Chapter 3: Biomolecules
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Organic molecules must consist of ___ and ___.
Hydrogen and Carbon
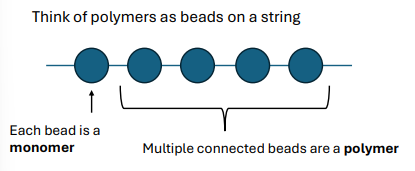
Four main classes of organic molecules:
Carbohydrates
Proteins
Nucleic Acids
Lipids (only non-polymer)
What does “like dissolves like” mean?
Polar things are hydrophilic. Non-polar things are hydrophobic.
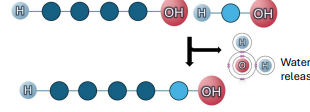
Dehydration synthesis
Additional polymer is synthesized
Water is lost
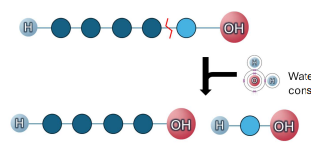
Hydrolysis
Piece of polymer is broken off (lysed)
Water is added back into products
Nucleic Acids
Nucleotide monomers
DNA and RNA
Lipids
Not quite polymers; more diverse
Cell membranes, energy, hormones, etc.
Carbohydrates
Monosaccharide monomers
Major energy source
Monosaccharides are rings containing carbon atoms and __ and __. (polar)
5-6, oxygen, hydrogen
3-100 monosaccharides are called ___ and 100 or more monosaccharides are called ___
Oligosaccharides and Polysaccharides
Proteins
Amino acid monomers
Enzymes, cellular respiration, more
A bond between two amino acid monomers is a ____.
peptide bond
Amino acids consist of an amino group, carboxyl group and an _ group. There are 20 different ones to choose from.
R
Polypeptide chains __ in a 3d space. Why?
FOLD, because R groups can have different charges. Via folding, these R groups can get closer to each other.
Alpha helix and Beta sheets are secondary structures within a single peptide strand. Both are formed by ____ between monomers.
Hydrogen Bonds
Multiple loops, sheets, and helixes (secondary structures) come together to form the ___ of the protein.
Tertiary structure
Higher-order protein structure is determined by ___
primary sequence! Certain R groups only want to participate in certain intermolecular interactions.