BIOCHEM EXAM 1
1/65
Earn XP
Description and Tags
amino acids, polarity/charge, structure, rough pKa, 3 letter and 1 letter codes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
essential amino acids
HILKMFTWV
cannot be synth by body, come from diet
nonessential amino acids
ANDESCQGPY
can be synth by body
Asp pK
4
Glu pK
4
His pK
6
most common interaction and strongest between amino acids and small molecules (drugs)
hydrophobic
Lys pK
10.5
Arg pK
12.5
G/Gly/glycine
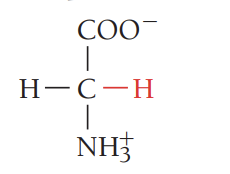
A/Ala/alanine
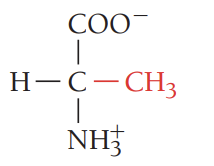
V/Val/valine
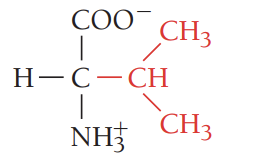
L/Leucine/leucine
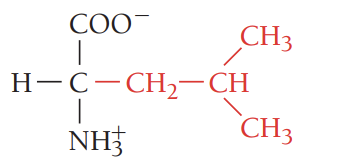
I/Ile/isoleucine
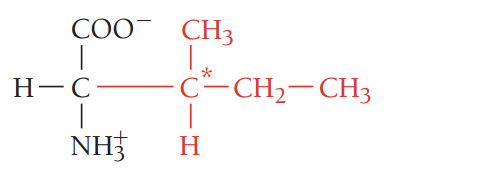
M/Met/methionine
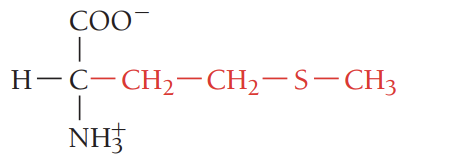
P/Pro/proline
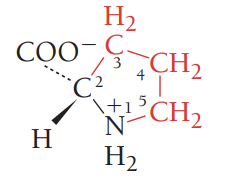
F/Phe/phenylalanine
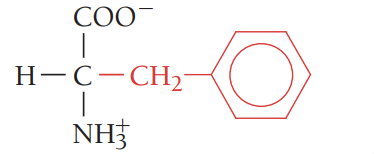
W/Trp/tryptophan
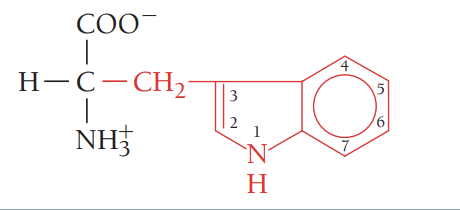
S/Ser/serine
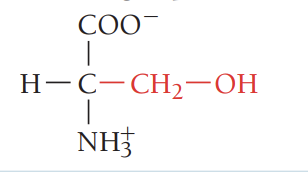
T/Thr/threonine
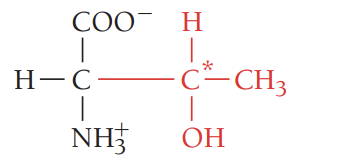
A/Asn/asparagine
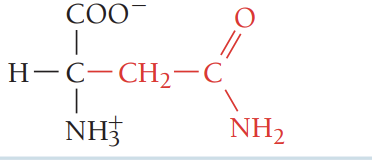
Q/Gln/glutamine
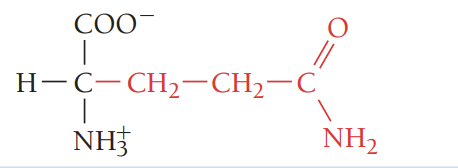
Y/Tyr/tyrosine
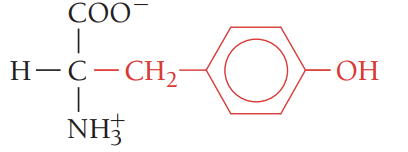
C/Cys/cysteine
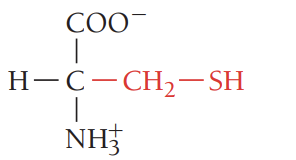
K/Lys/lysine
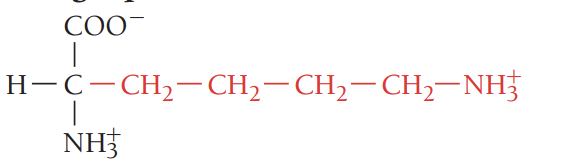
R/Arg/arginine
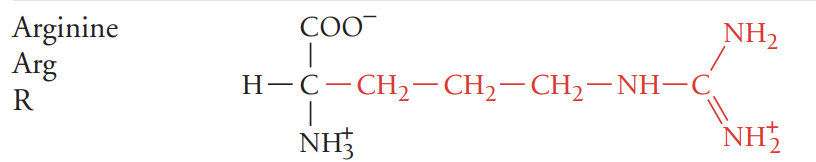
H/His/histidine
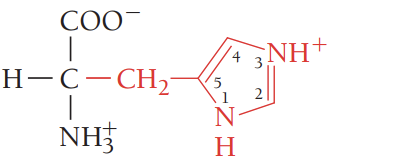
D/Asp/aspartic acid (aspartate)
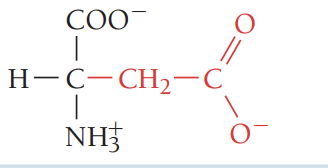
E/Glu/glutamic acid (glutamate)
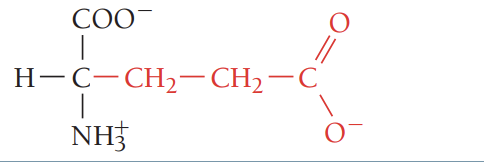
AAs w/ nonpolar side chains
AFILMGVWP
(Aw Fuck I Left My Goddamn Violin With Patrice)
AAs w/ uncharged polar side chains
STNQYC
No, Stop! Quit That, You Clown
AAs w/ charged polar side chains
