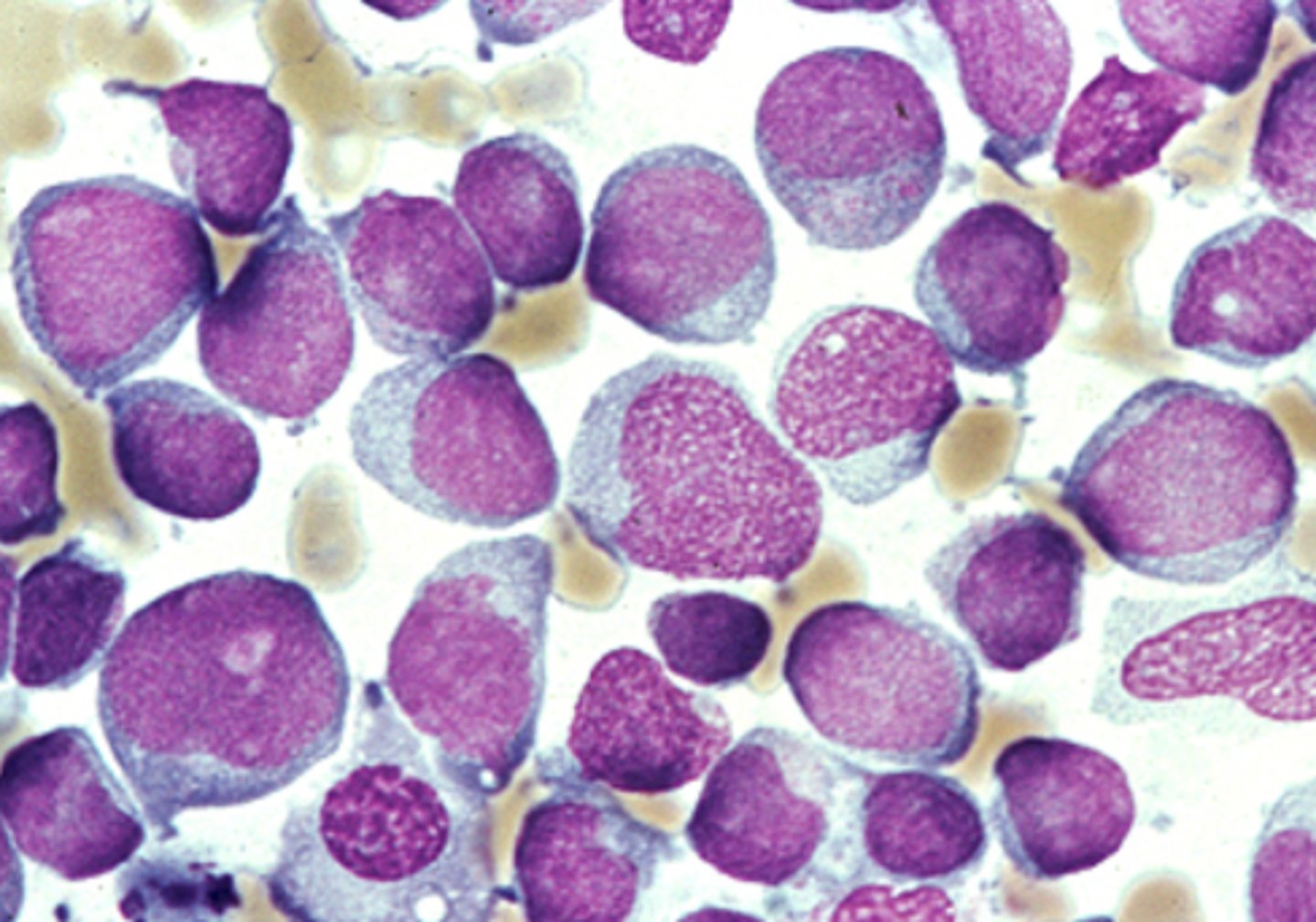
bone marrow aspirate
-blasts are large, moderate amount of grayish blue cytoplasm, no distinct nucleoli
acute lymphoblastic leukemia
-most common childhood malignancy
-most common cause of cancer death in pts under 20
2-5 years old
peak incidence of ALL
down syndrome
genetic syndrome related to ALL
children complaining of bone pain
-fatigue, infections, bleeding, dyspnea, petichiae, mucosal bleeding, fever
most common presenting symptoms of ALL
-CNS penetration---> meningeal signs, CN deficits, AMS
these symptoms are a MAJOR issue with ALL, but not that common
testicular swelling, neurologic findings, mediastinal mass
less common findings associated with ALL
-CBC w/ diff, peripheral smear, bone marrow exam
-lymph node if there is one
lab orders for workup of suspected ALL
acute leukemia
a high level of blasts in peripheral blood smears should make you suspicious for
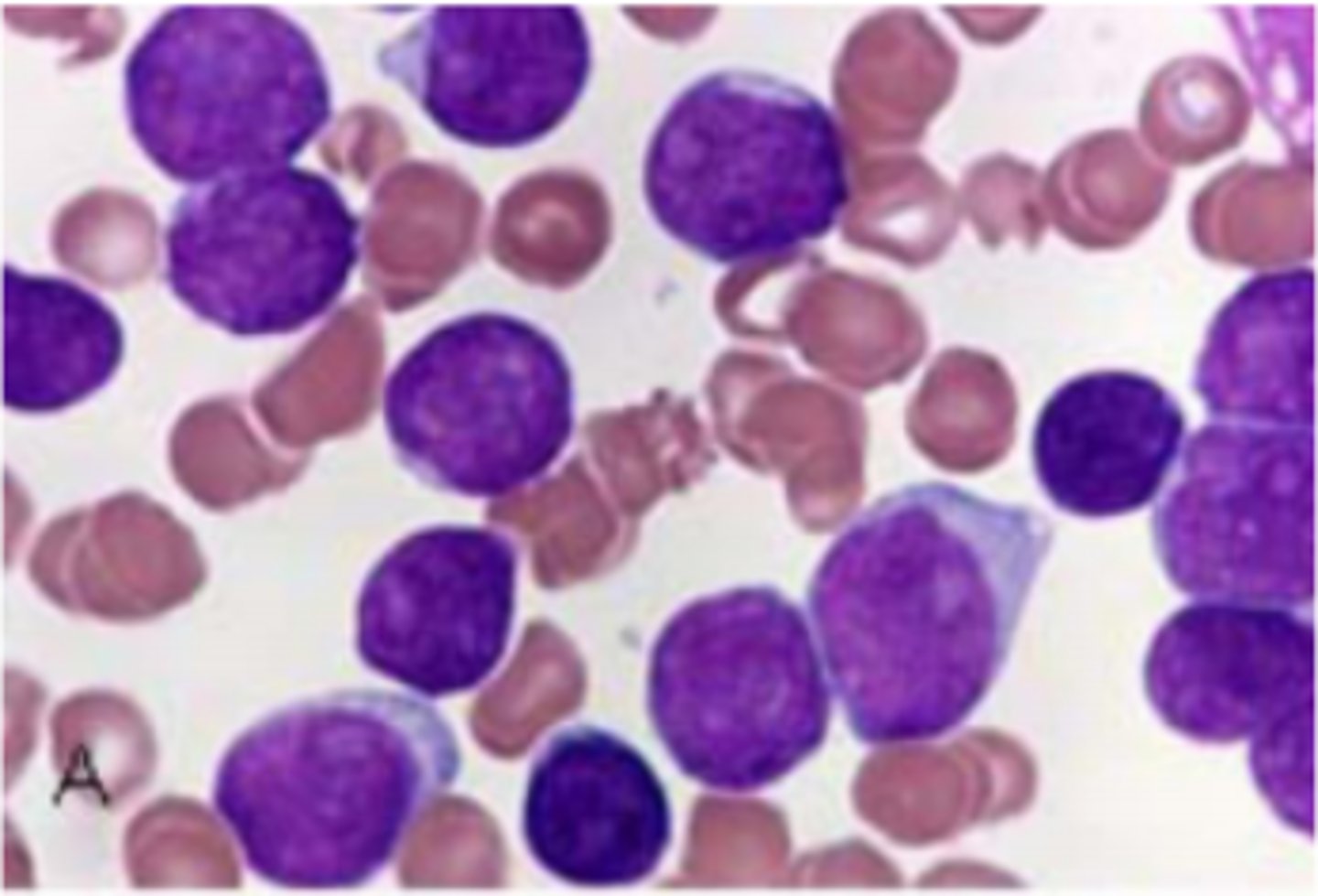
lymphoblast
