Physics Applications of Newtons Laws
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
What is the difference between weight and mass?
Weight is mass affected by gravity(it’s a force), while mass is universal, meaning it will remain the same everywhere.
What is an Atwoods machine?
A single pulley suspended from the ceiling, with a string hanging down to either side with a mass on either end of the string.
What is a modified Atwoods machine?
Places one mass on a frictionless table while the other hangs over a pulley with equal magnitude tension forces acting in opposite directions on each mass.
How does a modified Atwood’s machine accelerate?
The system accelerates due to gravity on the hanging mass, but at less than gravity because that gravitational force must accelerate both the hanging mass and the mass on the table.
What
What is tangential velocity?
The magnitude of velocity while its going in a circle.
What forces are capable of producing circular motion?
Tension, gravity, friction, and normal force.
What assumptions should we make about the pulley when analyzing a pulley system?
Its massless and frictionless
What assumptions should we make about the strings when analyzing a pulley system?
It's non-elastic, massless, uniform tension in the string, a constant gravitational field, and all masses connected by the string have the same magnitude of acceleration
What rule should we follow for the FBD of a pulley system?
2 tensions for the pulley, 1 tension for the string. A movable pulley is supported by TWO segments of the same string, so it feels two upward tensions (2T), while a single string has ONE tension value everywhere (T)
What is an example of tension?
Like swinging a yo-yo at the end of it’s string.
What is an example of gravity?
Like the force holding the moon or satellites in orbit.
What is an example of friction?
Like a car turning
What is an example of normal force?
Like swining a bucket of water over your head.
What is an example of combinations of forces?
Like friction and normal force on a car going around a banked turn.
Component of forces
consists of tension, mass, and centripetal force
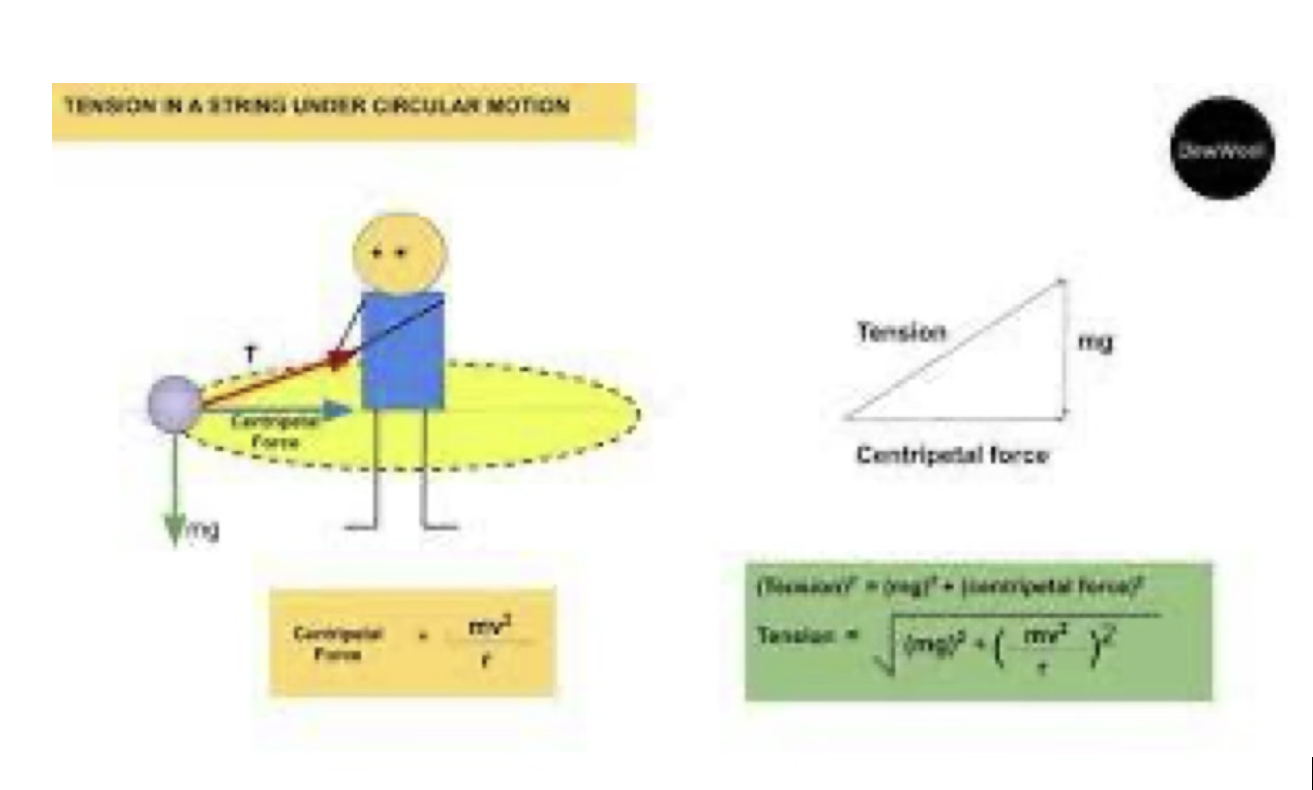
What happens when centripetal force is higher than whats needed?
The object will be pulled toward the center, either spiraling into the center or pressed into the surface of contact.
How is gravity on Earth an example of too much centripetal force?
It creates the force we need to stay on the planet while it rotates, but it’s much stronger than it needs to be, so the rest goes to pressing us into the ground, creating the normal force we experience and our apparent weight.
What happens when the centripetal force is lower than needed?
The object will spiral off its path.
What happens when the centripetal force is removed completely?
The object will immediately start to follow a straight line path in the direction of its velocity at the time the force was removed.
How does a satellite move?
In a circular orbit, there is a force acting on the satellite in a centripetal fashion.
What is the only force present in satellite movement?
gravity
What are problems with the gravity formula?
Can’t just use mass x acceleration due to gravity to determine the force due to gravity because we have evidence that the force due to gravity gets weaker the further you are from the planets surface.
What does gravity is a paid force mean?
Mass 1 will produce a force on mass 2 that is equal to but opposite in direction from the force mass 2 produces on mass 1.
Why does gravity follow an inverse square relationship?
The strength of the force is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the objects.
What happens if the distance between the objects is doubled?
the force experienced is cut to ¼ the original amount.
What happens if the distance is cut in half?
the force is 4 times as much
How does an object on an inclined plane stay still?
Friction will go up the ramp as the box tries to slide down to try to prevent the motion.
Where on the ramp is friction located?
It is always parallel to the surface of contact, so it is at tge angle of the ramp.
What is normal force perpendicular to?
The surface so it is perpendicular to friciton.
When is static friction present?
when the box is not moving/stationary.
When is kinetic friction present?
It is applied when the box is moving id the box is sliding down the ramp, kinetic friction is acting.
What 2 forces always meet at a 90 degree angle?
Friction and normal force
What should not be seen at equilibrium?
A gap shouldn’t be seen between the tail of gravity and the head of friction.
What type of force is tension?
a pull force
Whats the pully doing in a modified Atwoods machine?
redirects the tension force between the 2 masses. Both masses will have the same acceleration. This system can be treated as a single object with mass that’s equal to the combined mass of the 2 boxes.
what is a period?
The time it takes to complete a full cycle of an action.
What is the symnbol for period?
T(because its special time)
What are the units for a period?
seconds
What is a period for circular motion?
The time it takes to complete one full circle motion.
What is frequency?
The number of cycles completed each second. its measured in Hertz (Hz), (1Hz=1s), symbol is f, it is the INVERSE of a period.