HKRDE
Happy Kids Run During Exercise
methylation
Lys, Arg, His
Cell marker
hydroxylation
Lys, Pro
stabilization of structures
phosphorylation
Ser, Thr, Tyr
Hydroxyl replaced by phosphate
pH < pK
protonated form dominates
pH > pK
deprotonated form dominates
amino pK
~9-10
thiol pK
~8-10
carboxyl pK
~2-4
hydroxyl pK
~16
amino @ neutral pH
protonated (NH3+)
carboxyl @ neutral pH
deprotonated (COO-)
hydroxyl @ neutral pH
protonated (OH/neutral)
thiol @ neutral pH
protonated (SH/neutral)
acidic groups (low pK) at neutral pH
negative
basic groups (high pK) at neutral pH
positive
weak acids/bases (thiol/hydroxyl) at neutral pH
mostly neutral
intermolecular interactions ranked strongest to weakest
ionic (salt bridge) > h-bonding > hydrophobic effect > VDW
acidic amino acids
Asp, Glu
basic amino acids
Lys, Arg, His
pI (isoelectric point)
pH where net charge = 0
primary structure
linear seq of amino acids (peptide bonds)
secondary structure
alpha helices, beta sheets (stabilized by H-bonds in backbone)
tertiary structure
3D fold (side chain interactions, hydrophobic effect, H-bonds, salt bridges, disulfides)
quarternary structure
multiple polypeptide
proline affects helices by:
breaking helices, introduces loops and bends due to no backbone N-H for H bonding
glycine affects helices by:
flexible, no steric hindrance
cysteine affects helices by:
forming disulfide bonds through oxidation, structural stability
Q 1 on RC diagram
left-handed alpha helix, not favorable
Q 2 on RC diagram
upper middle, beta sheet (more favorable)
triple helix (favorable)
Q 3 on RC diagram
upper middle top, alpha helix (favorable)
Q 4 on RC diagram
forbidden except for glycines
proline on RC diagram
very strict and rigid structure so least coverage on the RC diagram
phi angle for proline
-60
phi
x axis
psi
y axis