-no auer rods, positive staining for TdT
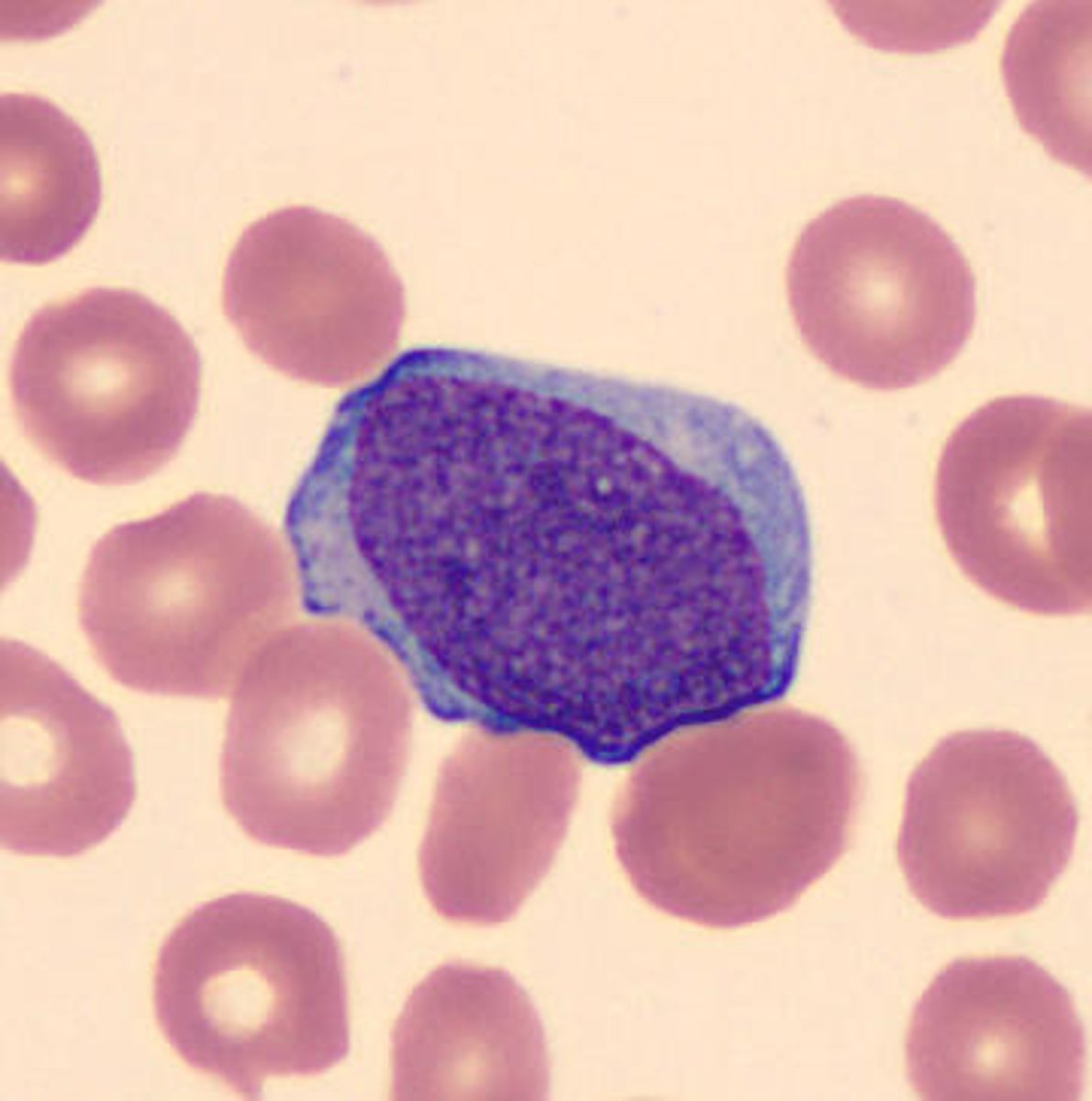
myeloblast
-cytoplasmic granules, may see suer rods
-increased prominence of nucleoli
immunophenotyping (flow cytometry)
DIAGNOSTIC lab for determinging lymphoid or myleoid lineage
•L1 small cells with homogeneous chromatin
•L2 large heterogeneous cells, irregular cytoplasm
•L3 large homogeneous cells, deep blue cytoplasm
what are the 3 subtypes of ALL as defined by FAB
TdT (terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase)
both B cell and T cell ALL are positive for
B cell ALL
type of ALL that is HLA-DR positive
the term lymphoma is used when the disease is confined to a mass lesion with little or no blood and marrow involvement
when to use the terrm lymphoma over leukemia
lymphoma type ALL
Mass & <25% blasts in marrow it is
leukemia type ALL
No mass & >25% blasts in marrow it is
5 year overall survival > 90%
prognosis of ALL
-older age (>35)
-high initial WBC count
-under one year old
-female
poor prognosis indicators of ALL
1-9
age to have ALL with the best prognosis
hyperploidy>hypoploidy
ploidy associated with most cases of ALL
•t(9;22) encodes BCR-ABL (activates TK activity)
translocation associated with very poor prognosis with ALL
•t(12;21) encodes ETV6-RUNX1 (transcription factors)
translocation associated with a favorable prognosis of ALL
-good prognosis if good response to steroids in one week, <5% blasts by day 8 or 15 with therapy
-<.01% minimal residual disease
describe how the treatment is a prognostic test in ALL
<5% blasts in bone marrow
bone marrow finding indicative of complete remission
•Poor predictor of prognosis due to poor sensitivity and interobserver variability
bone marrow eval a good predictor of prognosis?
leukemic cells present after therapy but not detectable by conventional morphological assessment; must be found by FISH, PCR, flow cytometry, etc
-BEST PREDICTOR OF PROGNOSIS
define what it means to be measurable residual disease positive
minimal residual disease
What is the best test to predict progosis with ALL?
-almost 2 years of 4-5 chemo regimens
-CNS prophylaxis
-allogenic transplantation in reaching the 1st remission
describe the therapy for ALL
in 1st remission
when can allogenic transplantation be considered for treatment of ALL
infertility, secondary malignancies, growth/maturation changes
complications of ALL after complete remission
-induction 4-6 weeks
-post remission consolidation
-maintenance therapy
what are the phases of treatment of ALL?
tyrosine kinase inhibitor (imatinib, dasatinib)
treatment to add in casess of ALL that are philadelphia chromosome positive
CD19
-may be treated with anti-CD19 immunotherapies
CD marker that is present in over 90% of ALL cases
-combo therapies typically consisting of methotrexate and/or cytarbine
-cranial radiationn reserved for highest risk pts
-incorporated into every phase of treatment
prophylactic CNS therapy regimens for ALL